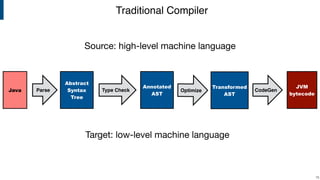
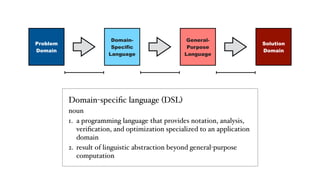
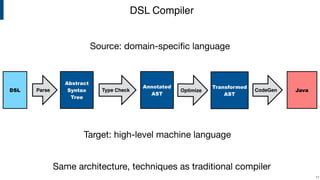
Compiler construction techniques are applied beyond general-purpose languages through domain-specific languages (DSLs). The document discusses several DSLs developed using Spoofax including:
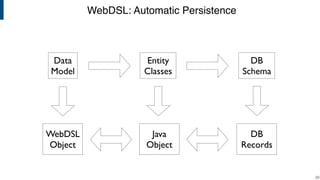
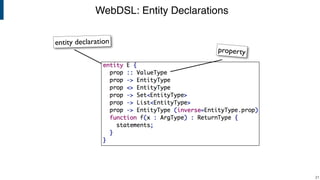
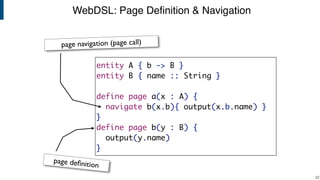
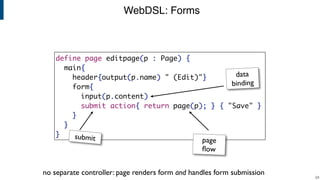
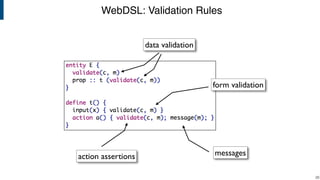
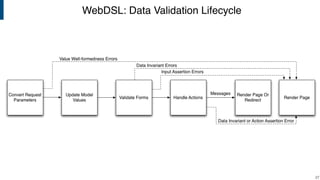
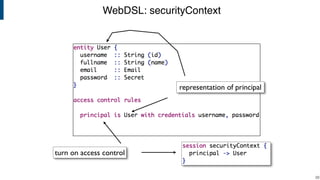
- WebDSL for web programming with sub-languages for entities, queries, templates, and access control.
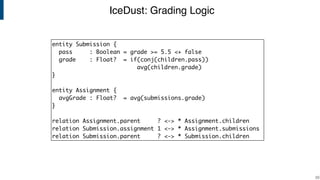
- IceDust for modeling information systems with derived values computed on-demand, incrementally, or eventually consistently.
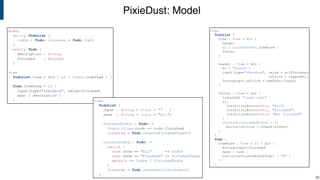
- PixieDust for client-side web programming with views as derived values updated incrementally.
- PIE for defining software build pipelines as tasks with dynamic dependencies computed incrementally.
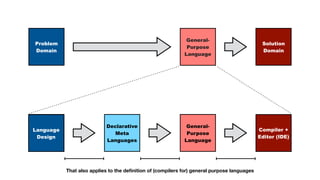
The document also outlines several research challenges in compiler construction like high-level declarative language definition, verification of












![WebDSL: Templates (Page Fragments)
!23
define main() {
includeCSS("wiki.css")
top()
block[class="content"] {
elements()
}
}
define span top() {
navigate root() {"Wiki"}
}
parameter
template definition
template call](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs4200-2018-17-conclusion-190127215035/85/Compiler-Construction-Lecture-17-Beyond-Compiler-Construction-23-320.jpg)











![High-Performance Parsing
- JSGLR2: 2x to 10x speed-up compared to JSGLR
- More speed-up possible?
- Explore effects of different parse table formats (LR, SLR, LALR)
Error Recovery & Error Messages
- Apply error recovery approach of [TOPLAS12] to JSGLR2
- Generate high quality error messages
Incremental Parsing
- Re-parse effort proportional to change of program text
- Approach: adapt Graham/Wagner algorithm to SGLR
Extensible Syntax
- Extend syntax during parsing to support extensible languages
!41
Syntax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs4200-2018-17-conclusion-190127215035/85/Compiler-Construction-Lecture-17-Beyond-Compiler-Construction-41-320.jpg)




![Interpreters from dynamic semantic specification
- Prototype for DynSem [RTA15] applied to Grace [DLS17], Tiger
Frame-based interpreters
- Scope graph describes memory model [ECOOP16]
- Define in DynSem applied to realistic languages
- Correct-by-construction [POPL18] => dependently-typed DynSem
- Language-independent garbage collection
Partial evaluation
- Specialize DynSem interpreter to language-specific set of semantic rules
- Specialize language-specific rules to specific program
Compiler generation
- Derive compiler from dynamic semantics specification
!48
Dynamics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs4200-2018-17-conclusion-190127215035/85/Compiler-Construction-Lecture-17-Beyond-Compiler-Construction-48-320.jpg)
![Intrinsically Typed Definitional Interpreters
- For Middle Weight Java (MJ) in Agda [POPL18]
- Extend to more sophisticated type systems (generics, System F)
- Extend to more sophisticated effect systems (continutations, algebraic effects)
- Extend approach to other operations: transformation, code generation
Extrinsic Proofs
- Generation of extrinsic type soundness proof
- Other properties
Other Verification Challenges
- Semantics preservation of DSL code generators
- Correctness of meta-DSLs
!49
Verification](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs4200-2018-17-conclusion-190127215035/85/Compiler-Construction-Lecture-17-Beyond-Compiler-Construction-49-320.jpg)










