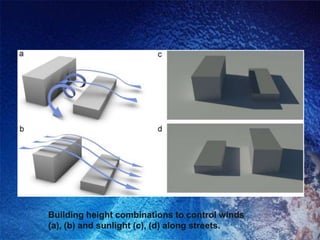
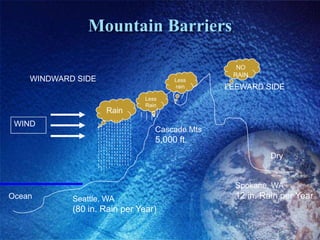
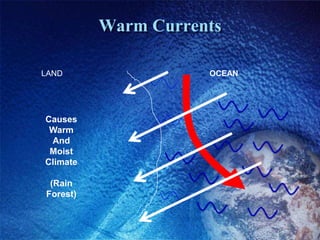
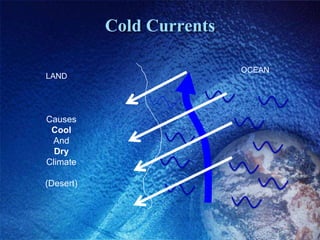
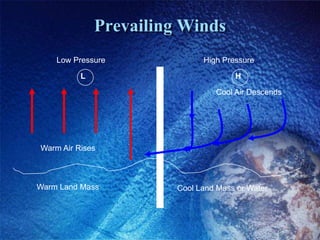
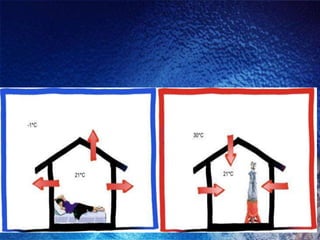
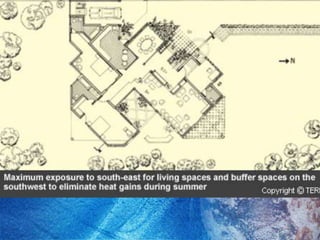
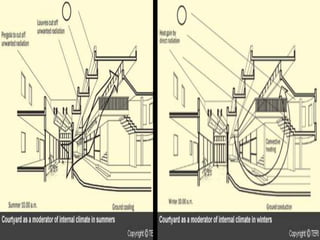
The Bidani House project demonstrates how to design a climate-responsive building on a constrained urban site. Located in Faridabad's composite climate zone, the house has large temperature swings throughout the year. Key sustainable features include developing the house form around a central courtyard to act as a heat sink, using buffer spaces on the overheated southwestern exposure, allowing solar penetration according to seasonal changes through the building form, and using local stone for thermal mass to moderate temperature swings. The project shows how responsive design is possible even on a fixed small urban site.