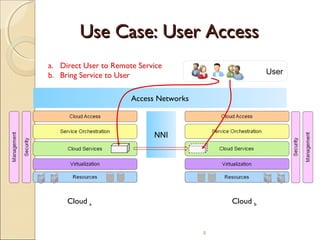
The document discusses cloud interoperability and standards. It defines interoperability as the ability of cloud systems to exchange data and information. This allows applications and workloads to seamlessly move between cloud platforms. The document outlines motivations for interoperability such as customer choice, competition, and innovation. It also discusses functional scope, policy objectives, use cases, and enabling user access across clouds through standards.