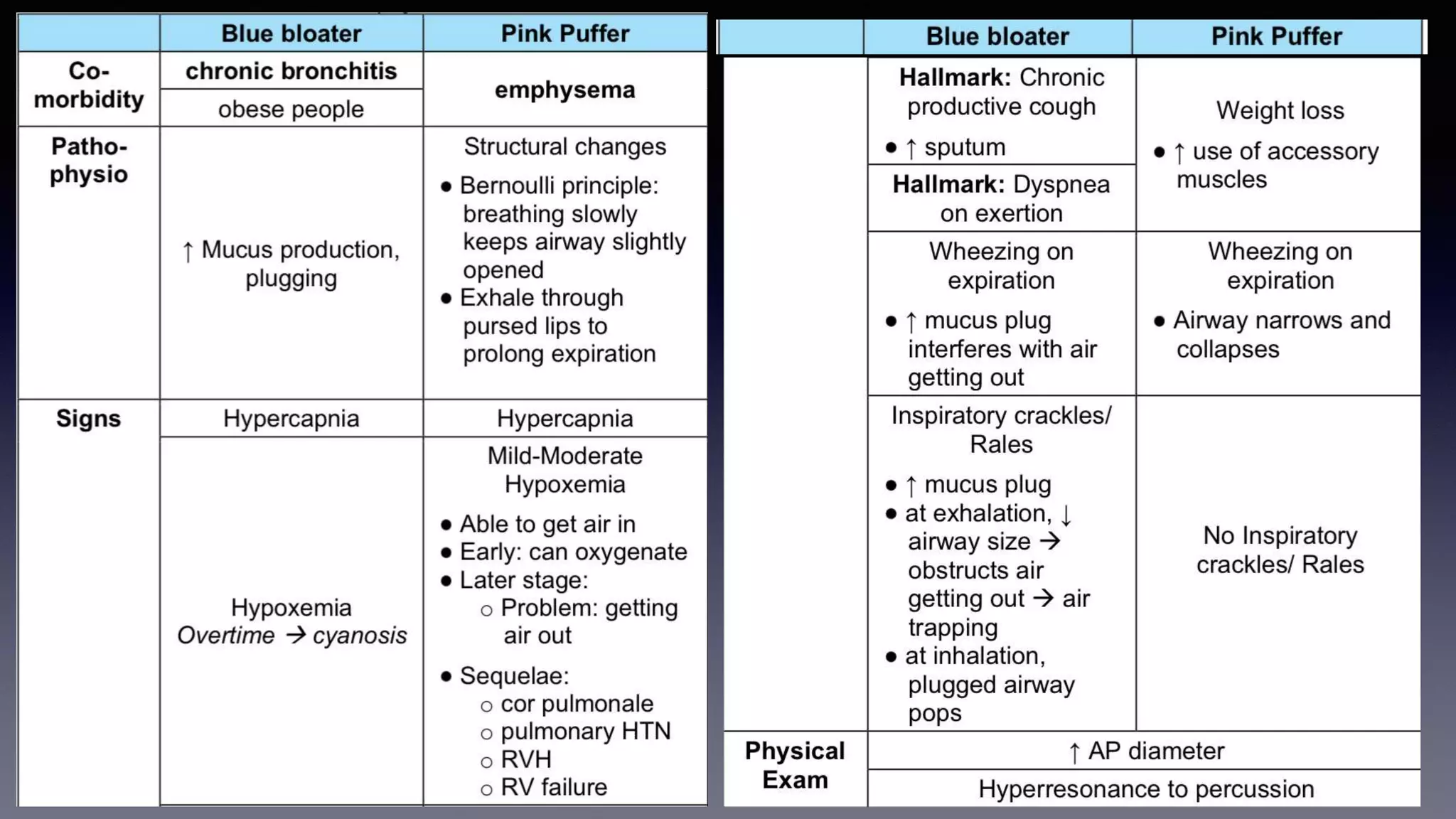
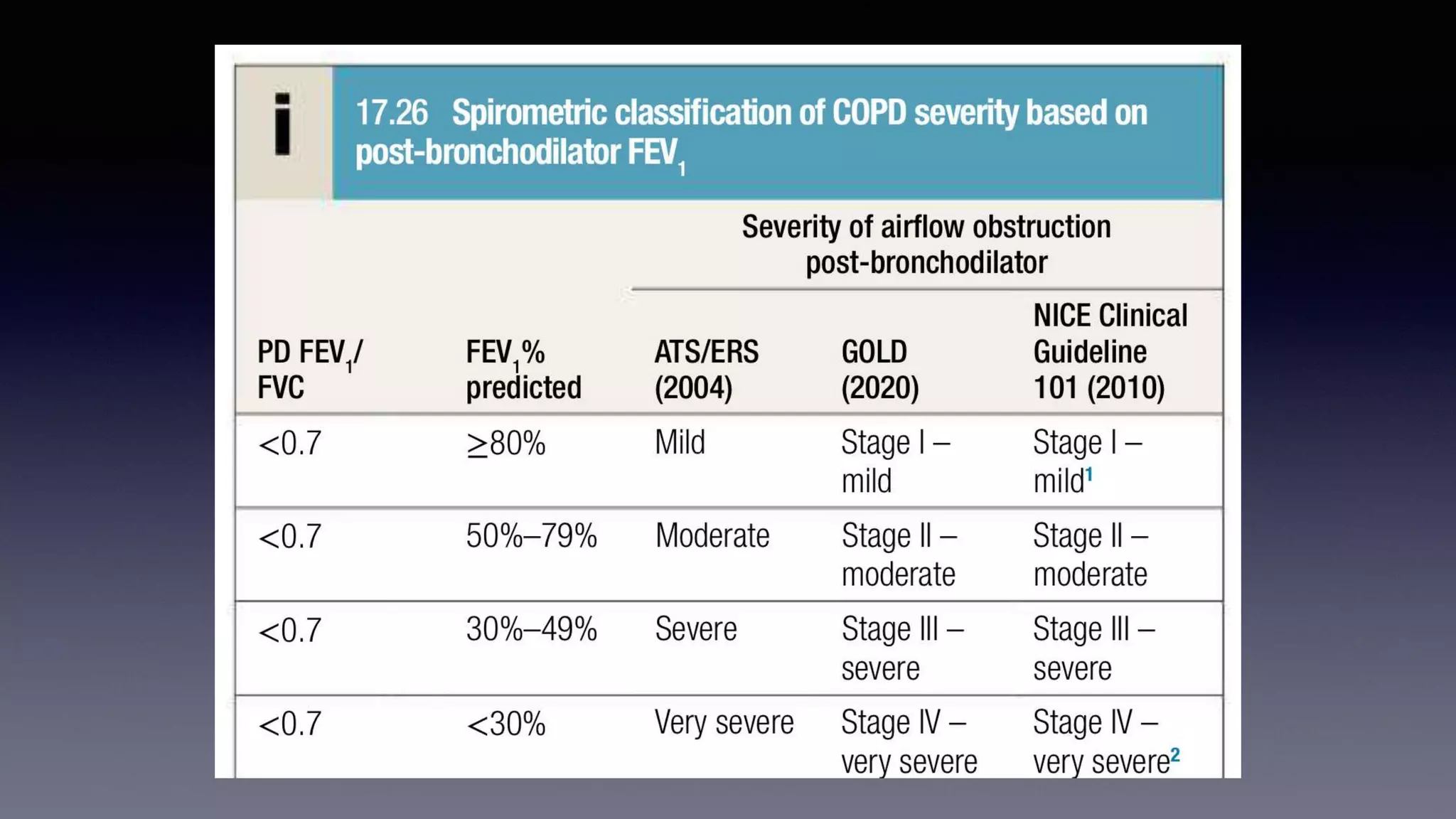
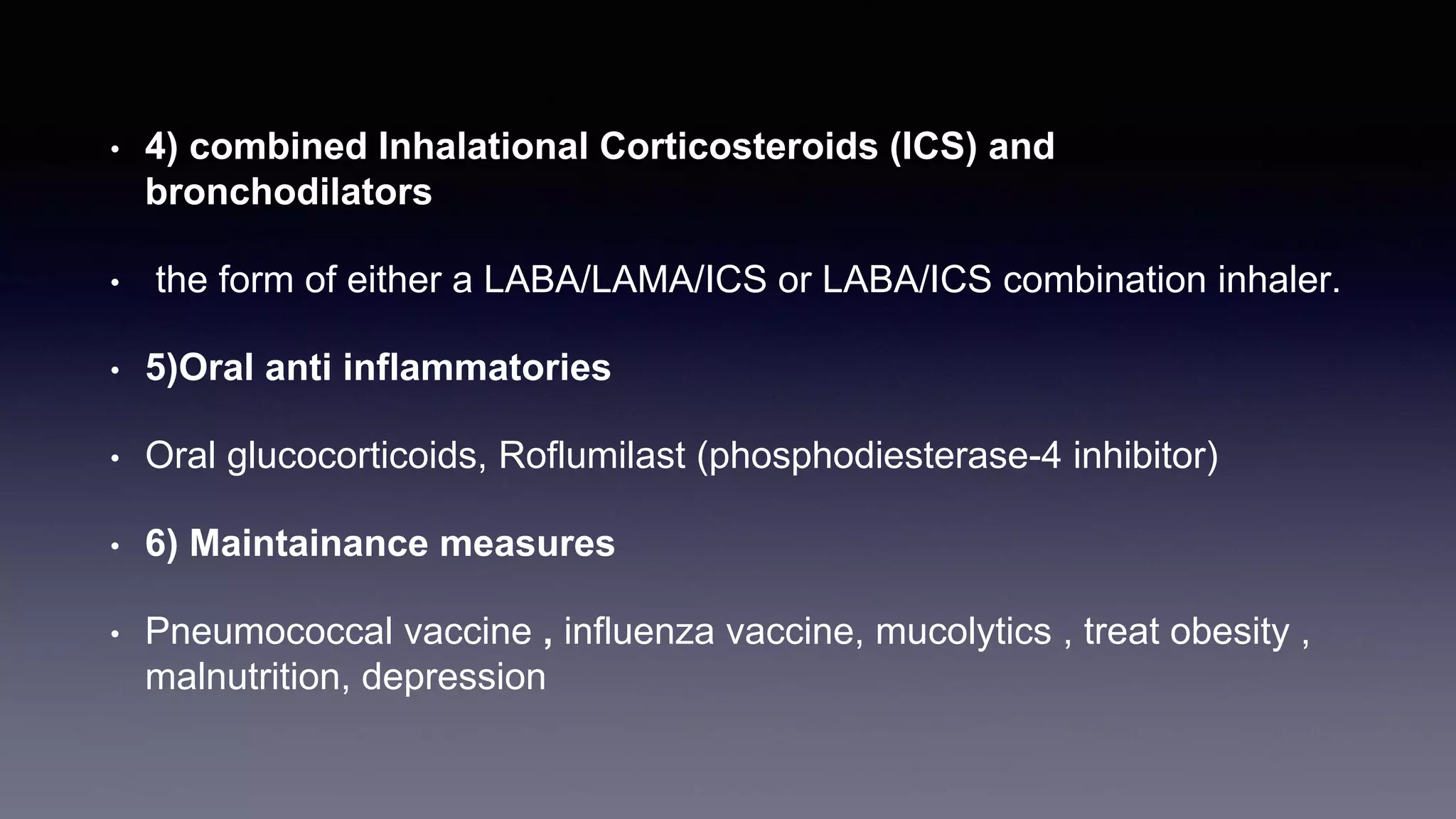
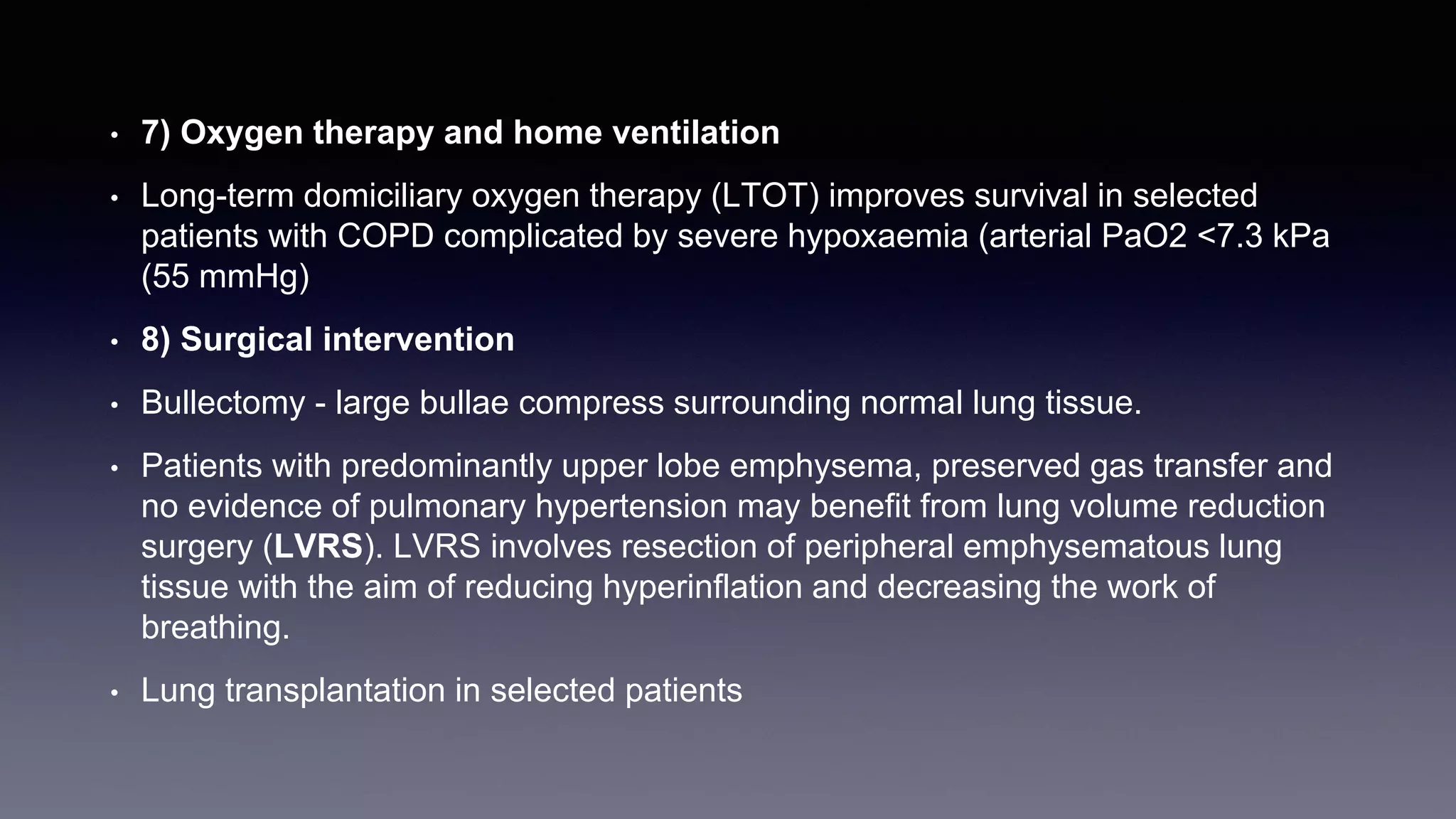
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation caused by exposure to noxious particles or gases. The two main conditions that make up COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Cigarette smoking is the most significant risk factor. Management of COPD includes reducing exposure, pulmonary rehabilitation, bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, and surgical interventions in some cases. Acute exacerbations are characterized by increased symptoms and deterioration in lung function, often triggered by infection. Treatment focuses on bronchodilators, glucocorticoids, antibiotics if sputum is purulent, and non-invasive or invasive ventilation if needed.