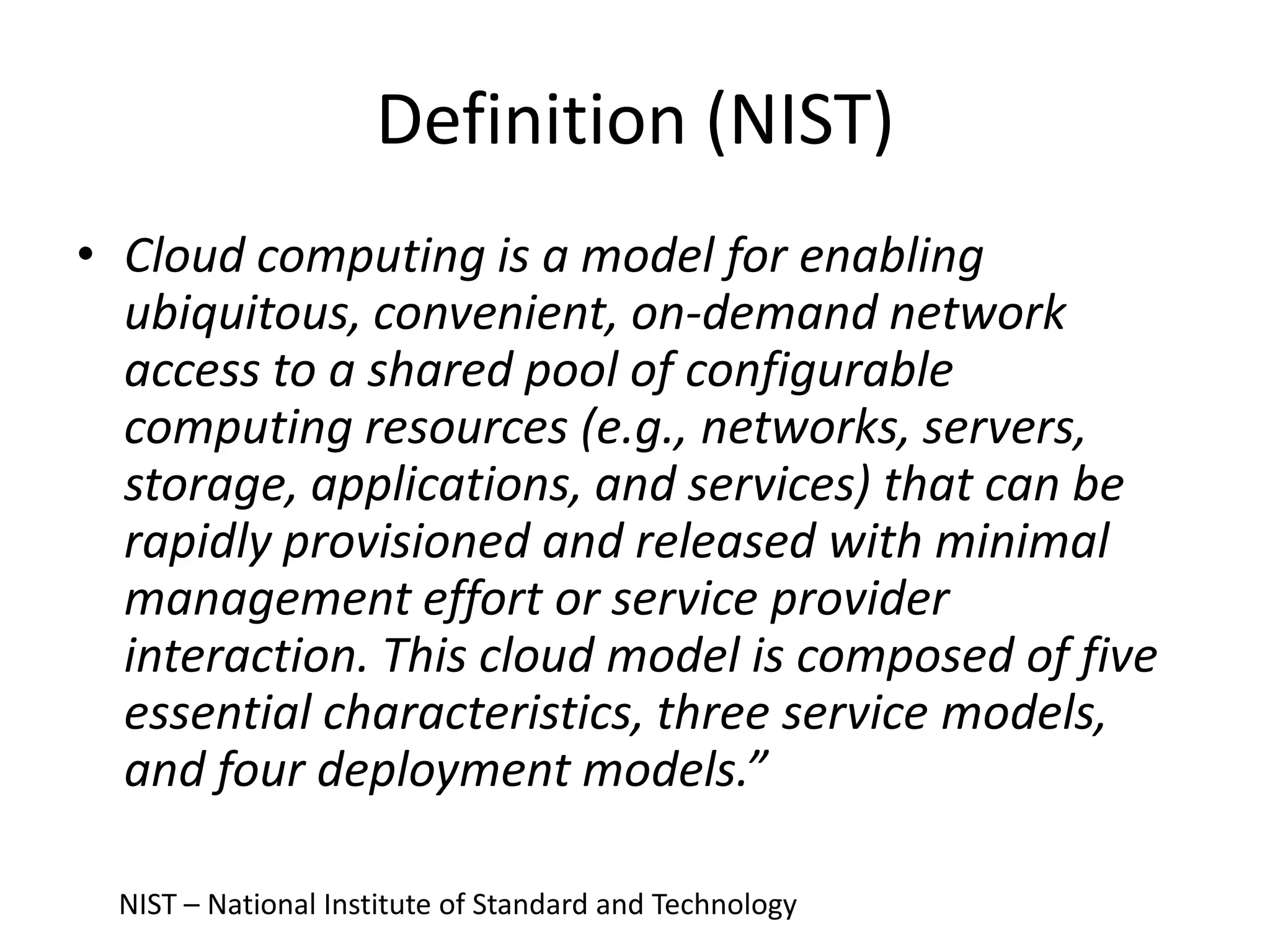
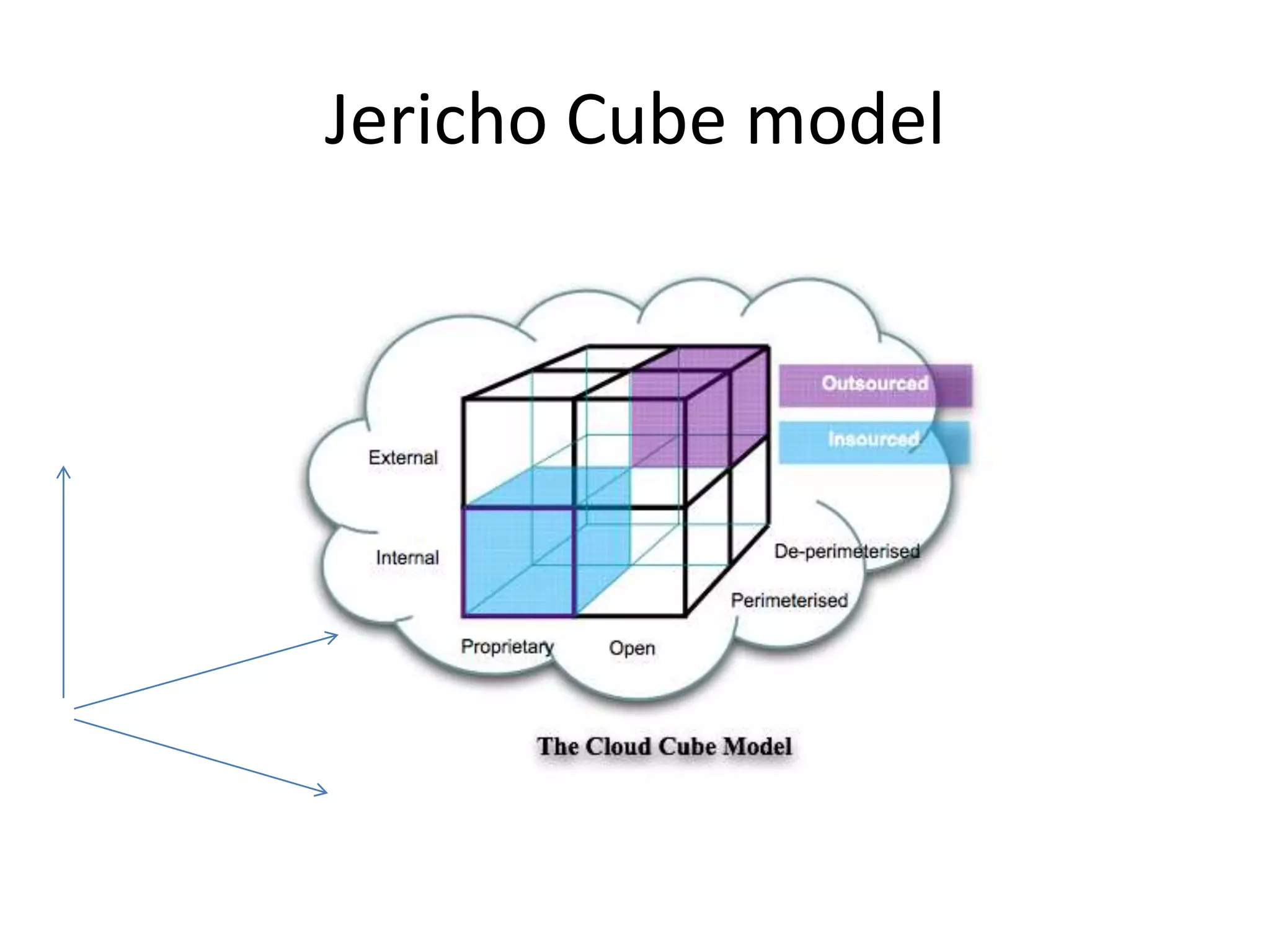
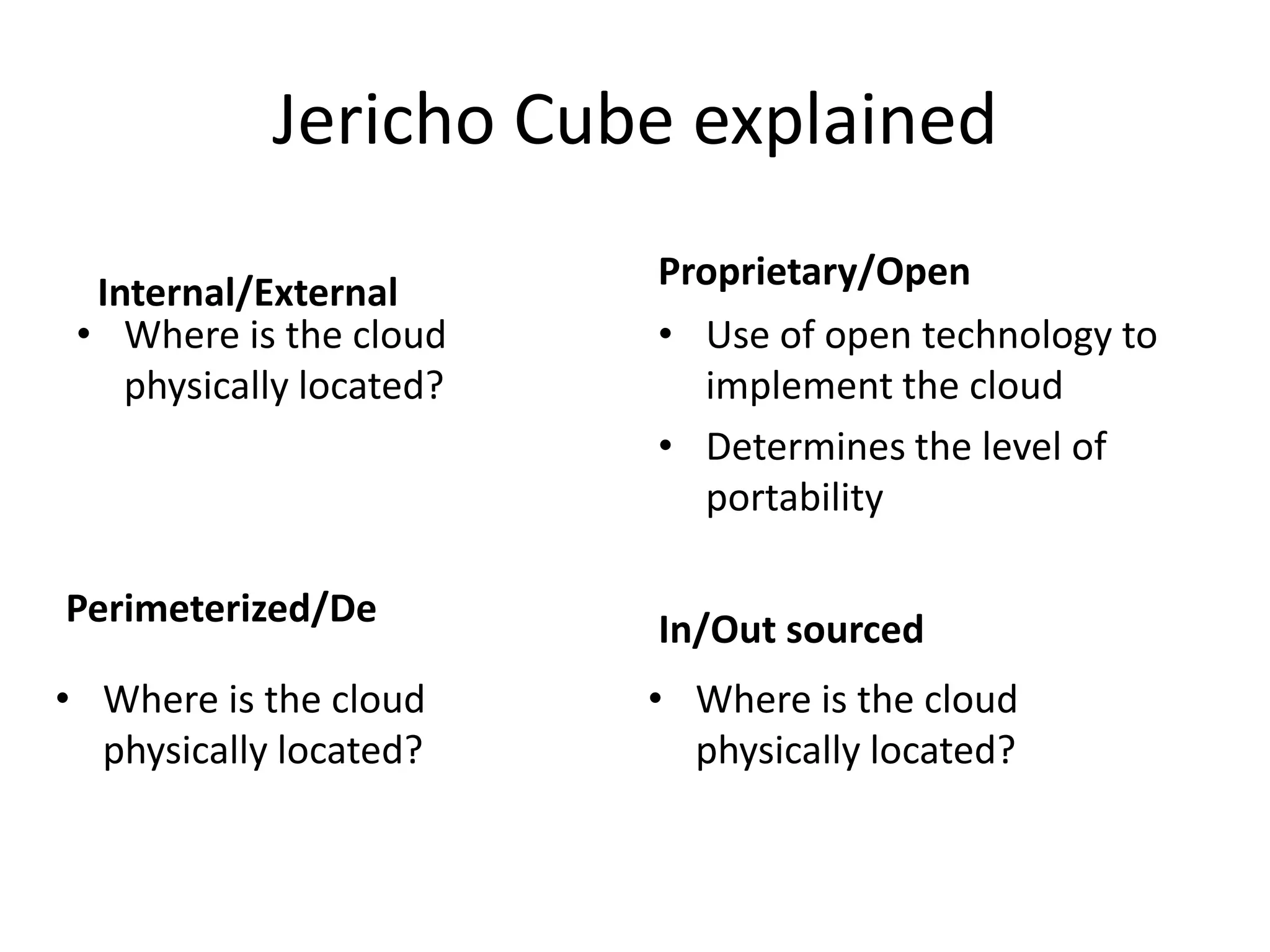
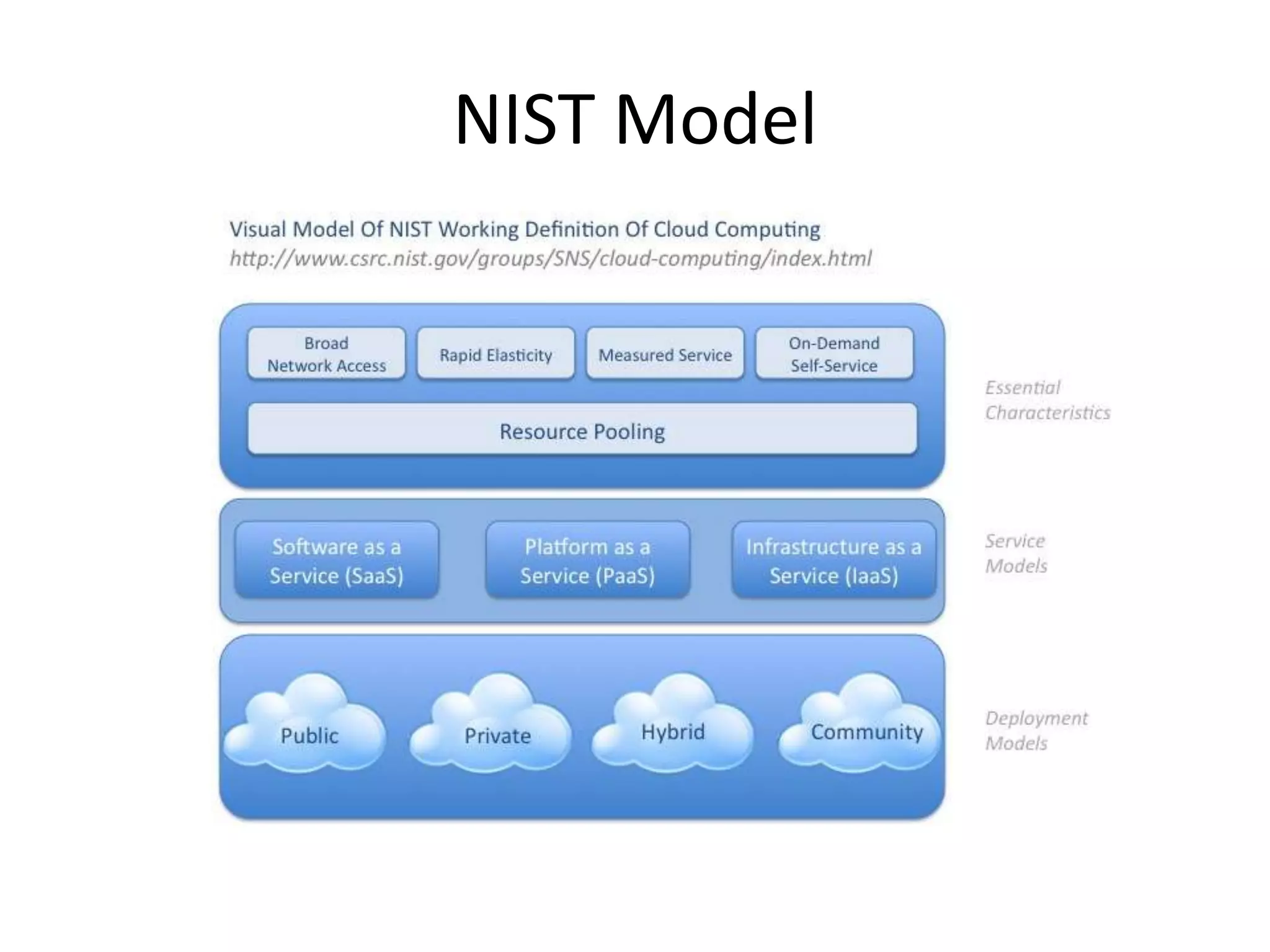
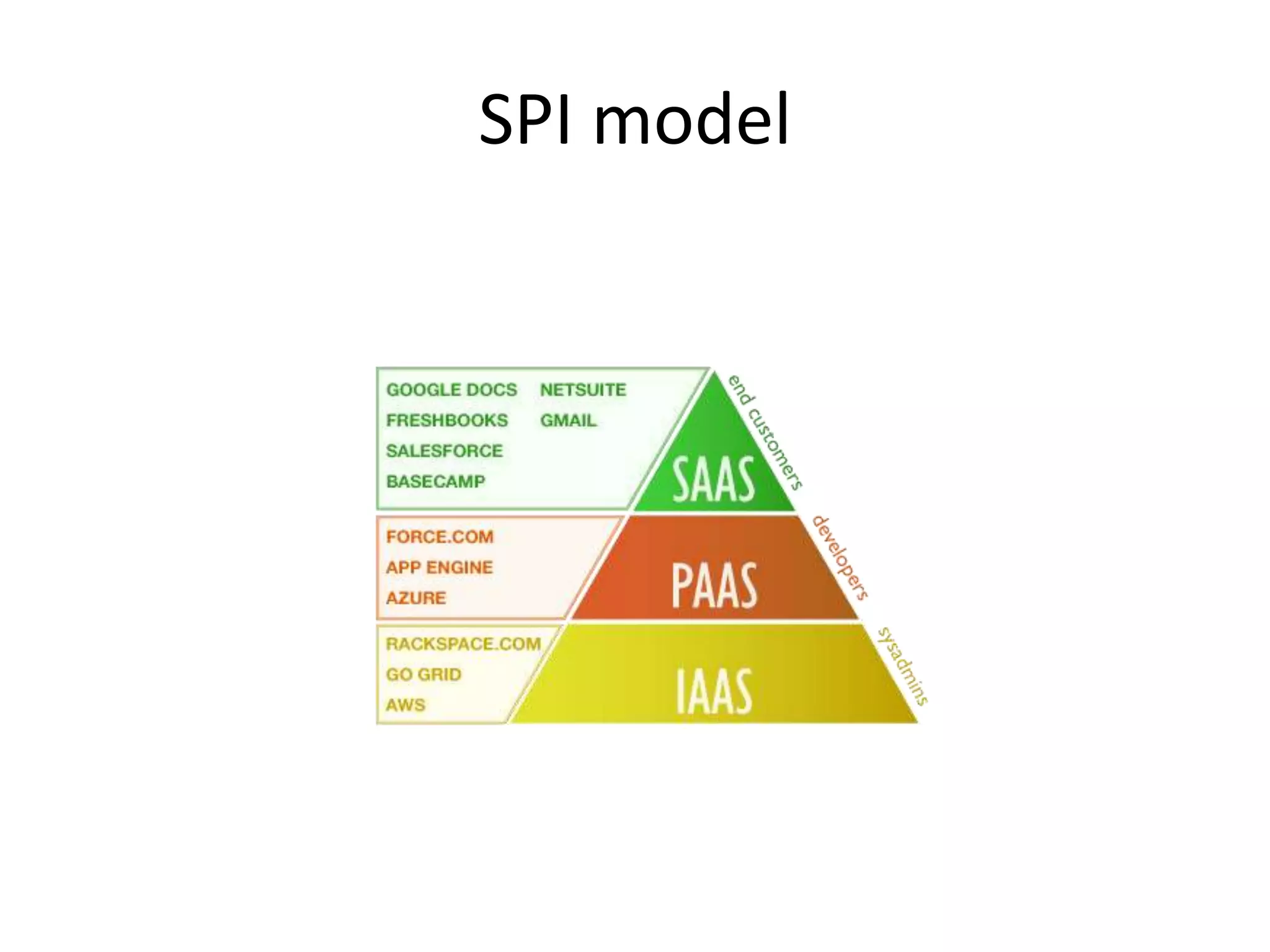
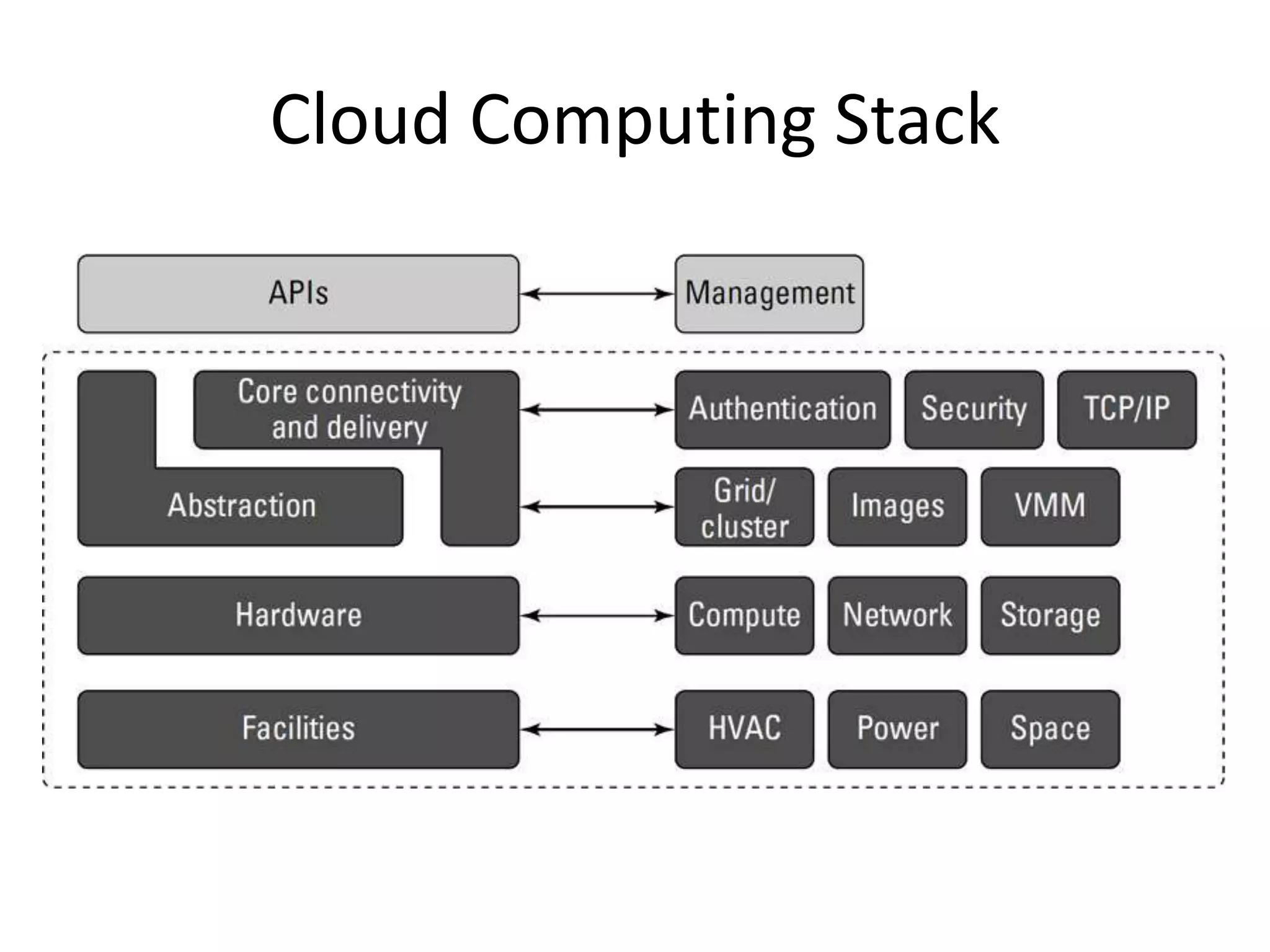
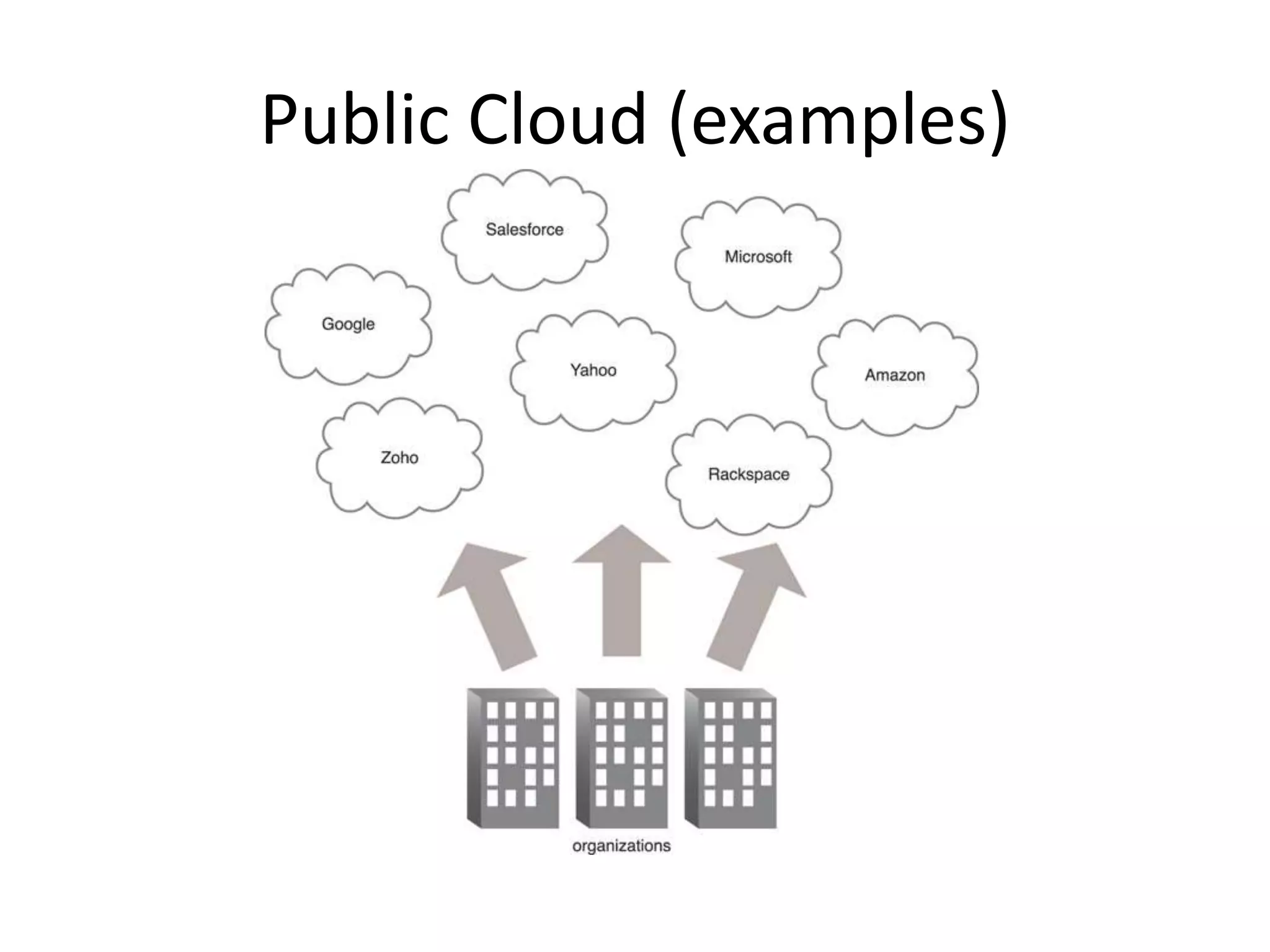
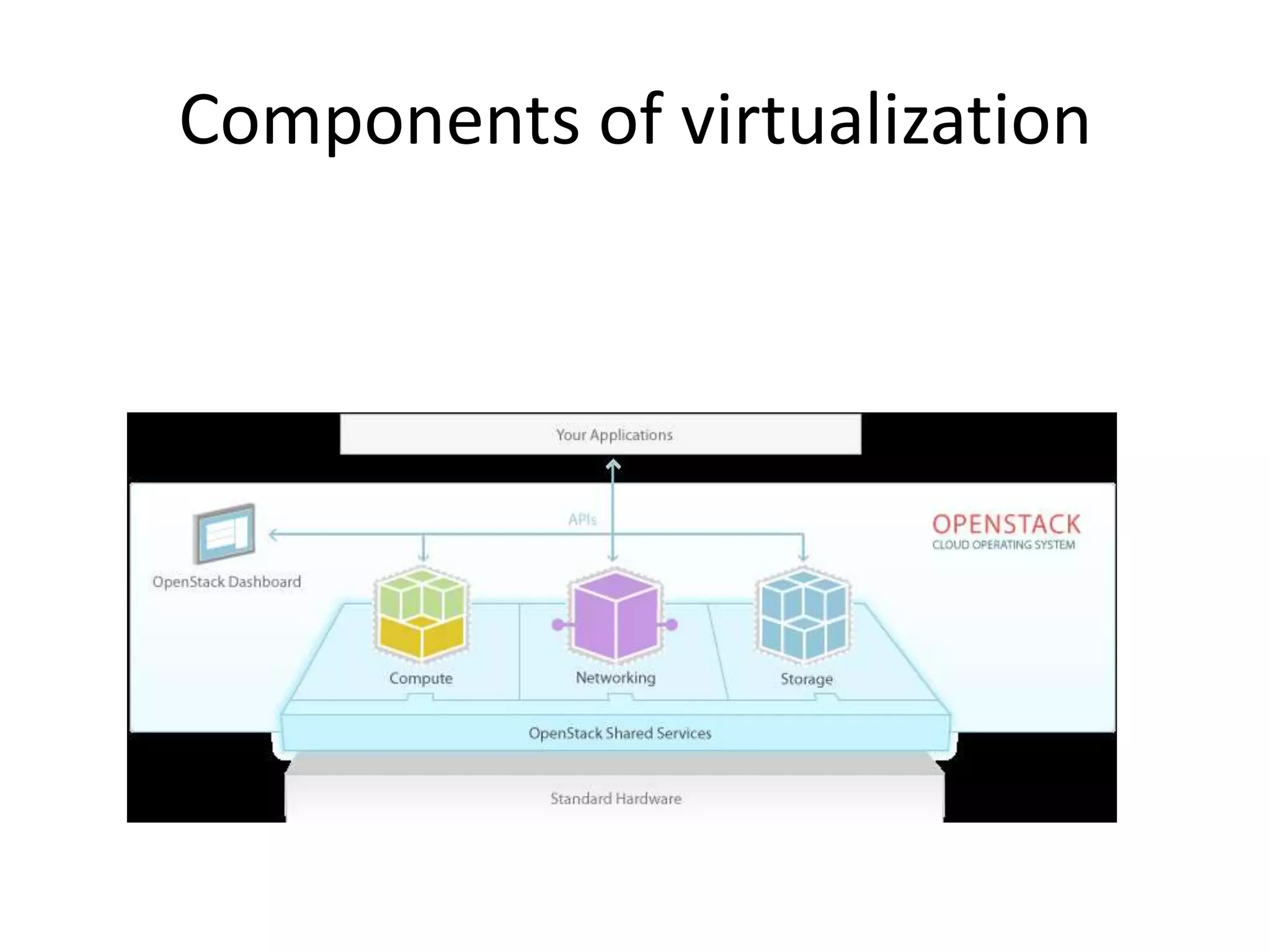
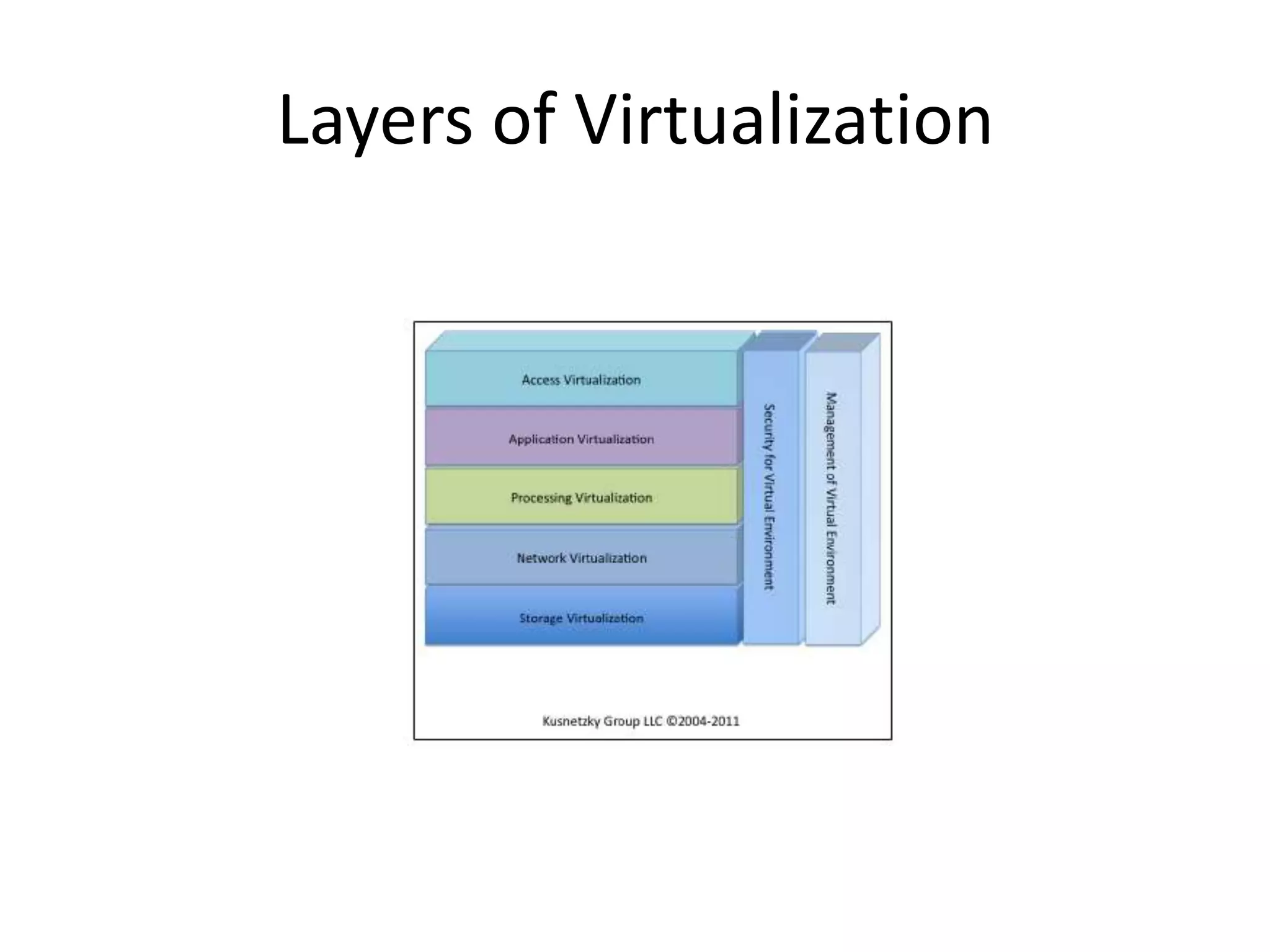
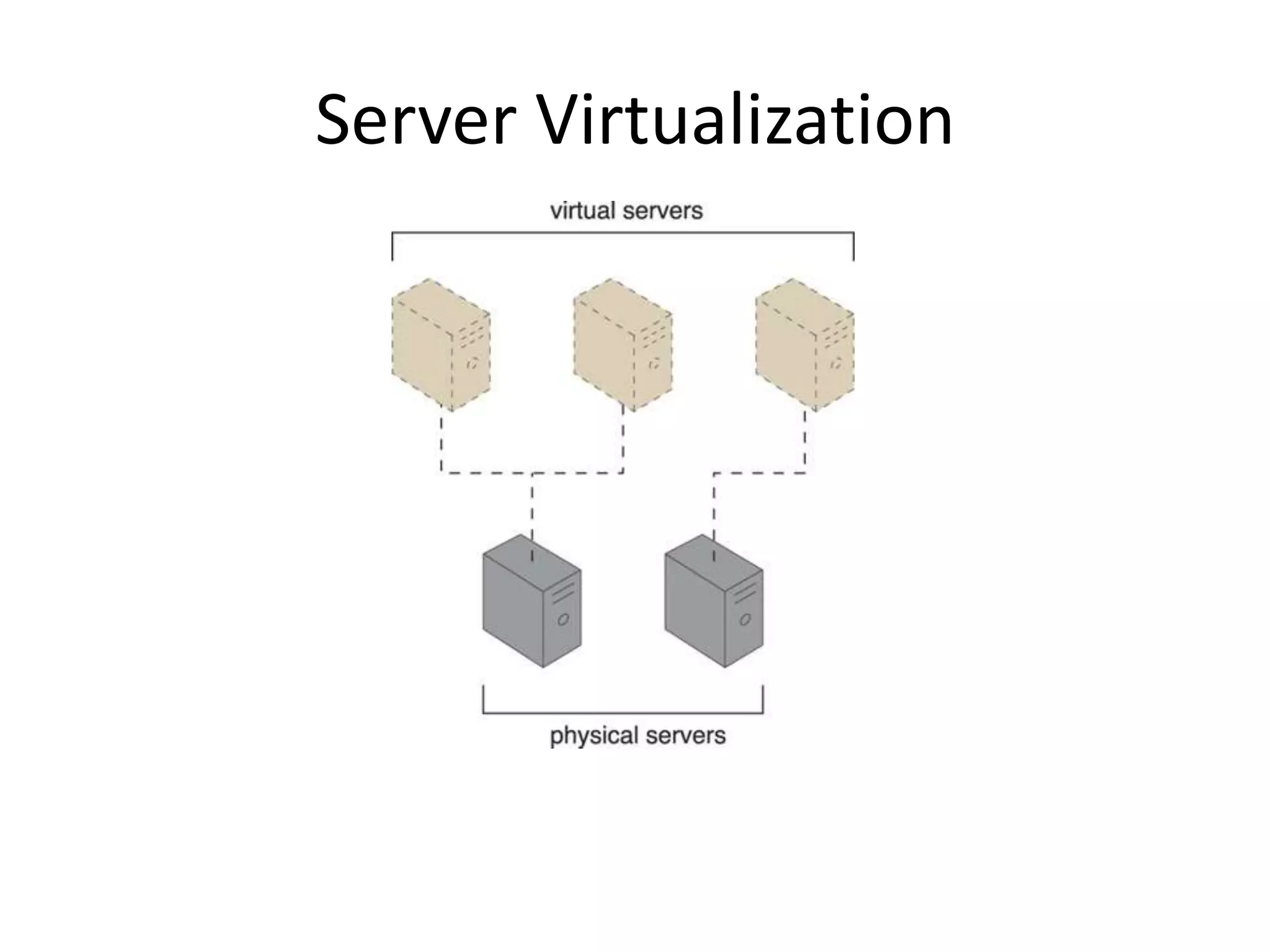
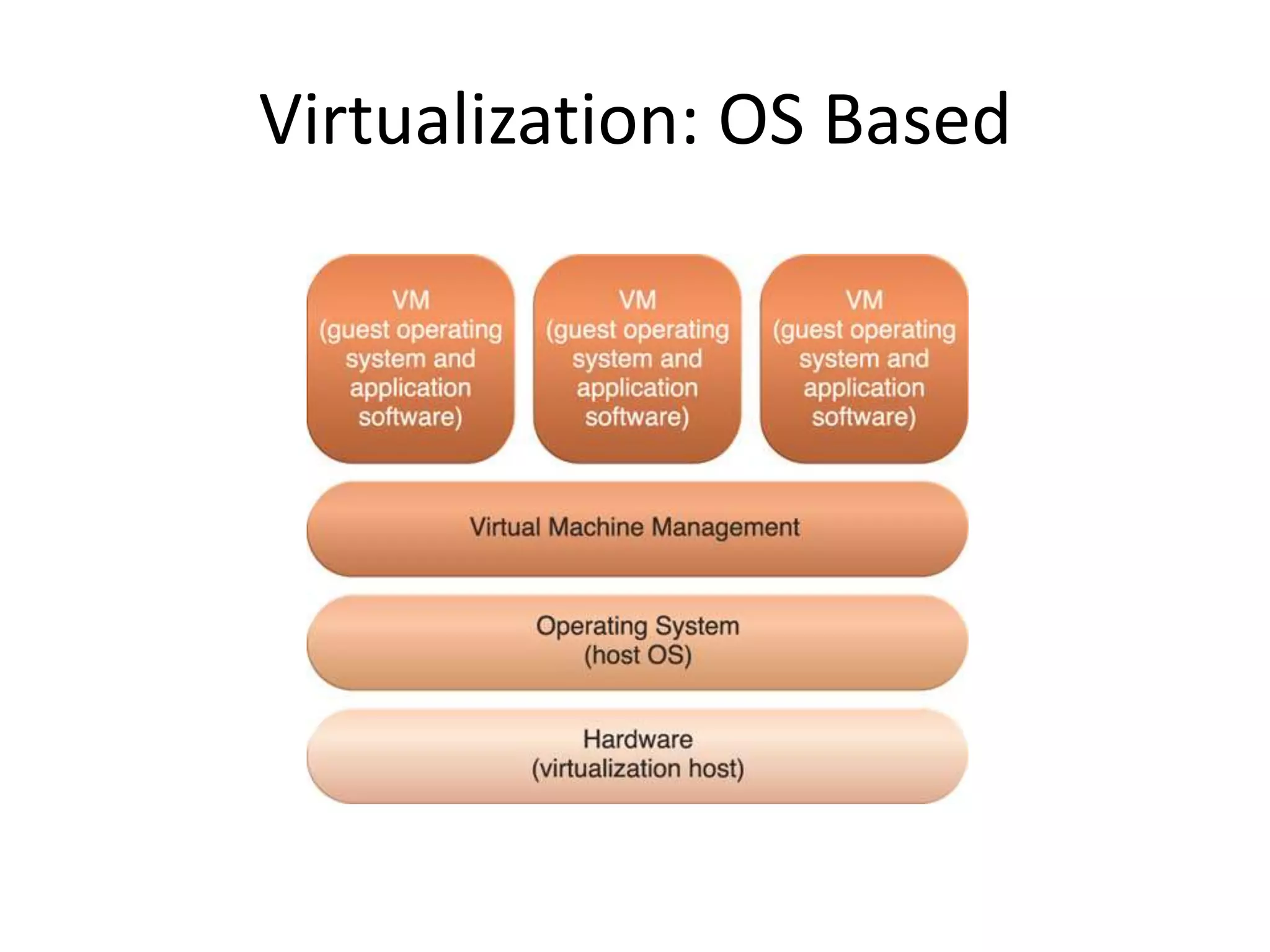
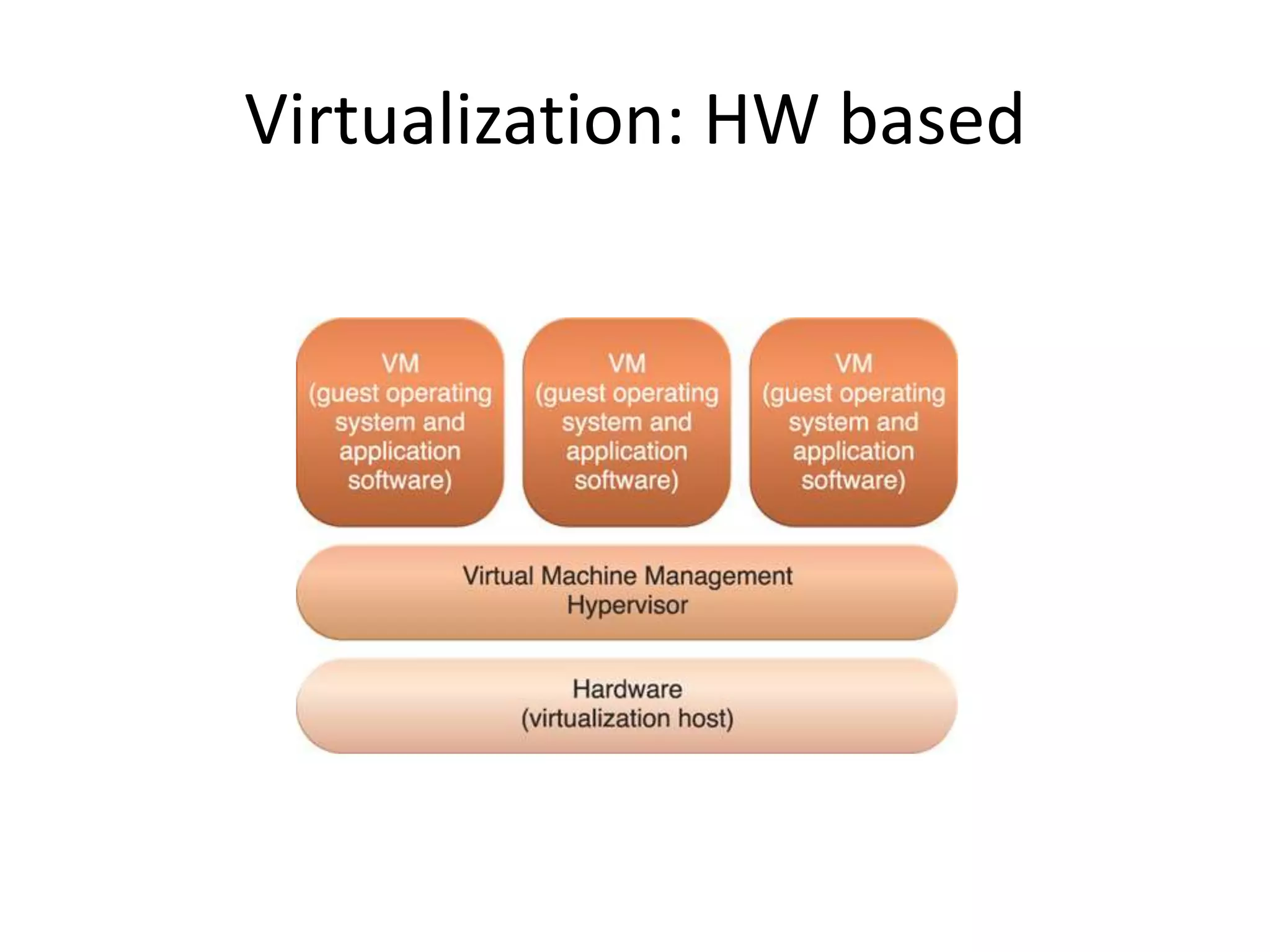
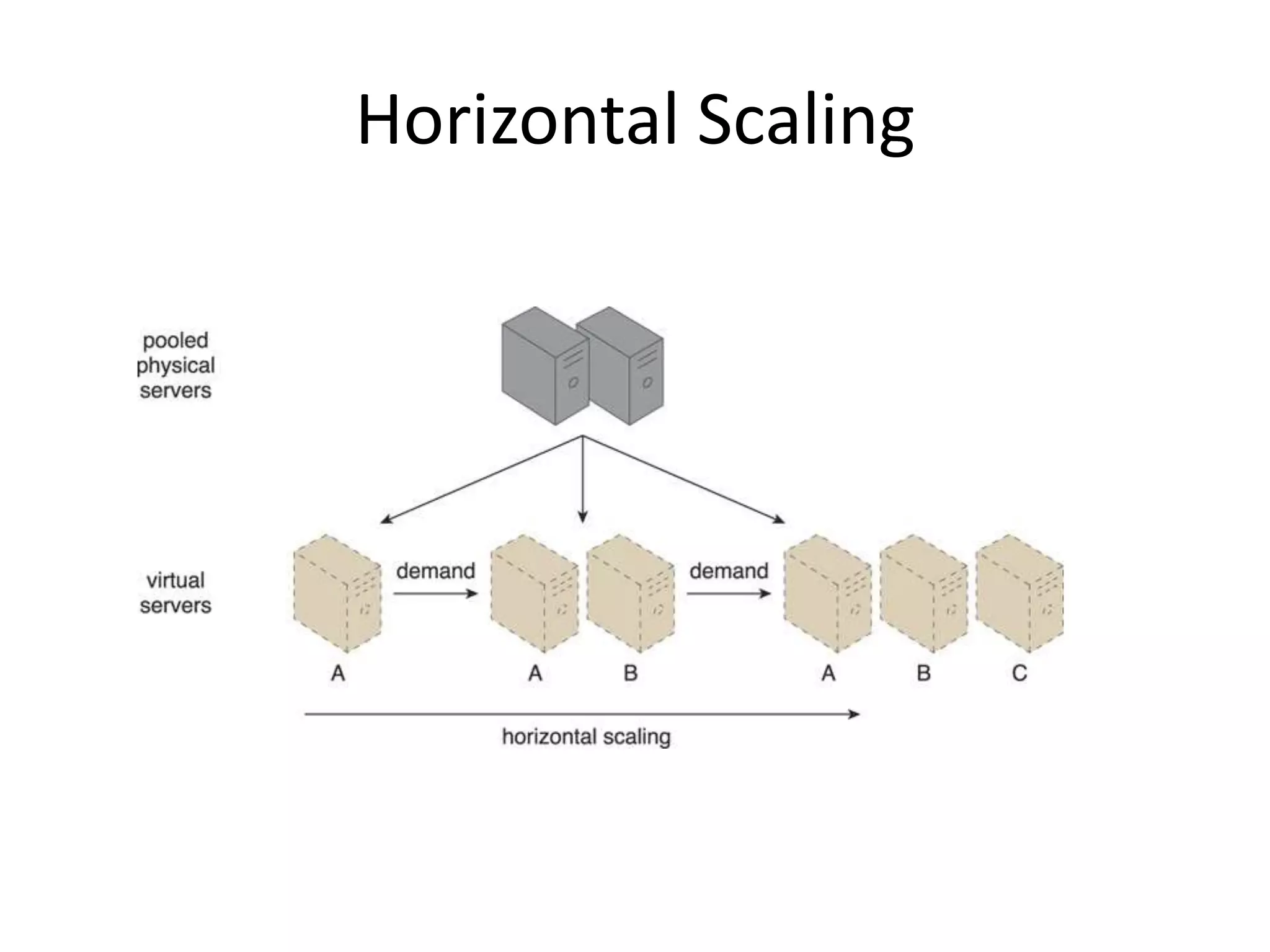
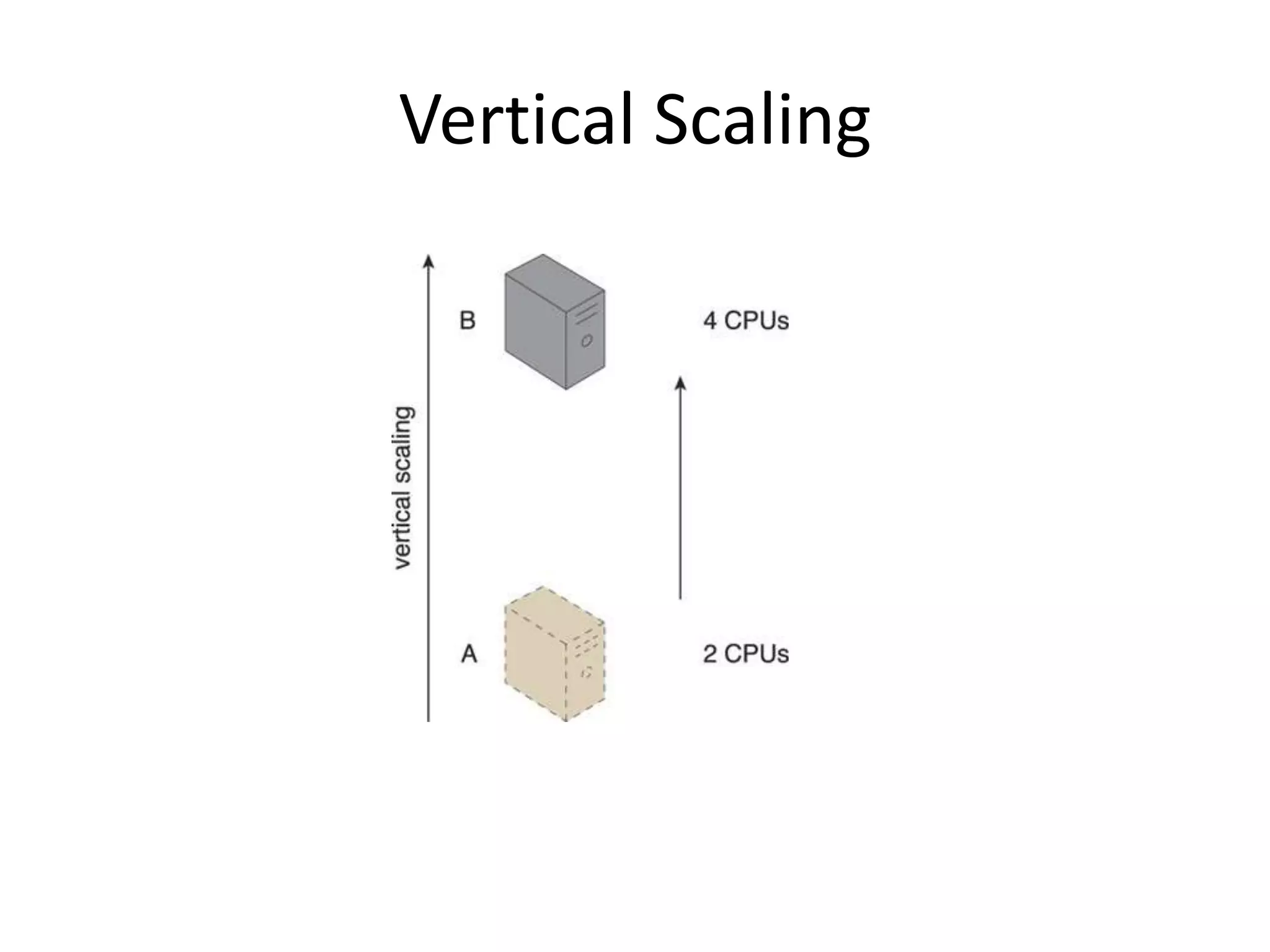
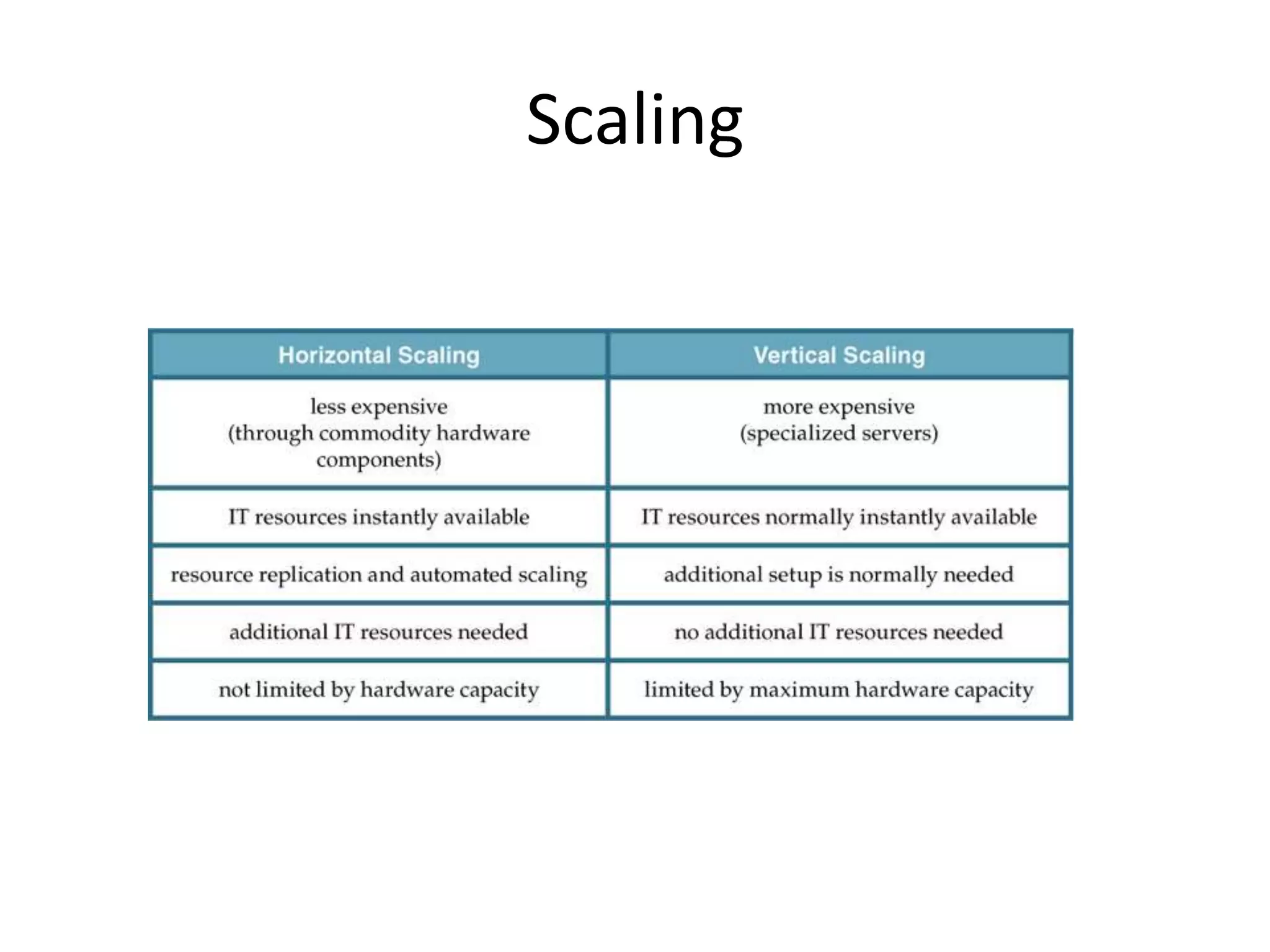
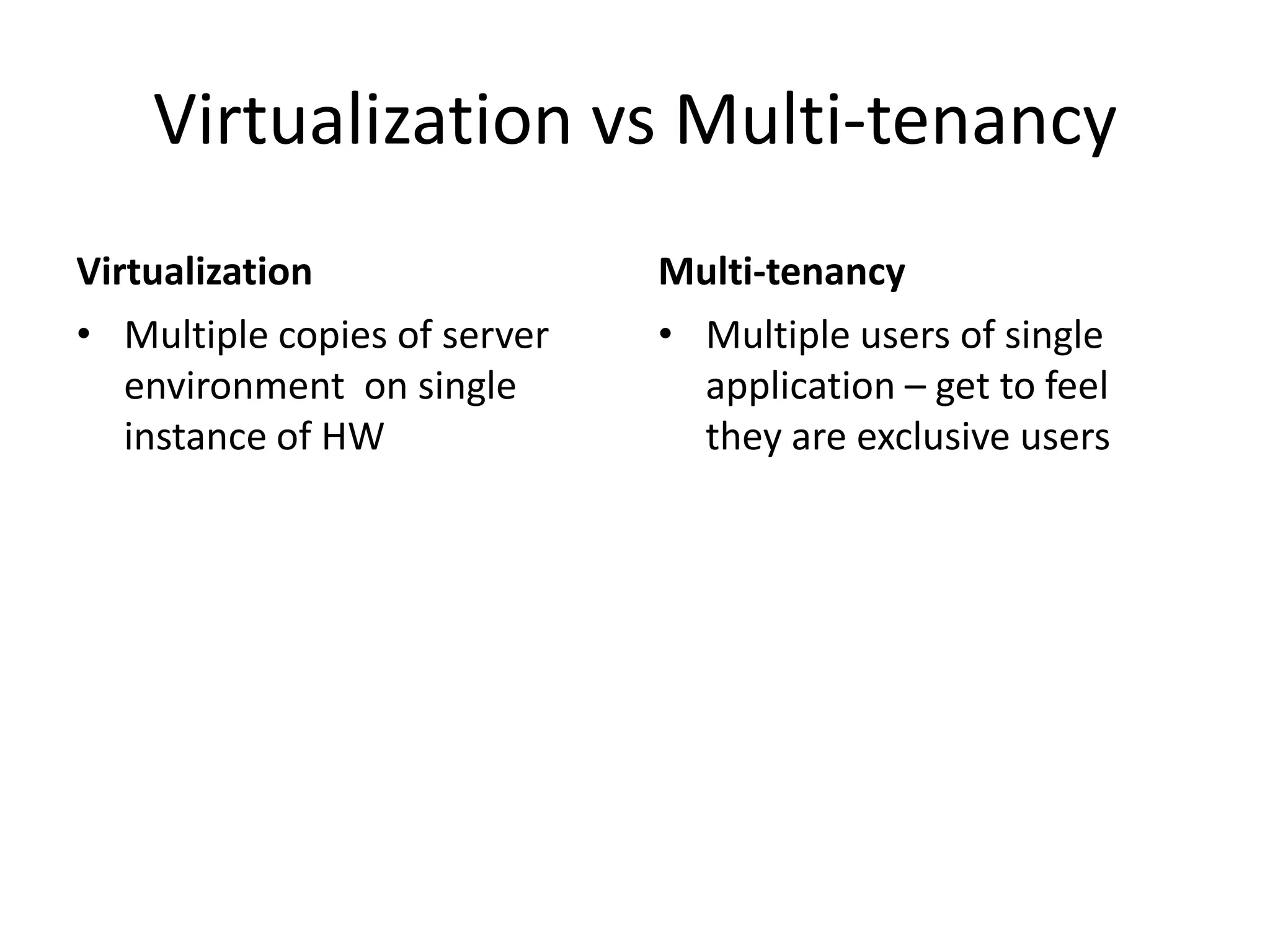
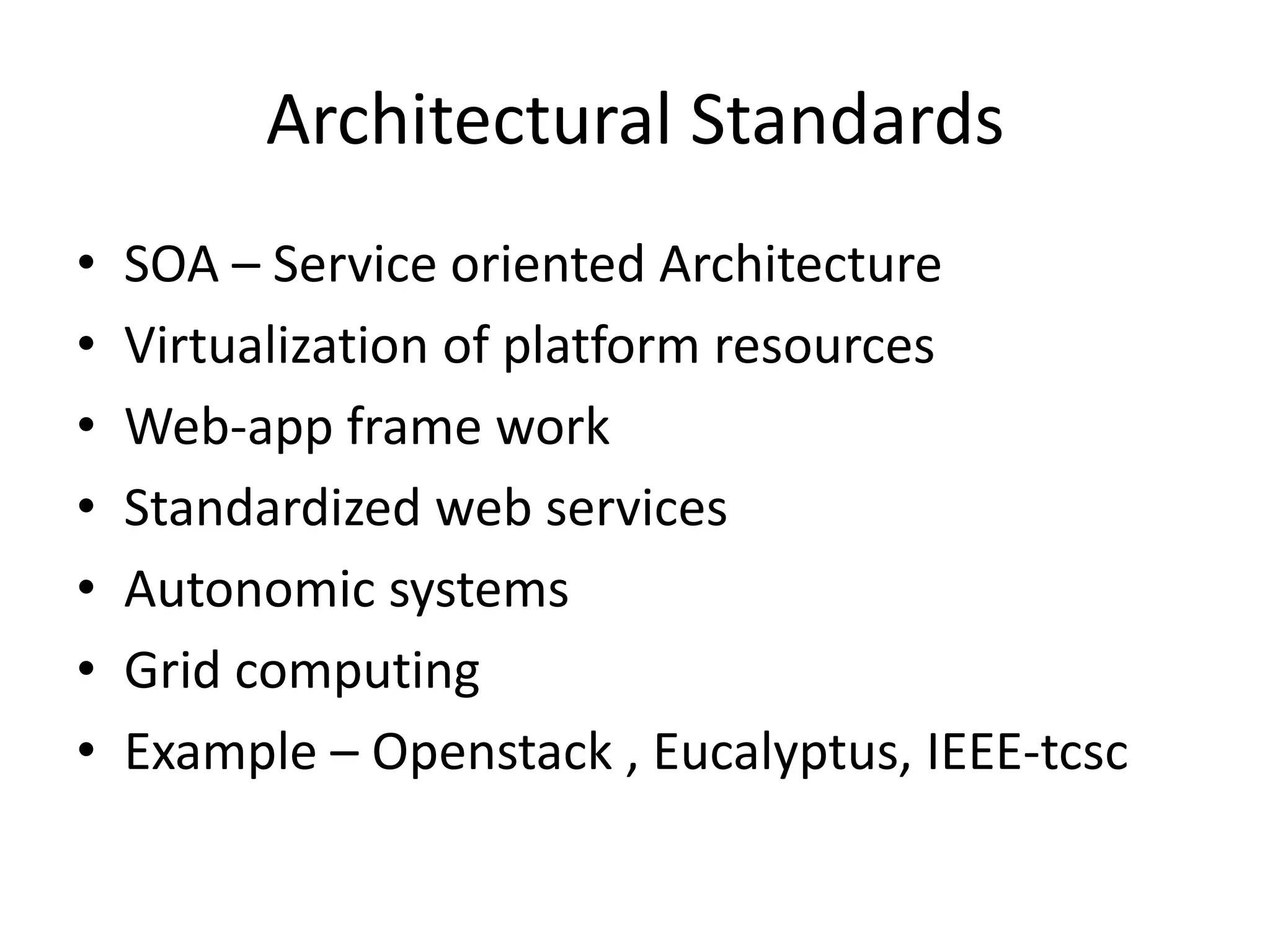
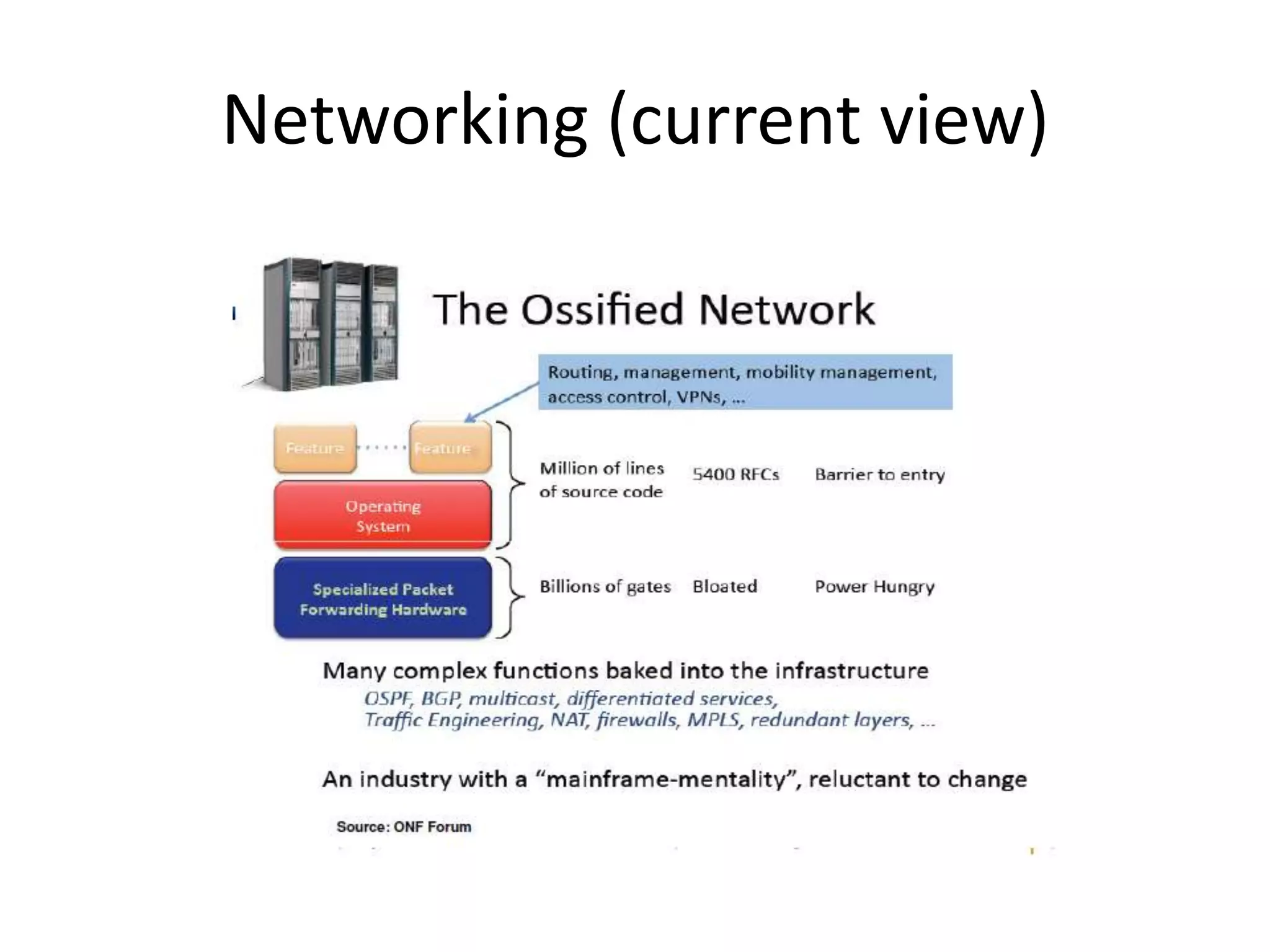
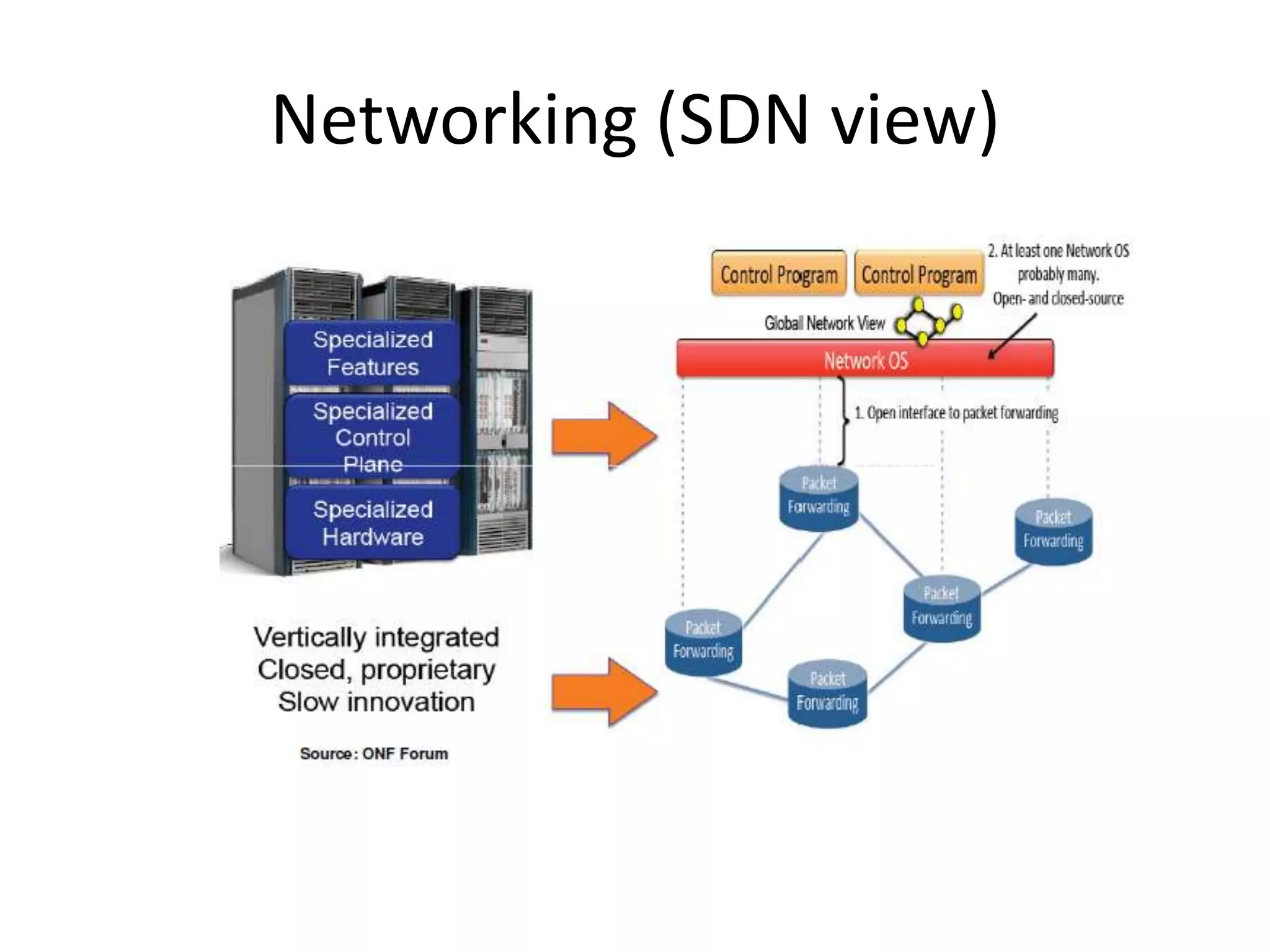
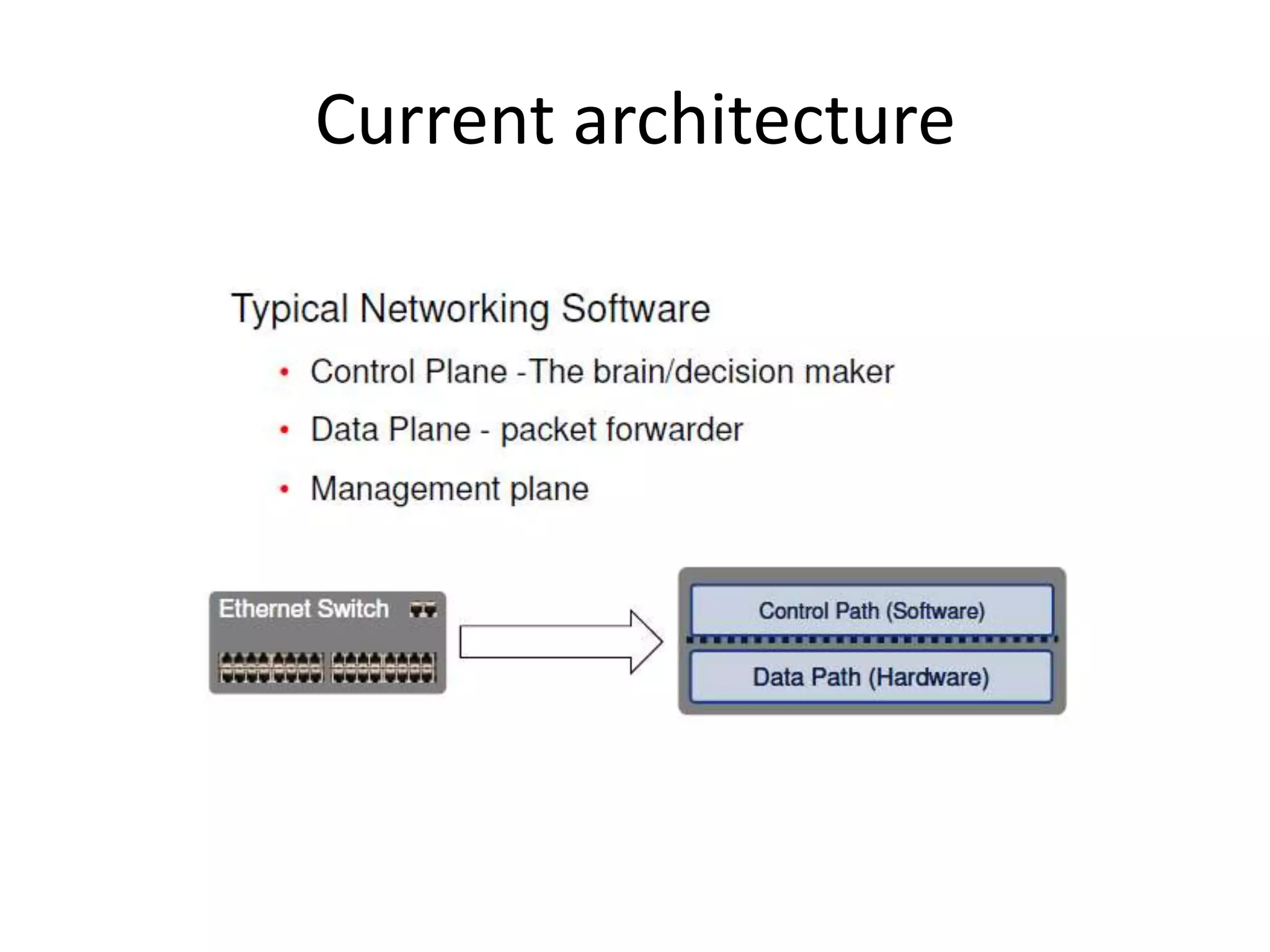
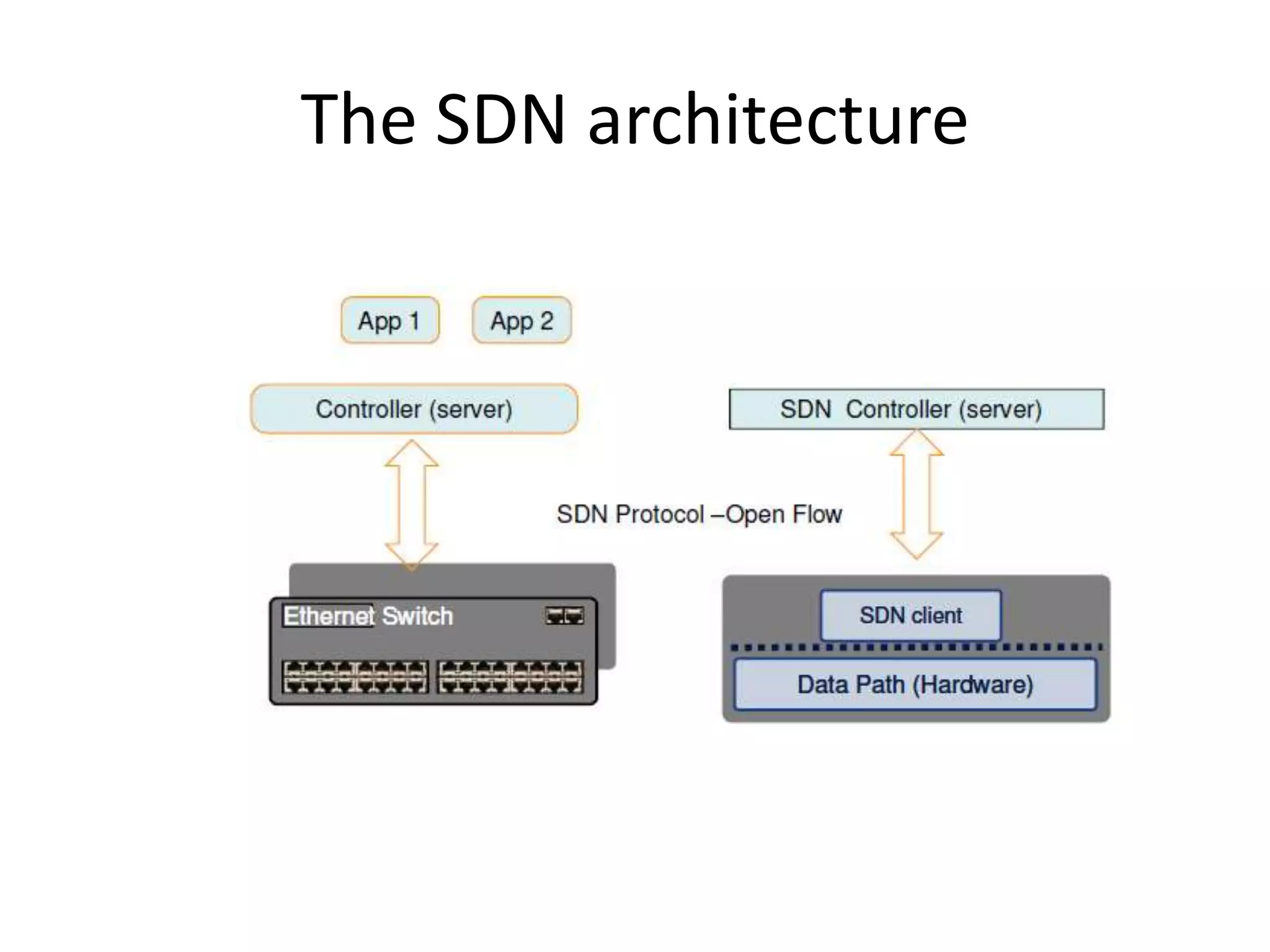
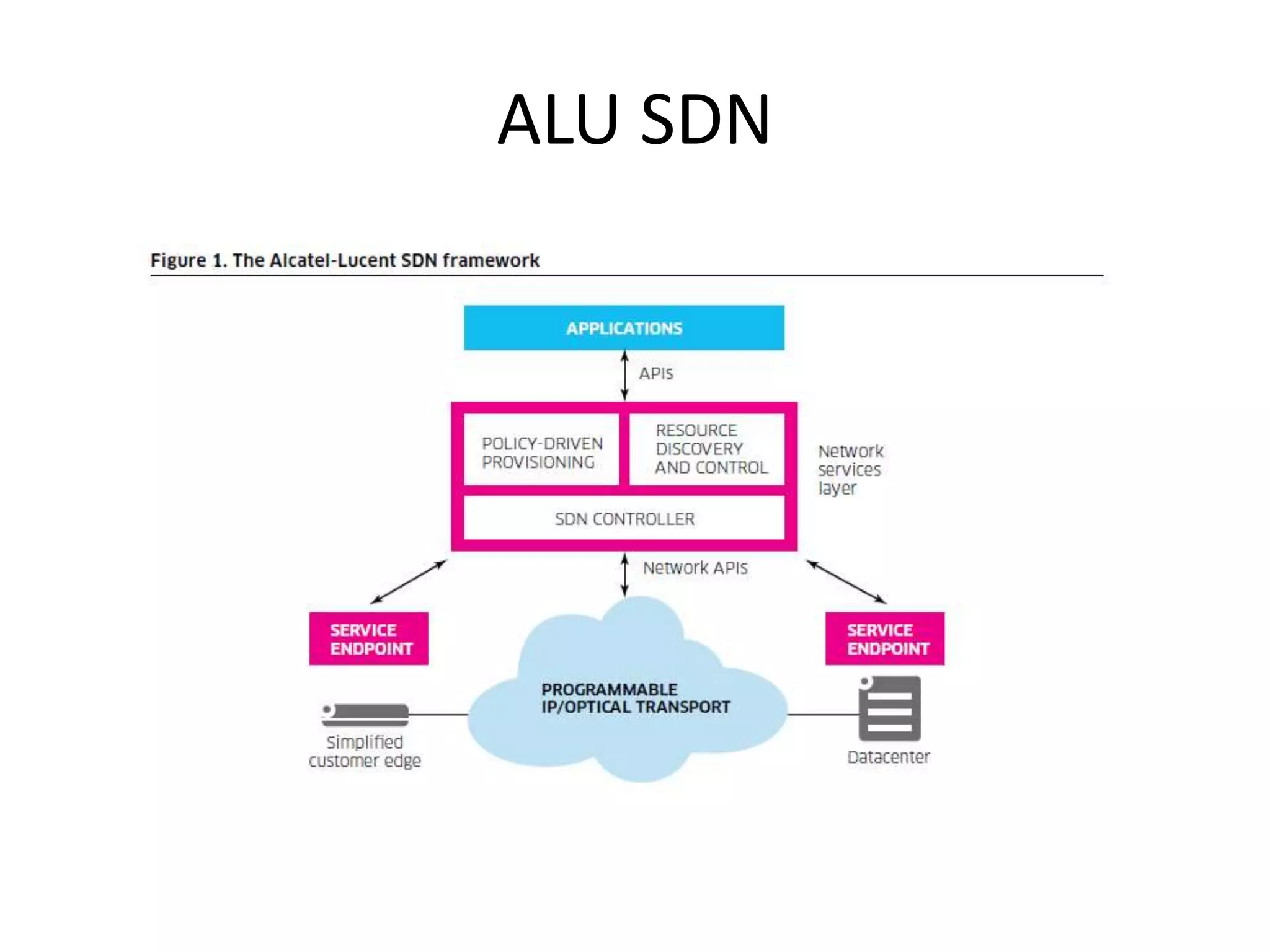
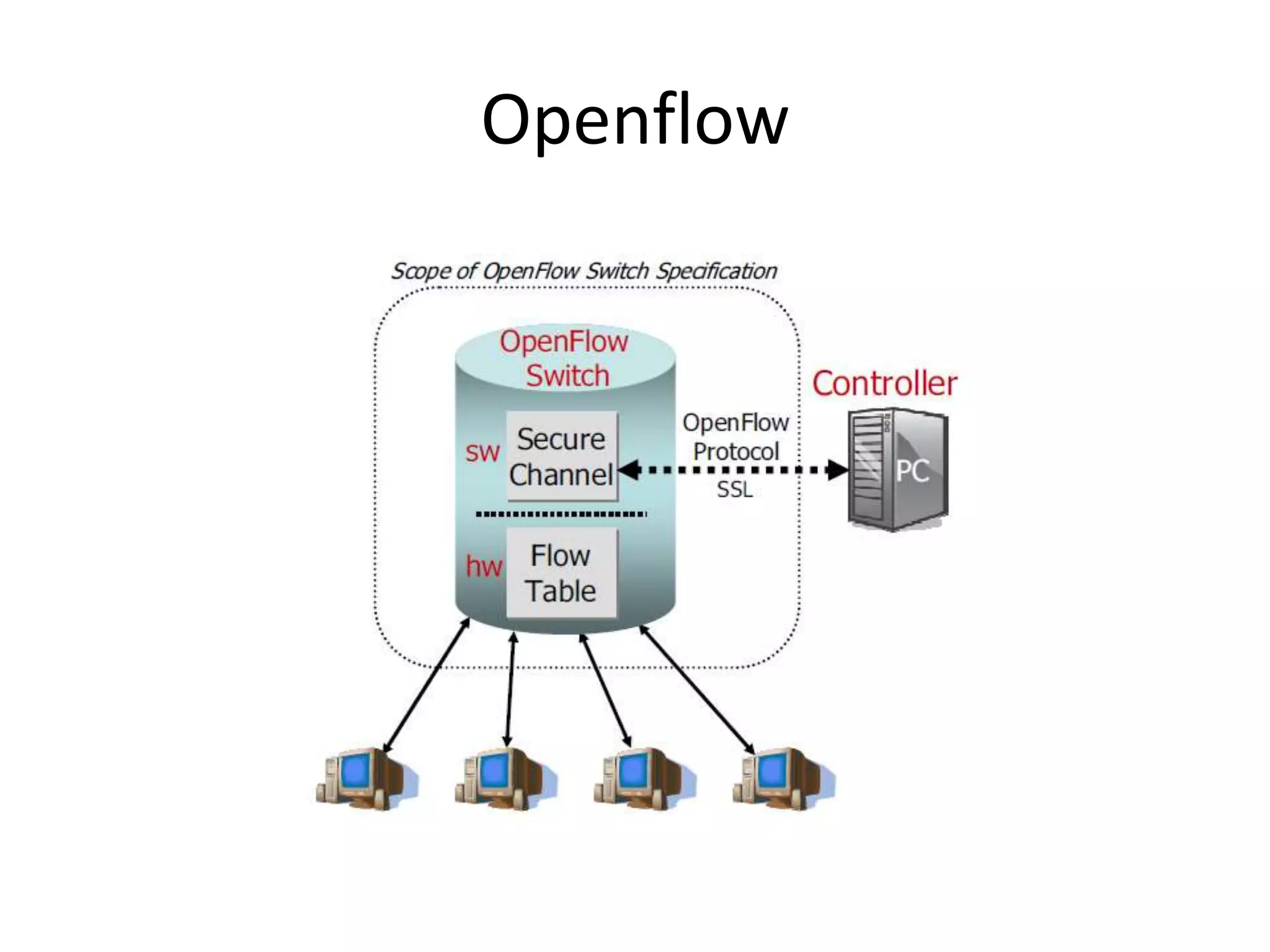
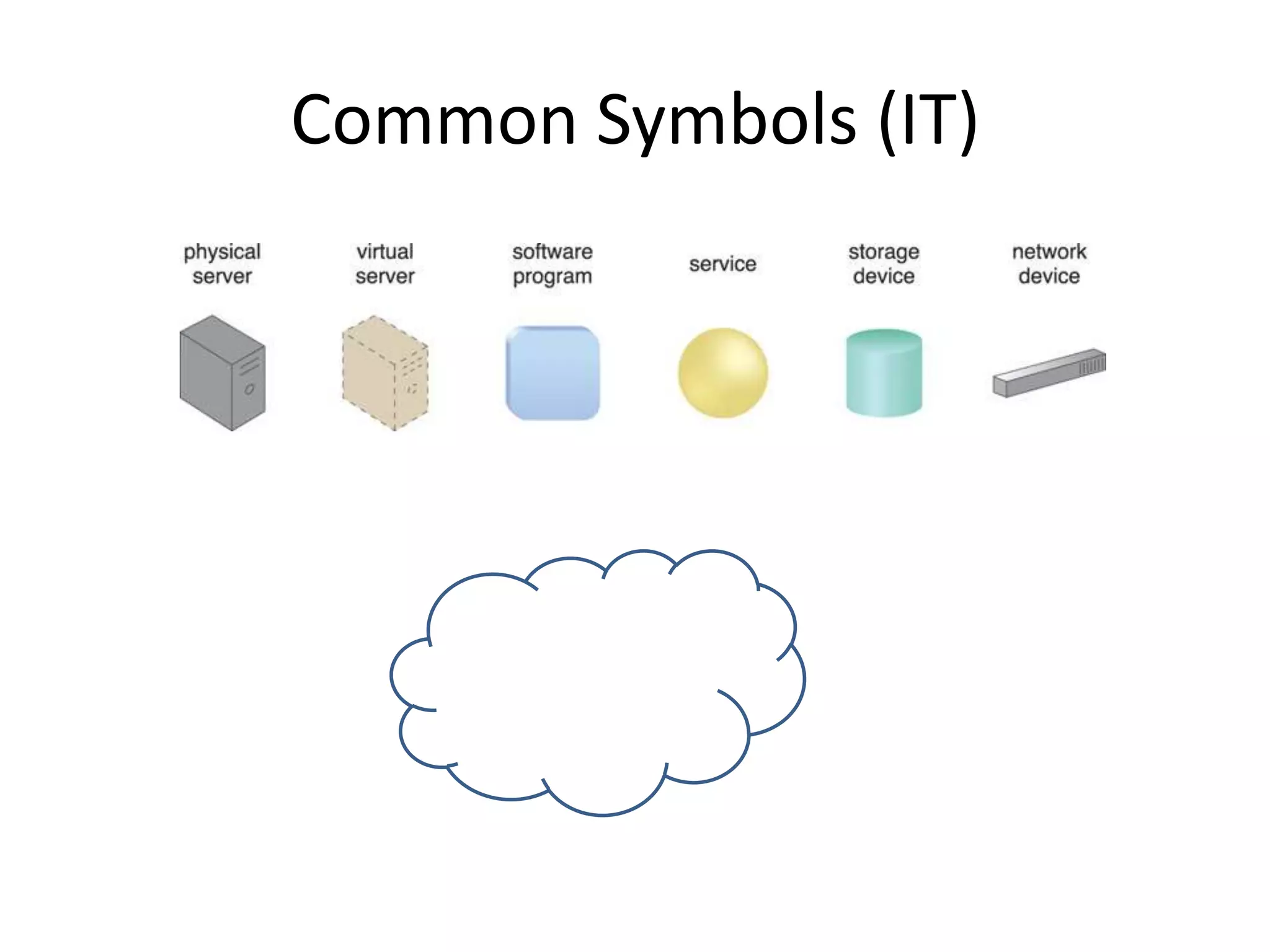
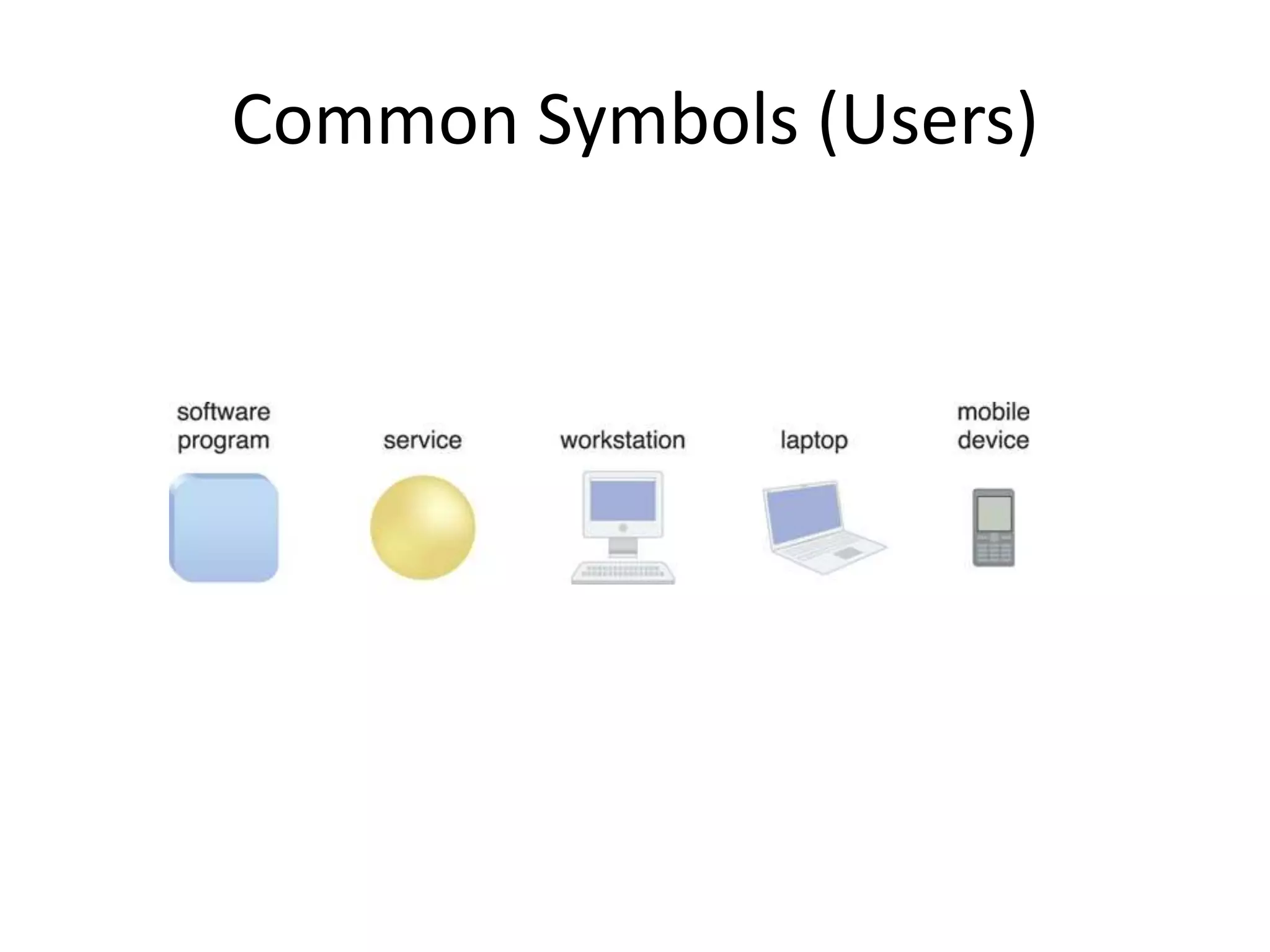
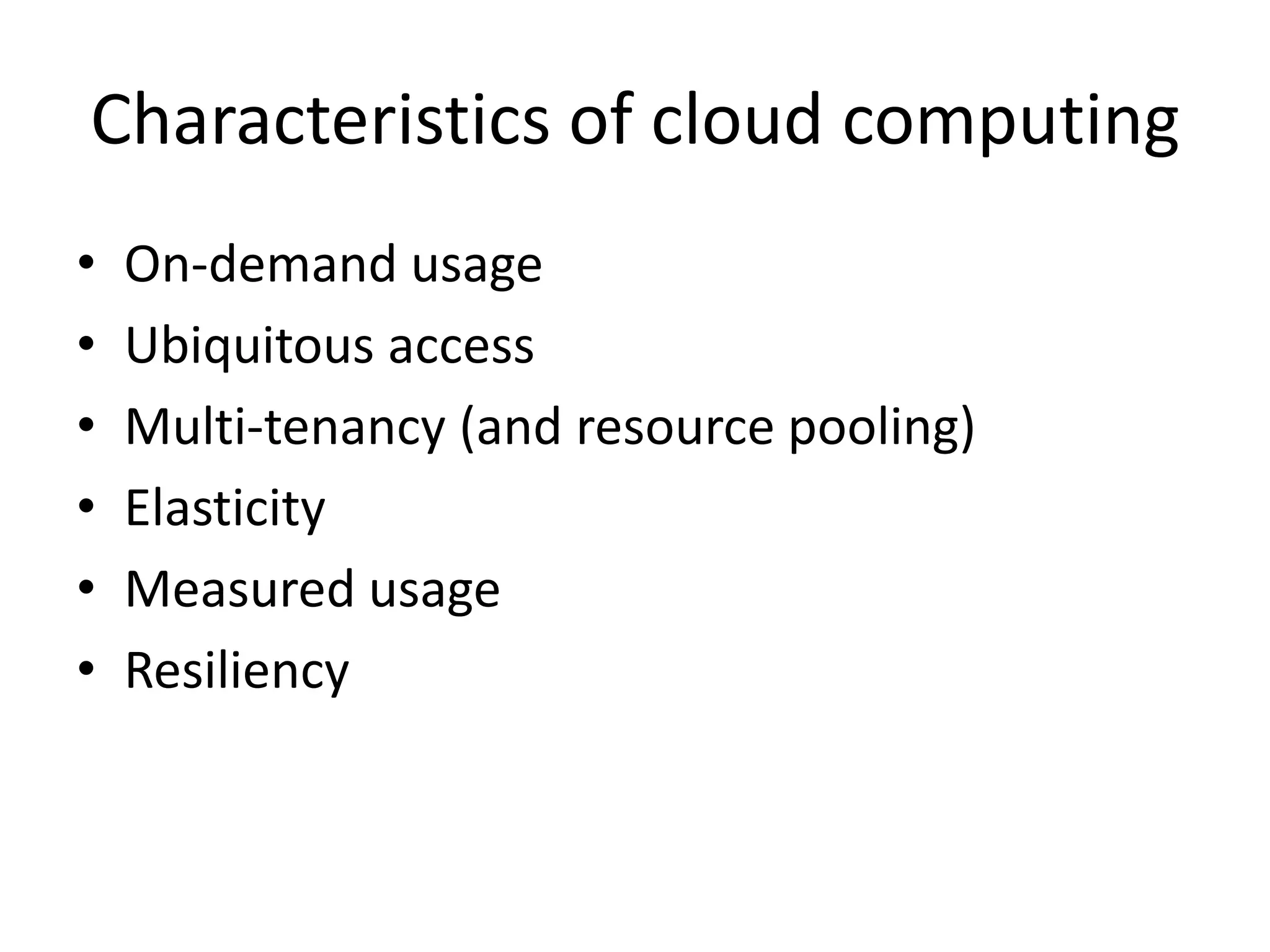
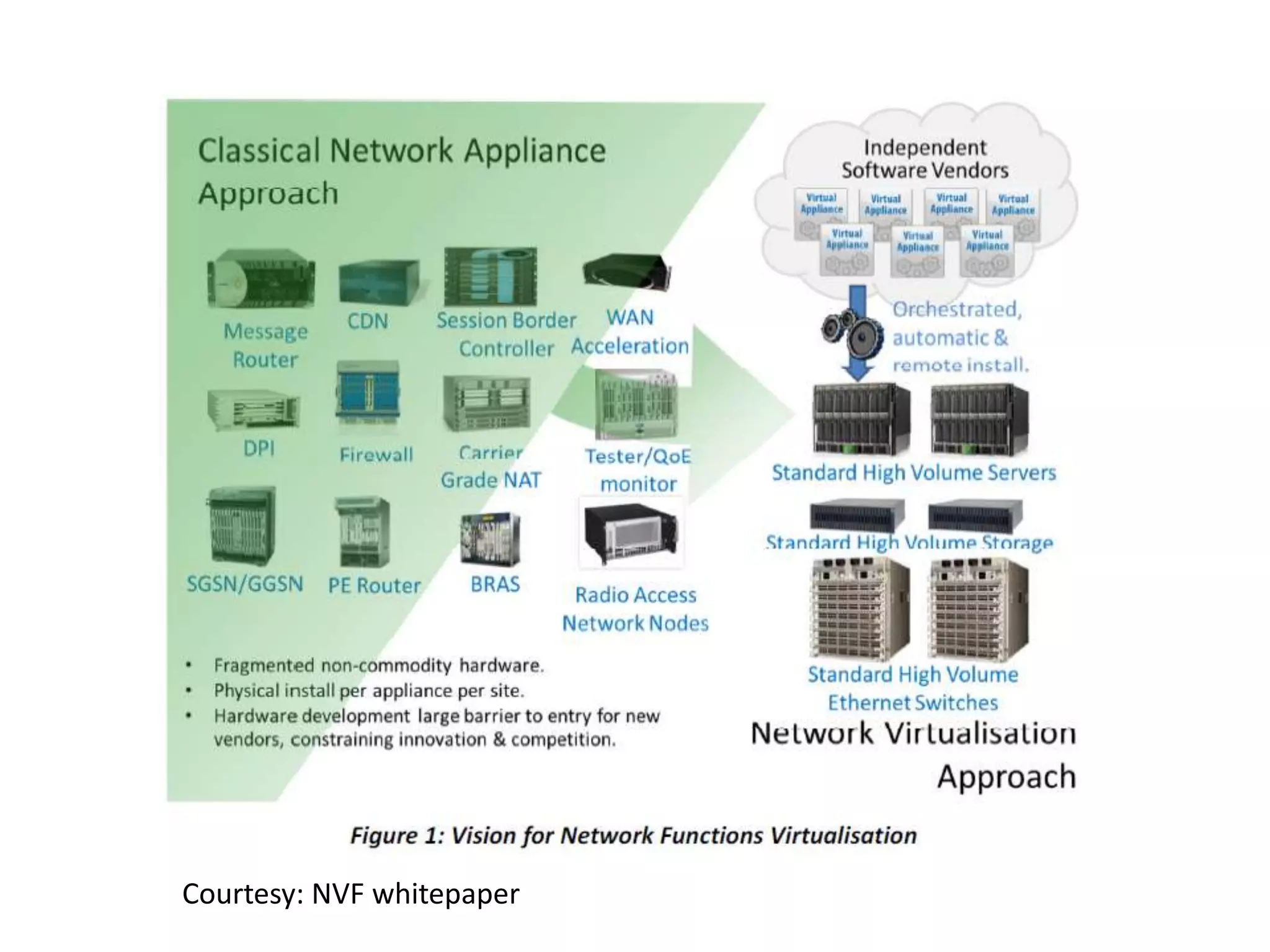
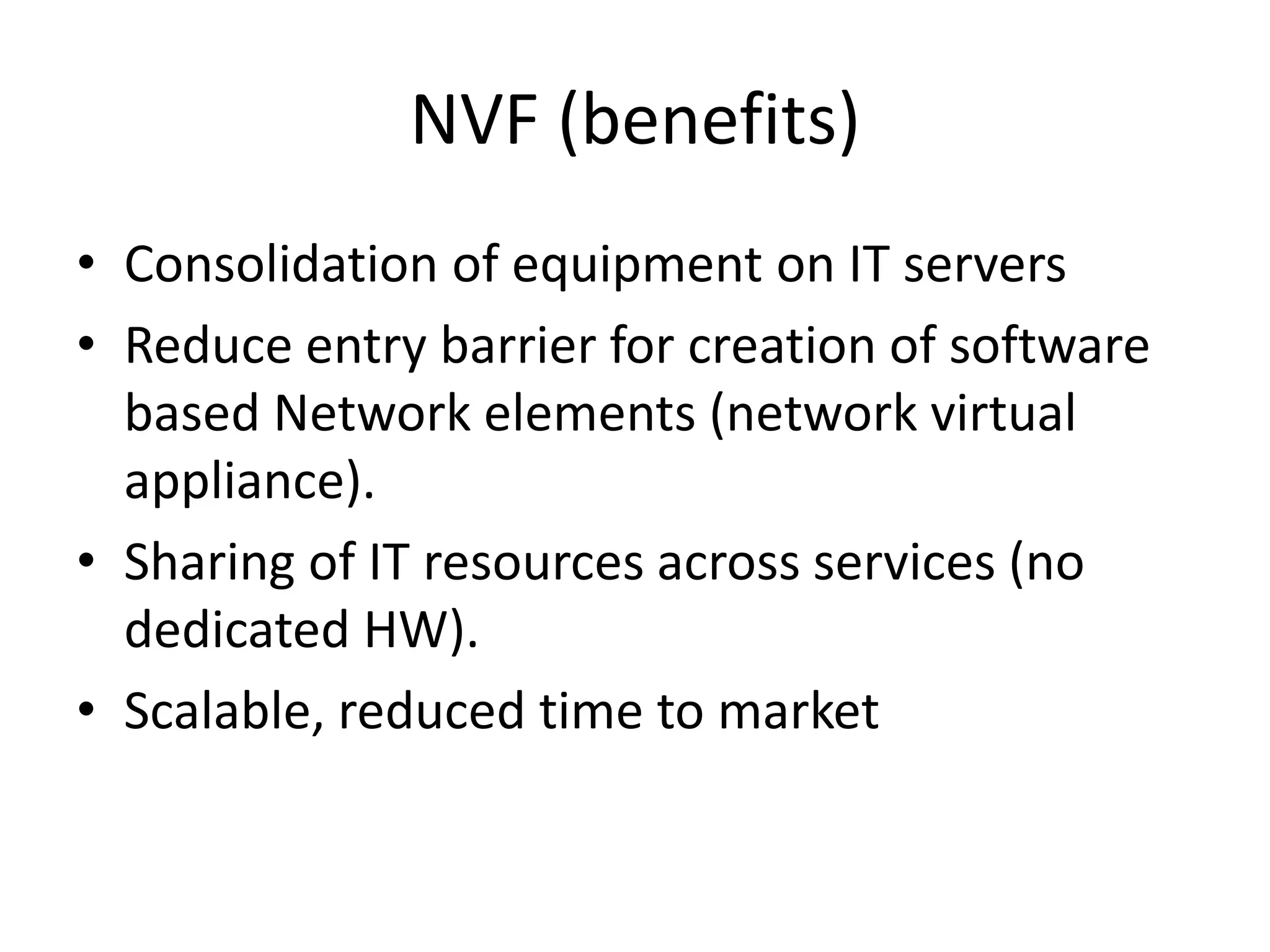
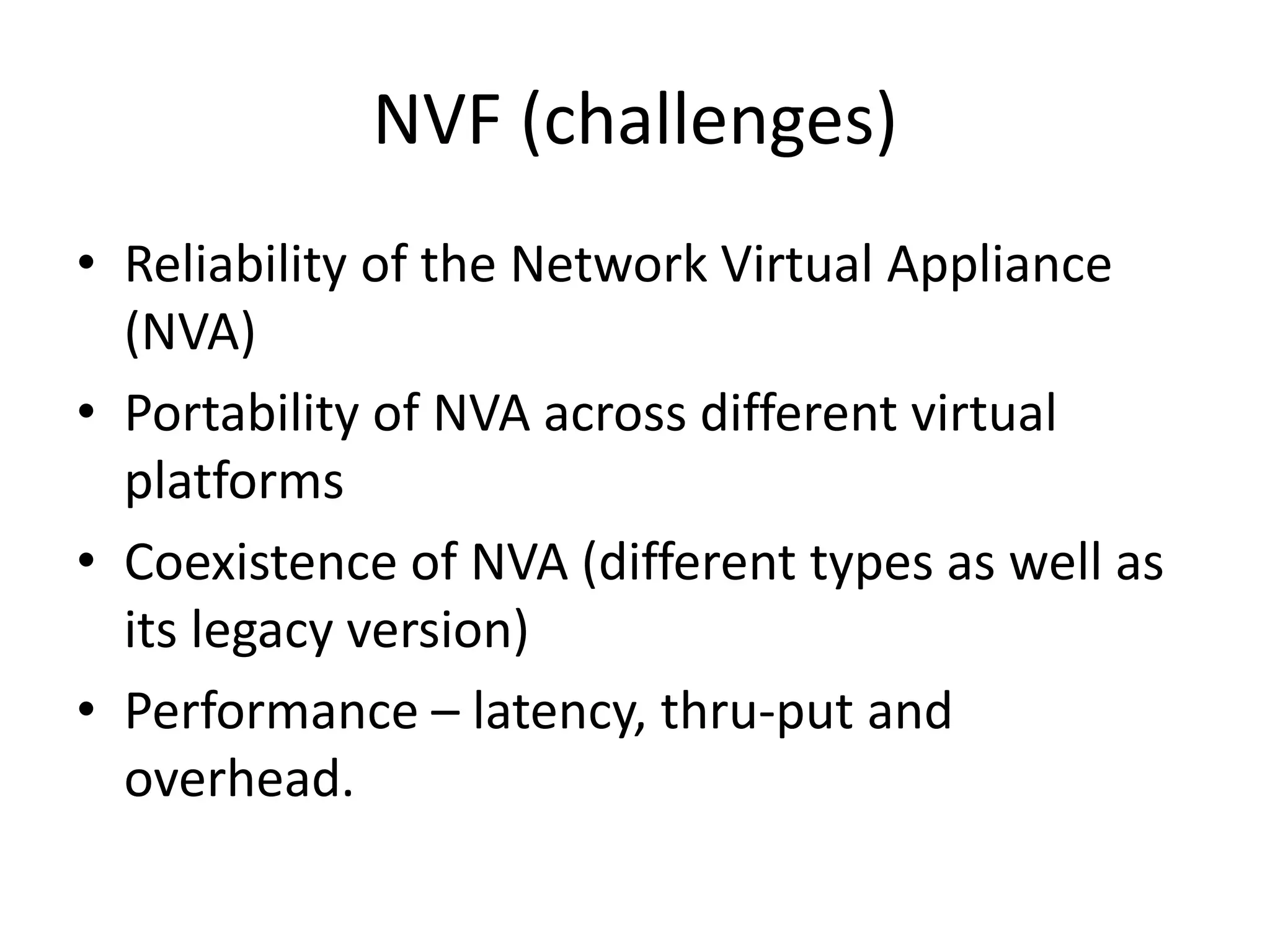
This document provides an introduction to cloud computing, covering its origins, definitions, models, layers, virtualization, software-defined networking, network functions virtualization, benefits, and challenges. Key topics include the NIST cloud computing definition, SPI service models (infrastructure, platform, software as a service), public/private/hybrid cloud deployment models, and how cloud computing delivers scalable IT resources over the internet on a pay-per-use basis.