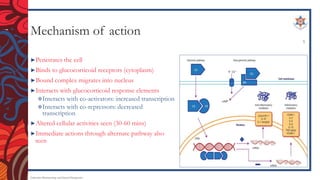
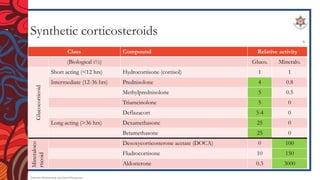
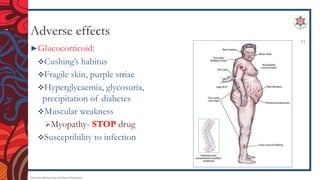
The document discusses corticosteroids, including their mechanism of action, types of synthetic corticosteroids, and their indications and side effects. It begins by explaining that the adrenal cortex secretes mineralocorticoids like aldosterone and glucocorticoids like cortisol. Synthetic corticosteroids work by penetrating cells, binding glucocorticoid receptors, and altering gene transcription. Common synthetic corticosteroids include hydrocortisone, prednisone, and dexamethasone, which are used to treat conditions like adrenal insufficiency, arthritis, allergies, and lung/skin diseases. However, they can cause side effects like edema, high blood pressure, infections,