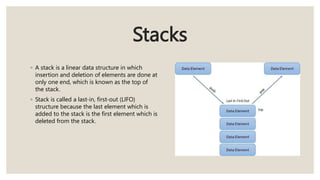
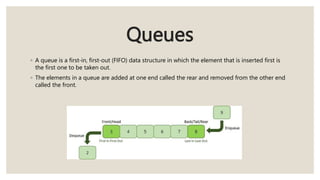
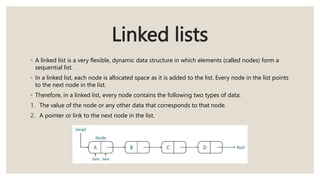
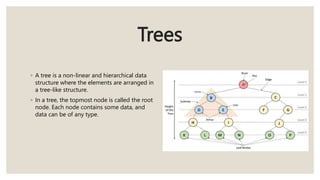
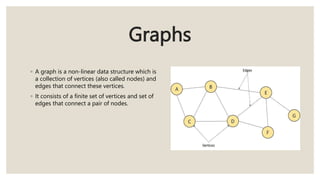
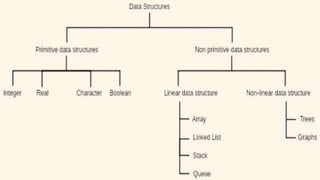
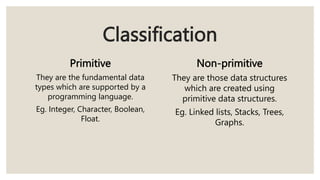
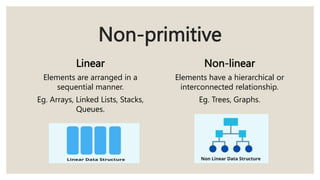
This document discusses the classification of data structures. It categorizes data structures as either primitive or non-primitive. Non-primitive data structures are further divided into linear and non-linear categories. Linear data structures like arrays, stacks, queues, and linked lists arrange elements sequentially. Non-linear structures like trees and graphs have hierarchical or interconnected relationships between elements. Common linear and non-linear data structures are then defined, including their basic properties and usages.


![Arrays
◦ An array is a collection of similar data elements. These data elements have the same data type.
◦ The elements of the array are stored in consecutive memory locations and are referenced by an
index.
◦ For example: int marks[6];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classificationofds-240229151833-77509d66/85/Classification-of-DS-Presentation-Harsh-pptx-6-320.jpg)