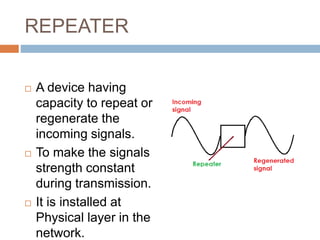
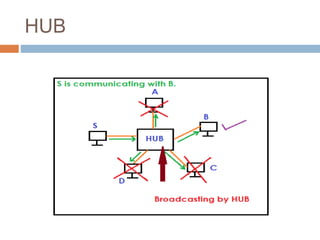
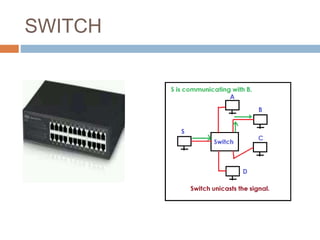
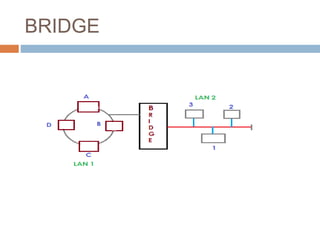
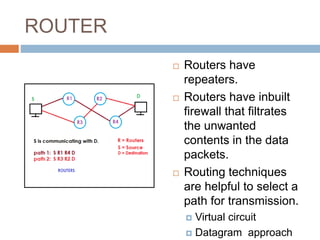
This document discusses various connectivity devices used in computer networks. It describes a transceiver as a device that can both receive and transmit signals. A repeater is used to regenerate incoming signals to maintain signal strength during transmission. A hub and switch are central devices in star networks that connect other devices, with the main difference being that a switch can deliver messages directly to the intended recipient while a hub broadcasts to all. A bridge connects two or more local area networks, while a router routes signals between similar networks and keeps routing information. A gateway interconnects dissimilar networks and is installed at the application layer.


![IDENTIFICATION OF A NODE IN
THE NETWORK
Each Node has an address
through which it is identified in
the network.
NIC [Network Interface Card]:
An special device connected
on the motherboard of the
computer having a 6 digit
hexadecimal address [MAC
Address] by which it is
identified by matching the
logical address[IP Address] at
network support layers .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/connectivitydevices-170215180709/85/Connectivity-devices-4-320.jpg)