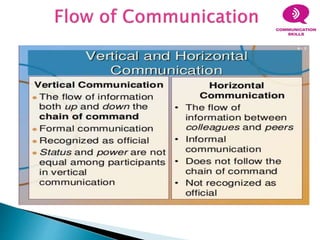
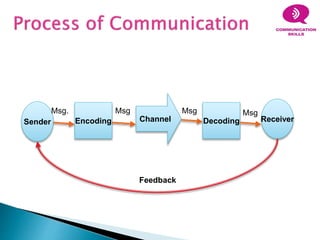
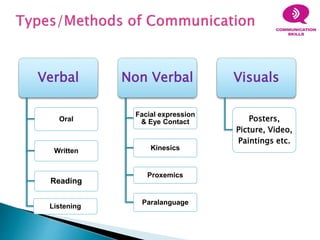
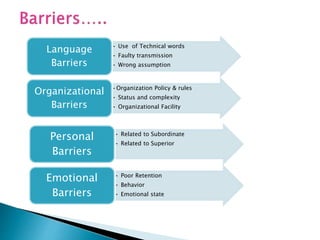
This document discusses various aspects of communication including the communication process, types of communication, barriers to communication, and principles of effective communication. It notes that communication involves a sender encoding a message that is sent through a channel and decoded by the receiver. Principles of good communication include being complete, concise, considerate of the receiver, clear, courteous, and correct. Barriers to communication can occur due to language differences, distractions, cultural factors, and personal or emotional issues. Both verbal and nonverbal forms of communication are addressed.