This document discusses different multiple access techniques used in satellite communication:
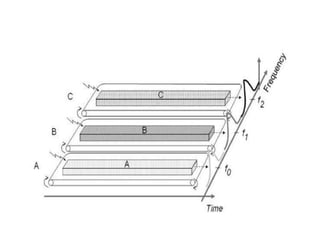
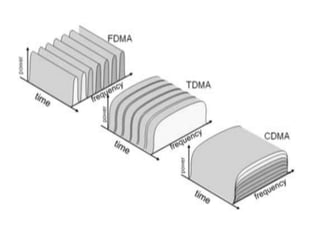
1. FDMA assigns each signal a different frequency band to avoid interference. Guard bands are used between signals. It has low interference but wastes capacity and requires narrowband filters.
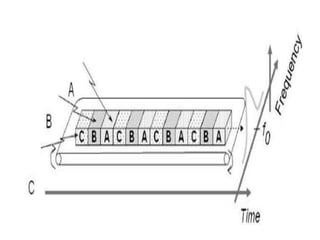
2. TDMA assigns each channel a time slot within a frame to access the full spectrum. It allows flexible data rates but requires complex synchronization and more bits for framing.
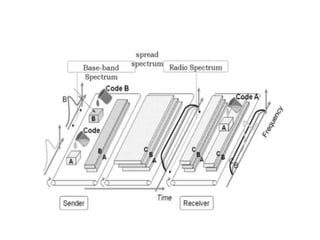
3. CDMA assigns each channel a unique spreading code. It has the highest spectrum efficiency but induces delay and has higher equipment costs.