The document provides an overview of classes and objects in Java, explaining that Java is an object-oriented, class-based programming language that allows for multi-threading. It defines key concepts such as the distinction between classes (blueprints) and objects (instances), their properties (state, behavior, identity), and how to create classes and objects, along with methods, encapsulation, and command line arguments. Additionally, it illustrates the syntax for creating classes and objects, accessing their members, and handling command line arguments in Java applications.




![Create a Class
To create a class, use the keyword class:
A class defines the state and behavior of the program components known
as objects.
Classes create objects and objects use methods to communicate between
them. Methods are just like functions.
The instance of the class is said to be object. Class variable is said to be
object.
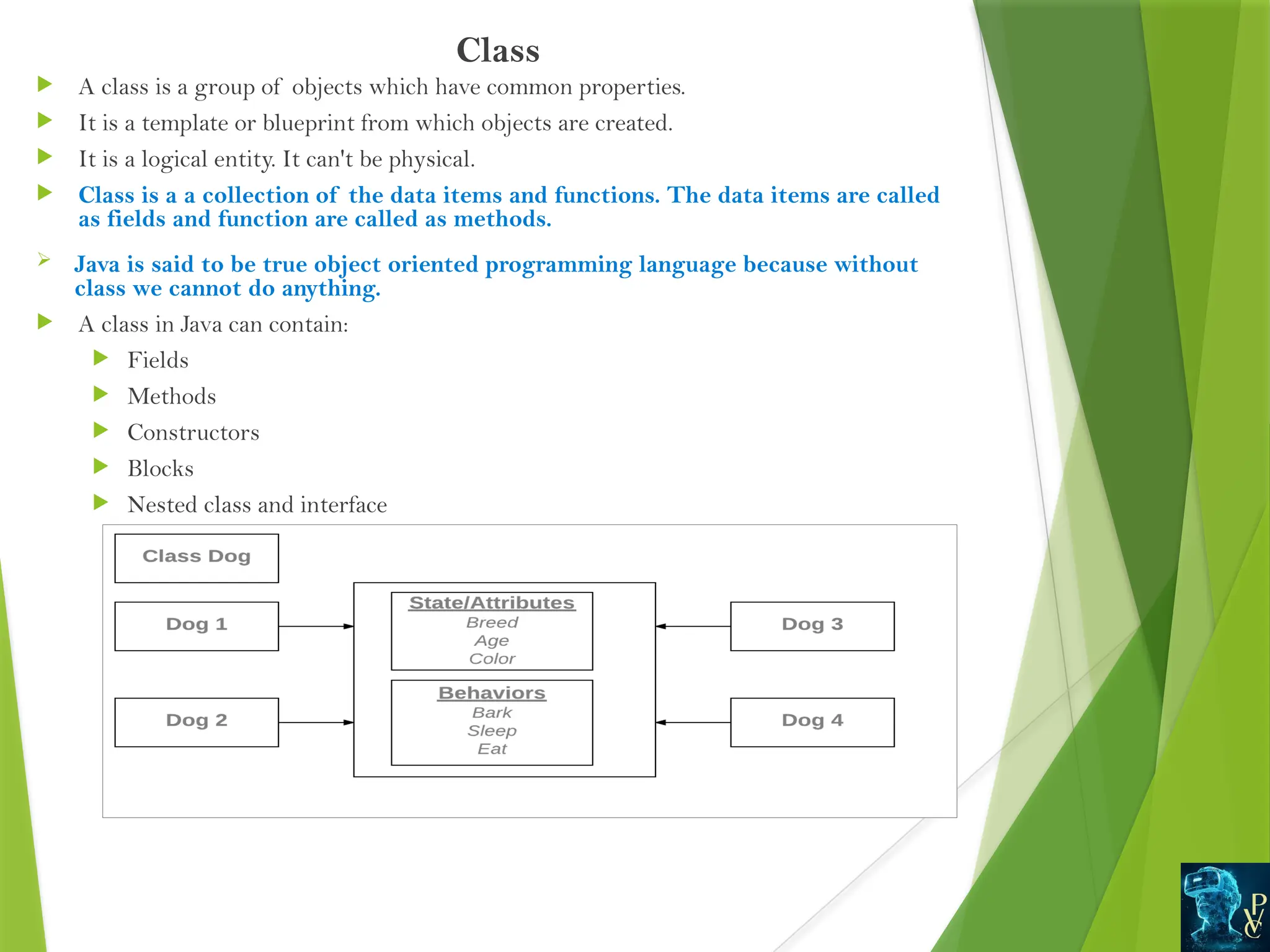
A class is a user-defined data type serves to define properties.
Once a class is defined we can create variables of that type using
declarations.
Example: Create a class named "MyClass" with a variable a:
Class classname [extends superclassname]
{
[variable/field declaration];
[methods declaration];
}
class MyClass
{
int a = 5;
}
Here
Everything inside the brackets is optional.
classname and superclassname are any valid java identifiers.
The keyword extends indicate that the properties of the superclass name are
extended to the classname class.
This concept is known as Inheritance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classes-objectsinjava-201023154255-240908142724-2c8460ee/75/classes-objects-in-oops-java-201023154255-pptx-7-2048.jpg)



![Accessing class Members: every object contains its own set of variables.
We should assign values to these variables in order to use them in our
program.
When we are outside the class we cannot access the instance variables and
methods directly. For this we use dot operator.
objectname.varaiblename = value;
objectname.methodname (parameter list);
Example: tri1.length = 15;
tri2.length = 20;
tri1.getData( 20,30)
public class MyClass {
int a = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass myObj = new MyClass();
System.out.println(myObj.a);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classes-objectsinjava-201023154255-240908142724-2c8460ee/75/classes-objects-in-oops-java-201023154255-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
![Ex: A javaprogramtodemonstrateapplicationofclasses, objectsandmethods.(Pra.Prog. 17)
classtriangle {
intlength,width;
voidgetData(intx, inty)
{
length= x;
width= y;
}
int triarea( )
{
intarea= (length*width)/2;
return(area);
}
}
classtriarea {
publicstatic voidmain (Stringargs[ ])
{
int area1, area2;
triangletri1= newtriangle();
triangletri2= newtriangle();
tri1.length= 20;
tri1.width=30;
area1=( tri1.length*tri1.width)/2;
tri2.getData( 10, 15);
area2=tri2.triarea();
System.out.println( "area1= "+area1);
System.out.println( "area2= "+area2);
}
}
Instance variables declared in a single
line
getData is a method, it does not return any value
so its type is void, we are passing two integer
values and they are assigned to length and width
triarea is another method, it returns a value of
data type int. We are not passing values, so
the parameter list is empty
class with main method
Creating objects
Accessing variables
Accessing Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classes-objectsinjava-201023154255-240908142724-2c8460ee/75/classes-objects-in-oops-java-201023154255-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![Command line Arguments
The java command-line argument is an argument i.e. passed at the time of
running the java program.
A Java application can accept any number of arguments from the command line.
The String array stores all the arguments passed through the command line.
Arguments are always stored as strings and always separated by white-space.
// Example using Commandline arguments
class Cmdargs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Command-Line arguments are");
// loop through all arguments
for(String str: args) {
System.out.println(str);
}
} }
1. To compile the code
javac Cmdargs.java
2. To run the code
java Cmdargs
Now suppose we want to pass some arguments
while running the program,
we can pass the arguments after the class name. For
example,
java Main apple ball cat
output.
Command-Line arguments are
Apple
Ball
Cat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classes-objectsinjava-201023154255-240908142724-2c8460ee/75/classes-objects-in-oops-java-201023154255-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![// Program to check for command line arguments
class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// check if length of args array is greater than 0
if (args.length > 0) {
System.out.println("The command line"+ " arguments are:");
// iterating the args array and printing the command line arguments
for (String s:args)
System.out.println(s);
}
else
System.out.println("No command line "+
"arguments found.");
} }
javac Hello.java
java Hello Lion Dog Cat Elephant
Output:
The Command-Line arguments are
Lion
Dog
Cat
Elephant
javac Hello.java
java Hello
Output
No Command-Line arguments foun](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classes-objectsinjava-201023154255-240908142724-2c8460ee/75/classes-objects-in-oops-java-201023154255-pptx-14-2048.jpg)

