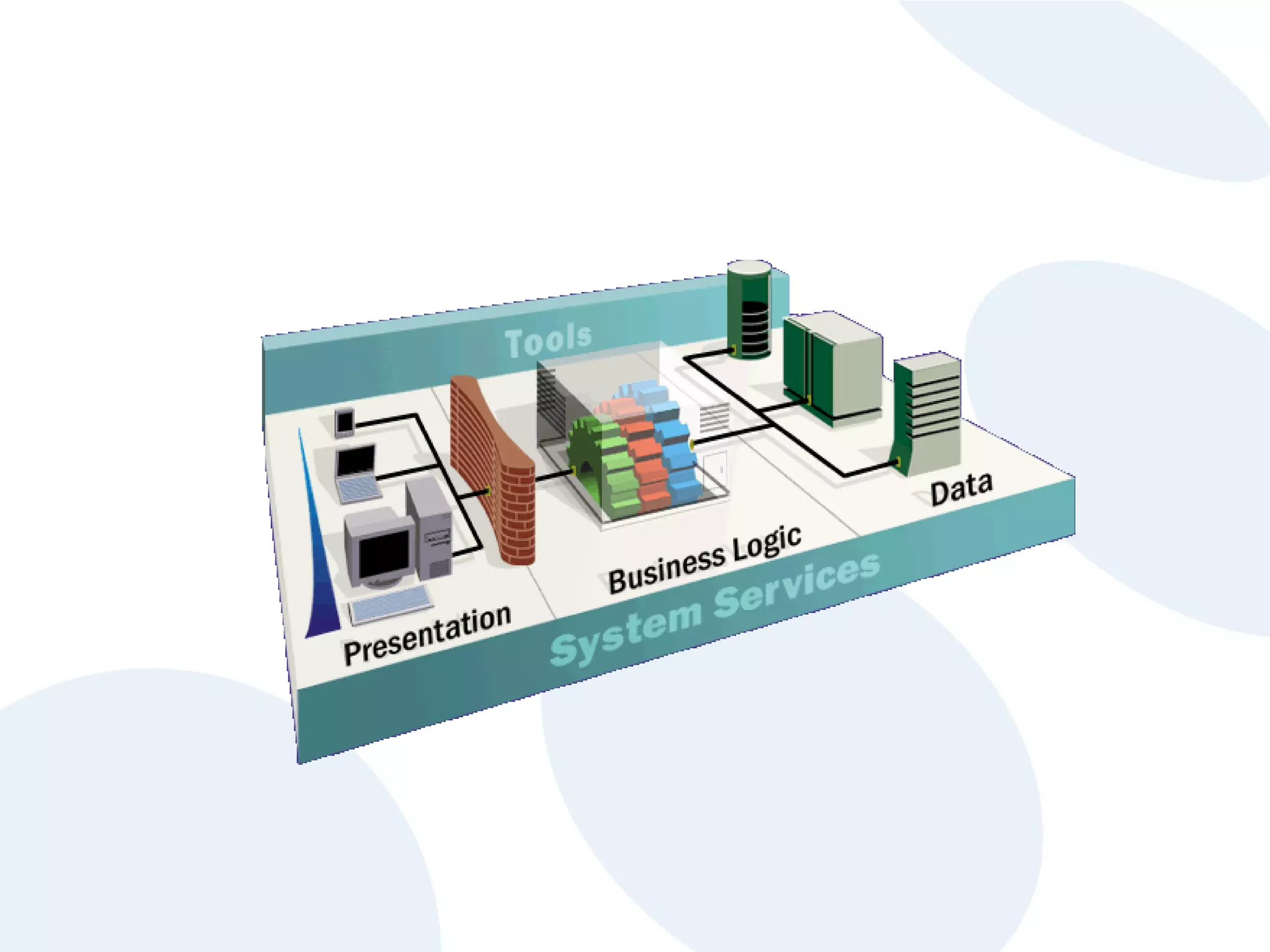
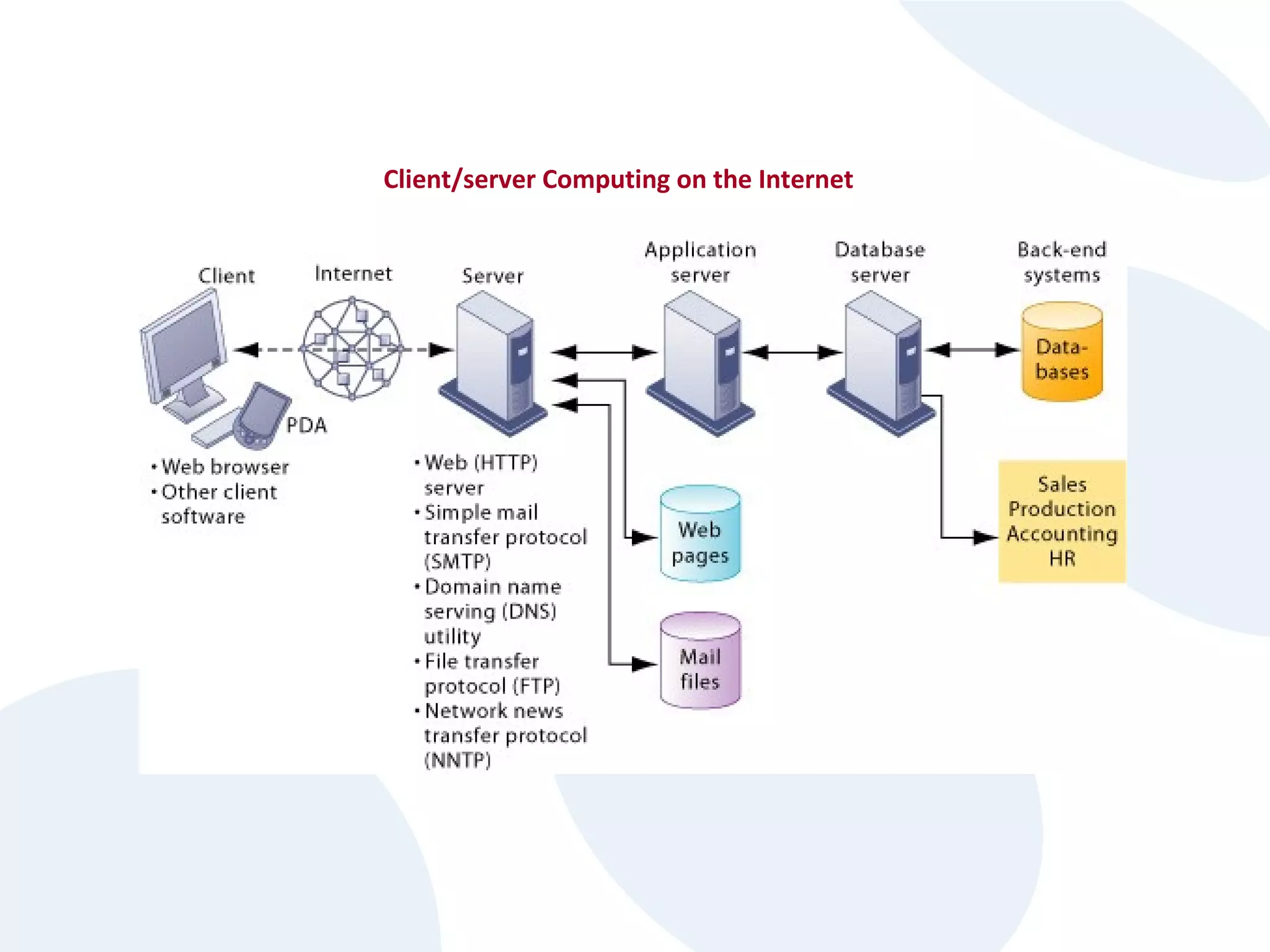
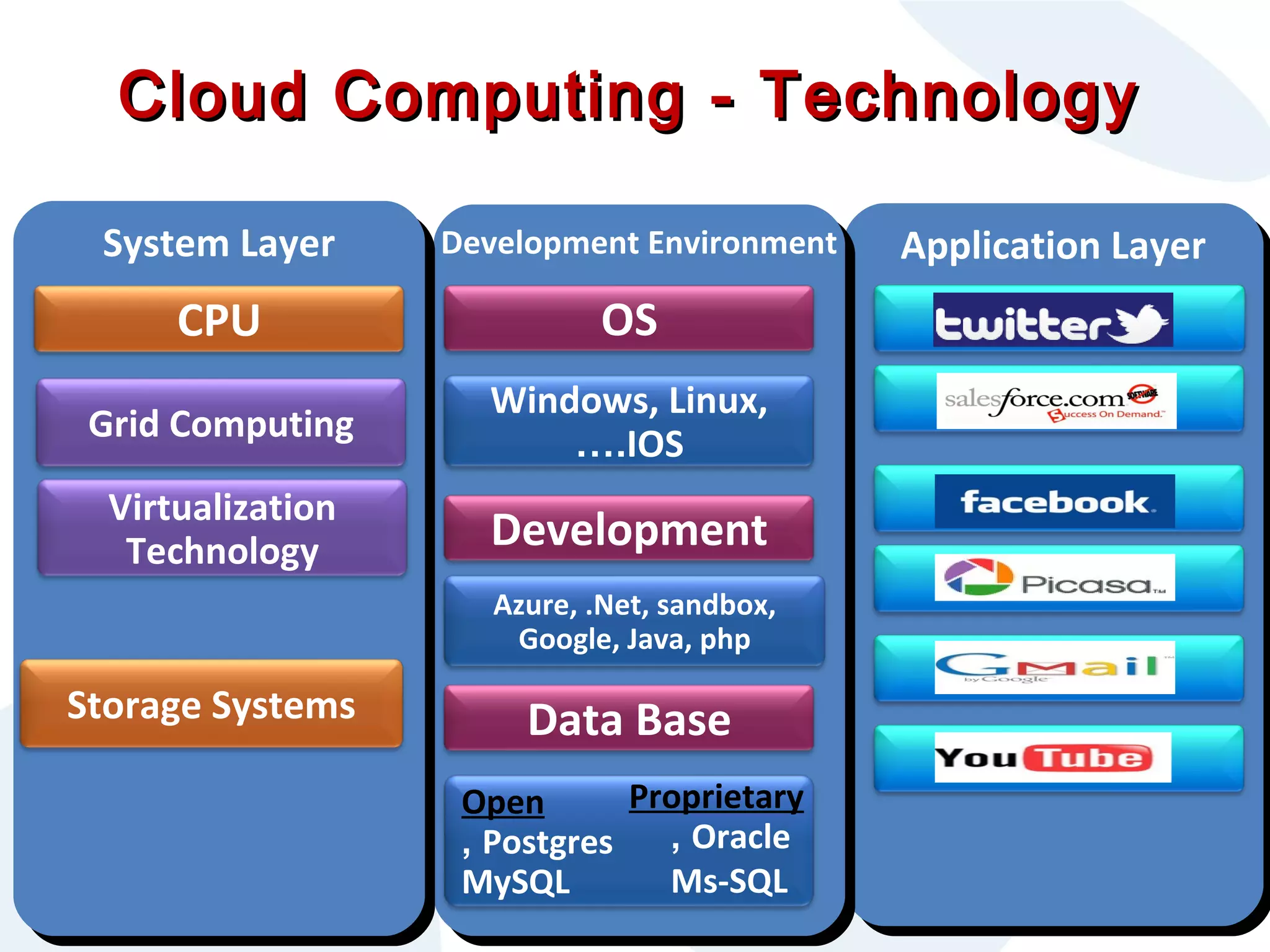
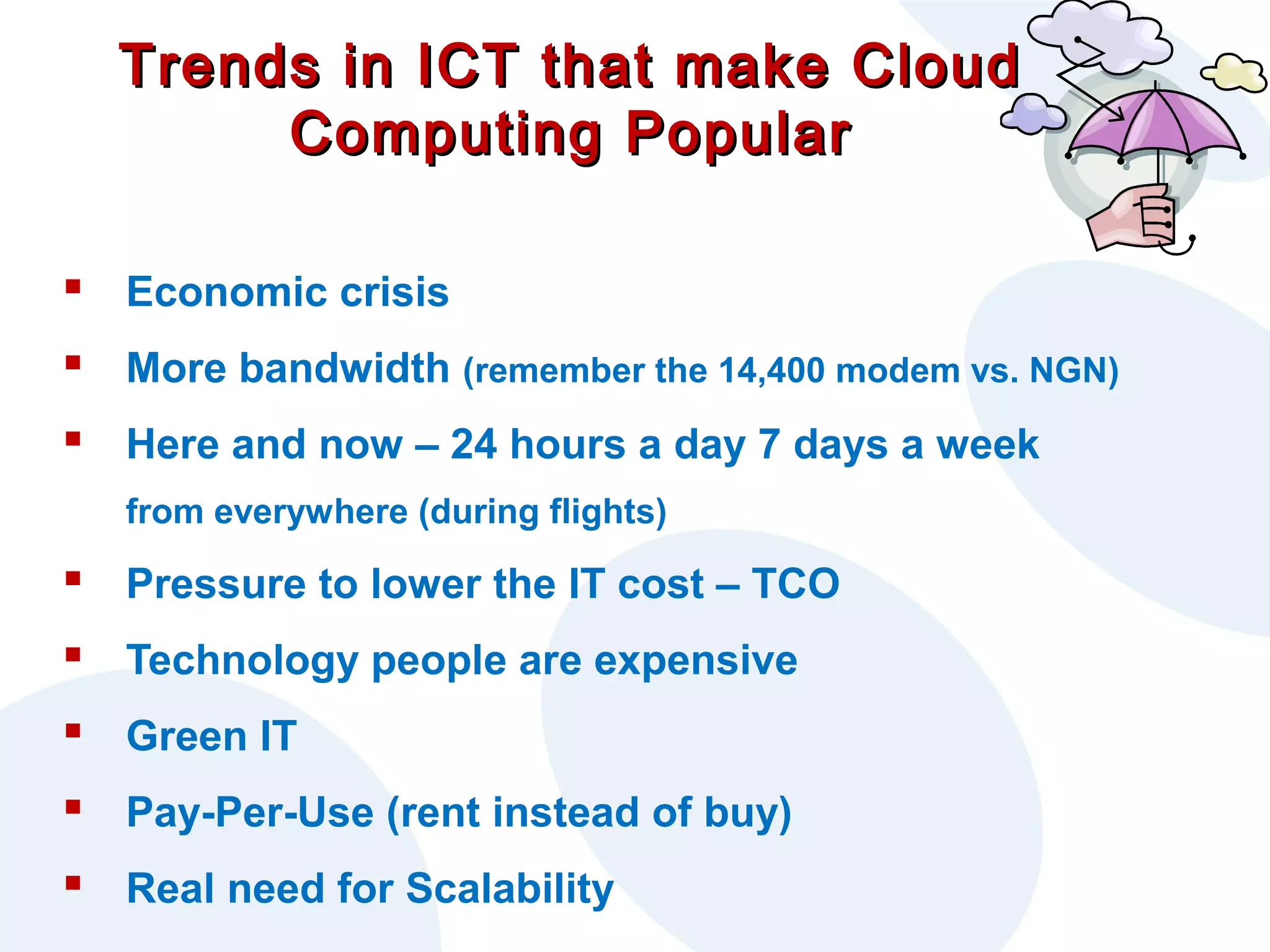
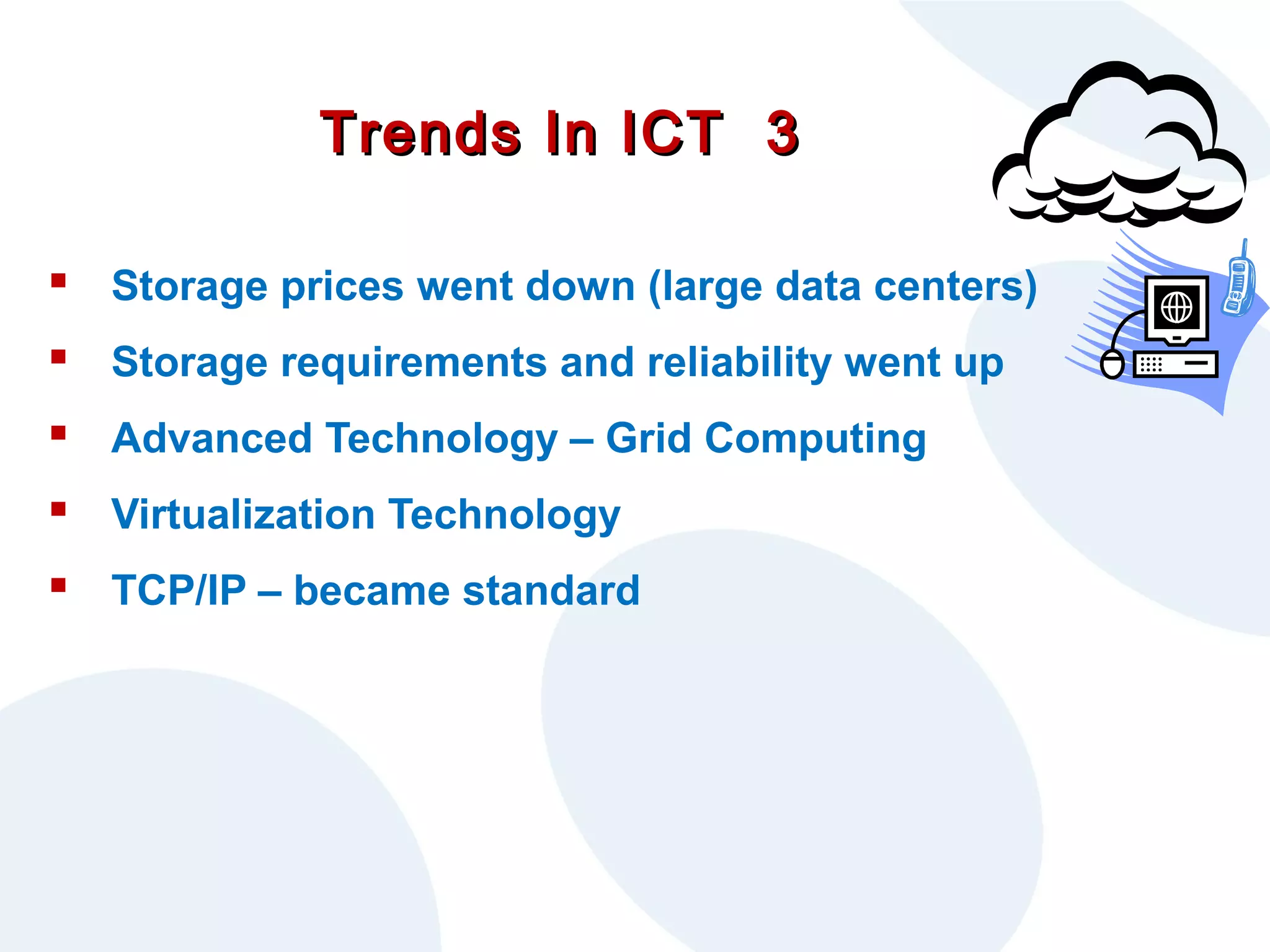
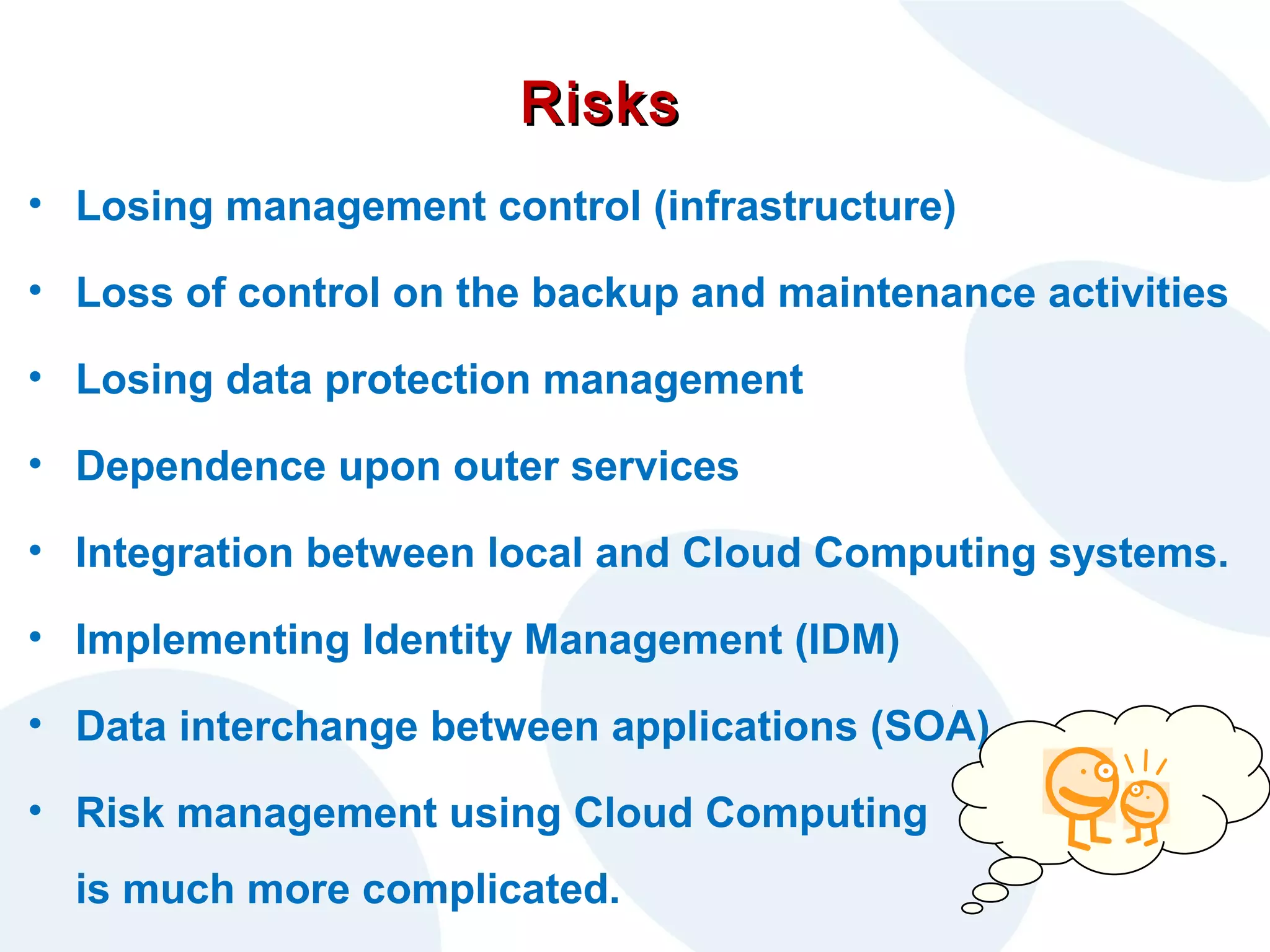
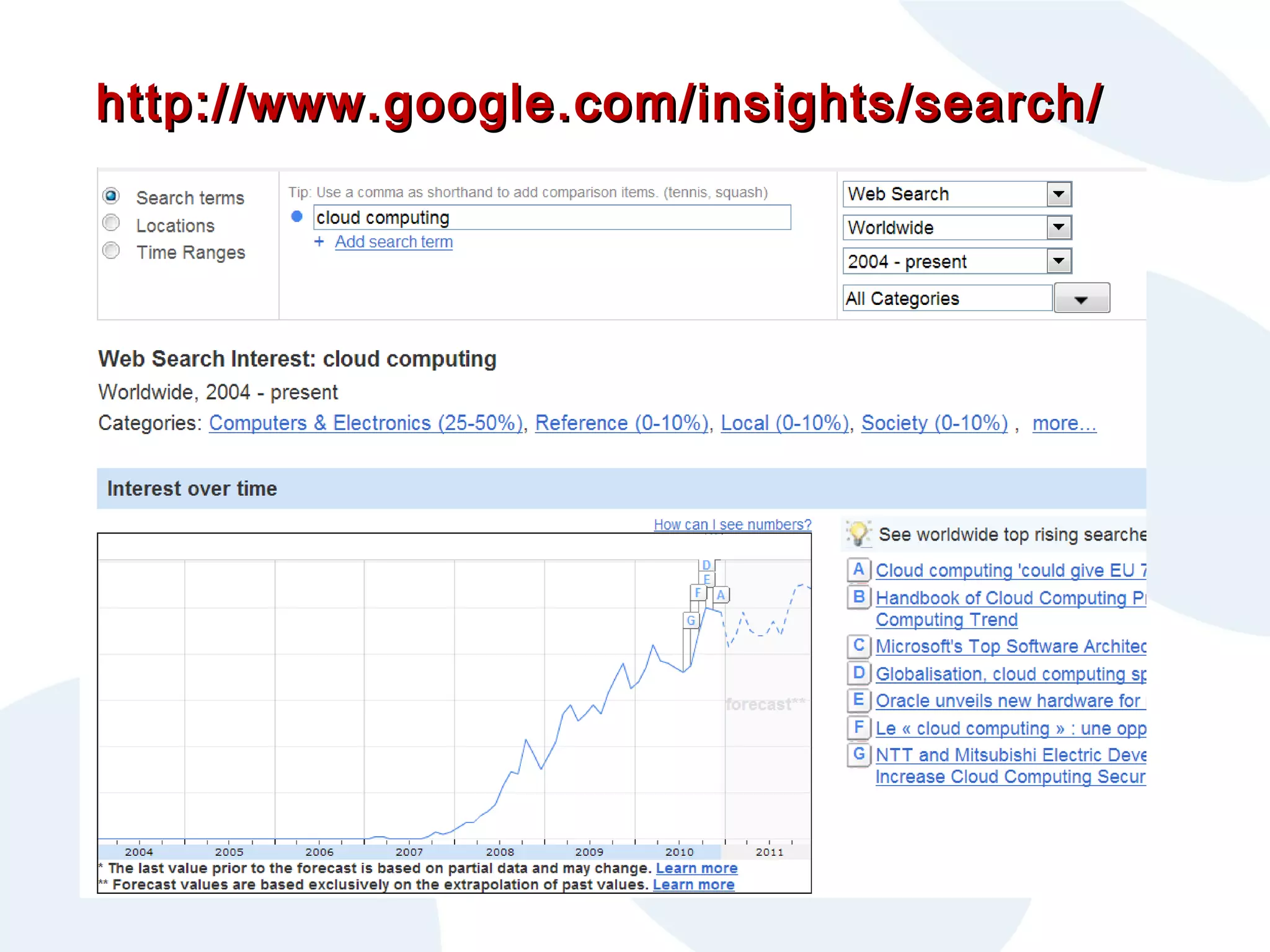
The document discusses cloud computing and its potential applications for academic eLearning. It defines cloud computing as accessing computer resources over the Internet rather than locally. Motivations for cloud computing include cost savings, scalability, and the growing market for cloud services. The document examines cloud computing types, trends driving its popularity, potential benefits for large/small organizations and individuals, risks, and COMAS College's experiences using cloud systems for various applications.