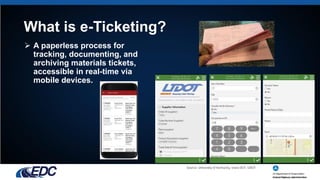
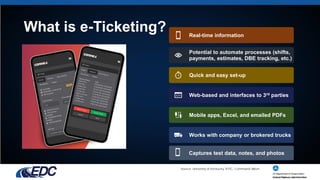
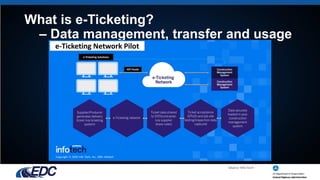
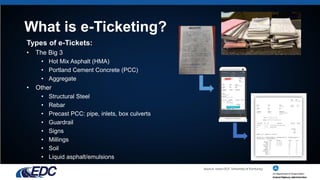
E-ticketing is a paperless method for tracking, documenting, and archiving material tickets in real-time through mobile devices, aiming to enhance worker safety, simplify ticket handling, and improve data integration. The document outlines the typical practices of e-ticketing, its advantages, and associated laws, as well as accomplishments and goals related to its deployment in construction. Challenges include gaining buy-in from various stakeholders, managing privacy concerns, and standardizing data usage across different state DOTs.