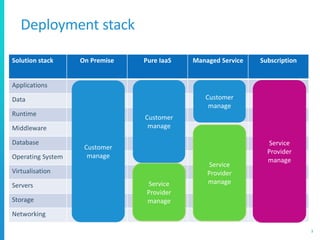
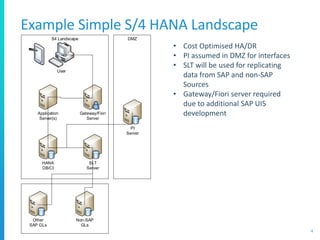
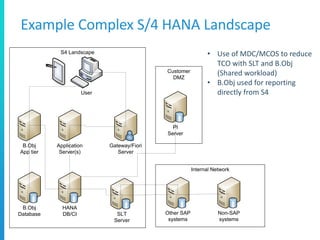
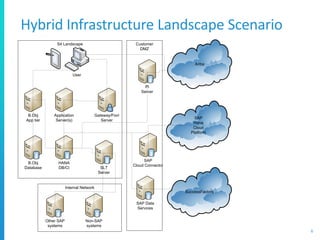
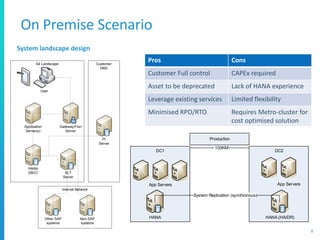
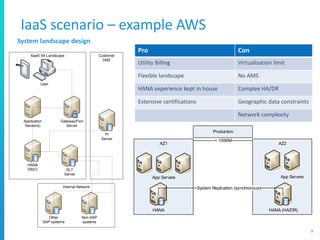
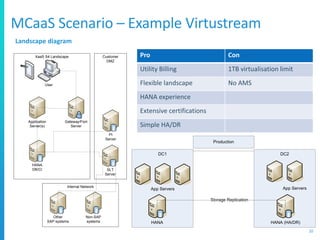
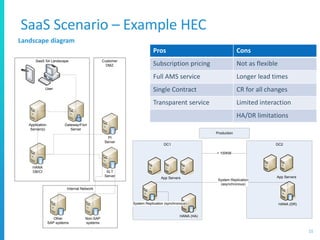
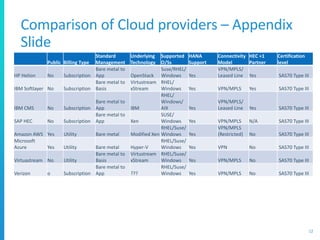
The document discusses various deployment options for SAP applications, including on-premise, IaaS, and managed cloud services, highlighting the advantages and trade-offs of each. It provides examples of simple and complex S/4 HANA landscapes, outlines key considerations for migration, business continuity, and customer interactions with service providers. Additionally, it compares cloud providers based on their offerings, technologies, and support for SAP environments.