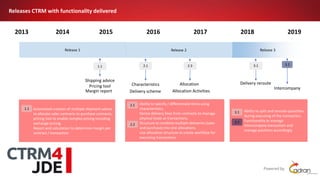
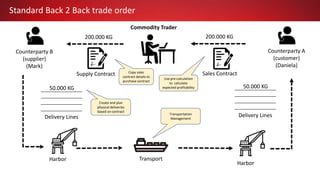
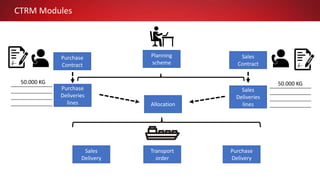
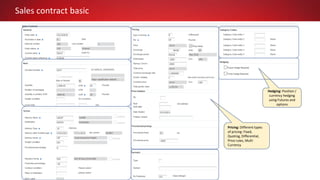
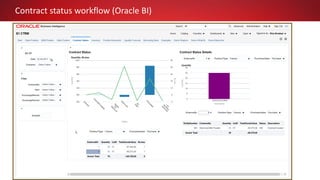
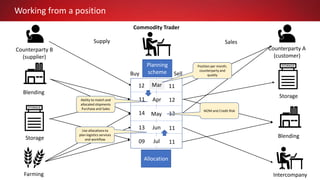
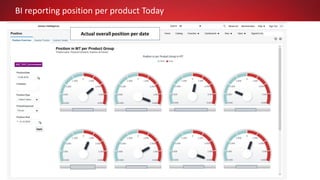
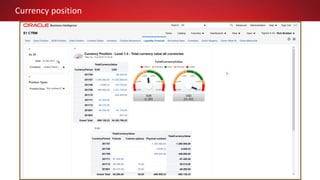
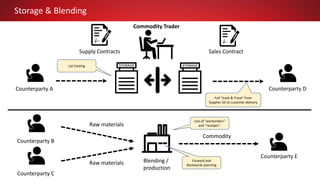
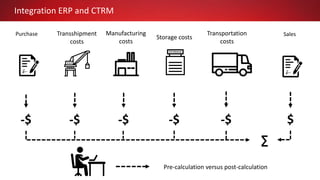
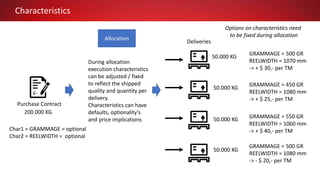
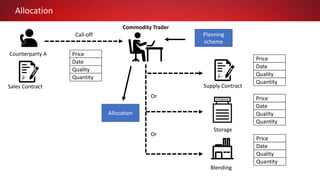
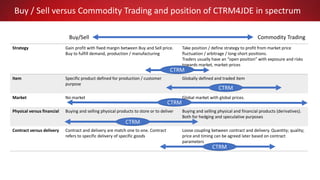
This document discusses Commodity Trading & Risk Management for Oracle JD Edwards (CTRM4JDE), an integrated commodity trading and ERP solution. It provides key functionality like position insight, risk management, contracts, allocations, and logistics services to help users manage the entire commodity trading process and reduce risks. The solution tracks functionality releases from 2013-2019, covering areas like allocation, pricing, margin reporting, and intercompany transactions. It also discusses how CTRM modules integrate with ERP systems and how CTRM4JDE positions itself between basic buy/sell operations and full commodity trading.