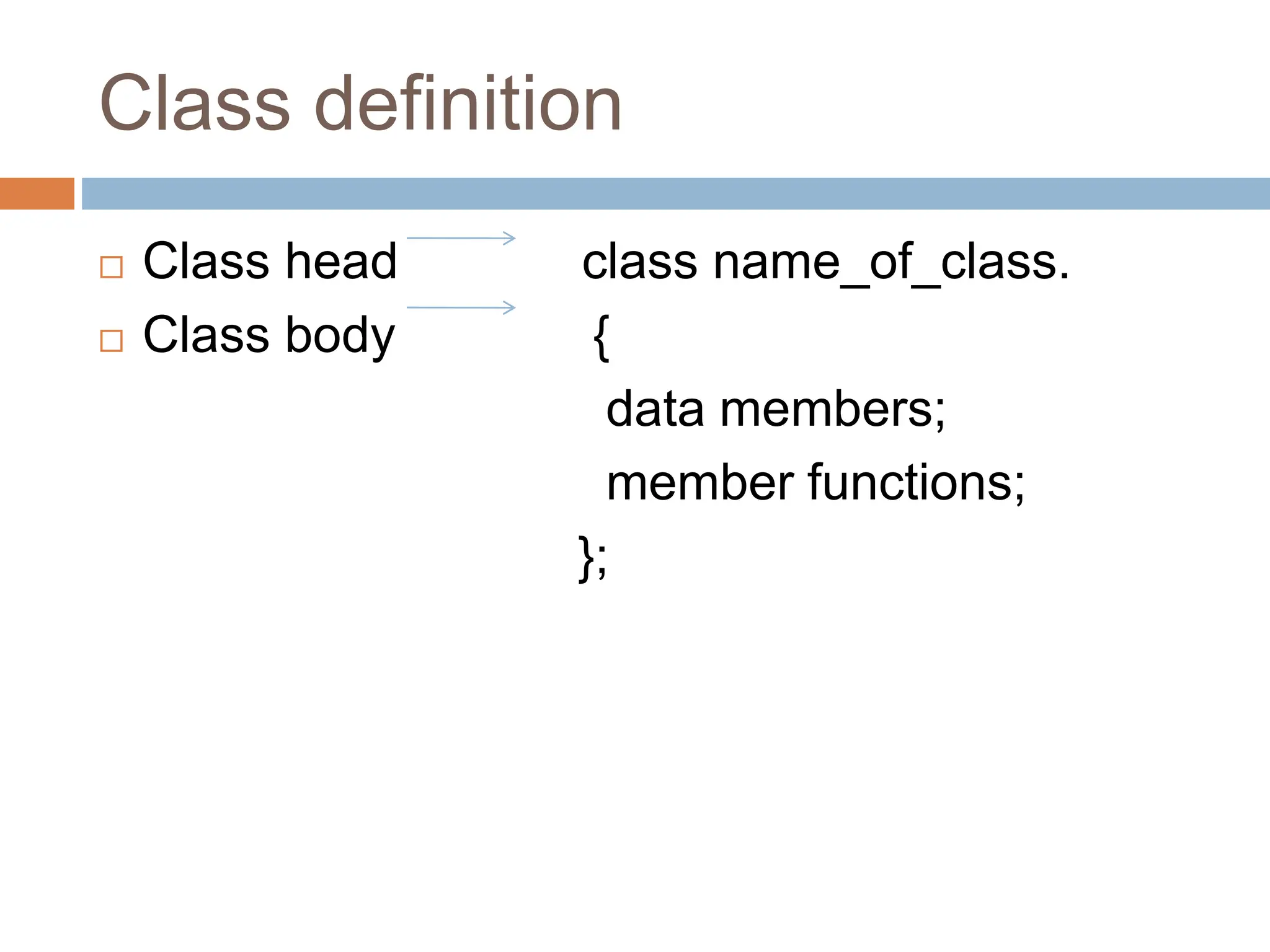
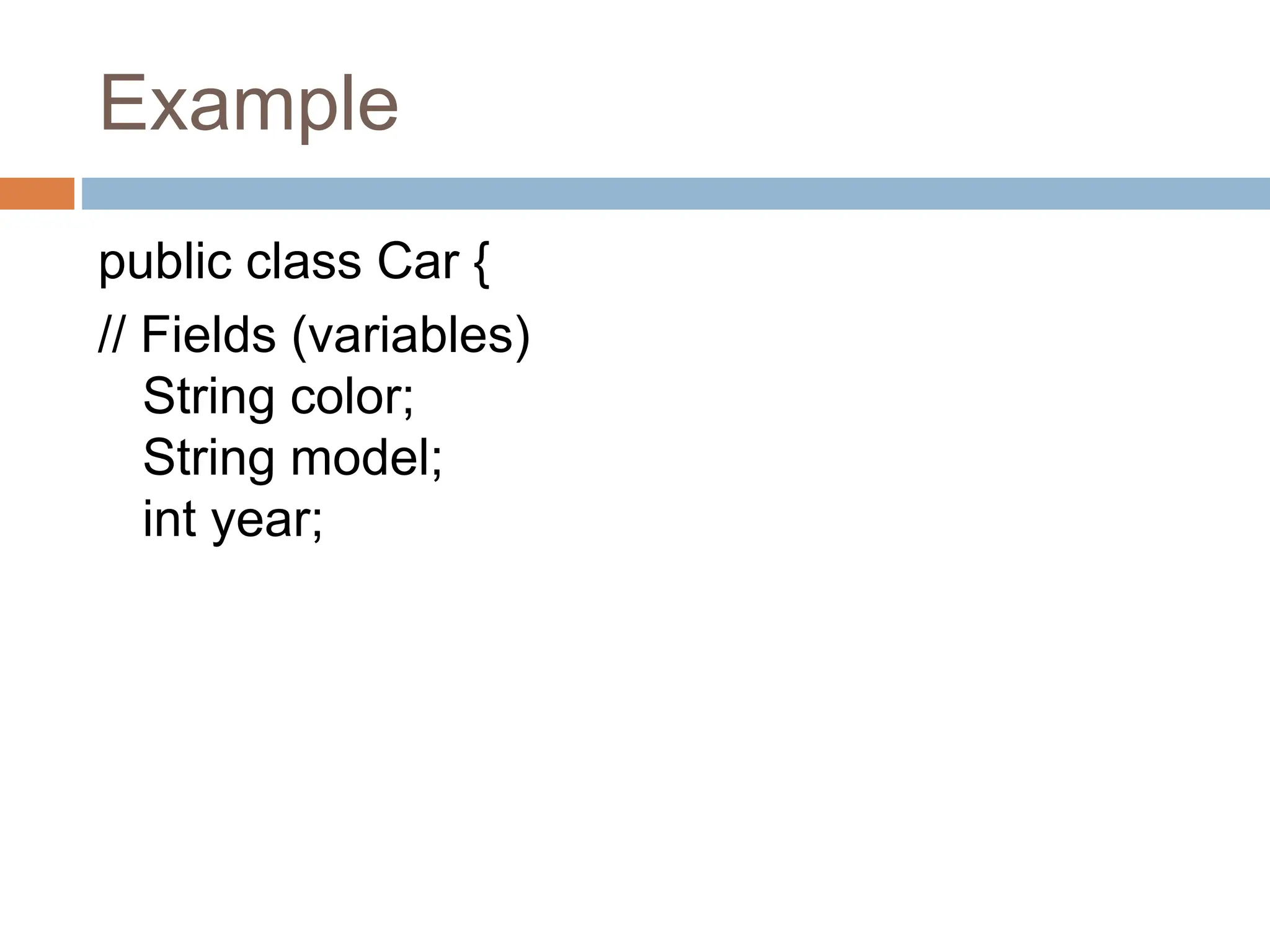
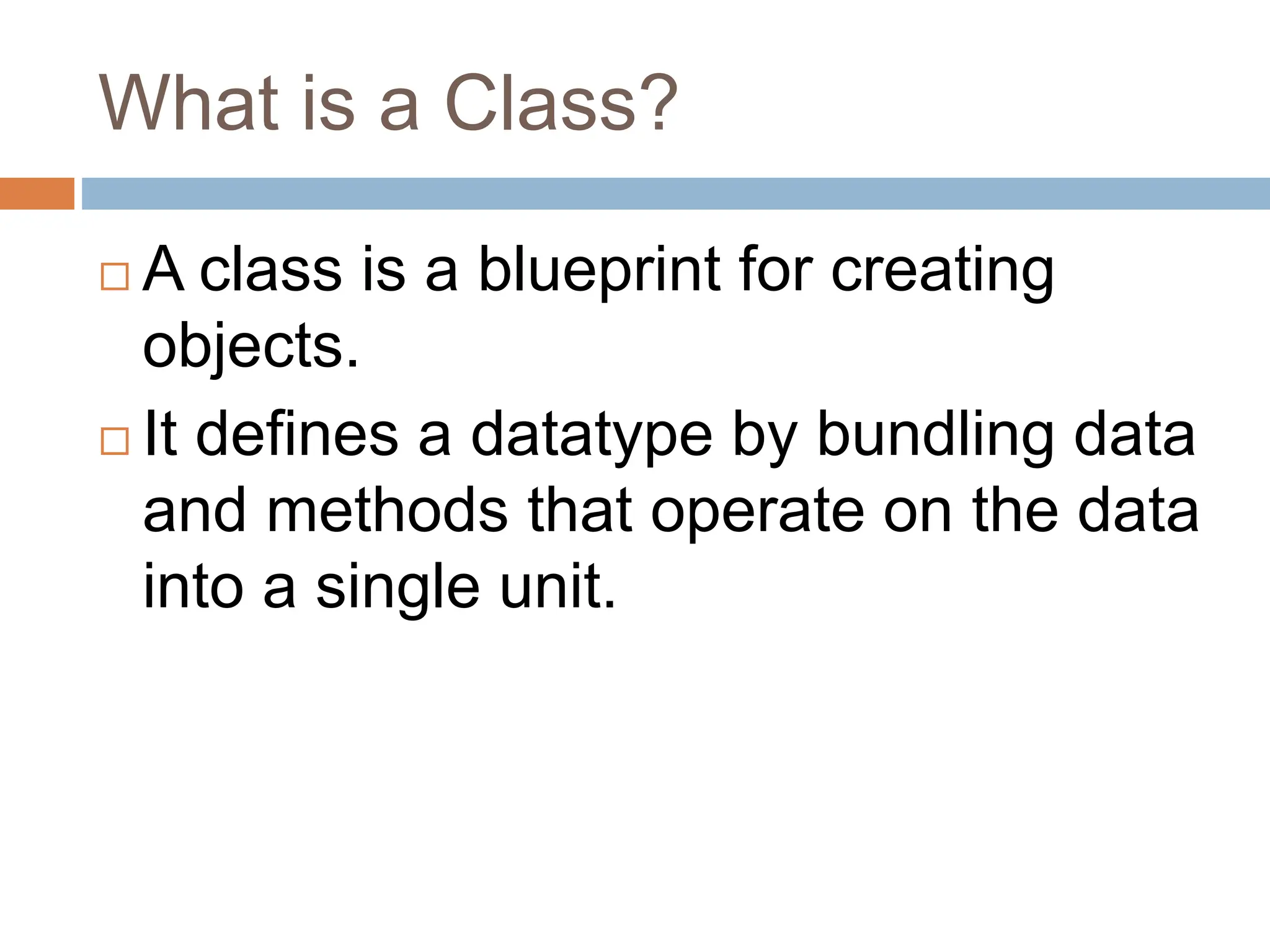
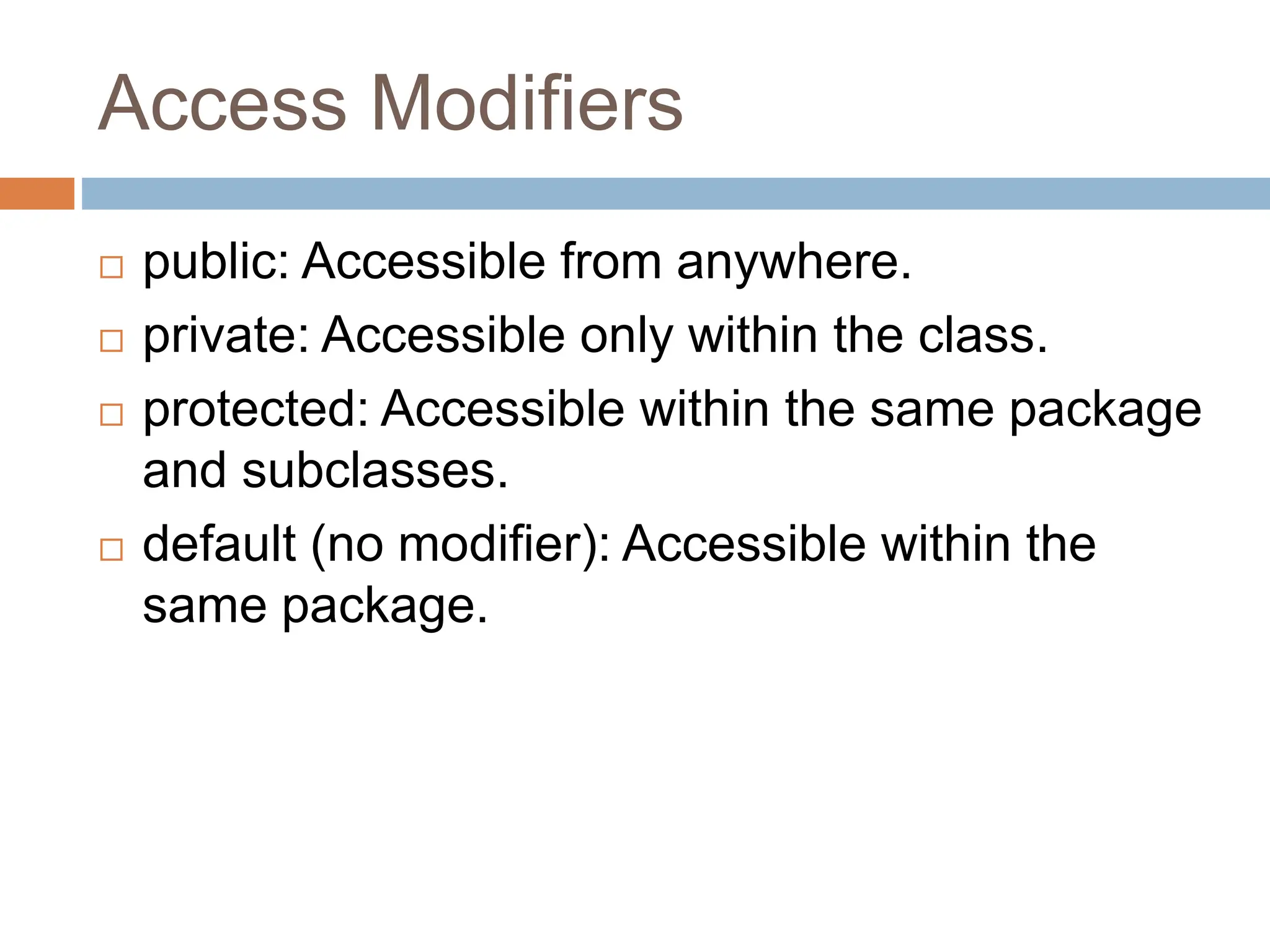
The document provides an introduction to Java's fundamental concepts of classes and objects, highlighting their roles in object-oriented programming. A class serves as a blueprint for creating objects, which are instances with defined state and behavior. Understanding these concepts, along with access modifiers and examples, is essential for effective Java programming.






![Example:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and create an object of the Dog class
Dog myDog = new Dog();
// Set the name field
myDog.name = "Buddy";
// Call the bark method
myDog.bark();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classesandobjectsample-240729023113-4bfcc474/75/CLASSES-AND-OBJECT-SAMPLE-use-for-discussion-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
