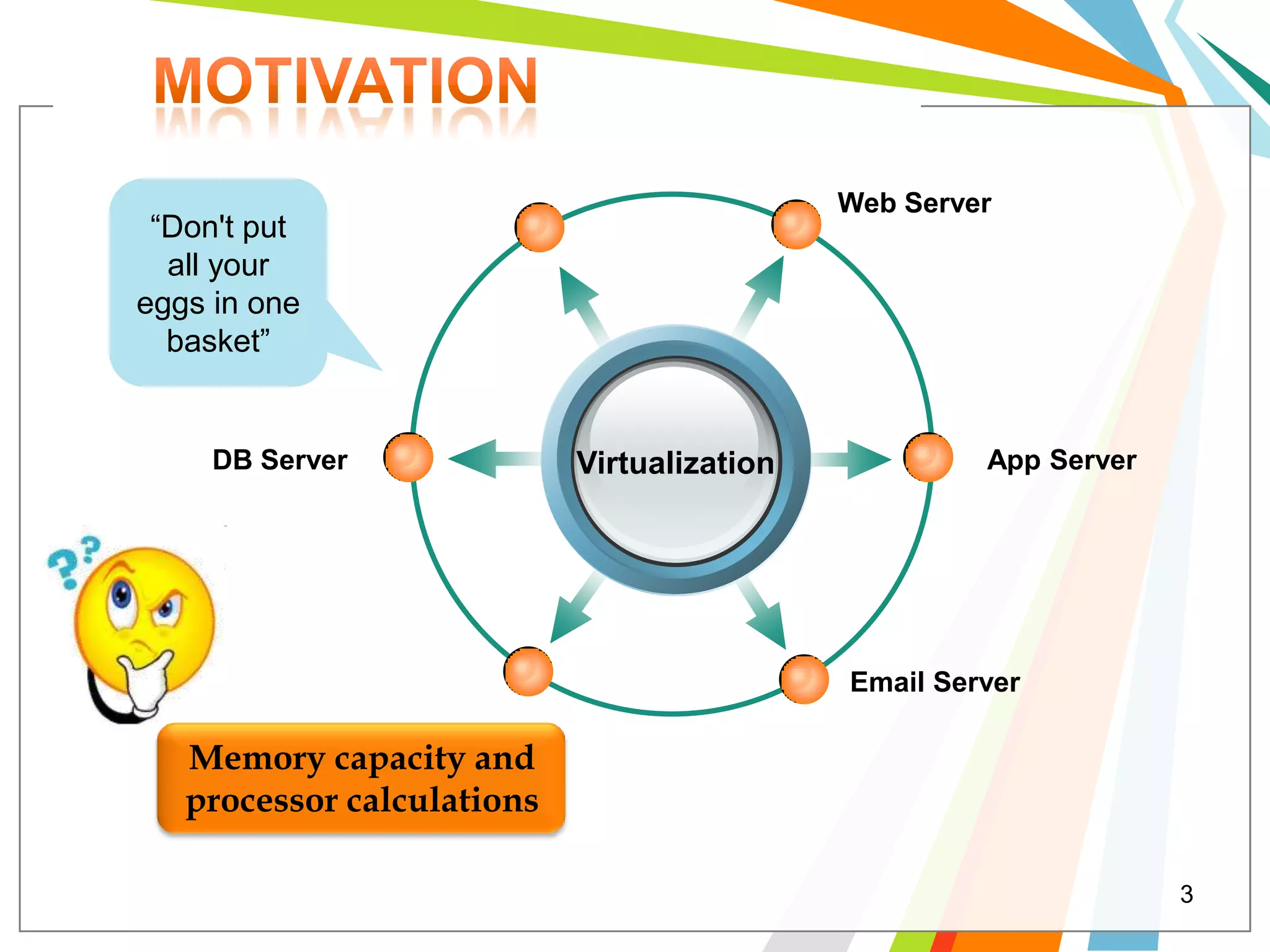
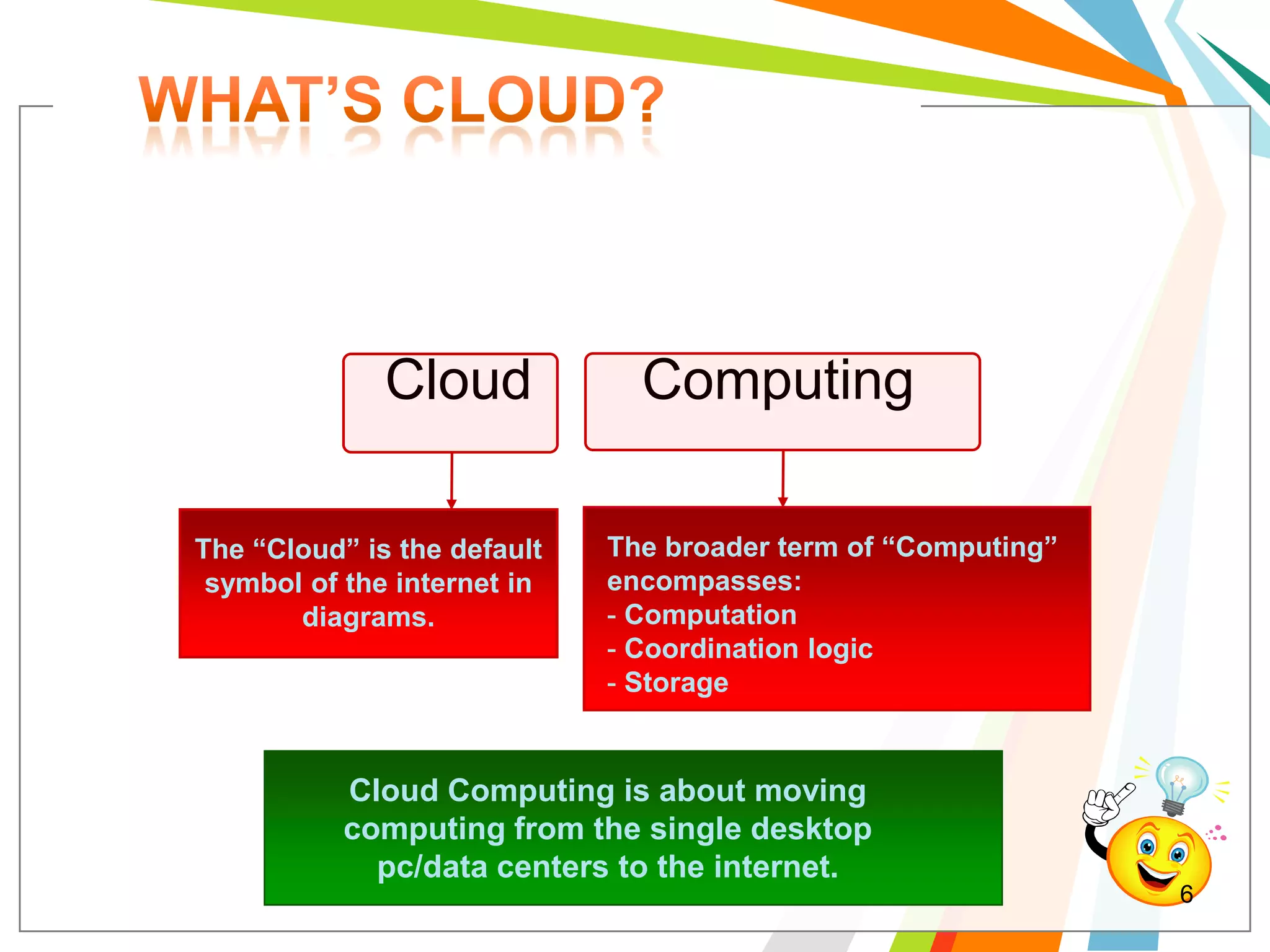
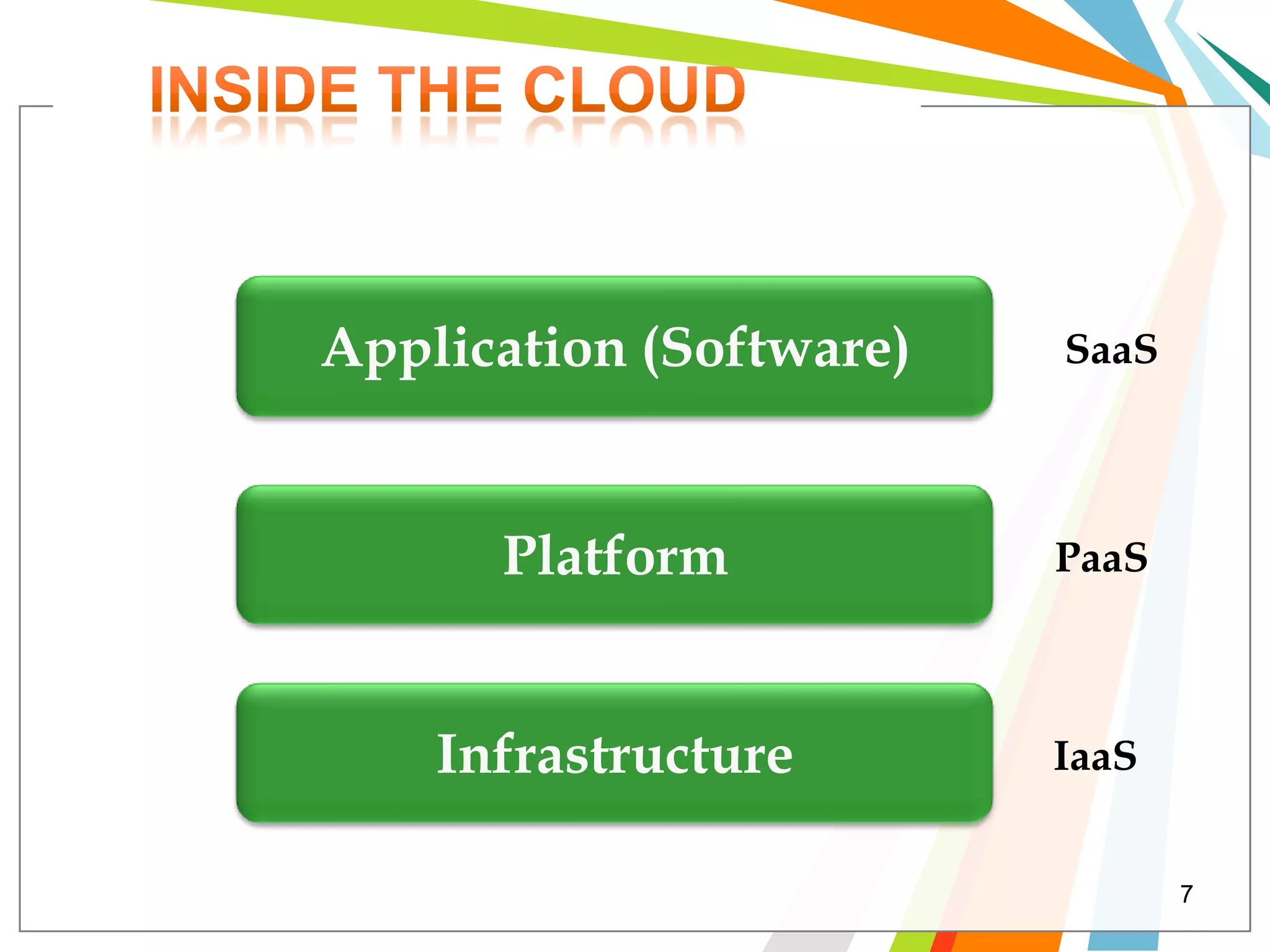
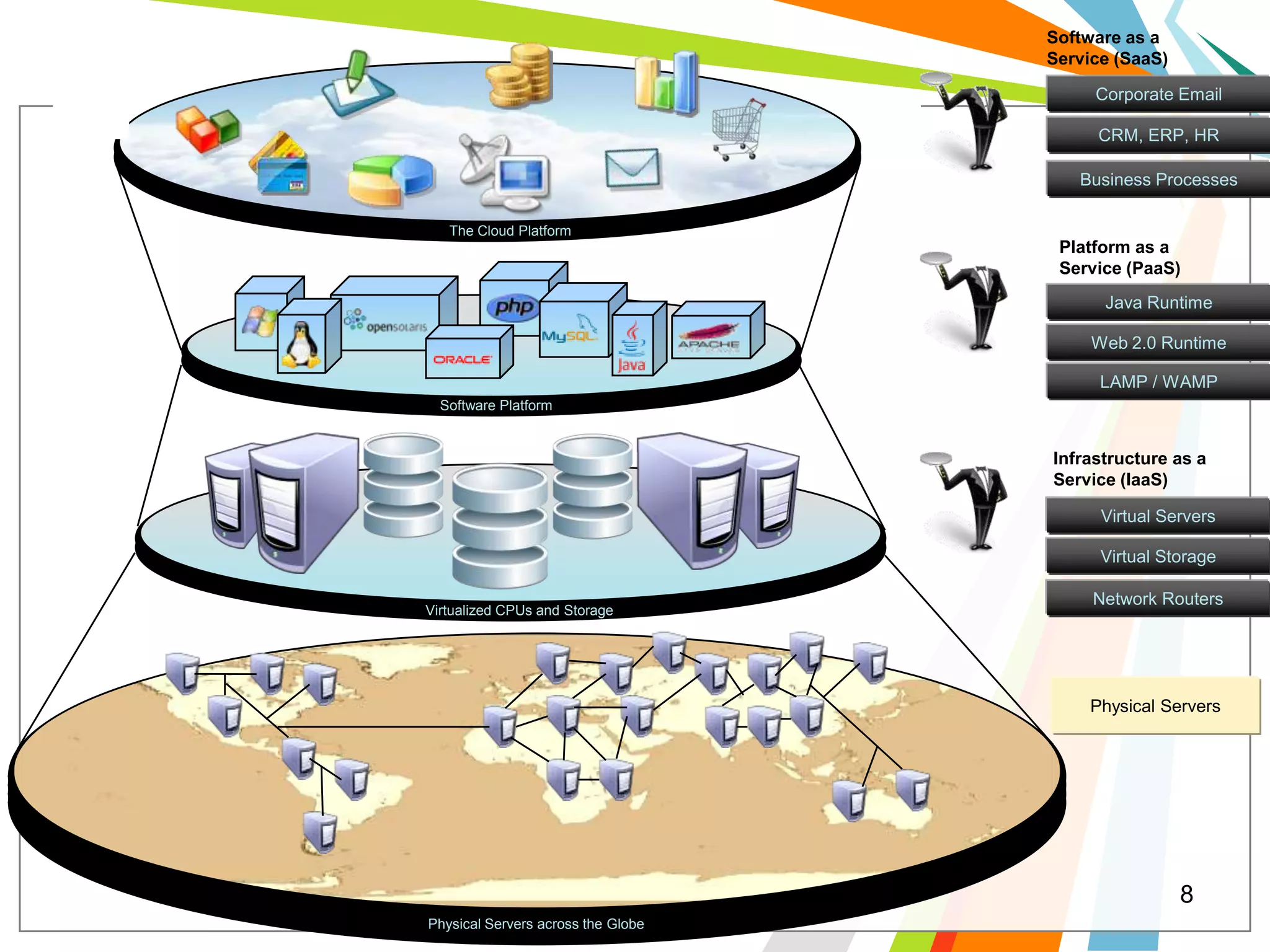
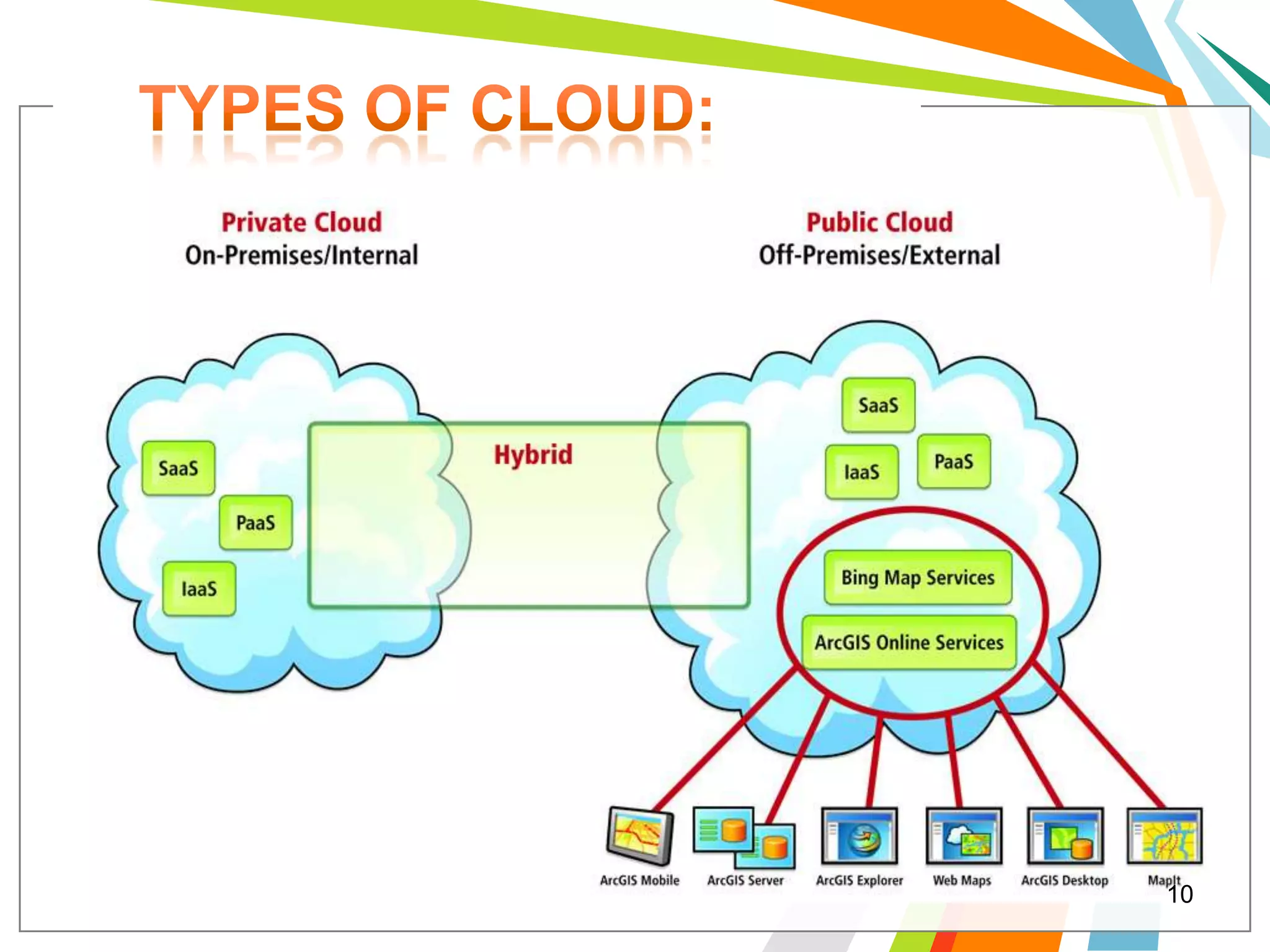
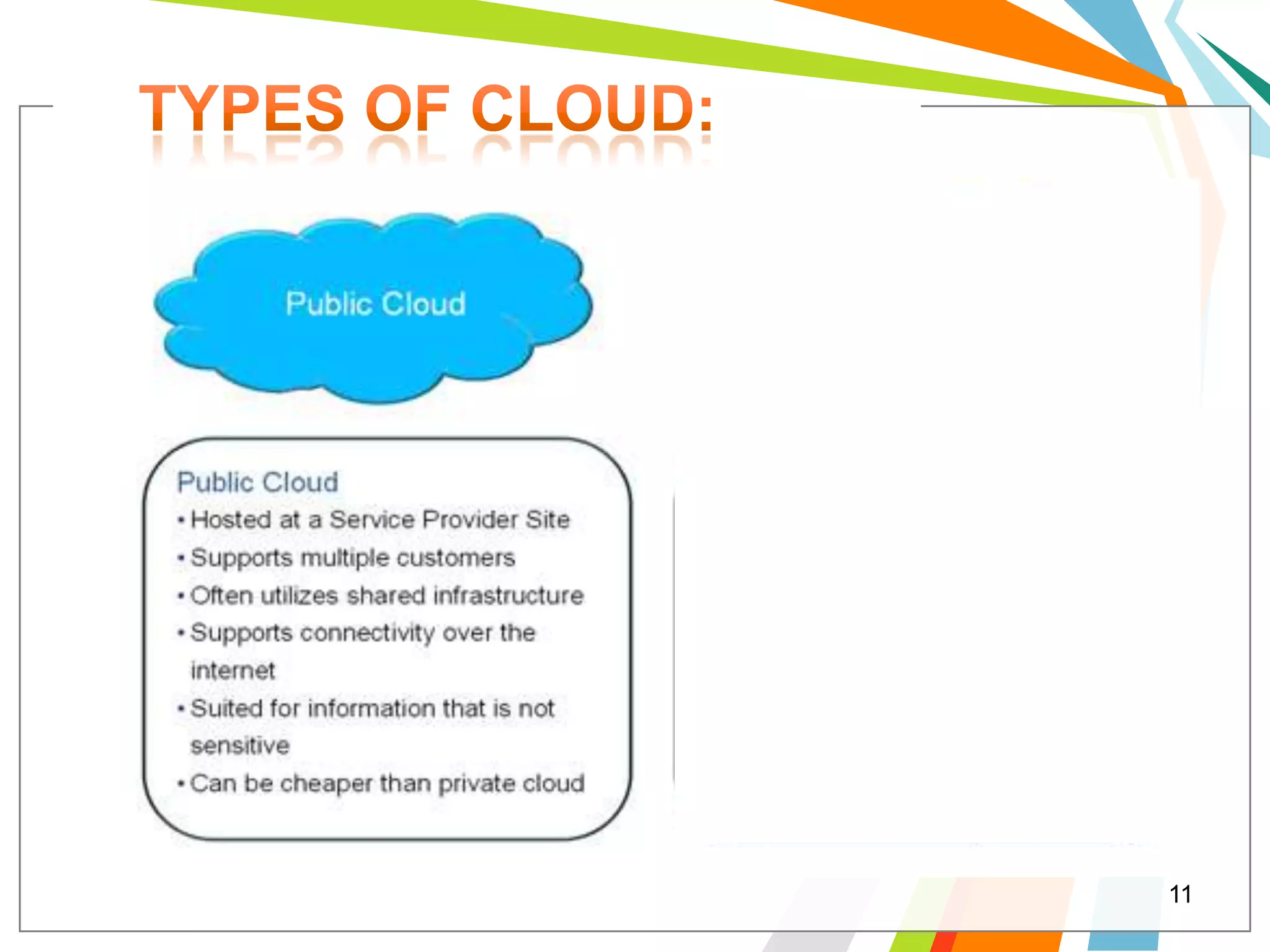
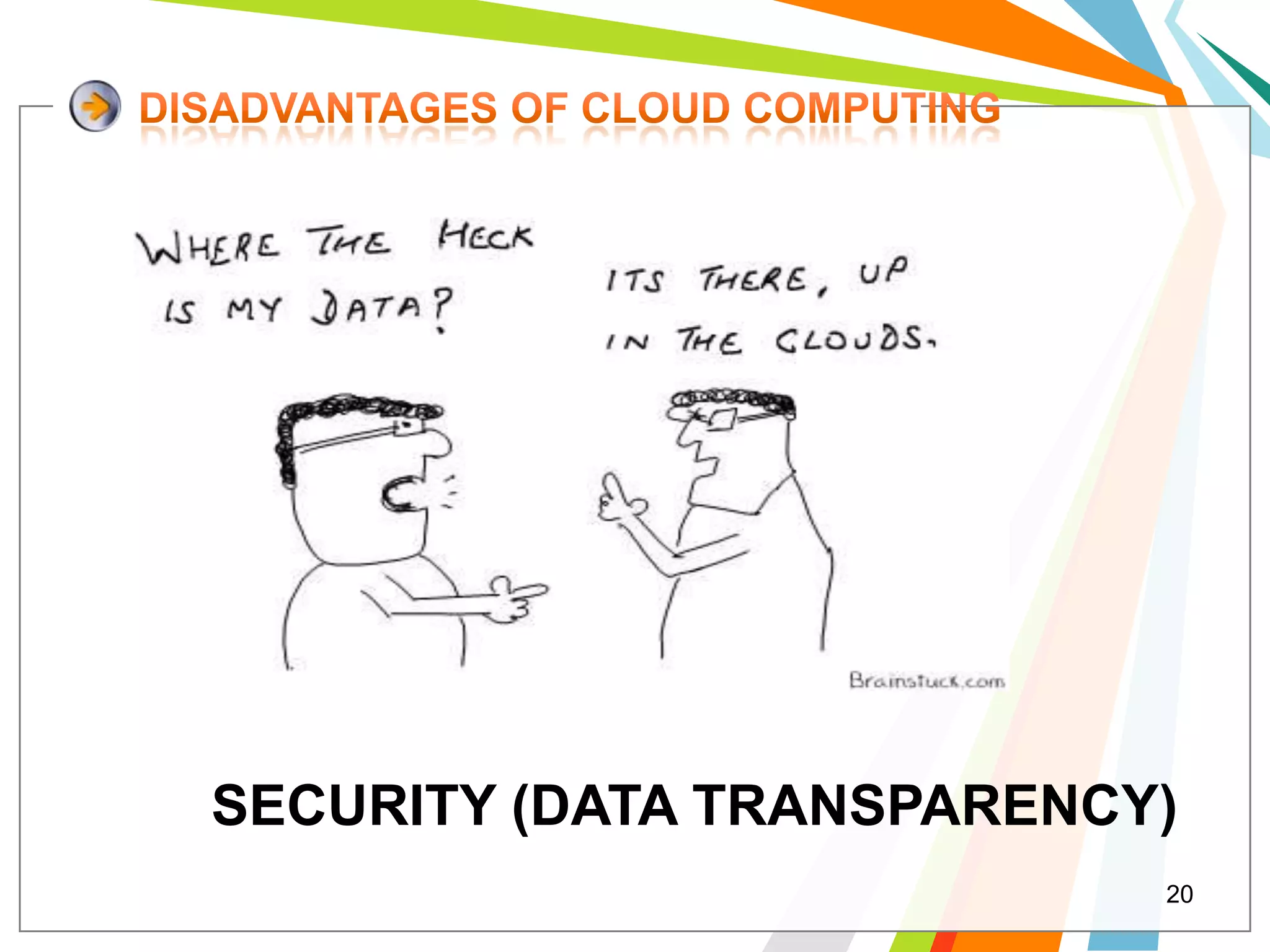
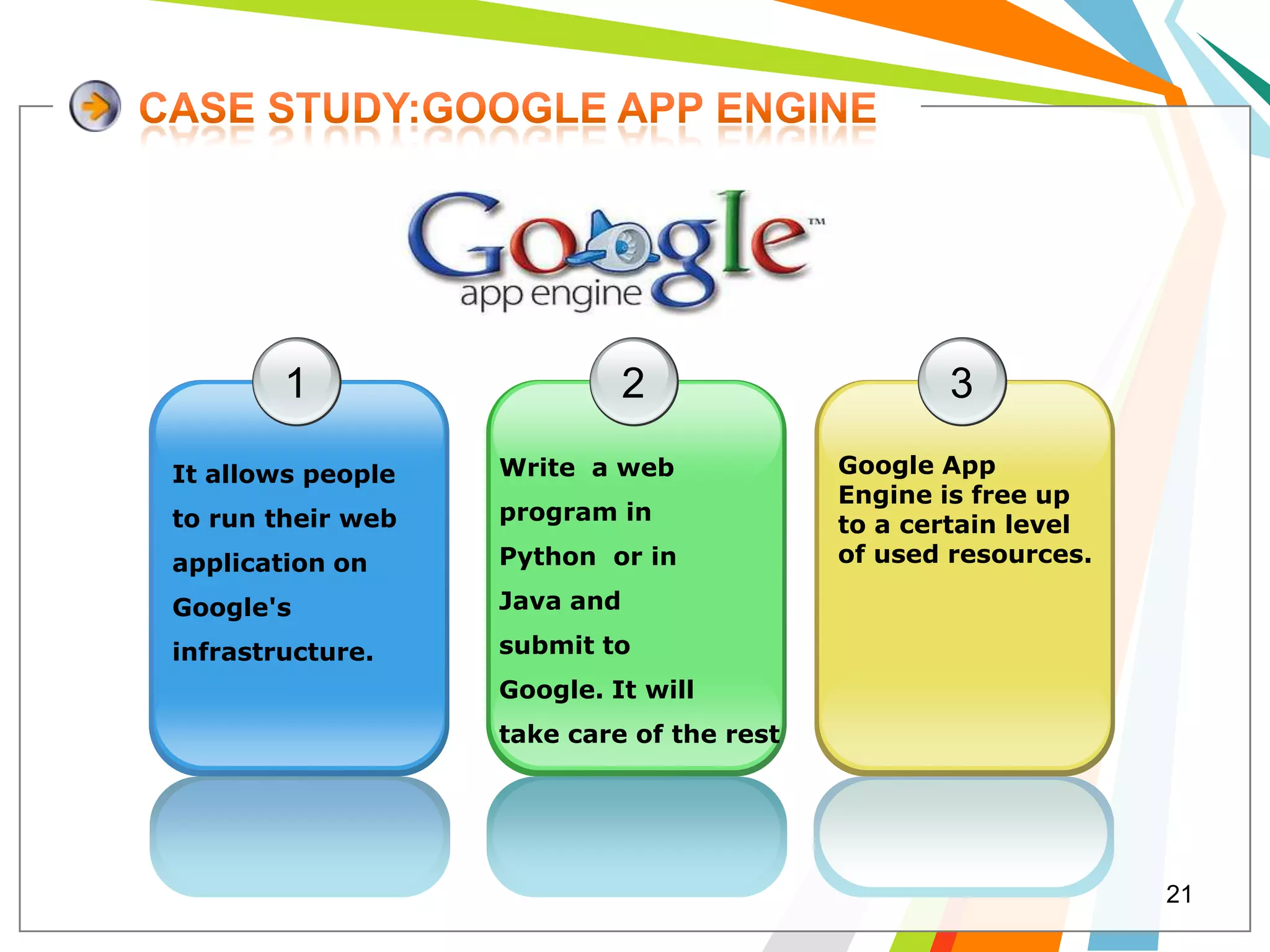
Cloud computing allows users to run web applications on large providers' infrastructure instead of their own servers. Google App Engine is one such platform that is free up to a certain level of usage. It initially only supported Python but now also supports Java. Users can deploy standard Java web applications to Google App Engine, which will handle the infrastructure. This provides scalability without upfront costs.

![DB Server EMail
Web Server App Server
Linux Windows
Windows Linux
MySQL Exchange
IIS Glassfish
significant infrastructure costs
Facebook spent $68 million on their servers in 2007 [1] 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing-111030092938-phpapp01/75/Cloud-computing-2-2048.jpg)