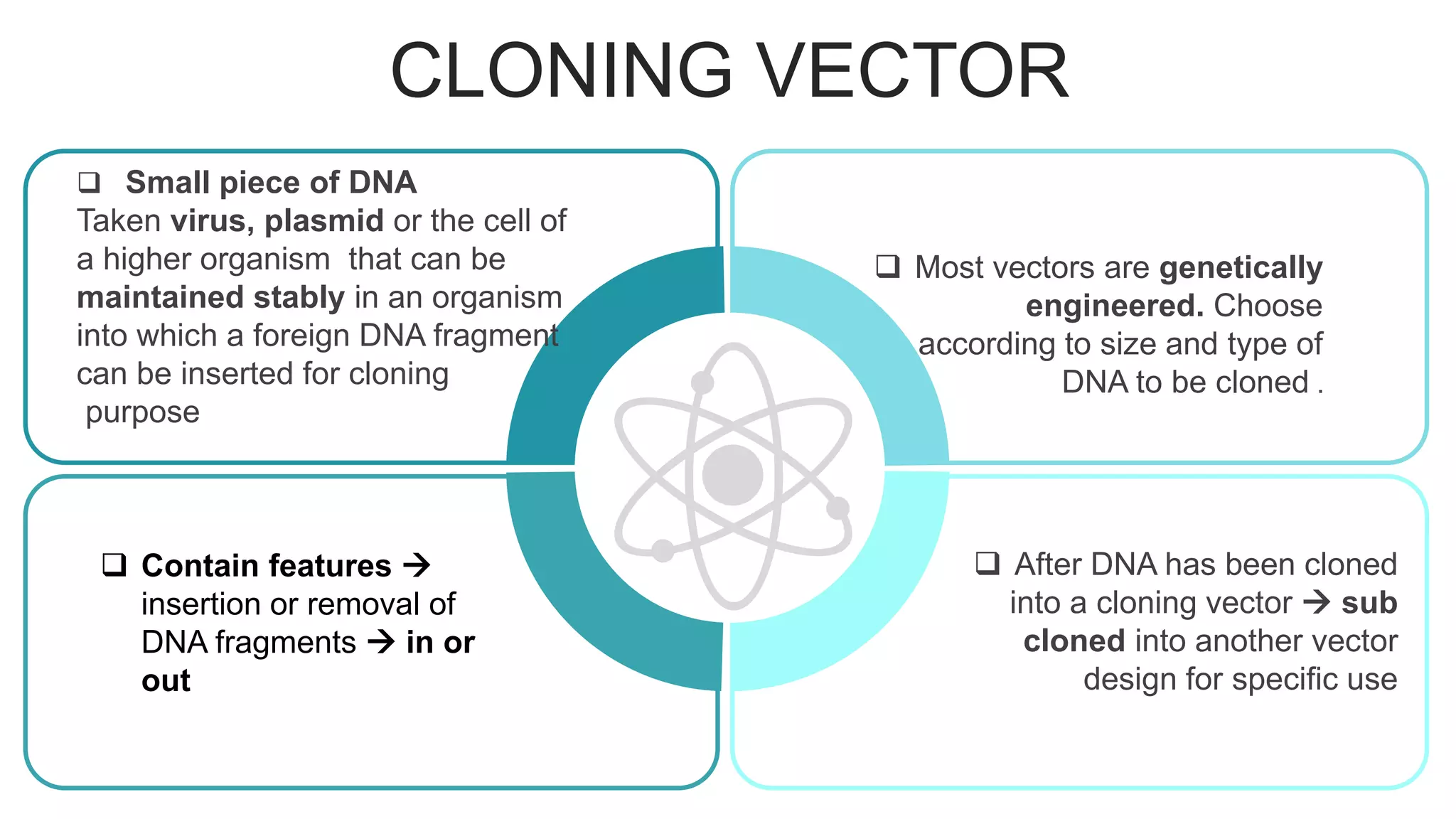
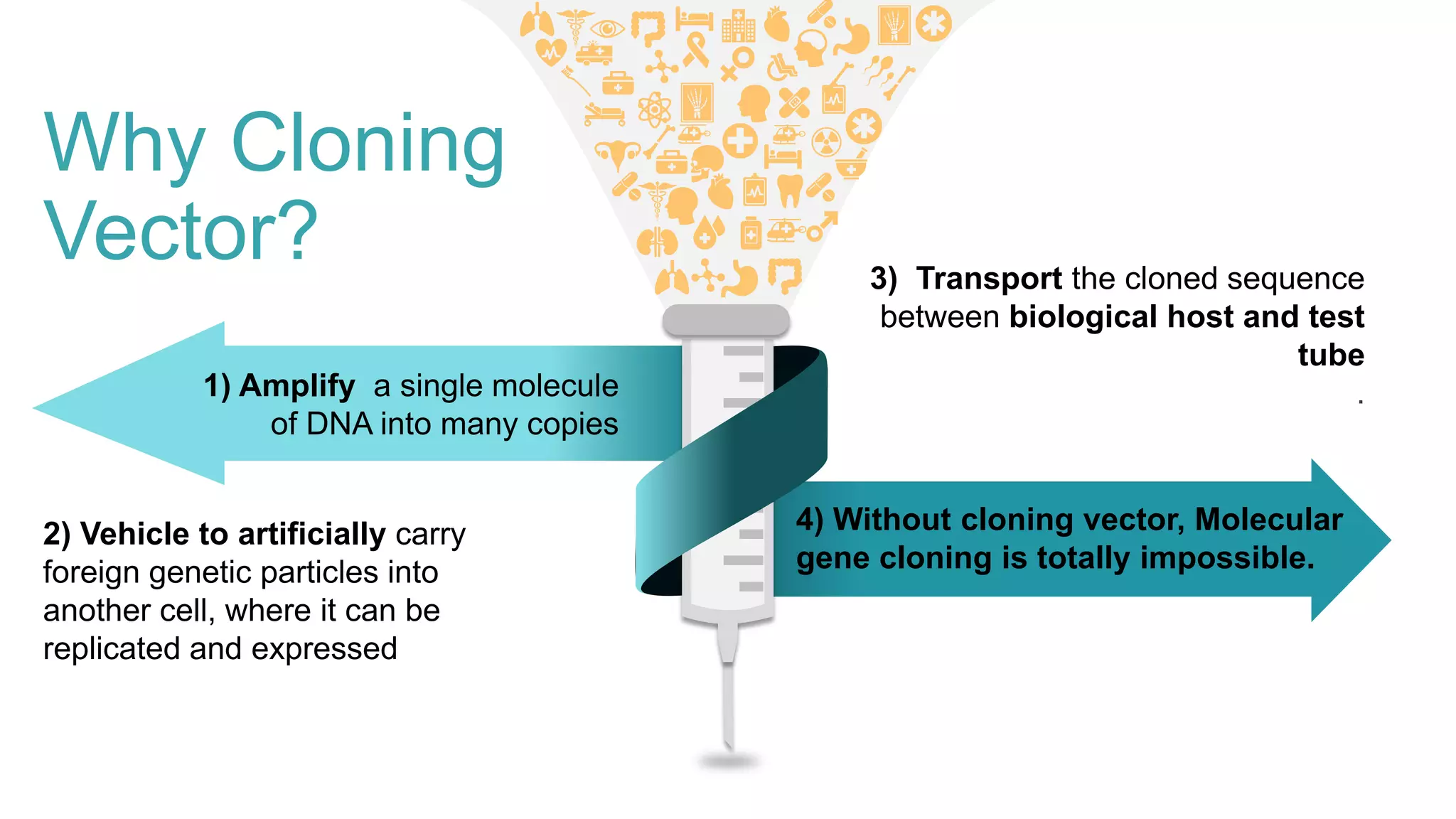
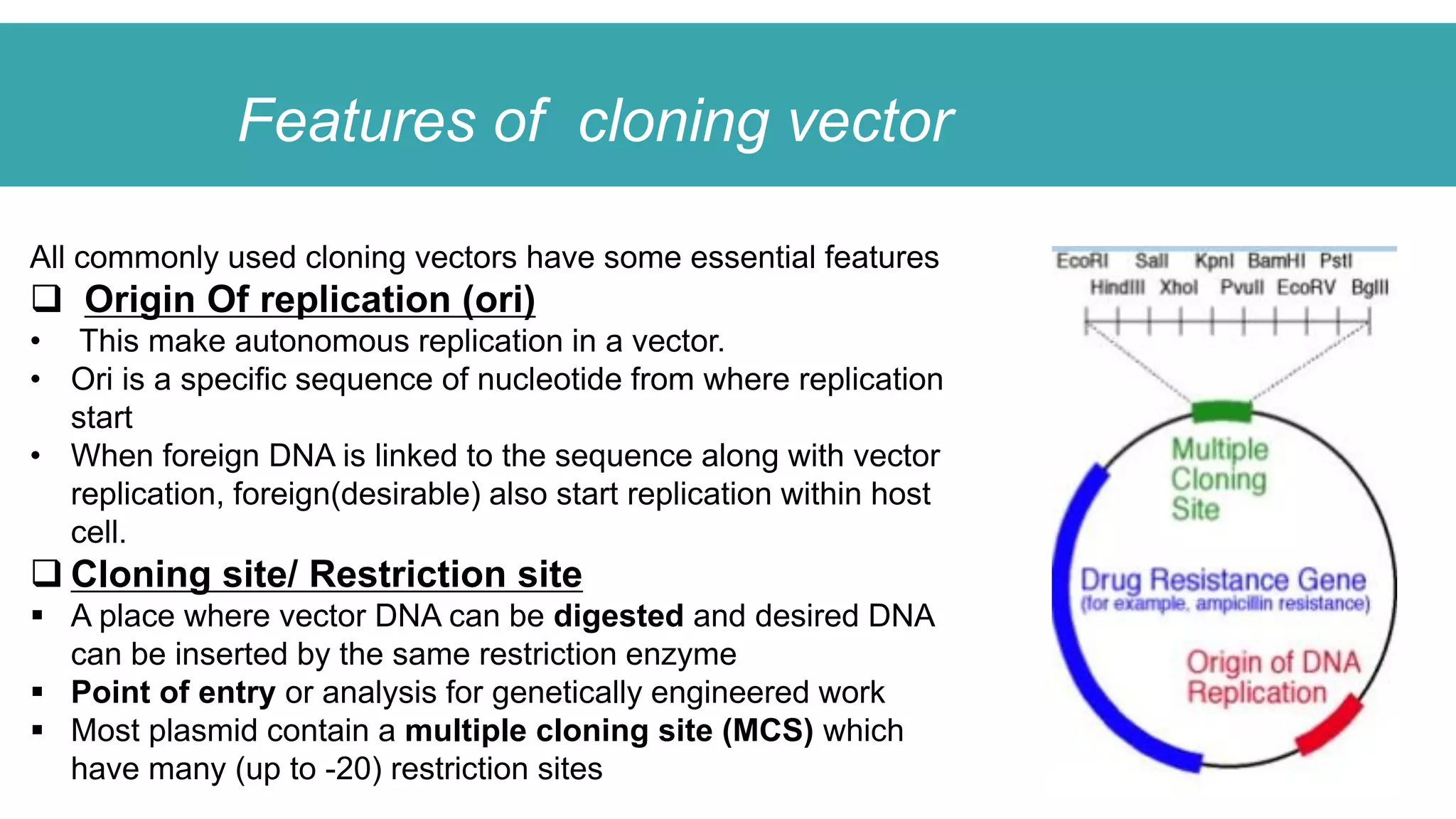
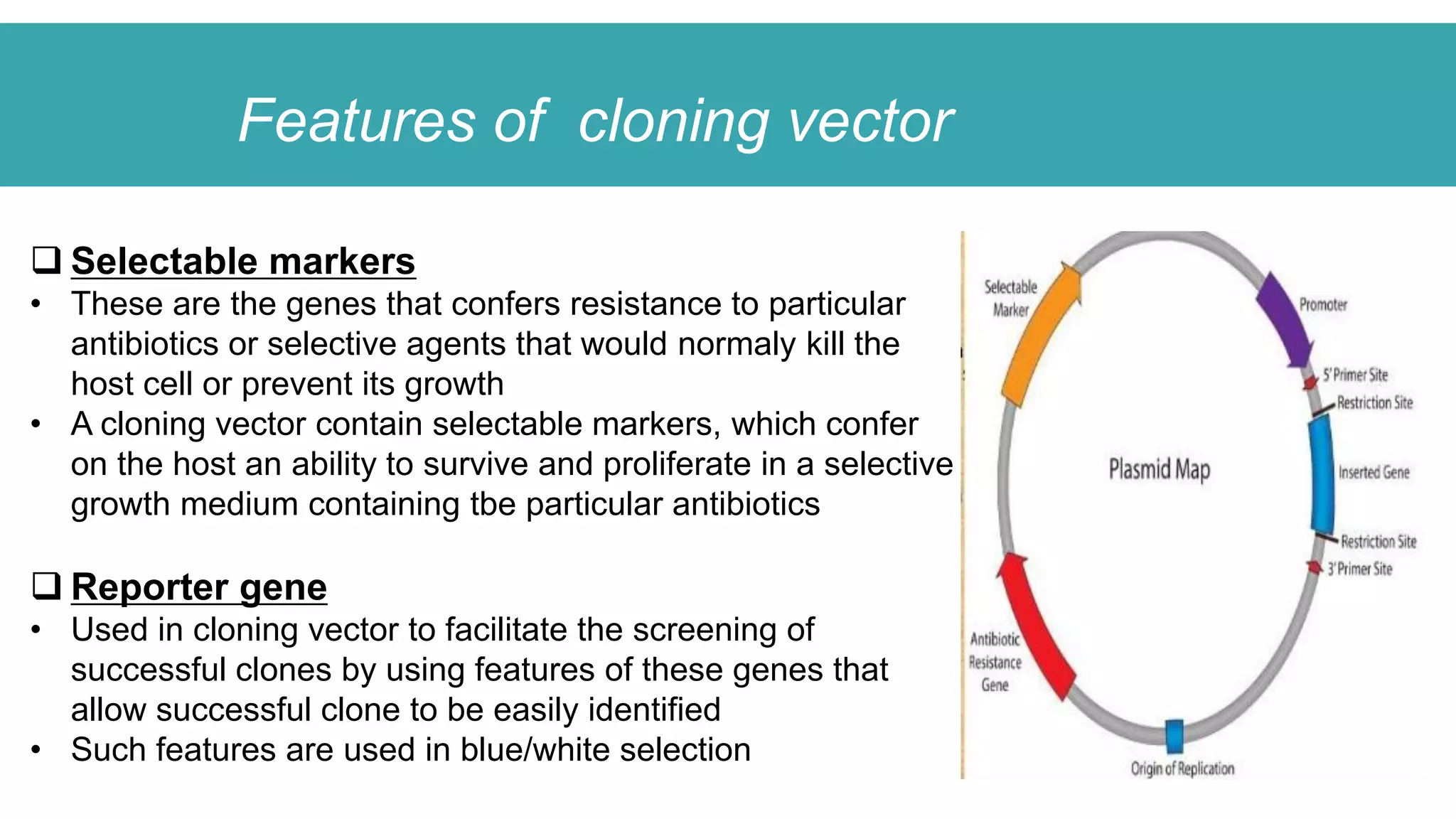
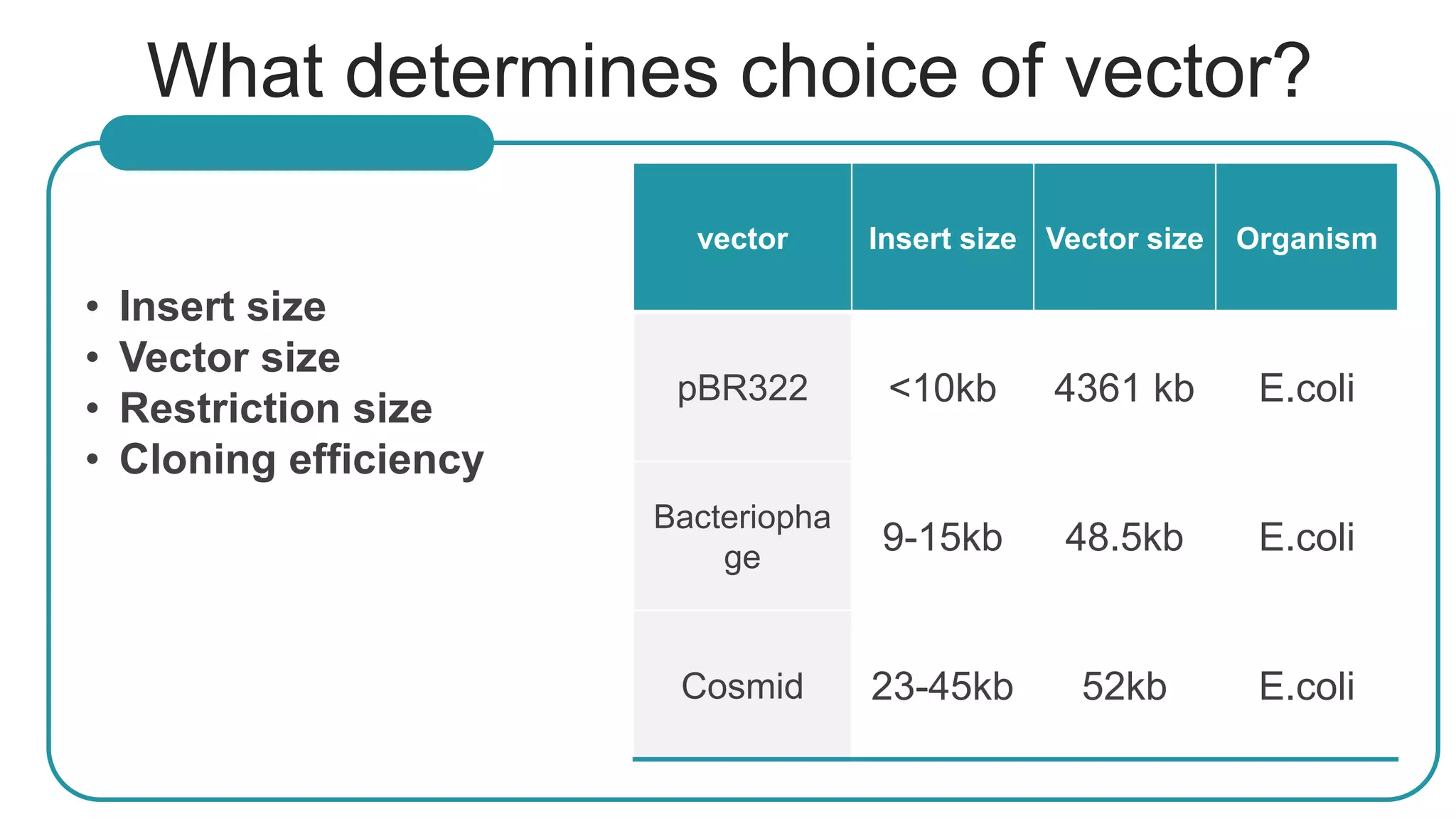
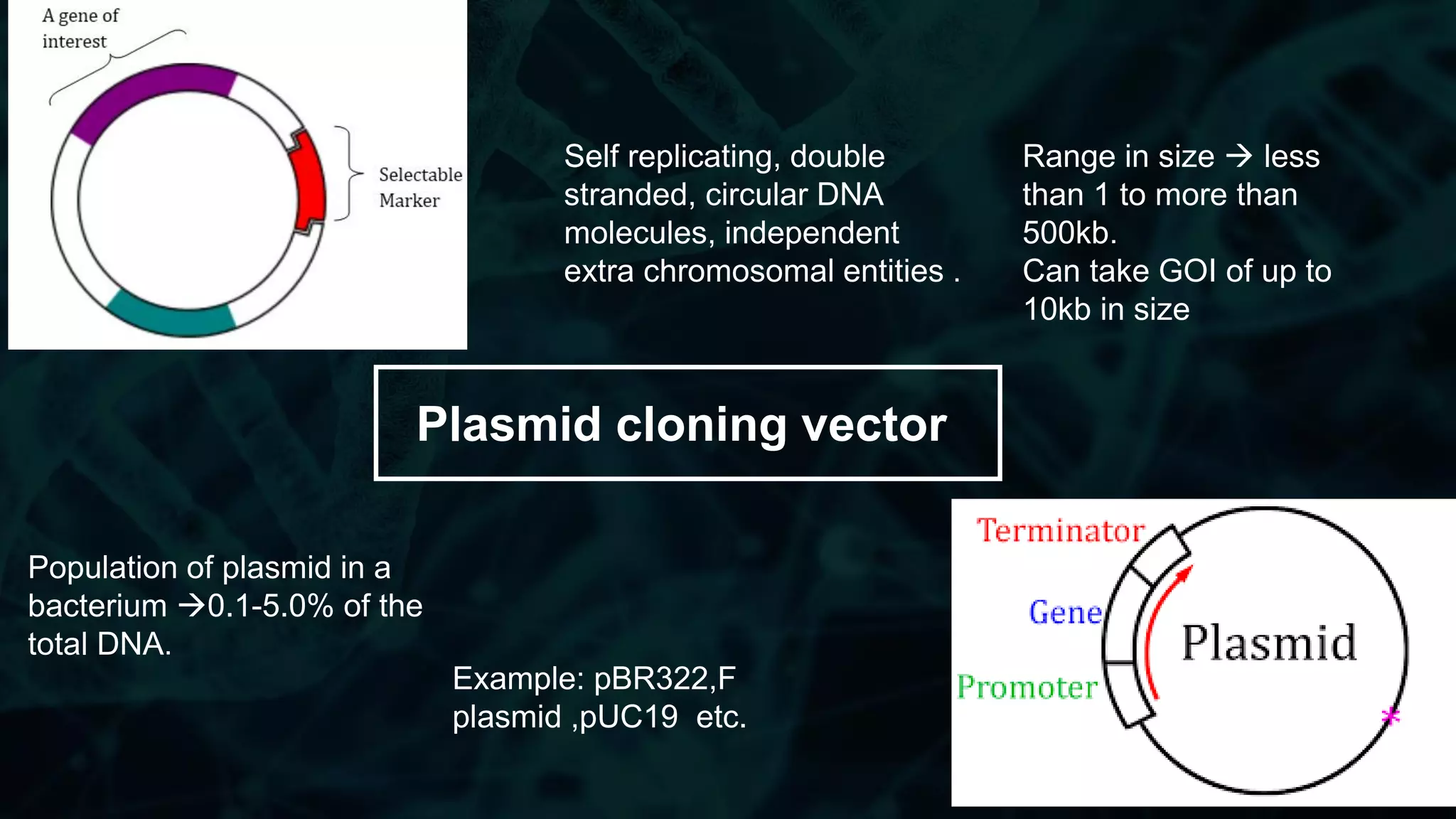
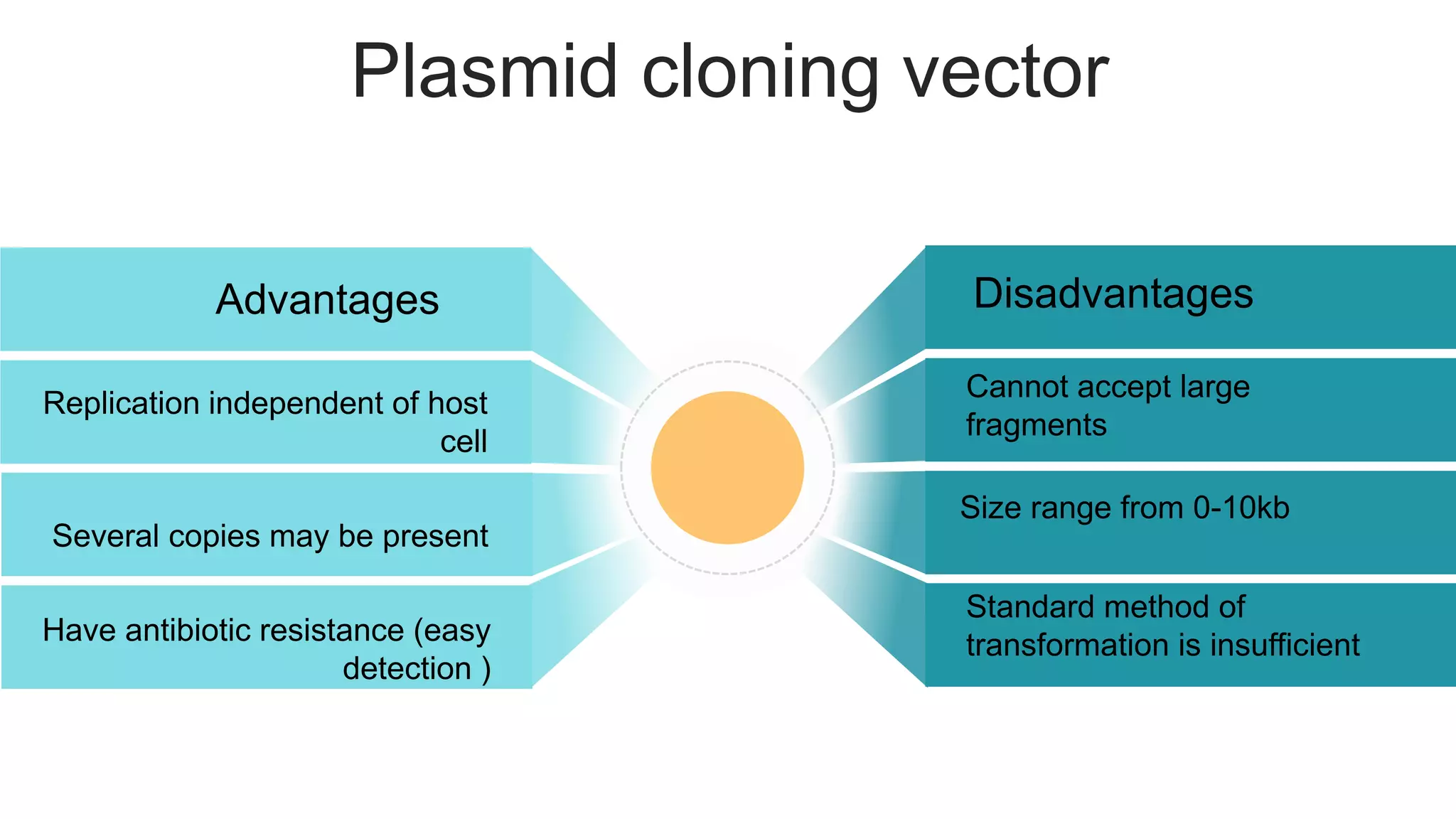
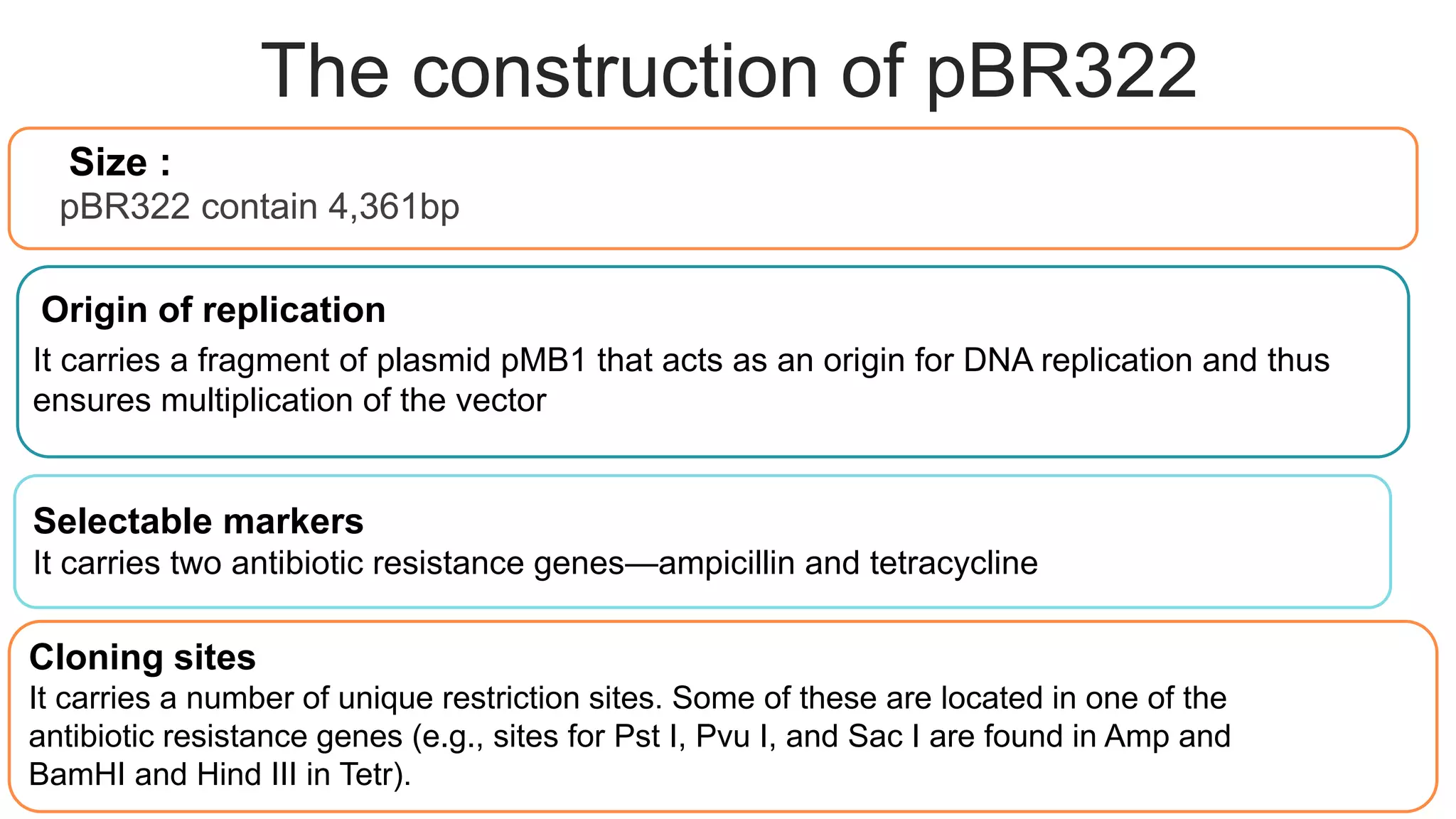
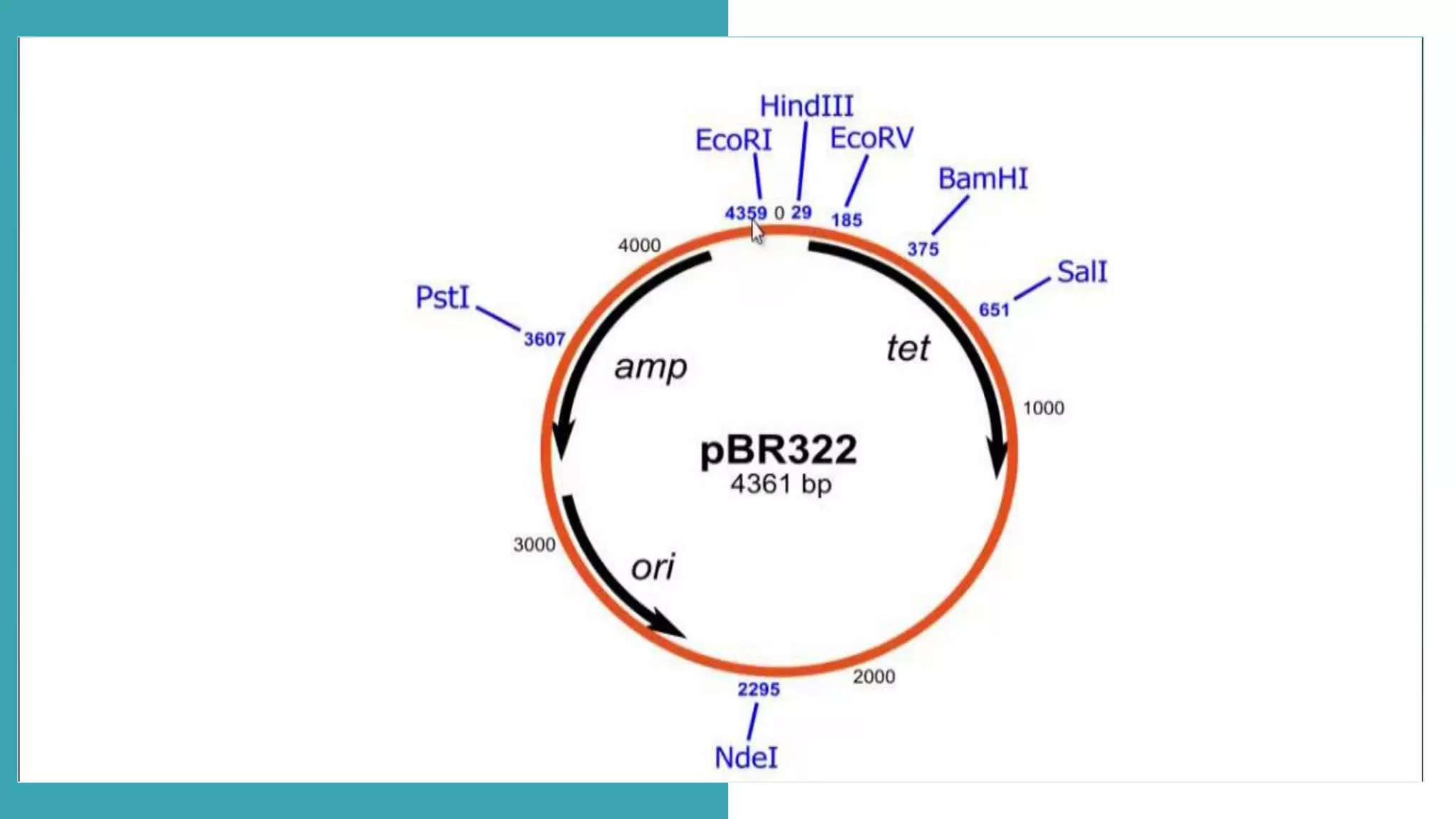
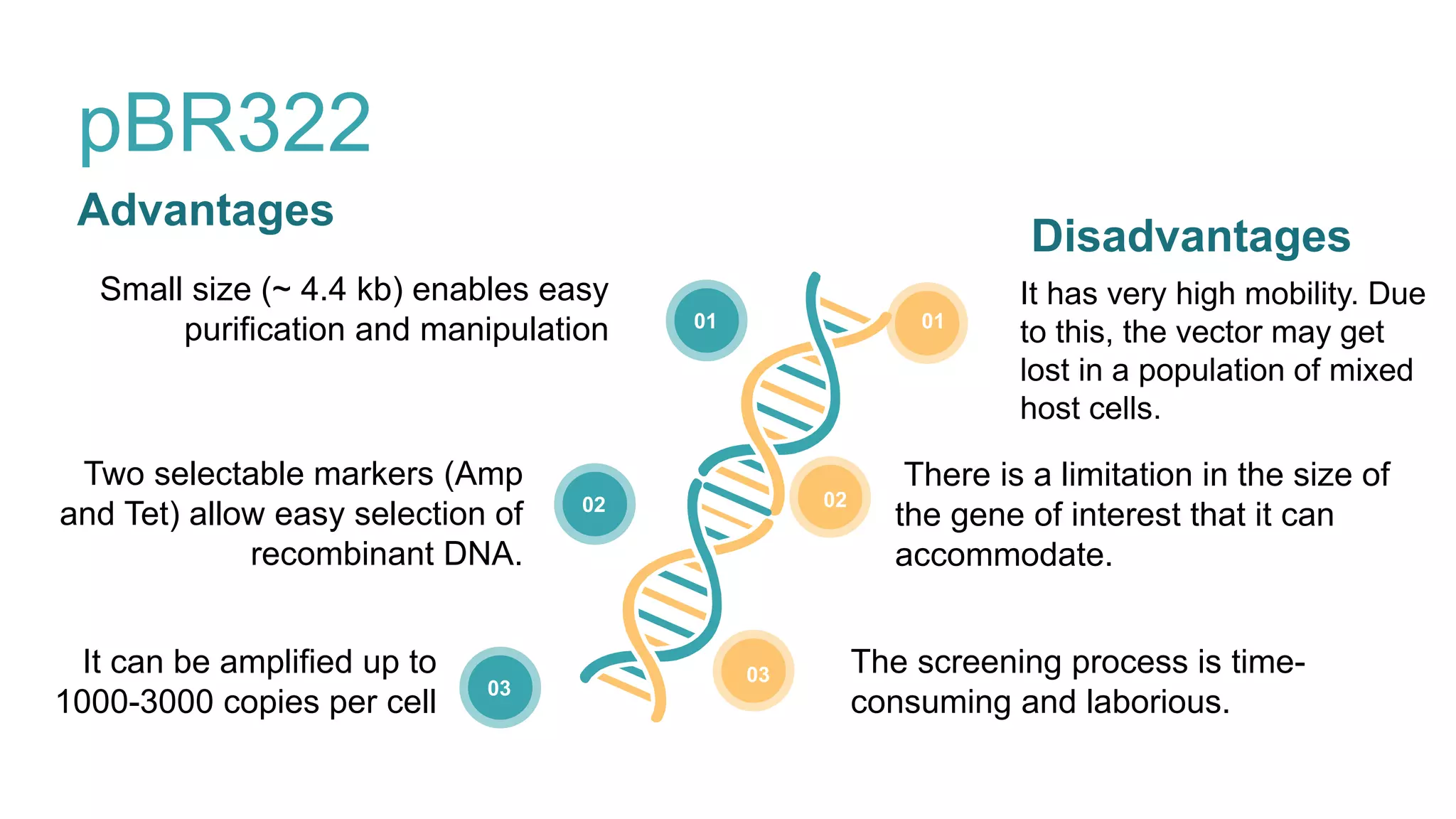
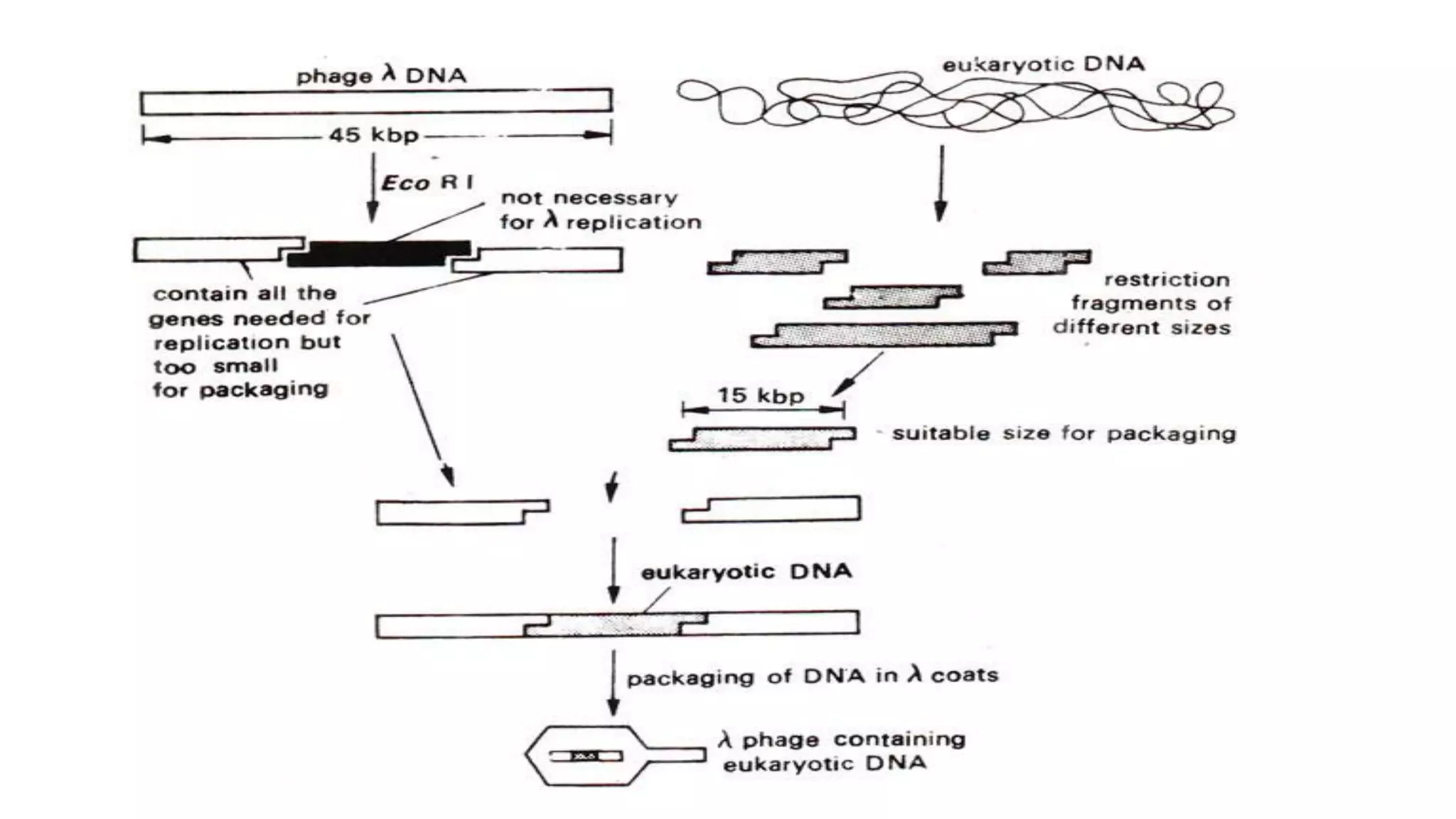
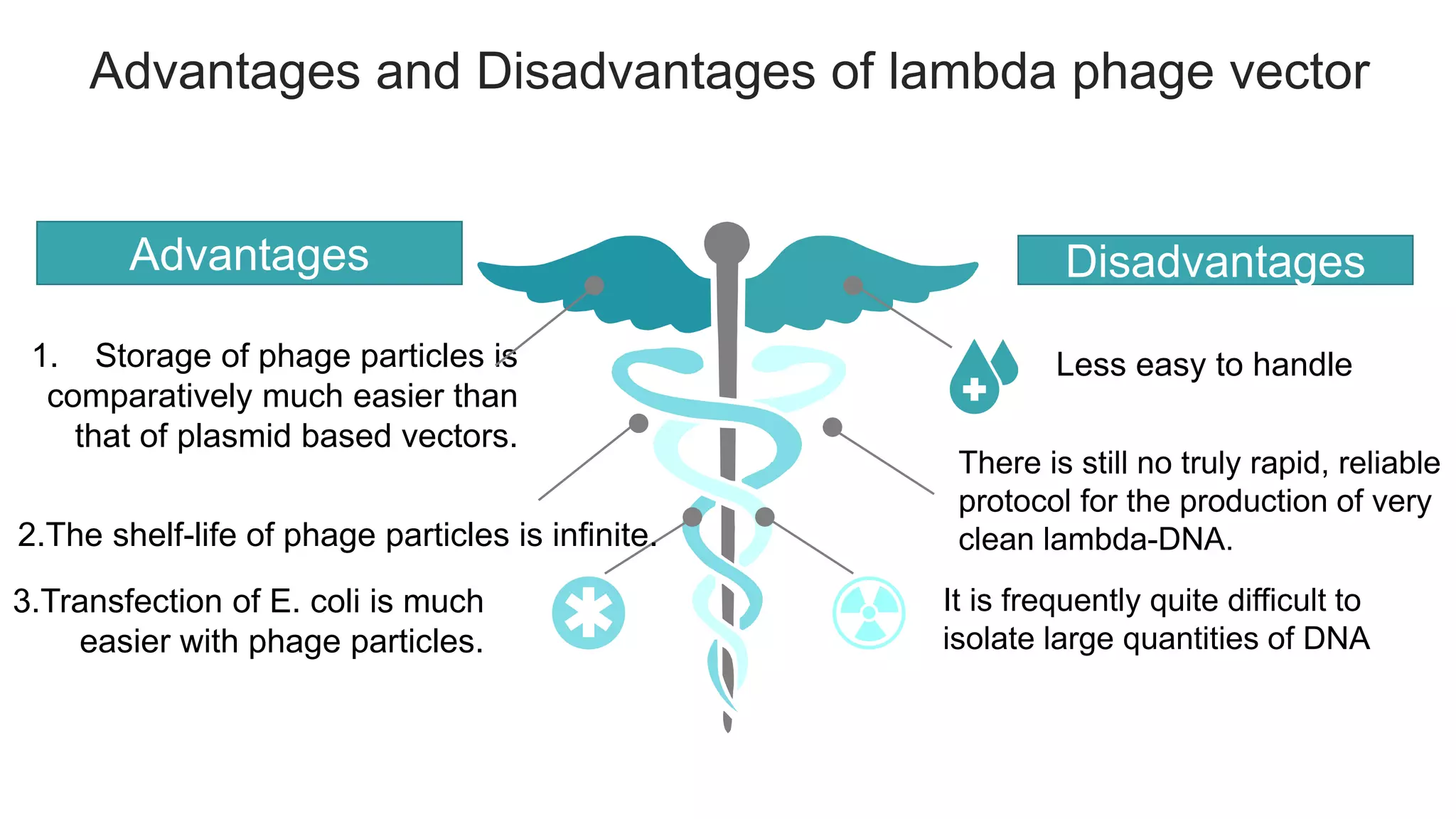
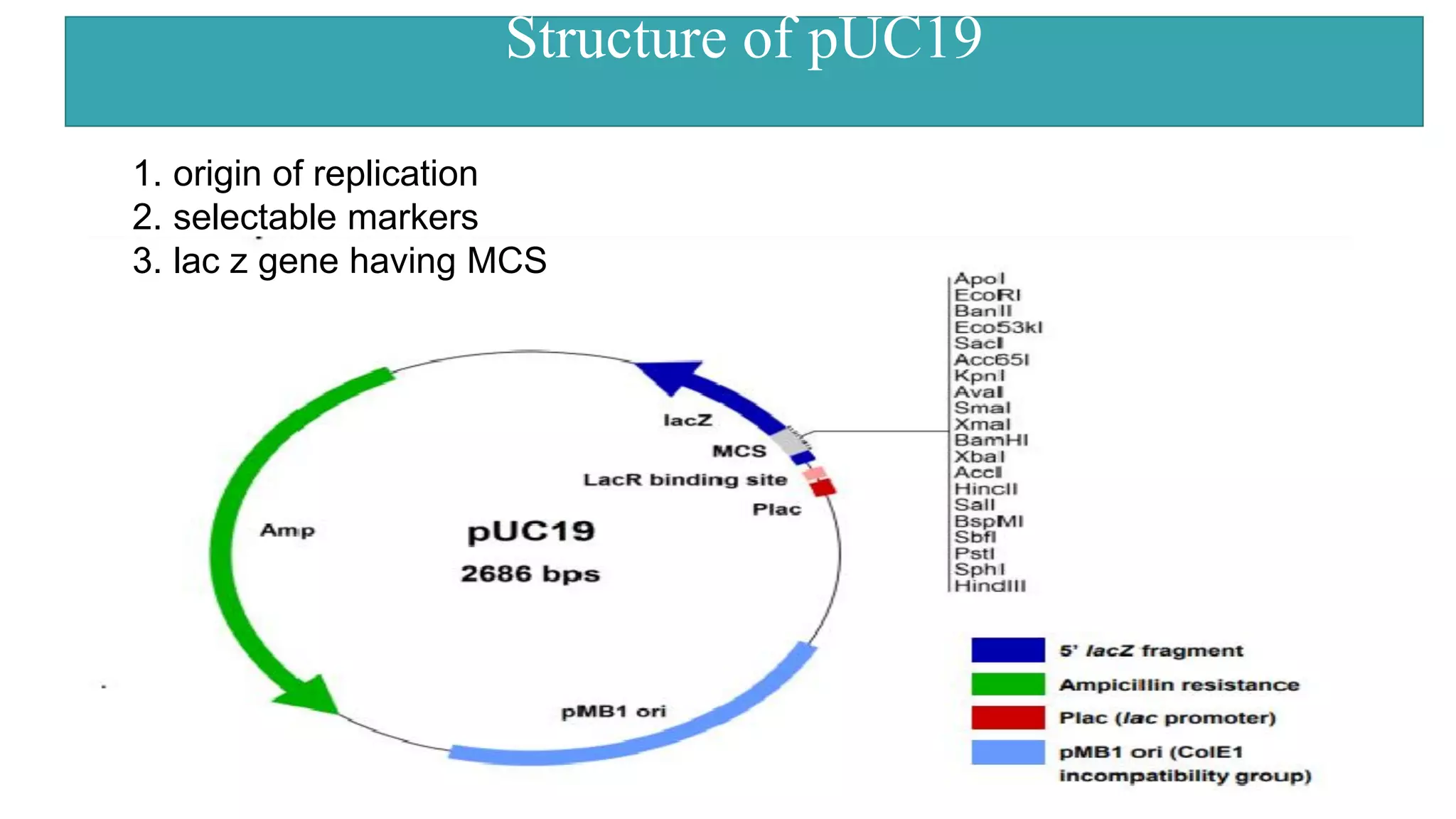
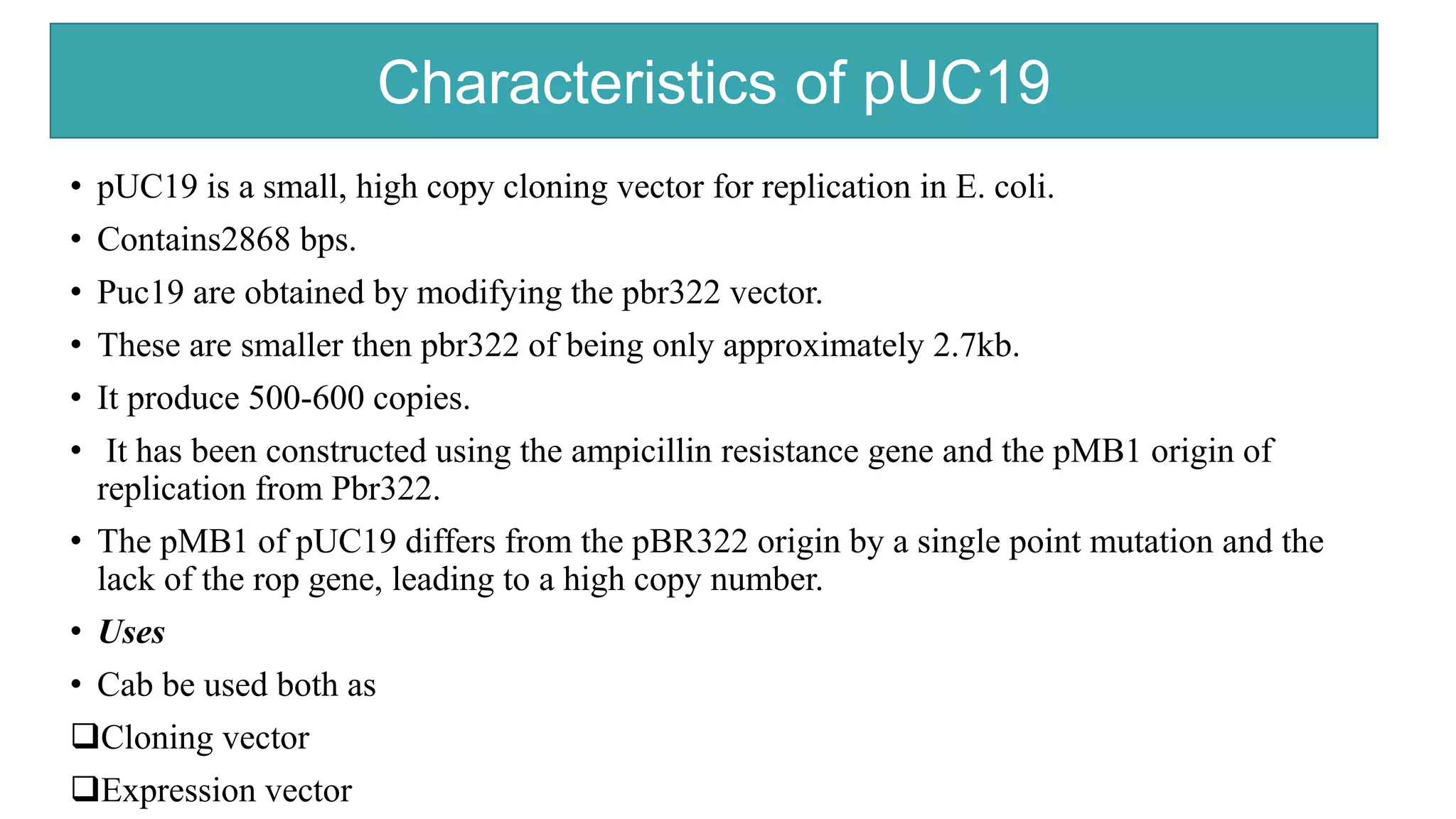
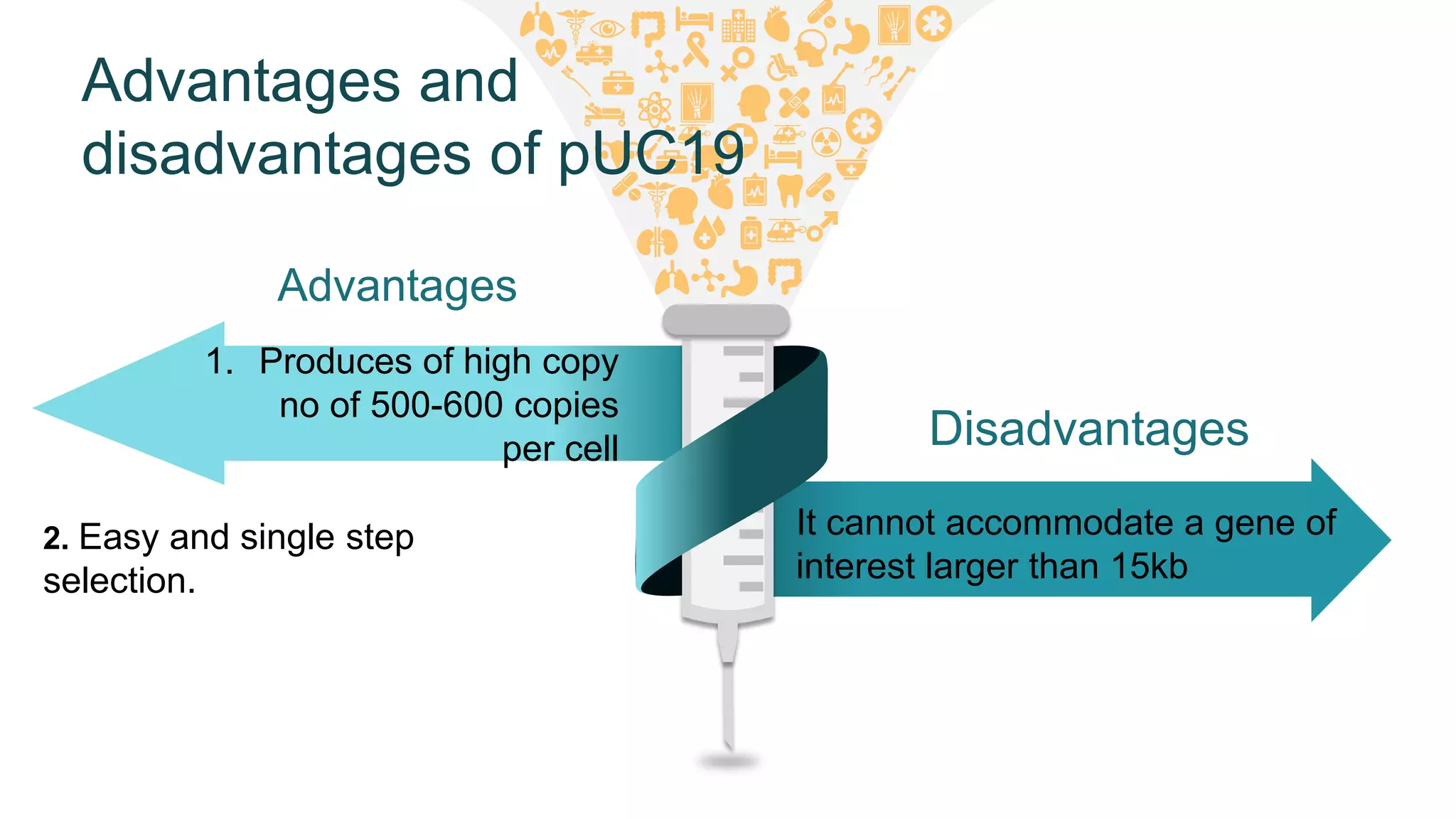
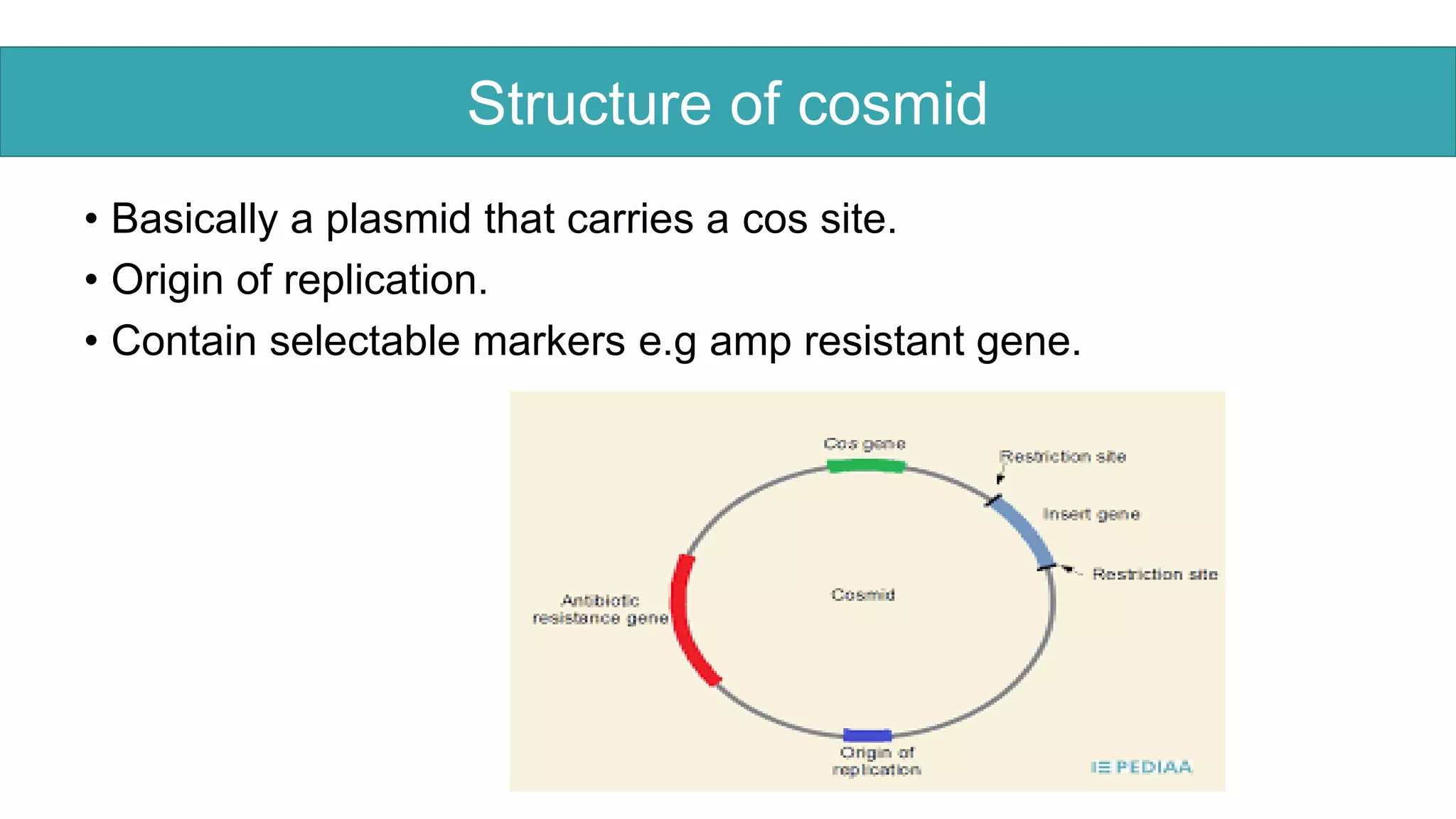
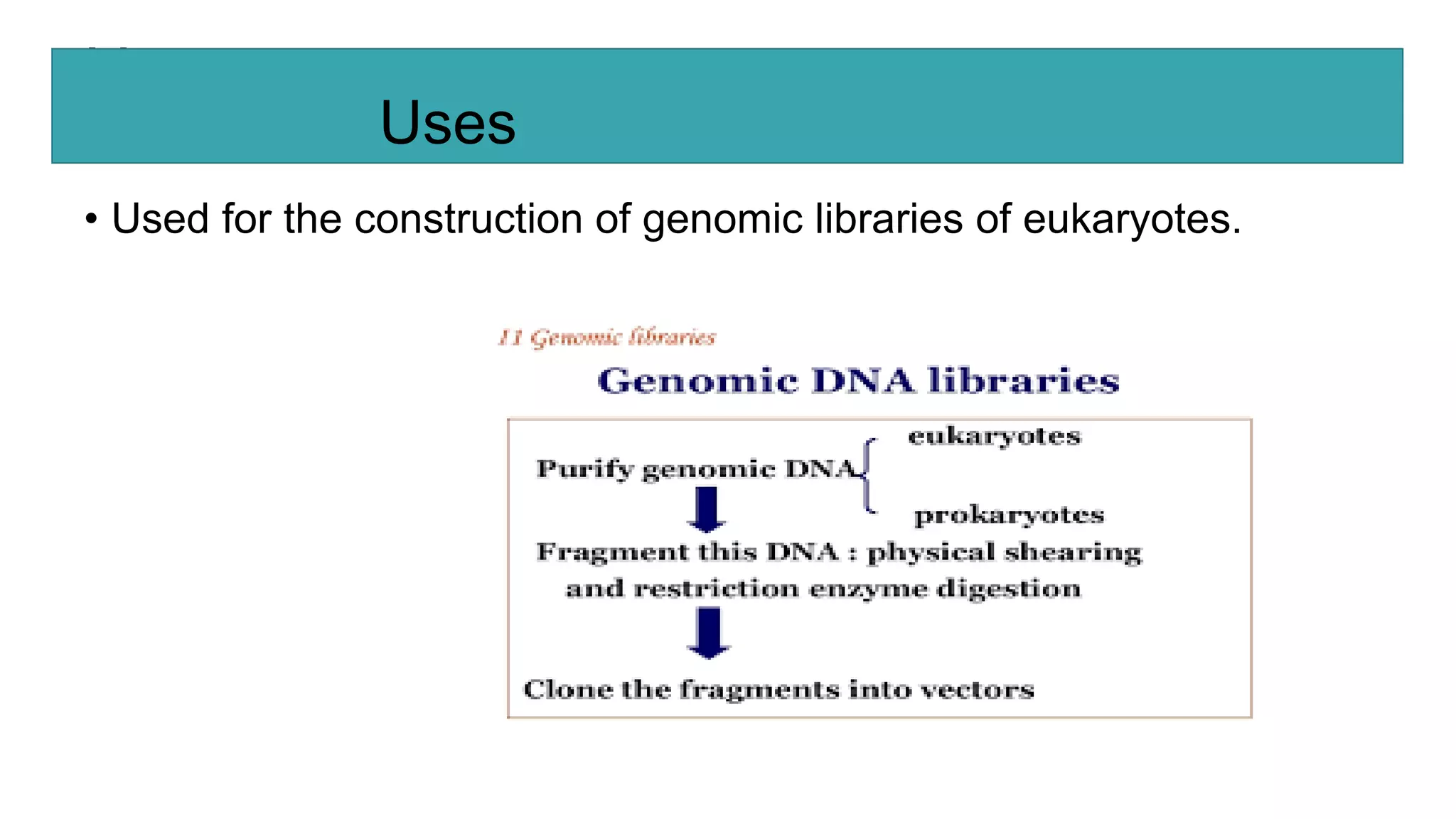
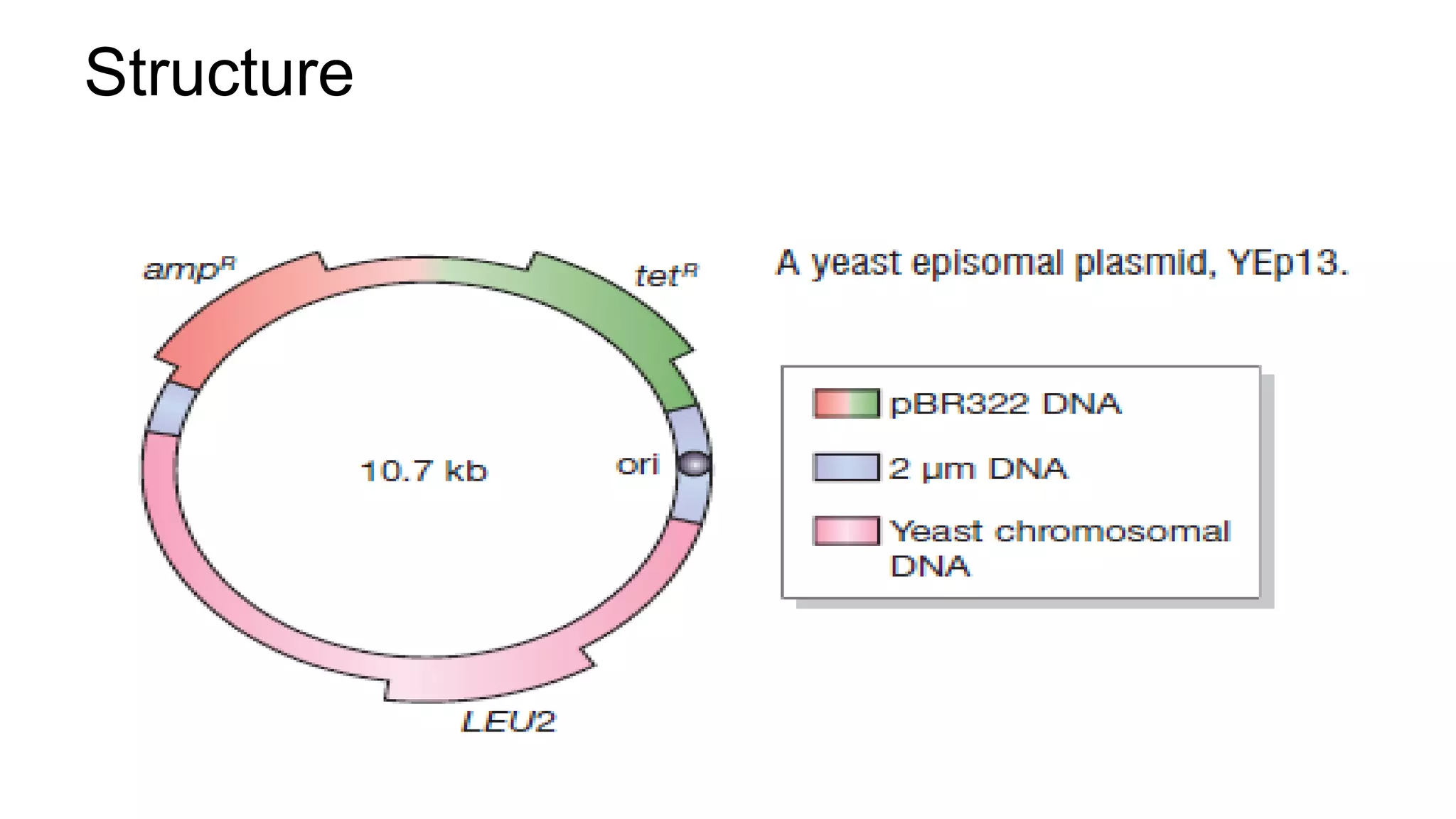
This document compares different types of cloning vectors, including plasmid vectors like pBR322 and pUC19, bacteriophage lambda cloning vectors, cosmid vectors, and shuttle vectors. Plasmid vectors are small, circular DNA molecules that can carry foreign DNA fragments of up to 10kb. Lambda bacteriophage vectors can accept larger inserts up to 15kb. Cosmid vectors can carry the largest foreign DNA fragments, up to 40kb, and shuttle vectors allow propagation in two different host species. Each vector type has advantages like insert size capacity and disadvantages like difficulty of manipulation.