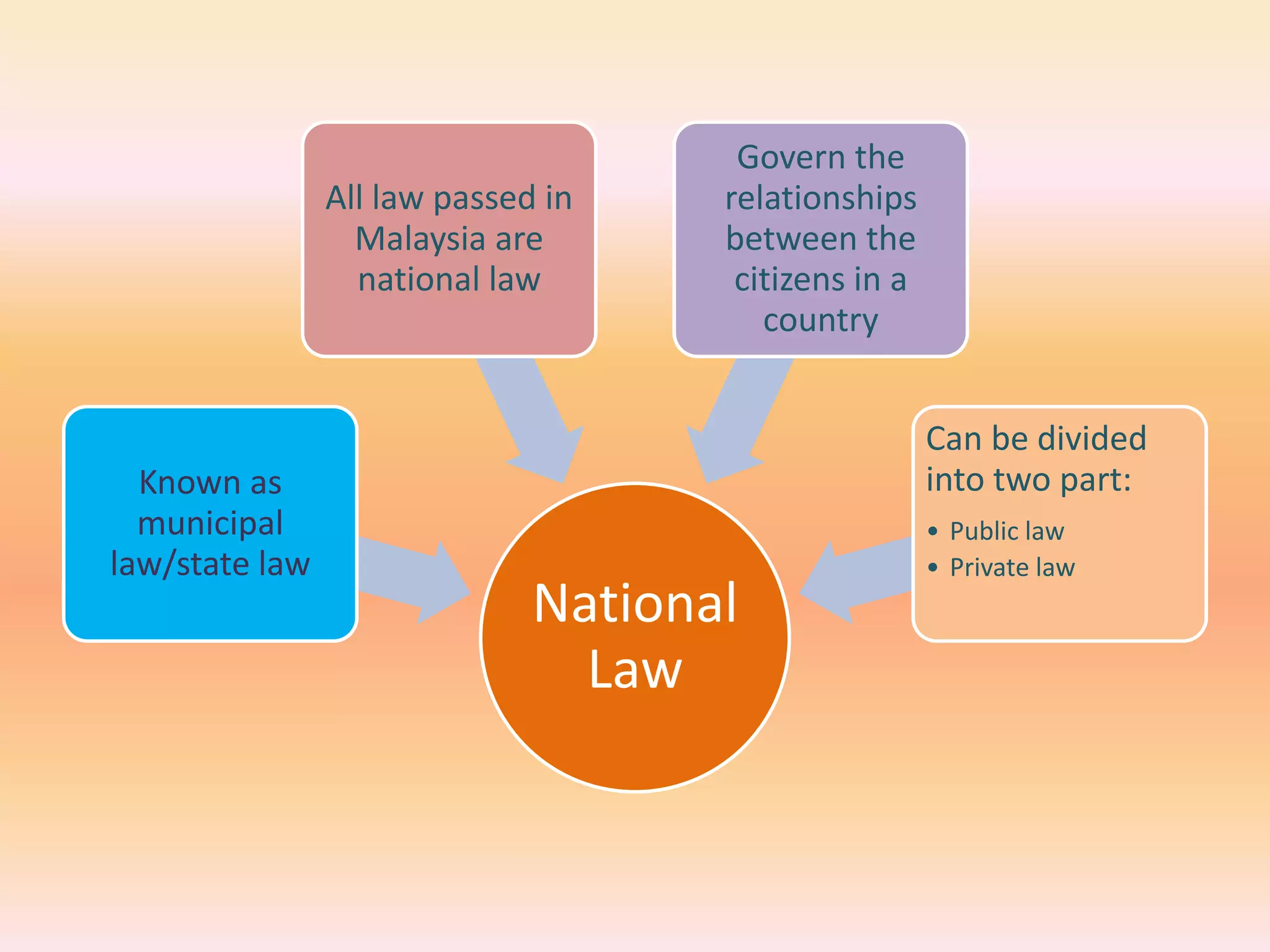
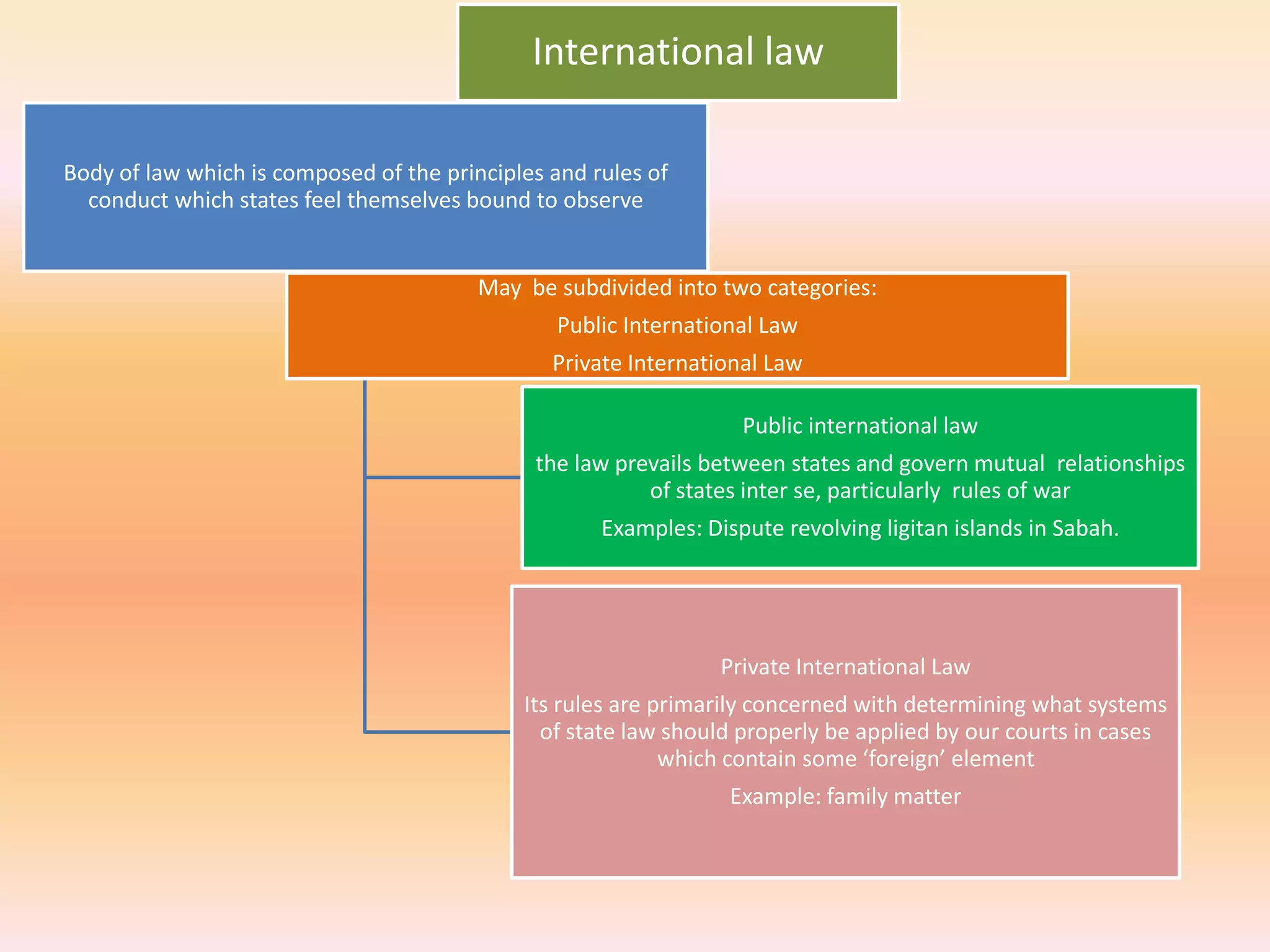
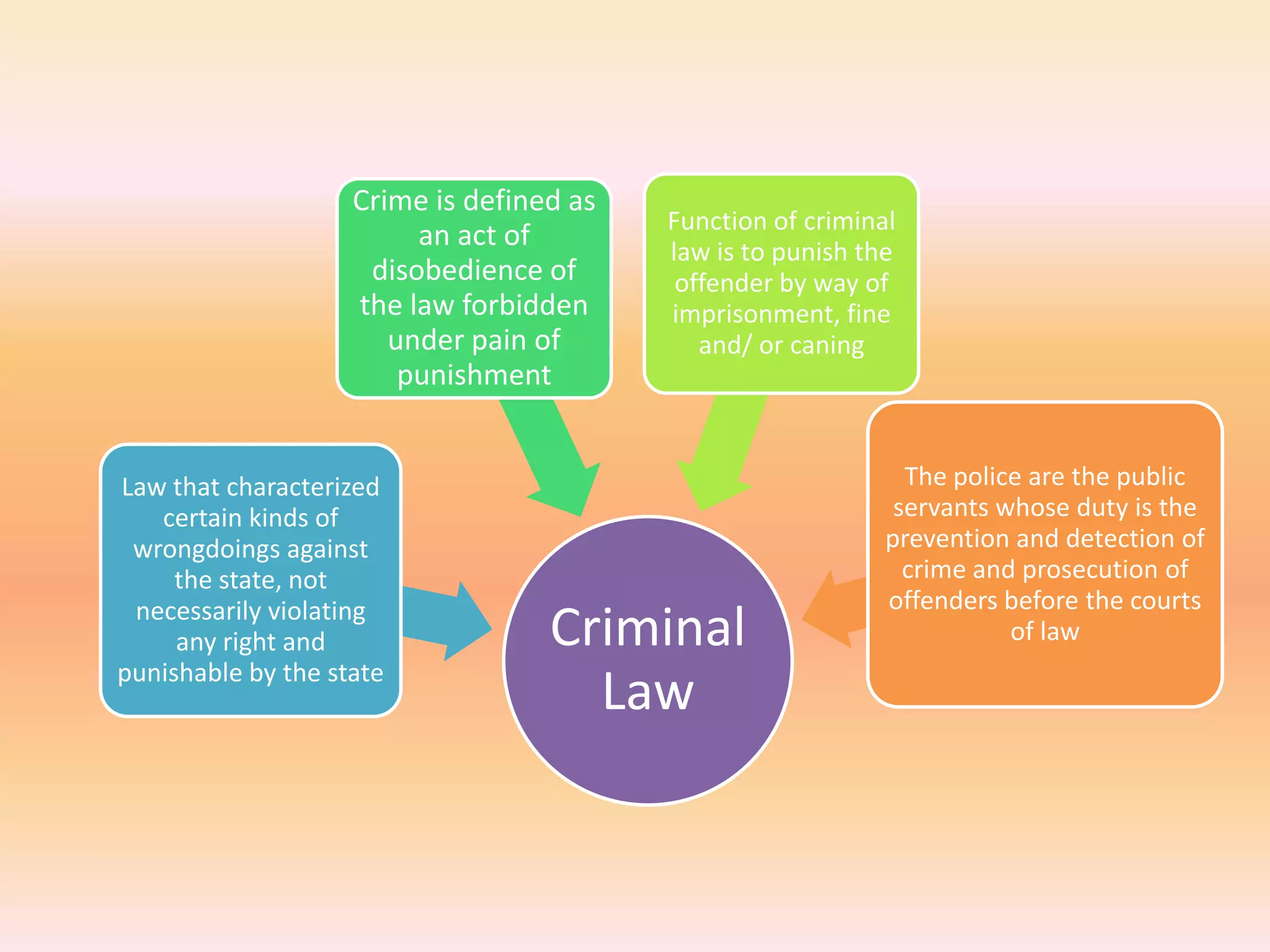
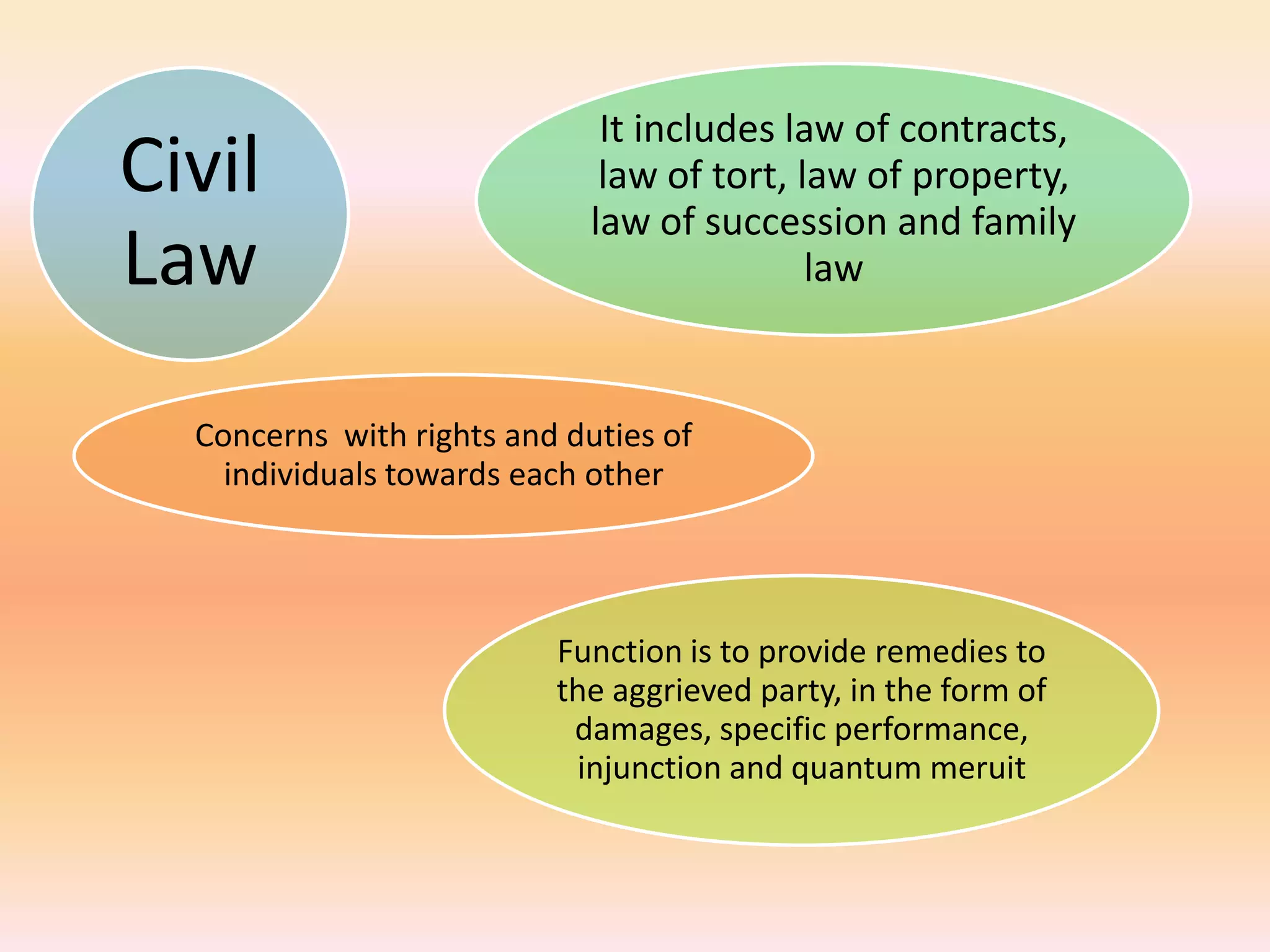
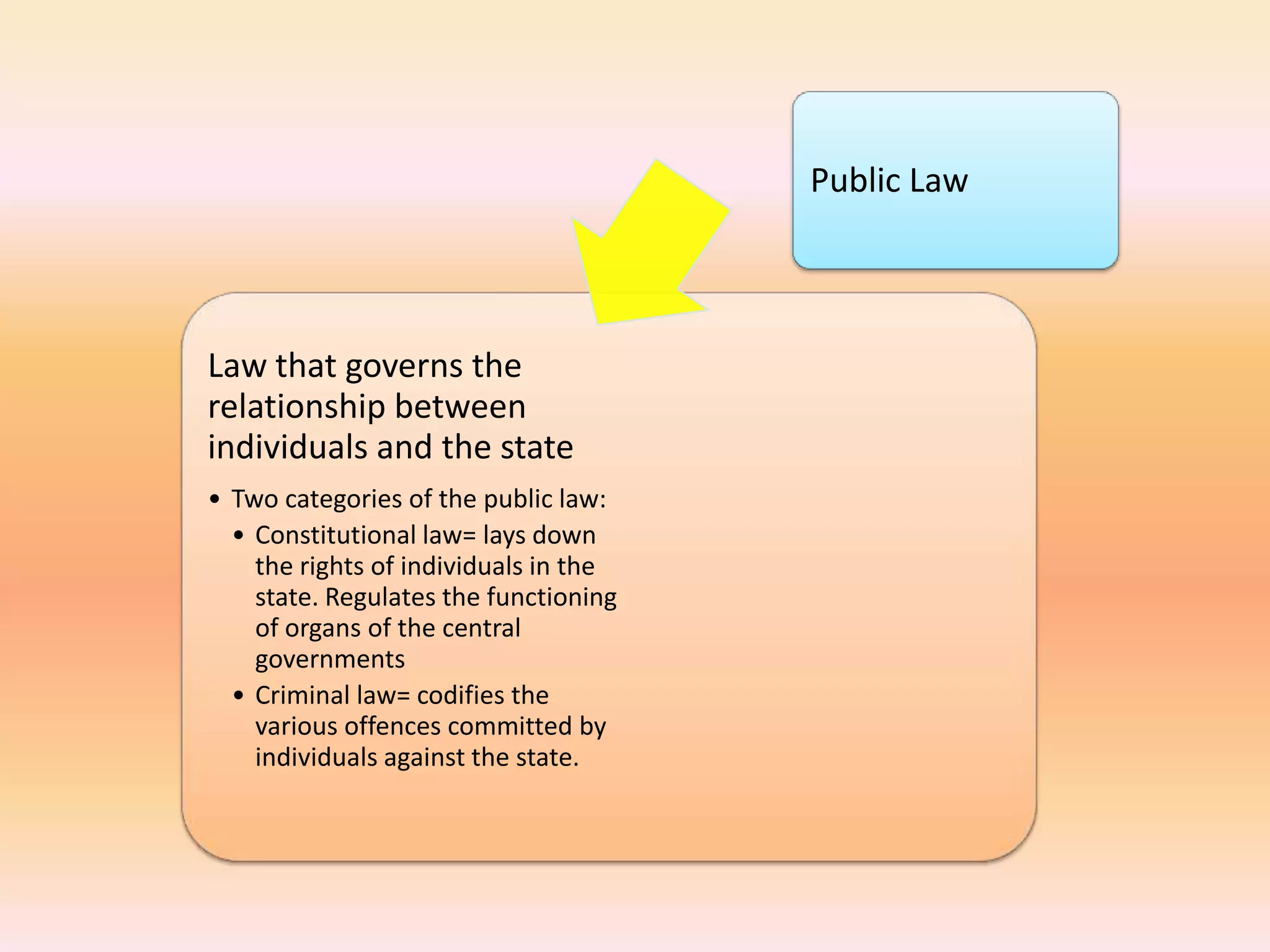
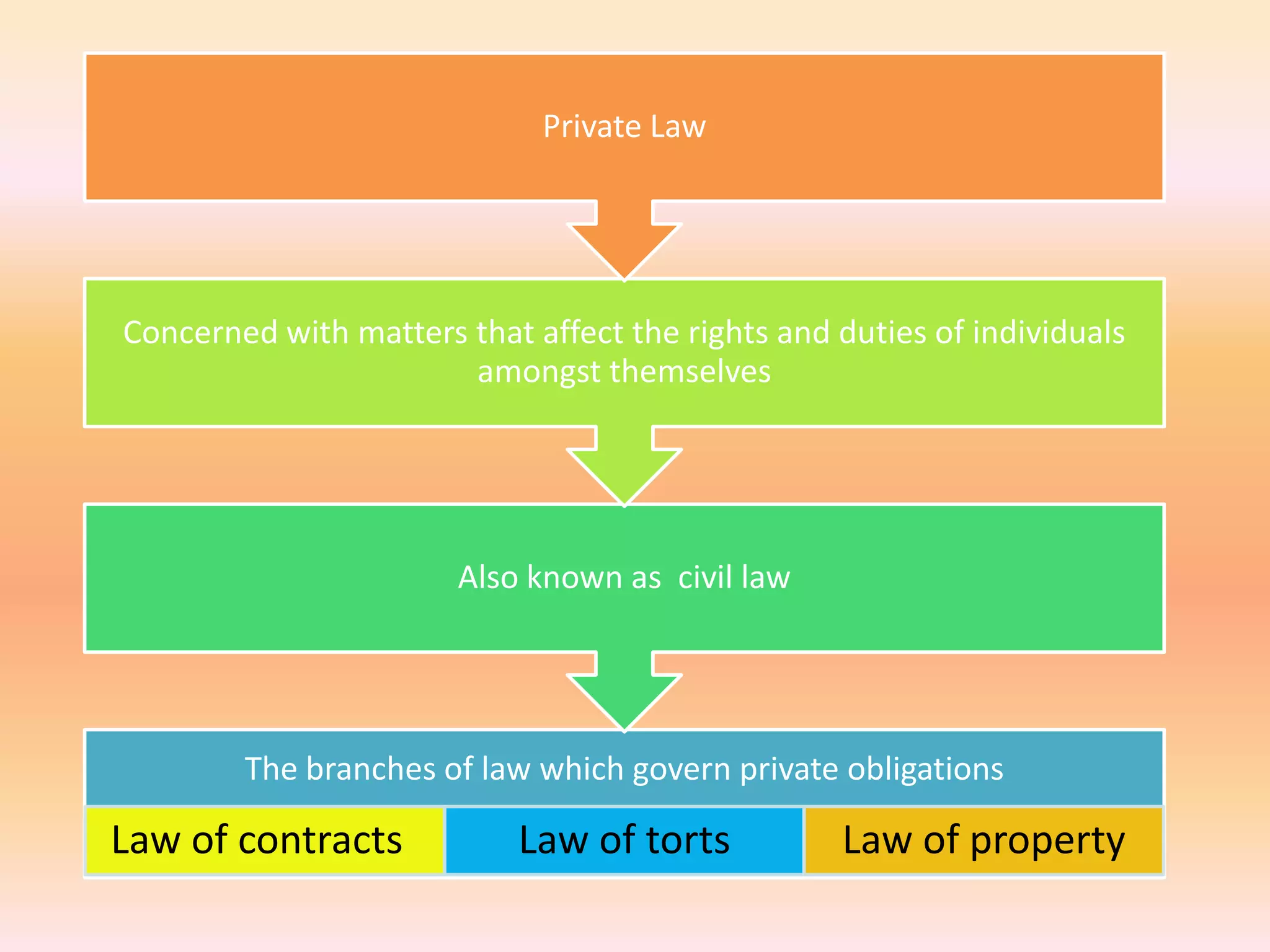
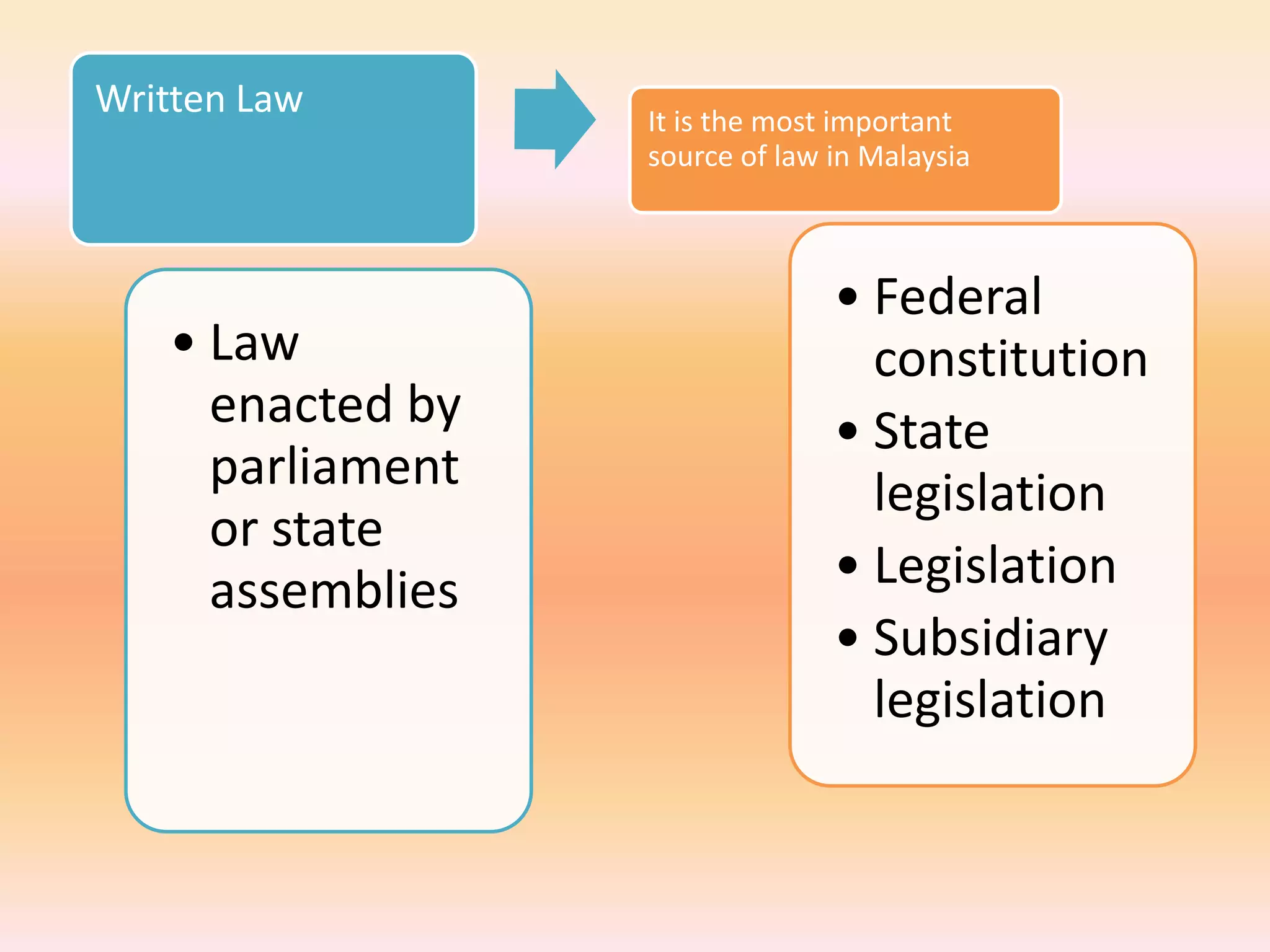
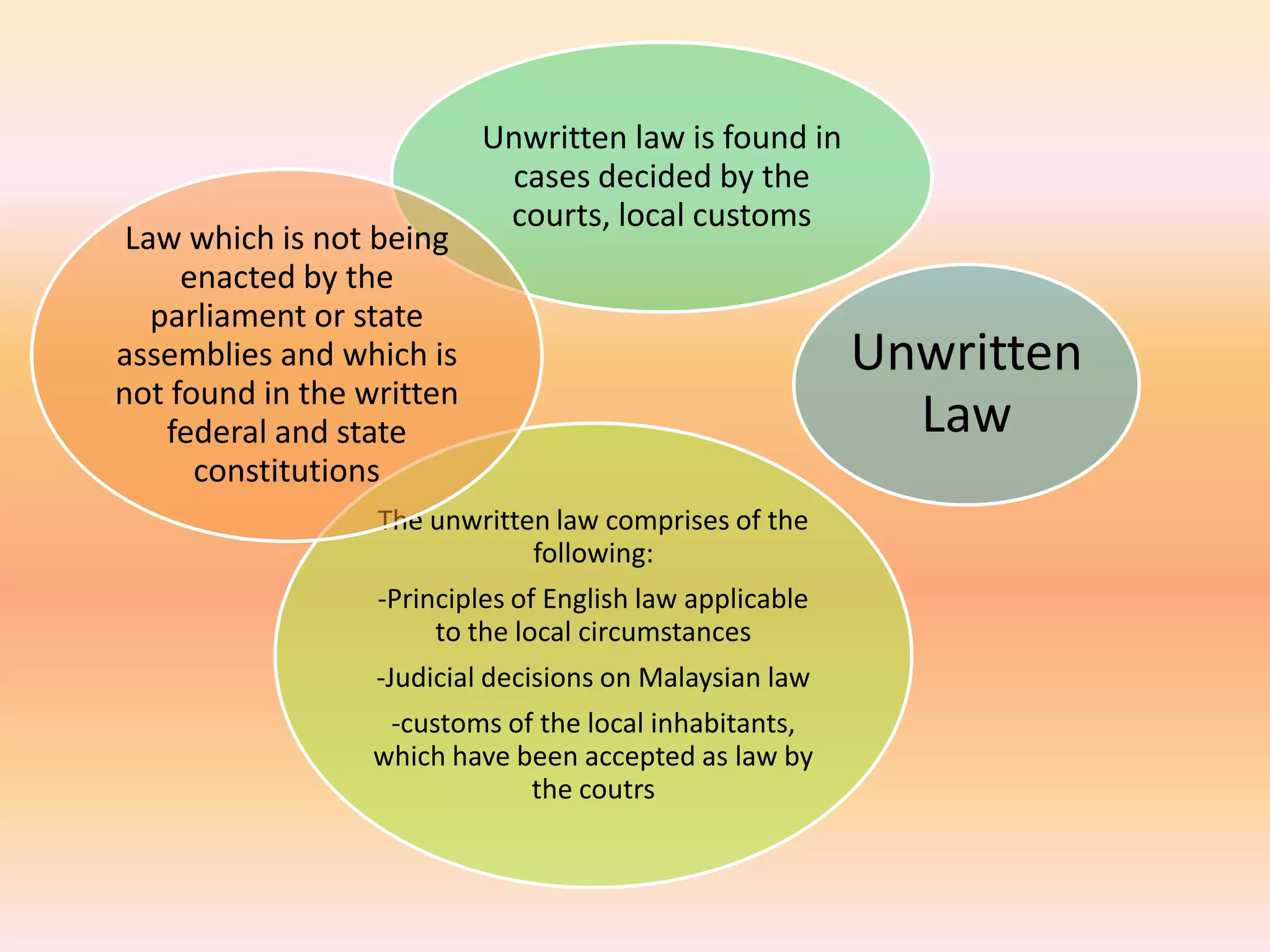
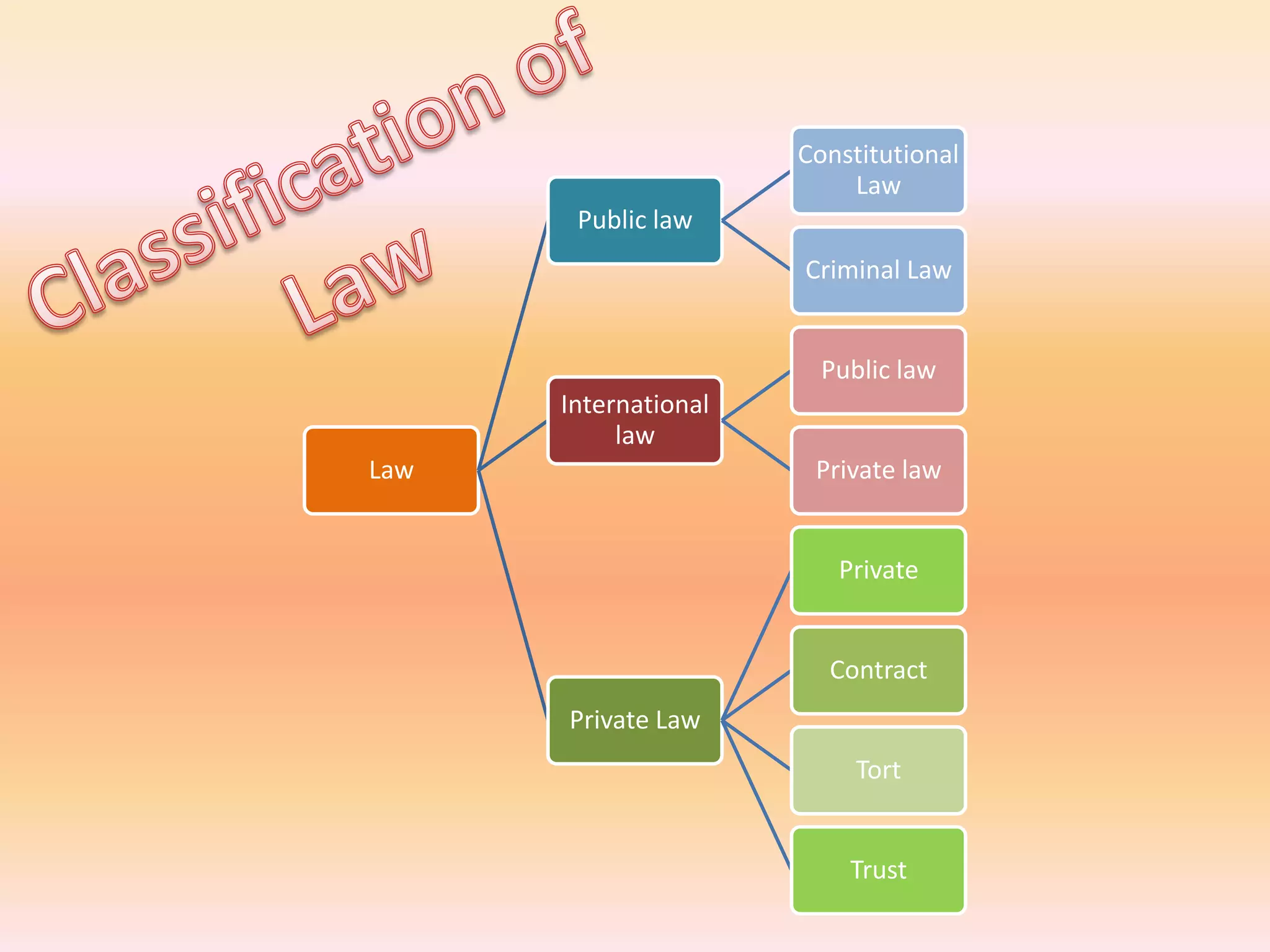
The document discusses different areas of law including public law, private law, constitutional law, criminal law, civil law, written law, and unwritten law. Public law governs relationships between individuals and the state, while private law concerns relationships between individuals. Criminal law punishes wrongdoings against the state, and civil law provides remedies for individuals. Written law includes legislation while unwritten law includes precedents and customs. Procedural law establishes rules for enforcing rights in civil and criminal matters.


![Equity
• The name given “Equity” is the set of legal principles in
countries following the English common law tradition,
which supplement strict rules of law where their
application would operate harshly, so as to achieve
what is sometimes referred to as “natural justice”
• It also means “fairness”
• Equity has been described as “a gloss [meaning a
supplement] on the common law, filling in the graps
and making the English legal system more complete
• In English Law, equity means that body of rules
originally enforced only by the court of chancery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classificationoflaw-130316055450-phpapp02/75/Classification-of-law-4-2048.jpg)