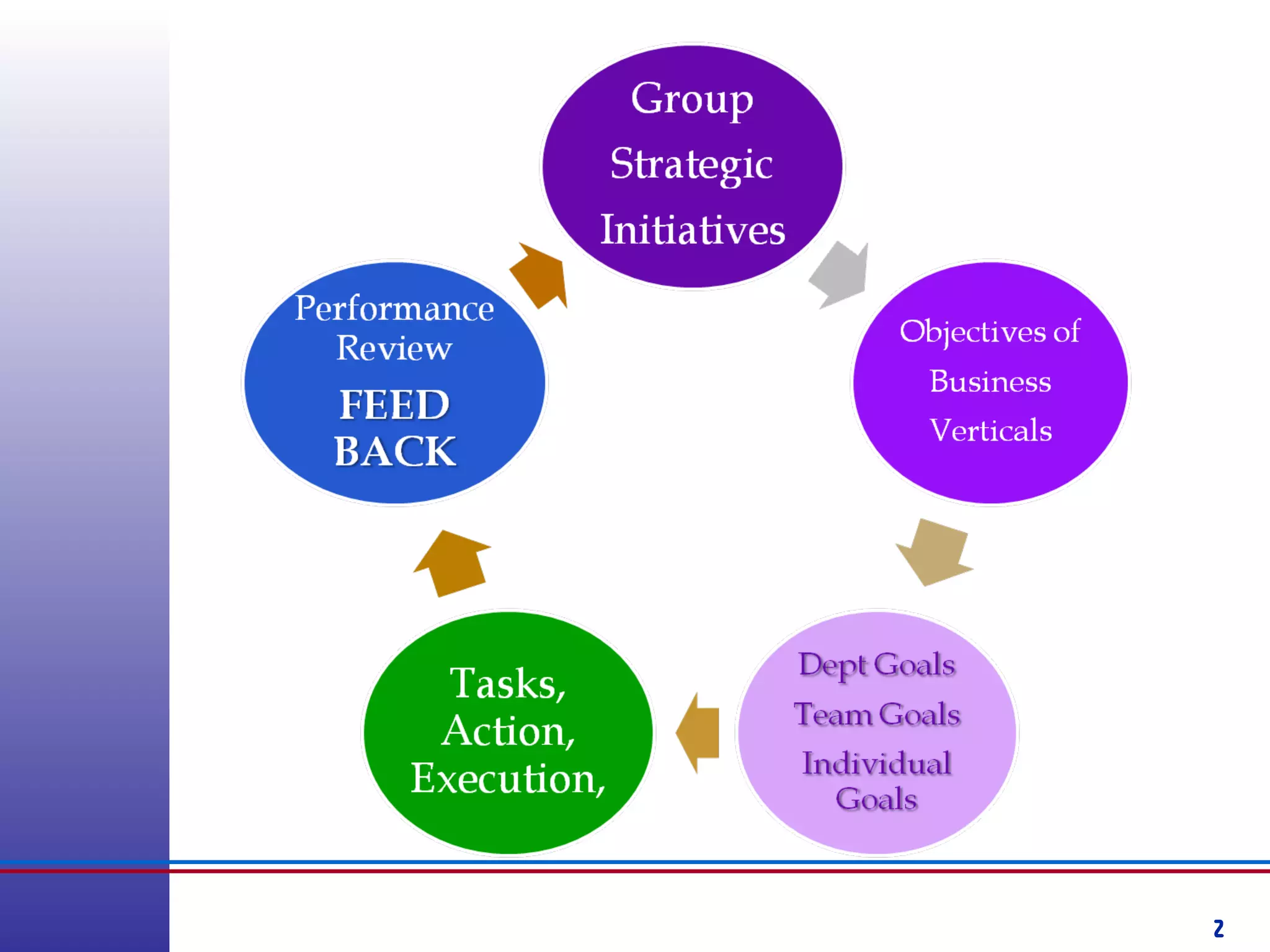
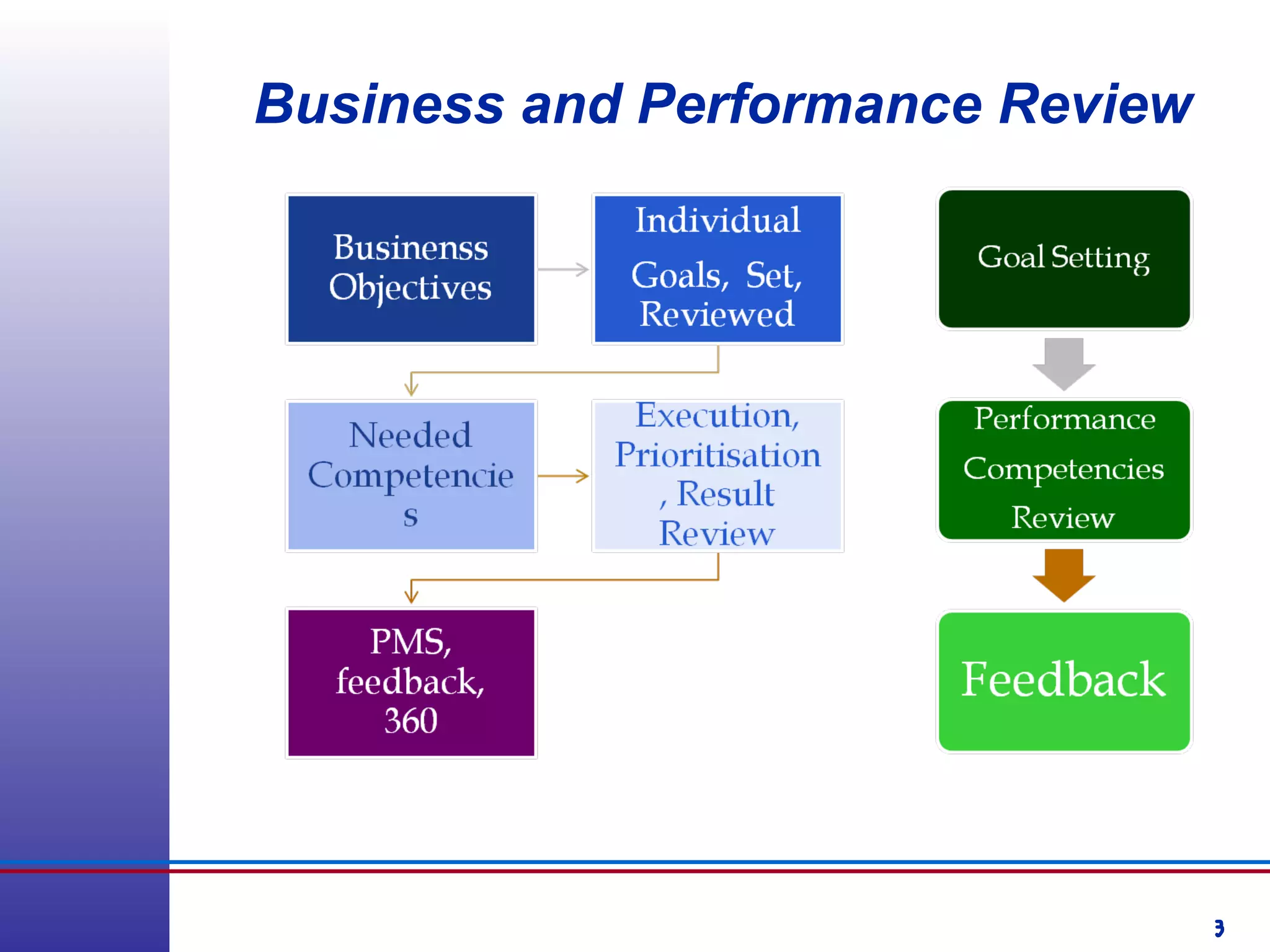
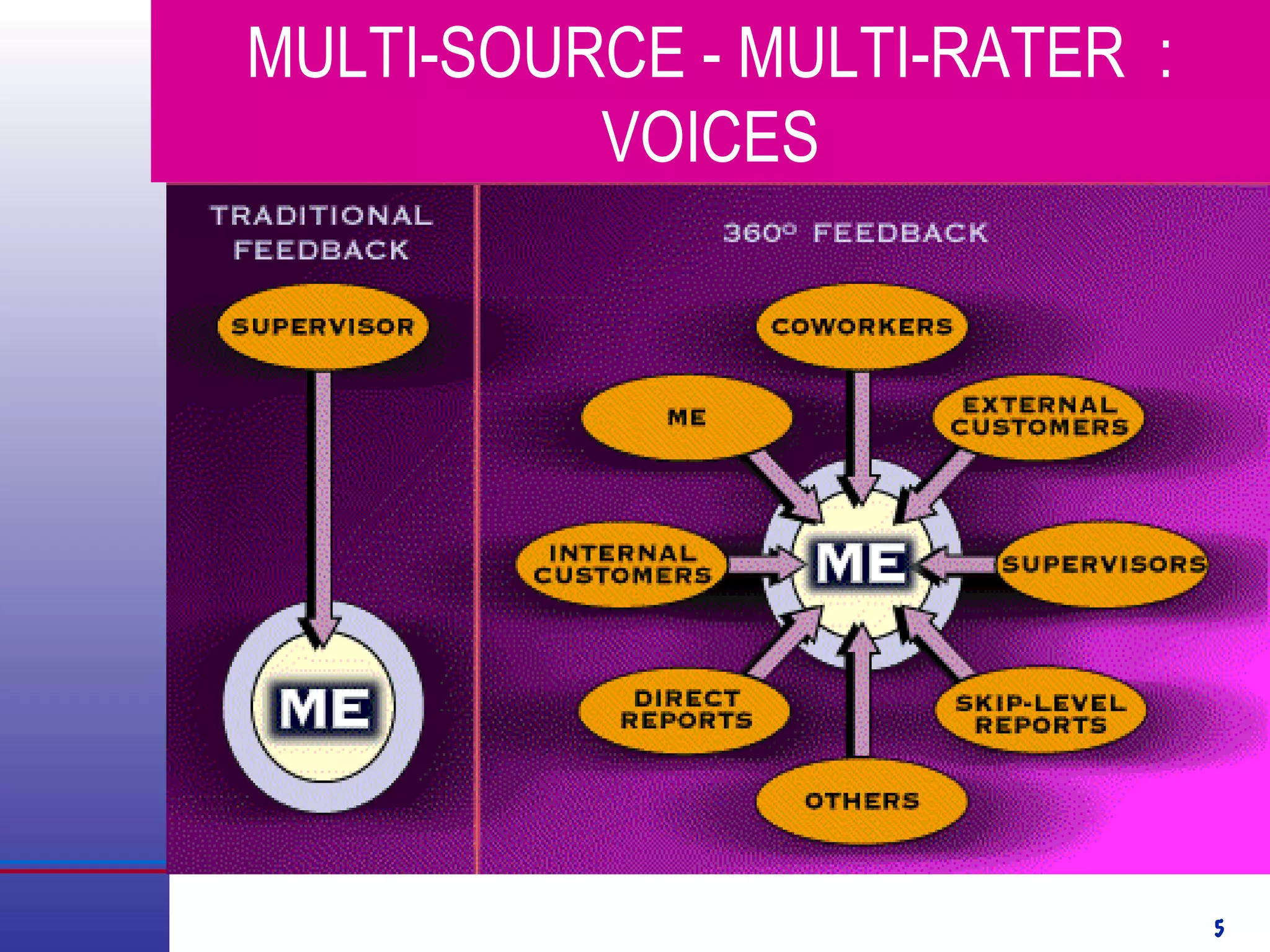
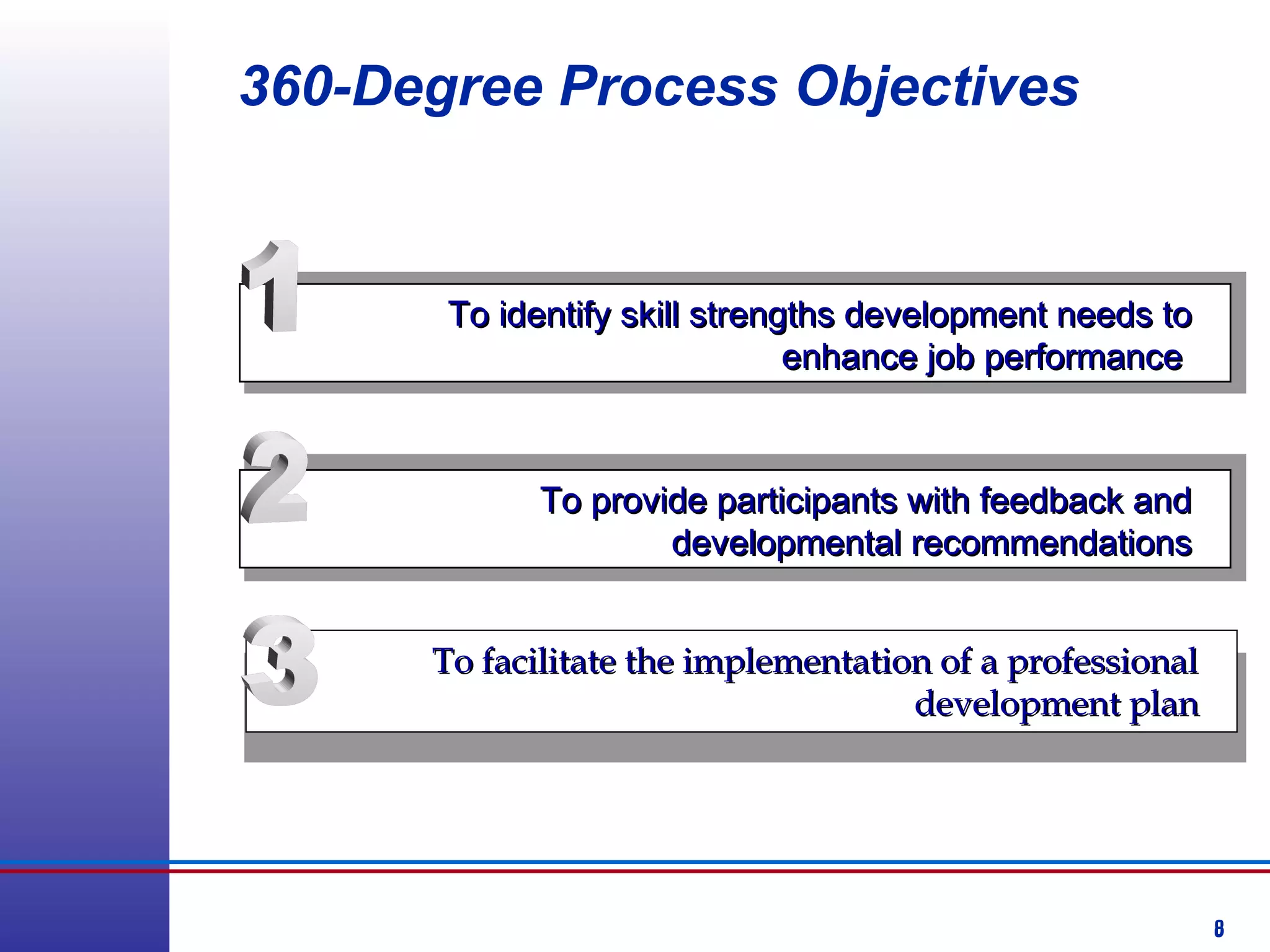
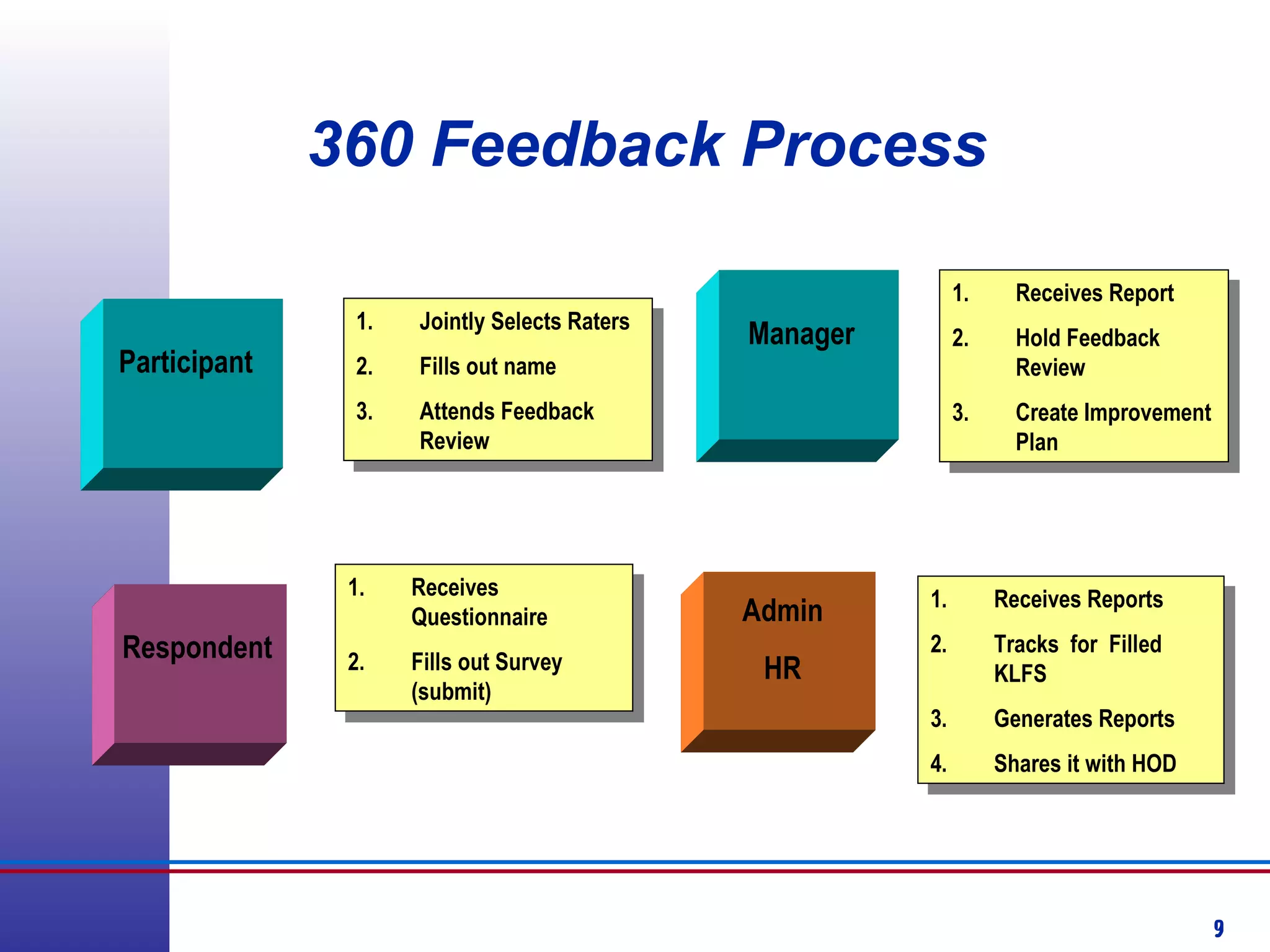
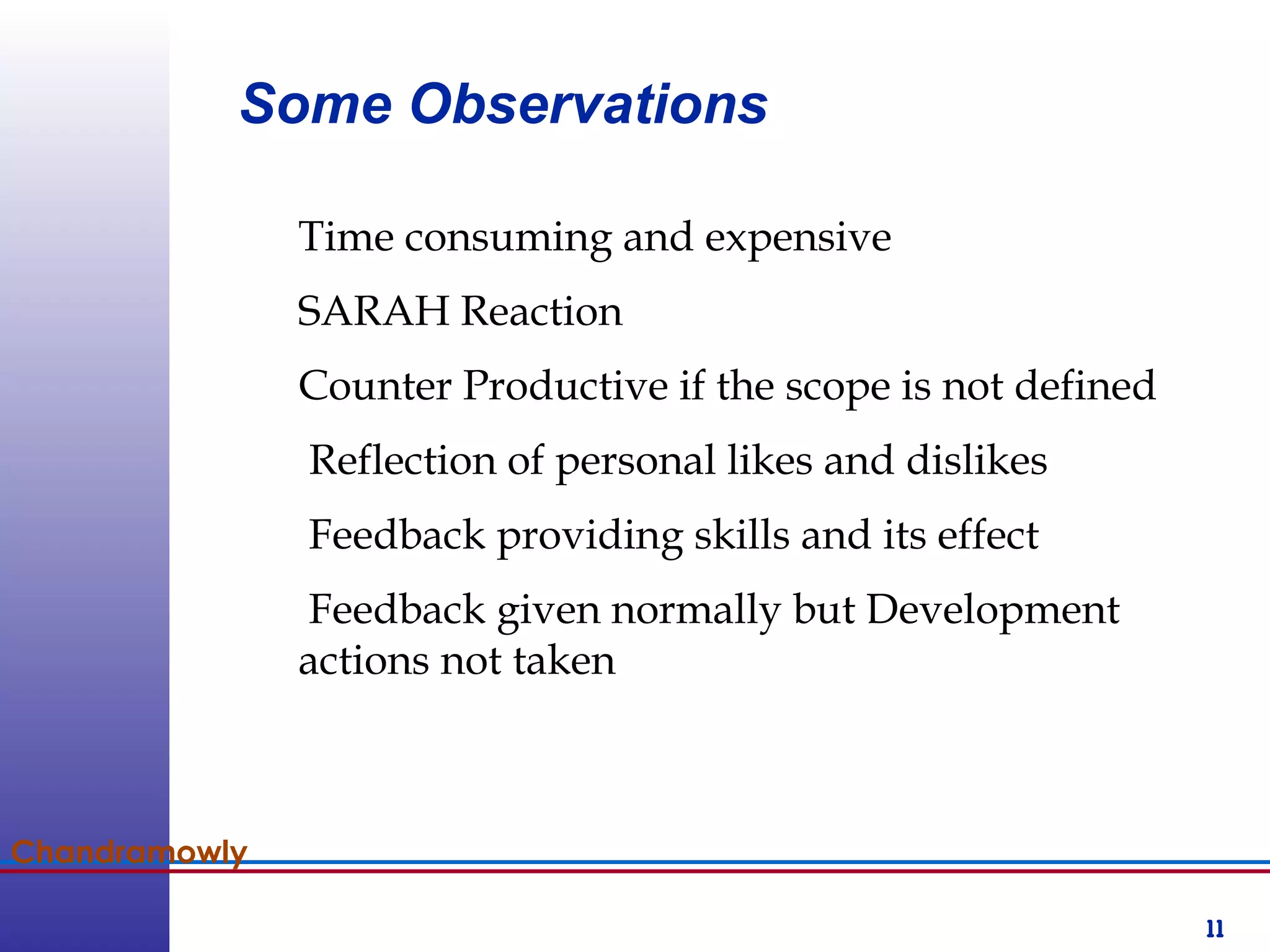
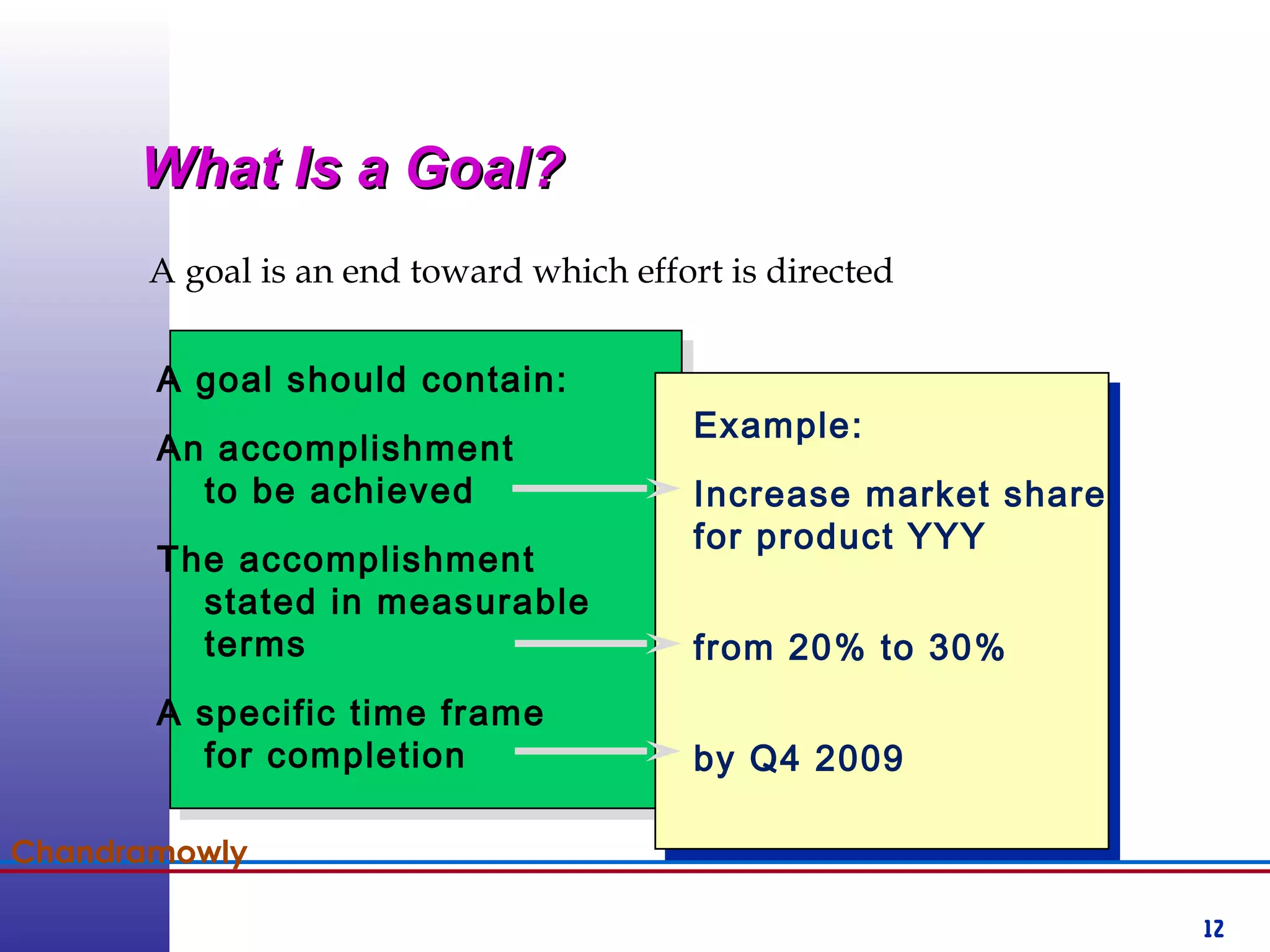
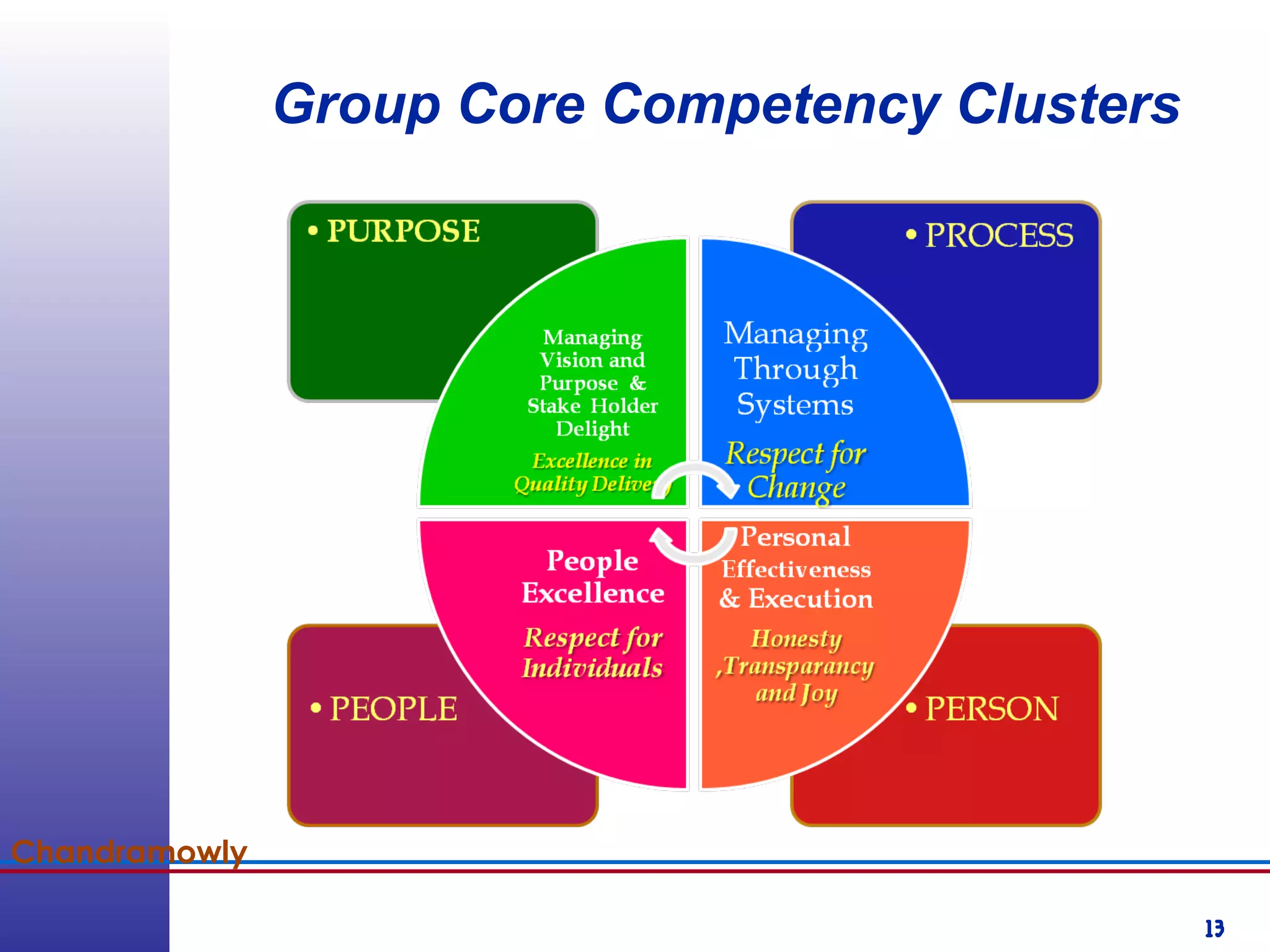
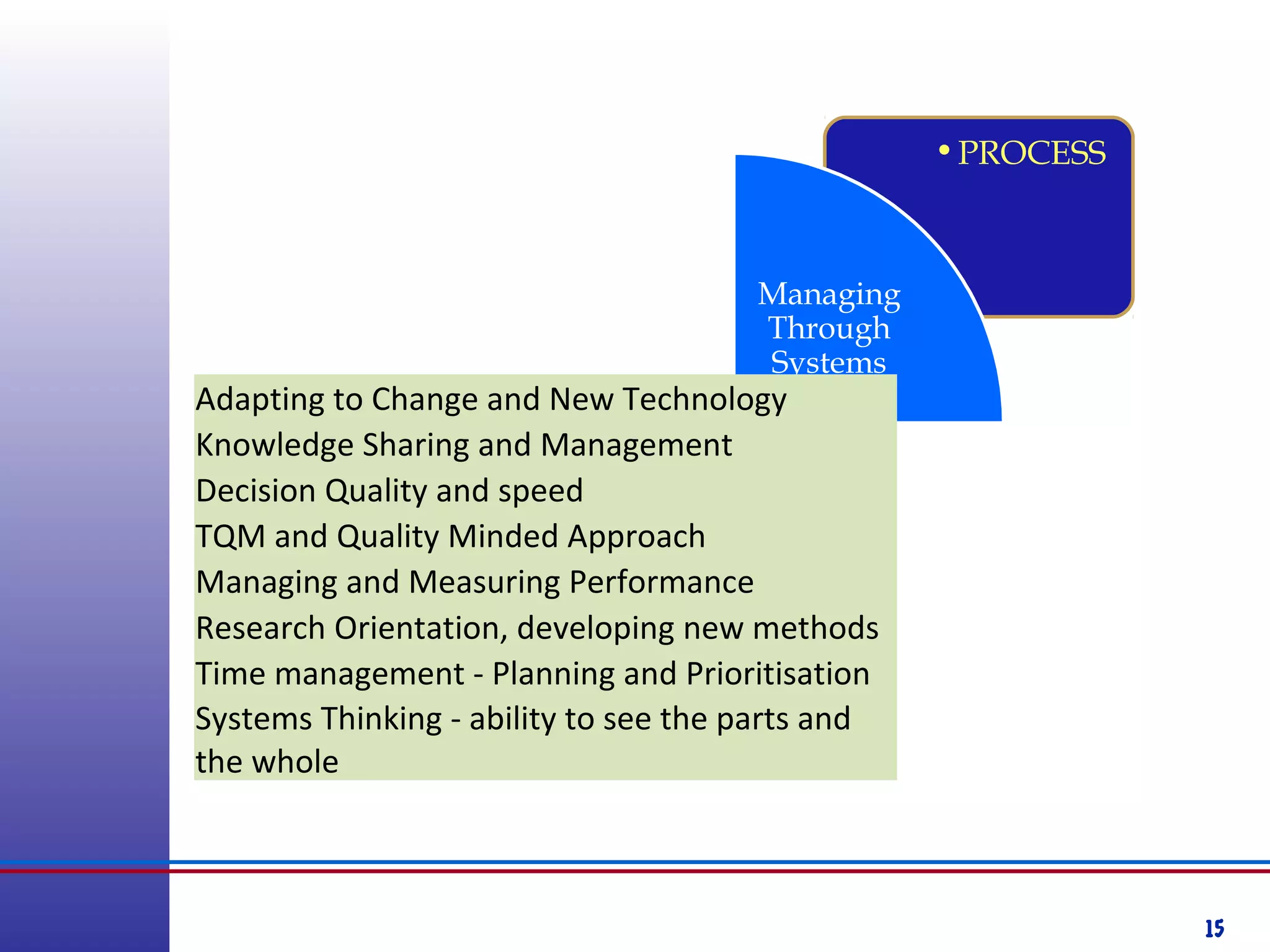
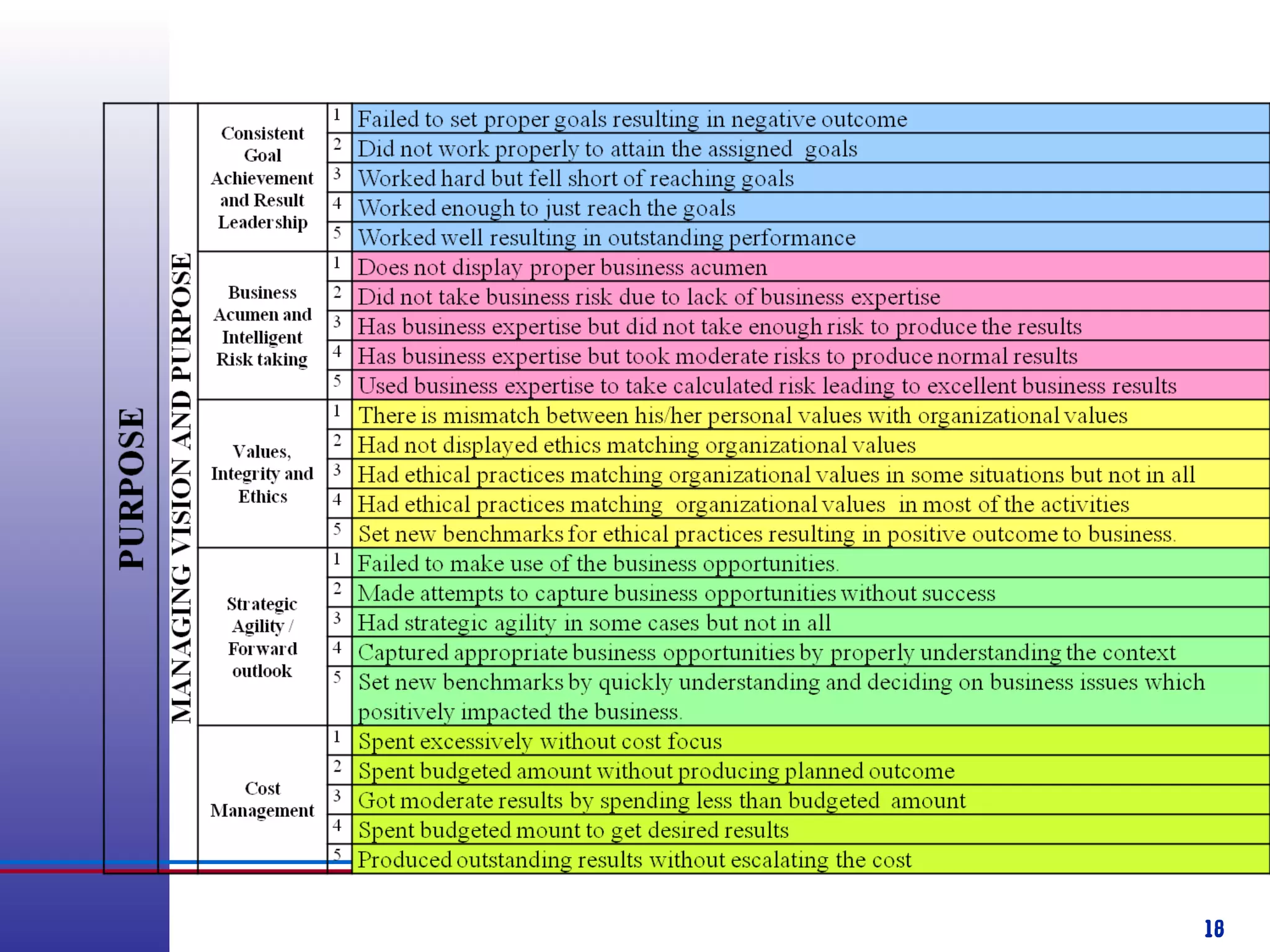
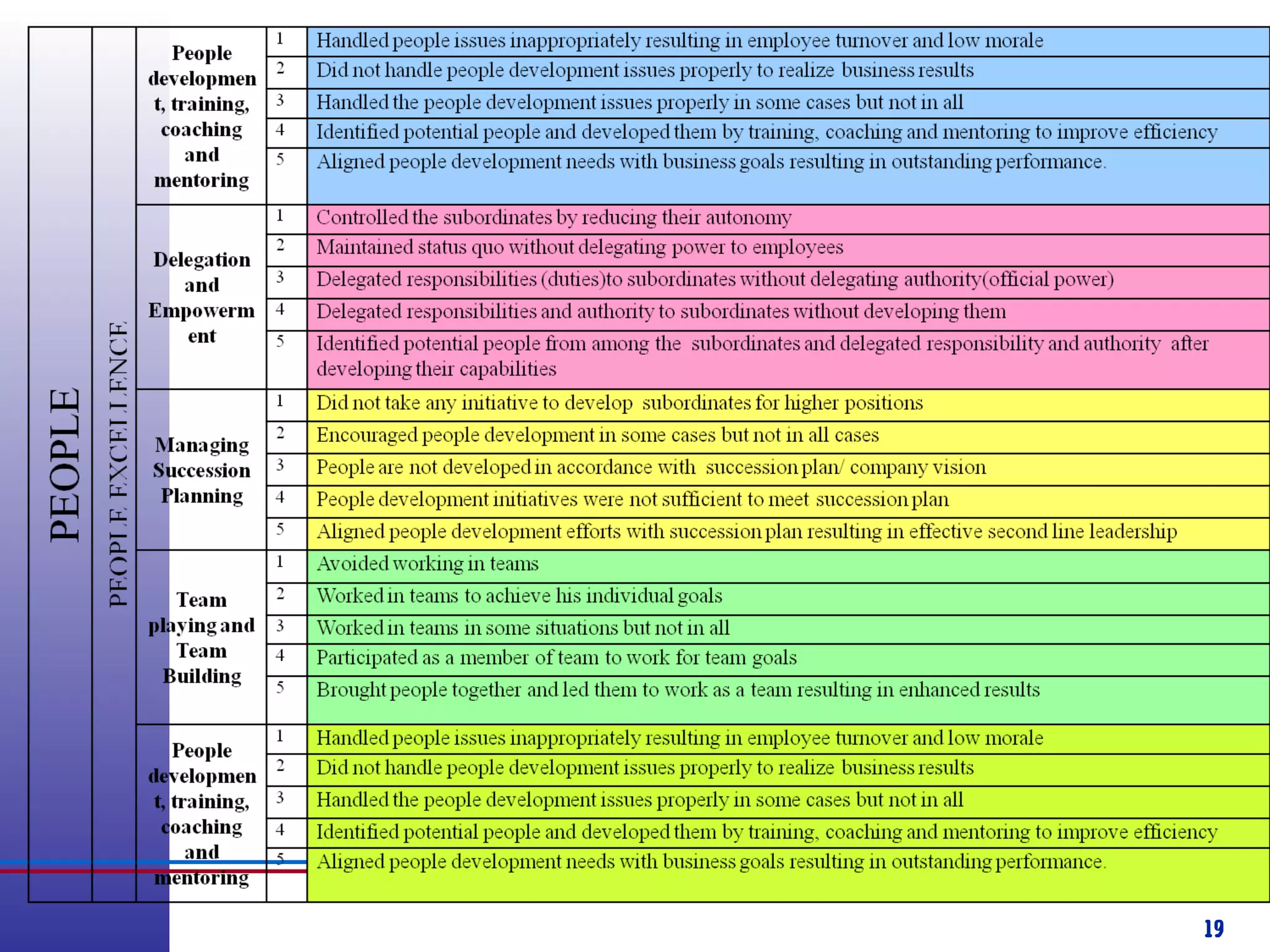
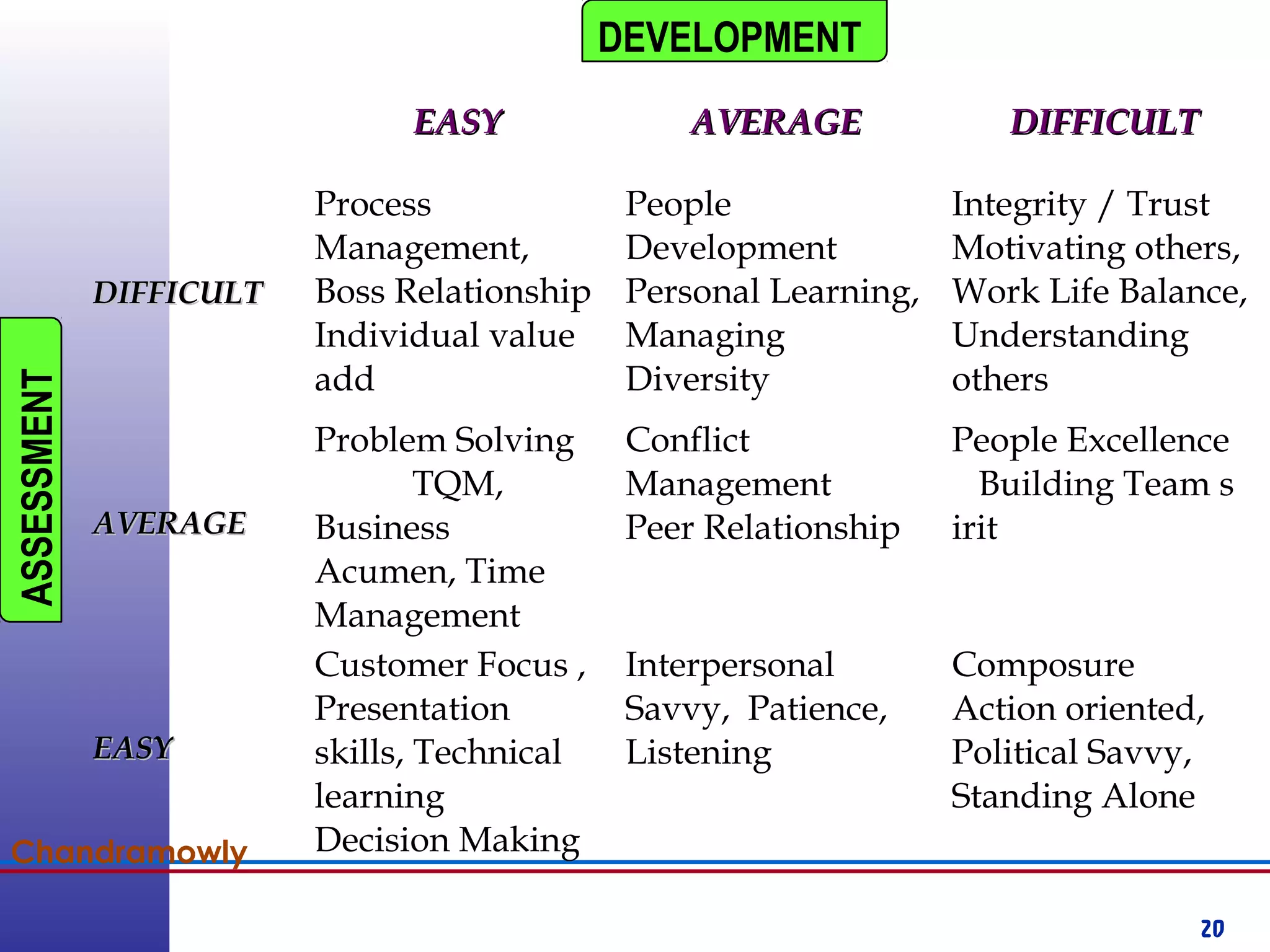
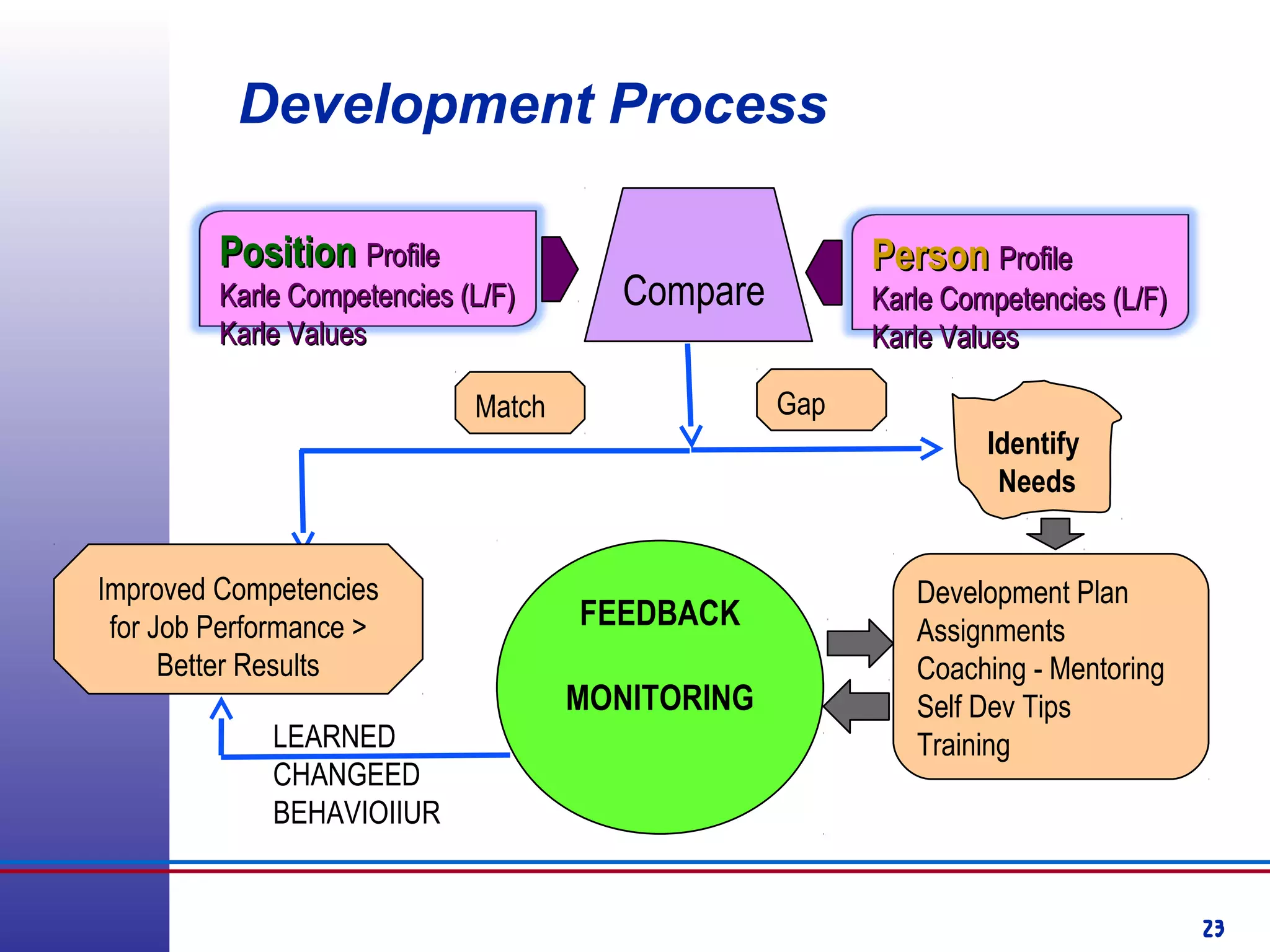
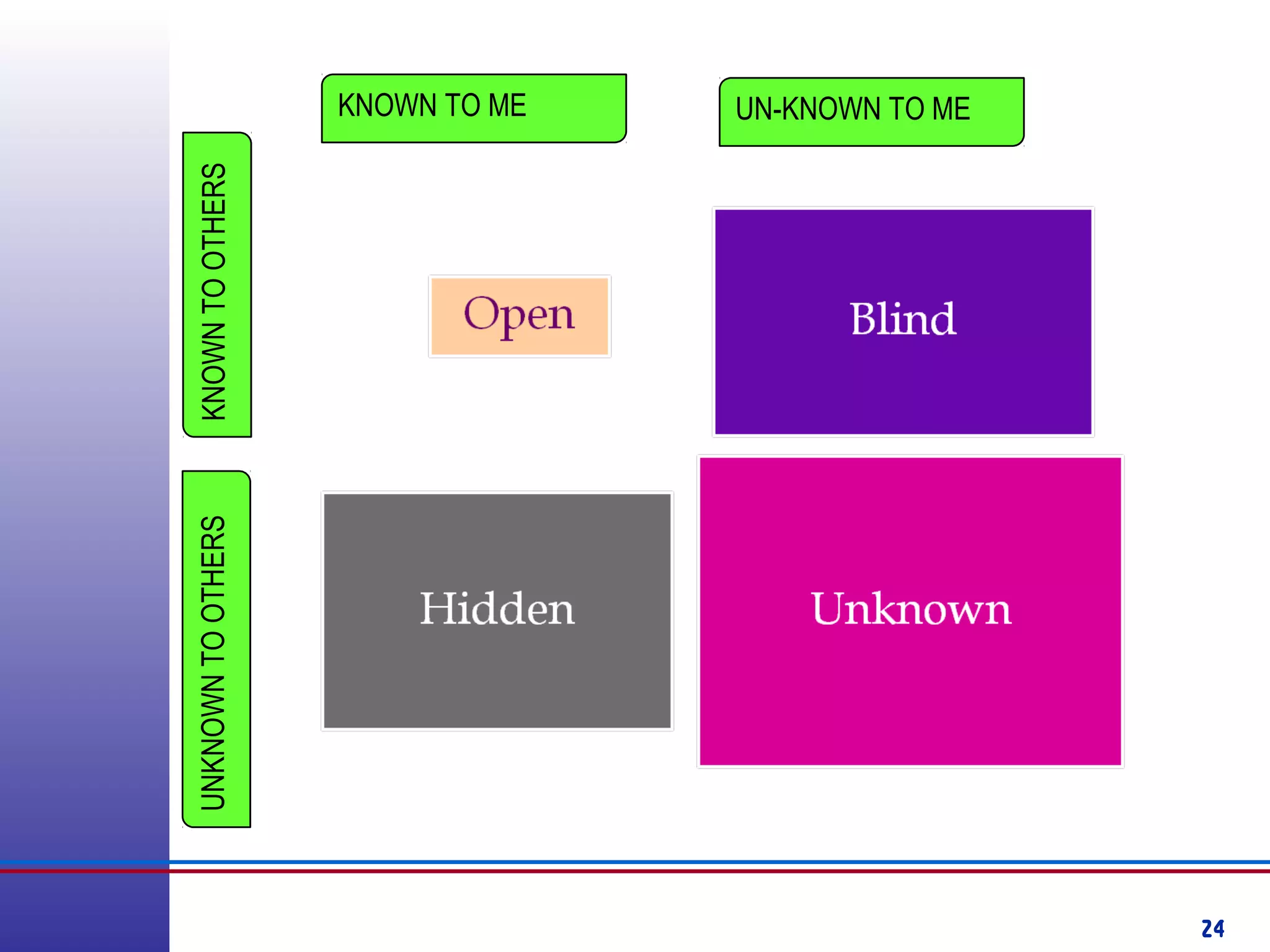
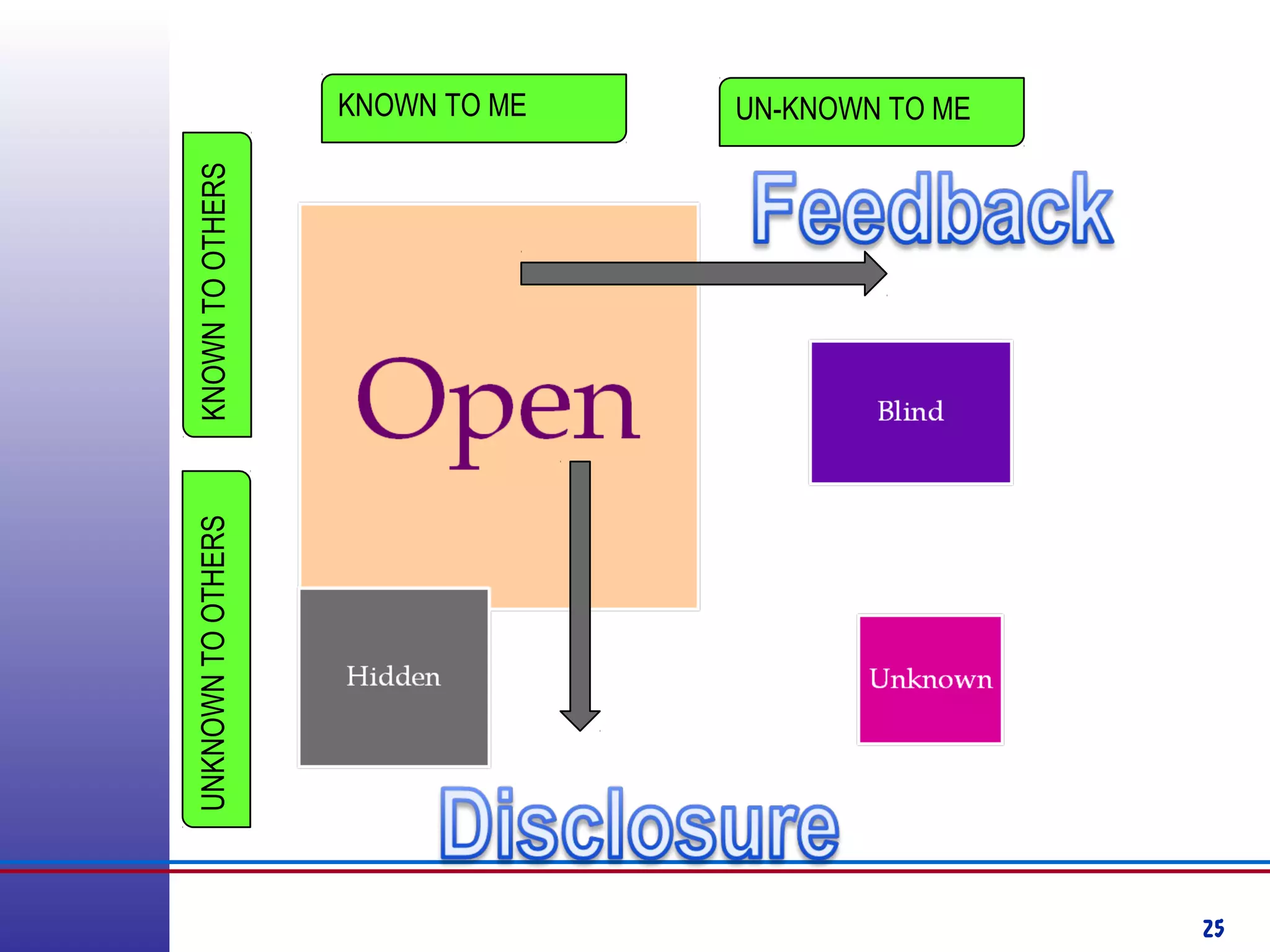
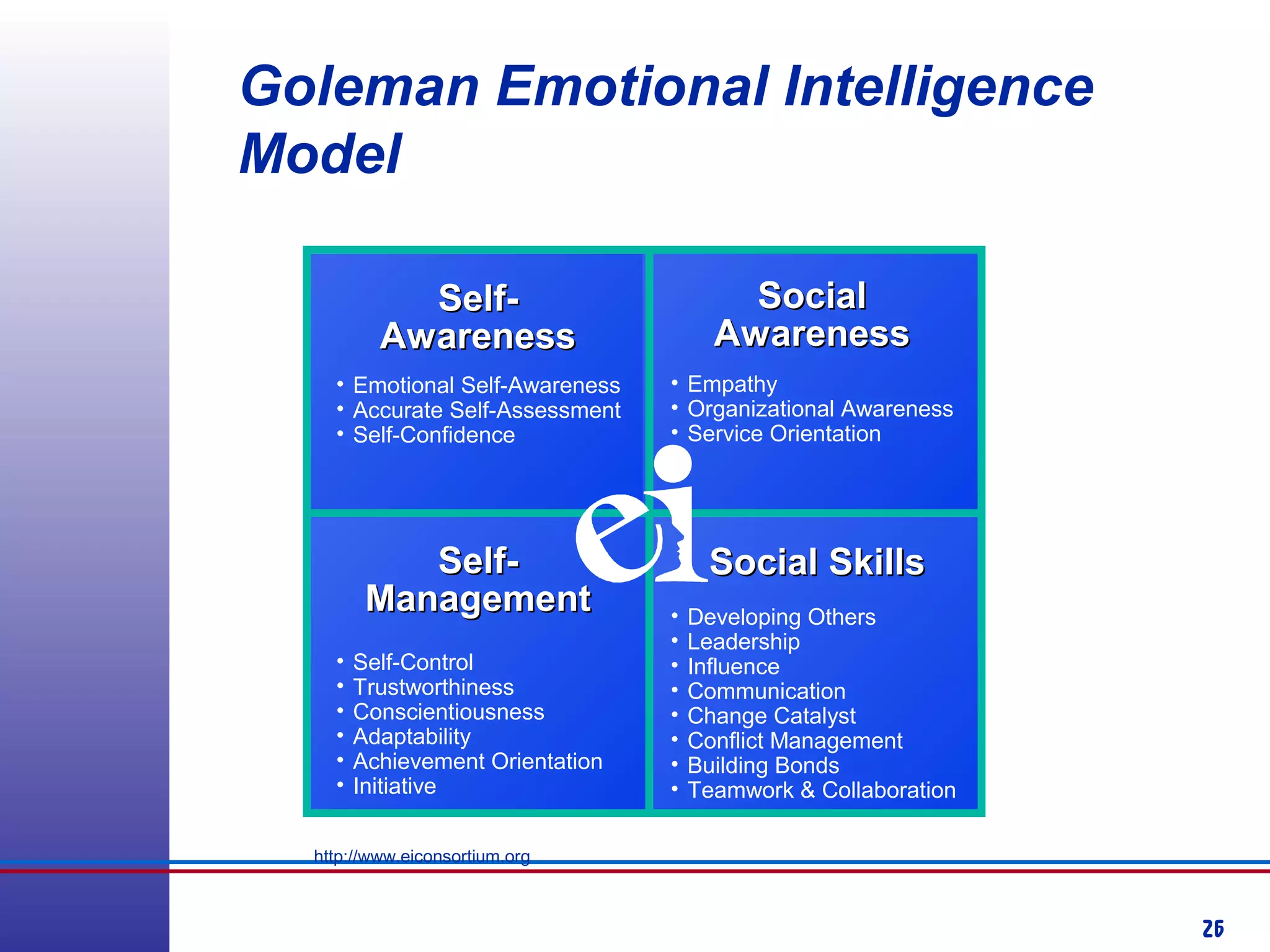
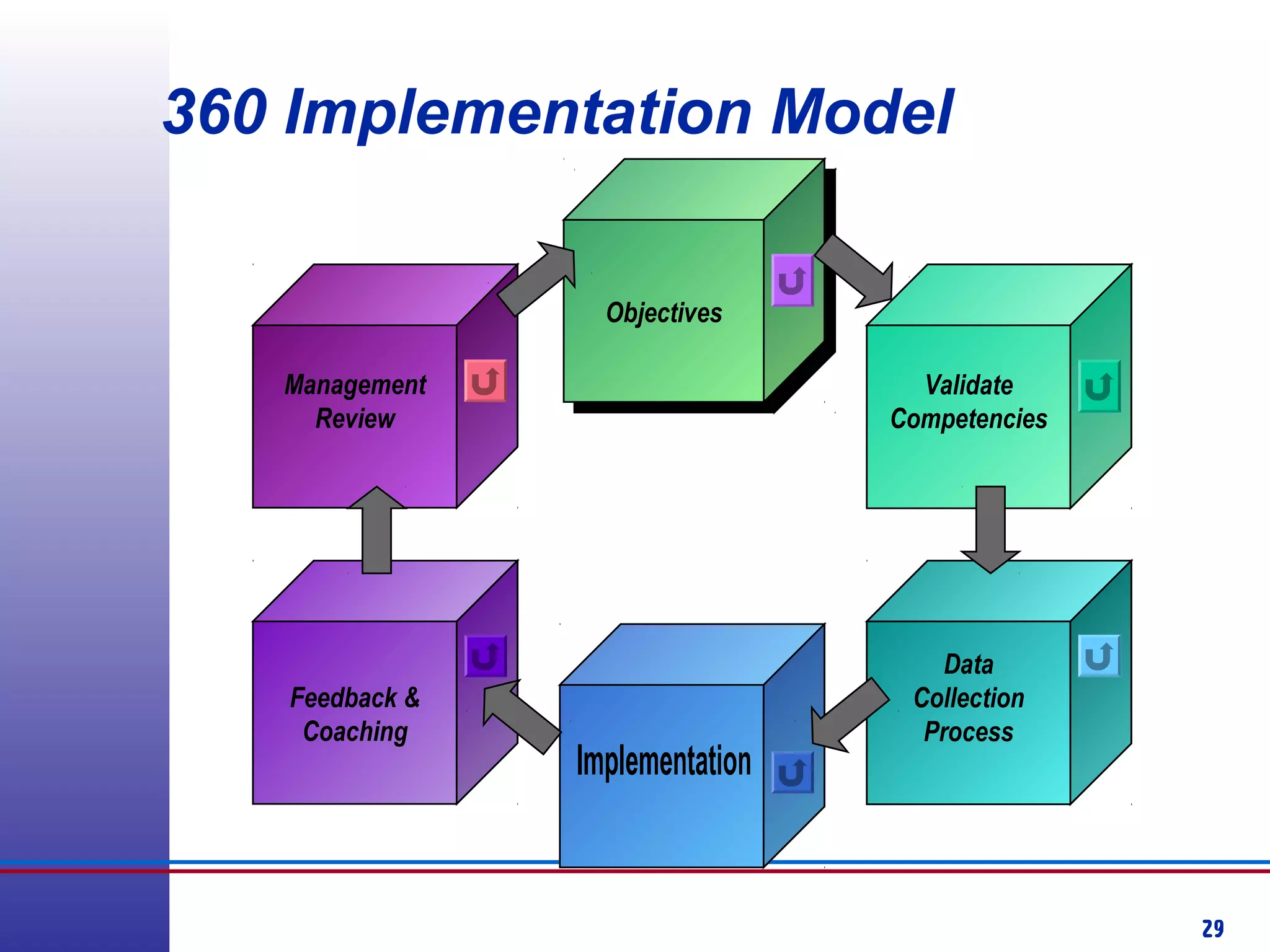
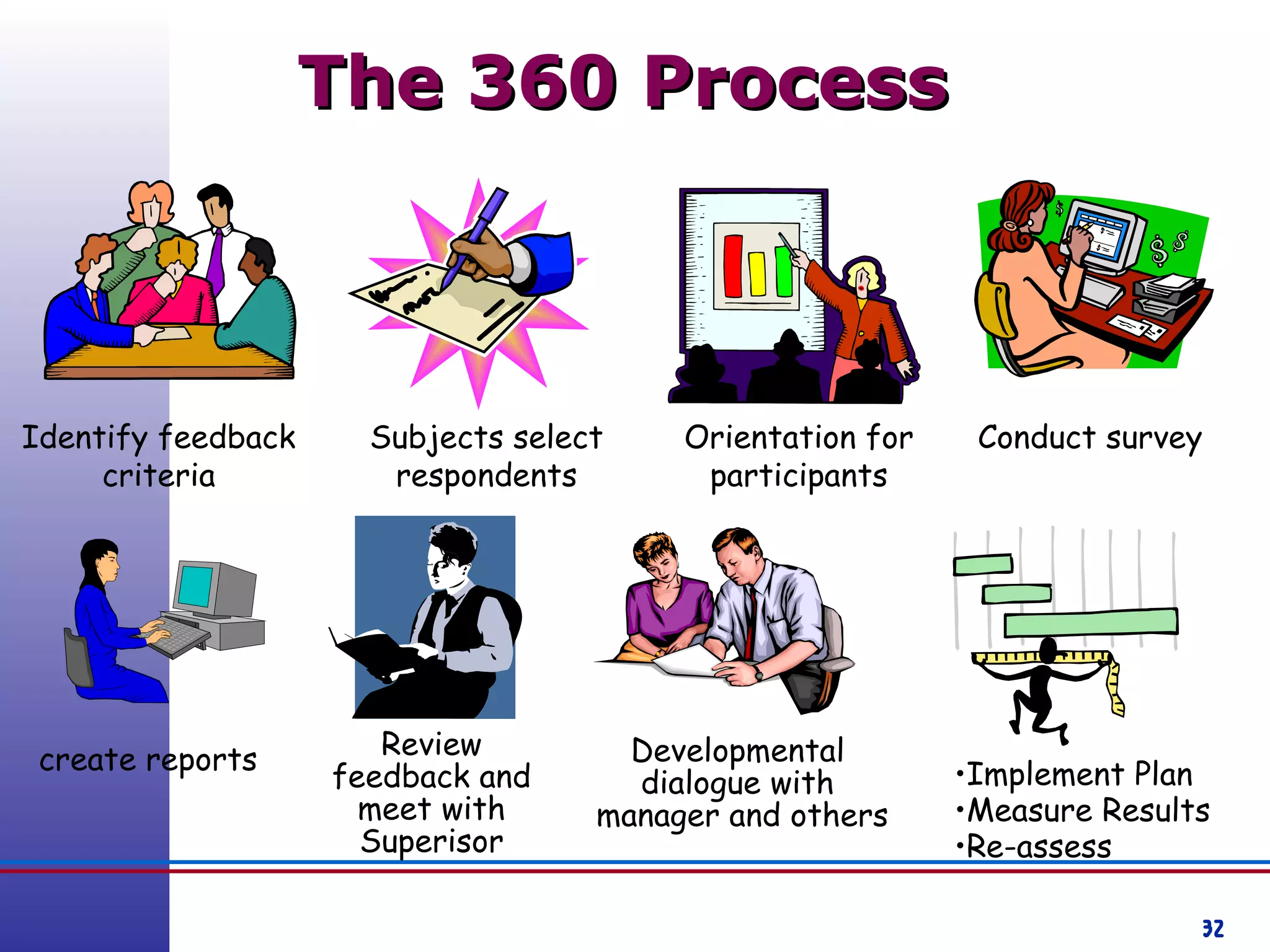
This document provides information about competency-based 360 degree feedback systems. It discusses how 360 degree feedback involves collecting performance ratings on an individual from their supervisor, peers, direct reports, and other stakeholders. The objectives of 360 degree feedback include facilitating professional development planning, identifying strengths and development needs to enhance job performance, and providing participants with feedback and recommendations. It also discusses theories on how 360 degree feedback can benefit individuals by increasing self-awareness and motivating them to address gaps between self-perceptions and perceptions of others.