Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Profile
Definition:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where the kidneys gradually lose their function, leading to the buildup of waste products in the body.
Causes:
1. *Diabetes*: High blood sugar levels can damage kidney blood vessels.
2. *Hypertension*: High blood pressure can damage kidney blood vessels.
3. *Glomerulonephritis*: Inflammation of the kidney filters.
4. *Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)*: Genetic disorder causing cysts to form in the kidneys.
5. *Other Causes*: Obstruction, infection, and certain medications.
Symptoms:
1. *Early Stages*: Often asymptomatic.
2. *Advanced Stages*: Fatigue, swelling, changes in urination, and electrolyte imbalances.
Stages:
1. *Stage 1*: Kidney damage with normal or increased function (GFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m²).
2. *Stage 2*: Kidney damage with mildly decreased function (GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73m²).
3. *Stage 3*: Moderately decreased function (GFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73m²).
4. *Stage 4*: Severely decreased function (GFR 15-29 mL/min/1.73m²).
5.
Complications:
1. *Cardiovascular Disease*: Increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. *Anemia*: Reduced red blood cell production.
3. *Bone Disease*: Mineral and bone disorders.
4. *Electrolyte Imbalances*: Abnormal levels of potassium, sodium, and other electrolytes.
Management:
1. *Blood Pressure Control*: ACE inhibitors or ARBs to slow disease progression.
2. *Blood Sugar Control*: For patients with diabetes.
3. *Dietary Modifications*: Low-protein, low-sodium, and low-phosphorus diet.
4. *Medications*: To manage complications like anemia and bone disease.
5. *Dialysis or Transplantation*: For end-stage renal disease.
Prevention:
1. *Manage Underlying Conditions*: Control blood pressure and blood sugar.
2. *Healthy Lifestyle*: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.
3. *Regular Check-ups*: Monitor kidney function, especially for high-risk individuals.
Early detection and management can slow CKD progression and improve quality of life.
Management of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Lifestyle Modifications
1. *Dietary Changes*: Low-protein, low-sodium, and low-phosphorus diet to reduce strain on the kidneys.
2. *Fluid Management*: Monitoring and managing fluid intake to prevent overload.
3. *Exercise*: Regular physical activity to maintain overall health and manage blood pressure.
4. *Smoking Cessation*: Quitting smoking to reduce cardiovascular risk.
5. *Weight Management*: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on the kidneys.
Medications
1. *Blood Pressure Control*: ACE inhibitors or ARBs to slow disease progression.
2. *Blood Sugar Control*: For patients with diabetes, medications like metformin or insulin.
3. *Anemia Management*: Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) and iron supplements.
4. *Bone Disease Management*: Phosphate binders, vitamin D analogs, and calcimimetics.
5. *Electrolyte Management*: Potassium binders or other medications to manage electrolyte imbalances.
KIDNEYRL
![CASE PRESENTATION ON
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
PRESETNED BY; D.DILIP
PHARM.D 4th
year [214T1T0016]
PRESENTED TO ;
Dr. SAI CHARITHA madam PHARM.D
Asst.PROFFESSOR
SRI LAKSHMI VENKATESWARA INSTITUTE OF
PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/75/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-1-2048.jpg)

![• HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS ;-
H/o High blood pressure
H/o Itching
H/o Loss of appetite
• PAST MEDICAL HISTORY ;-
HYPERTENSION
KIDNEY STONES
• PAST MEDICATION HISTORY ;-
-NOT KNOWN-
• FAMILY HISTORY ;-
His mother has chronic kidney failure
• PERSONAL HISTORY ;-
Allergy ;- yes Drug abuse ;- NSAID’s
Smoking ;- yes [since 10 years] Substance abuse ;- No
. Alcohol ;- yes[since 20 years]
• HABITS ;-
Food ;- Mixed Appetite ;- Loss of appetite
Sleep ;- Abnormal Bowel ;- Irregular
Bladder ;- Abnormal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-3-320.jpg)
![• GENERAL EXAMINATION ;-
DAY TEMP PR RR BP
1 99.6℉ 82 bpm 25 cpm 160/90 mm Hg
2 98.5 ℉ 80 bpm 23 cpm 150/87 mm Hg
3 97. 4 ℉ 74 bpm 20 cpm 135/82 mm Hg
4 98.6 ℉ 72 bpm 20 cpm 130/80 mm Hg
NORMAL TEMPERATURE [ in ] :- 98.6
℉ ℉
NORMAL PULSE RATE :- 60-100 bpm
NORMAL RESPIRATORY RATE :- 12-20cpm
NORAML BLOOD PRESSURE :- < 120/80mm Hg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-4-320.jpg)
![• SYSTEMS EXAMINATION ;-
CVS ;- Abnormal [Hypertension]
CNS ;- Abnormal [Confusion]
RS ;- Abnormal [ Dyspnea because fluid .
. accumulation in lungs ]
GU/GI ;- Abnormal [constipation , vomiting , loss
. decrease urine output, decrease GFR]
EENT ;- Abnormal [dry eyes]
DERM ;- Abnormal [ itchy skin]
EXTREMITIES[UL/LL] ;- Abnormal
OTHERS :- Anemia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-5-320.jpg)
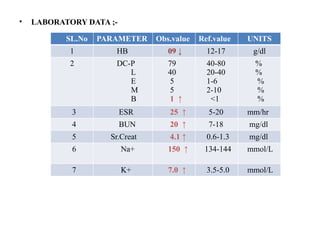
![SL.No PARAMETER Obs.Value Ref.Value UNITS
8 Cl- 109 ↑ 96-108 mmol/L
9 Uric acid 08 ↑ 2.6-7.2 mmol/L
URINALYSIS;-
10 PROTEIN ;- Increase levels of protein in urine [PROTEINURIA]
11 BLOOD ;- Presence of blood in urine [HEMATURIA]
12 pH ;- Acidic
> 24-Hr URINE COLLECTION;-
13 ↓ the amount of
creatinine excretion
from the body
0.5↓ 0.8-1.3 mg/dL
IMAGING STUDIES :-
14 CT SCAN ;- 8cm of kidney length [10-12 cm]
STAGE 3A OF CKD*
{GFR RATE ;- 45-59 mg/mmoL}
[Moderate to severe cause to kidney]
*CKD=CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-7-320.jpg)



![ SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS ;-
• Fatigue and Weakness: Decreased kidney function can lead to anemia, which often causes
fatigue and weakness.
• Swelling (Edema): Fluid retention can cause swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or around the eyes.
• Changes in Urination: You might notice changes in the frequency or amount of urine, or you
might experience difficulty urinating.
• Urine with Blood or Protein: Blood or protein in the urine can be a sign of kidney damage.
[Hematuria or Proteinuria]
• Persistent Itching: Accumulation of waste products in the blood can cause itching.
• Nausea and Vomiting: Toxin buildup can lead to nausea and vomiting.
• Loss of Appetite: A decrease in appetite is common.
• Bad Breath: Uremia (a buildup of waste products) can cause bad breath.
• Shortness of Breath: Fluid buildup in the lungs or anemia can cause difficulty breathing.
• High Blood Pressure: CKD can contribute to or worsen high blood pressure.
• Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating: Toxin buildup can affect brain function.
• Metabolic acidosis ; Due to increase production of acids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-12-320.jpg)
![ PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ;-
ETIOLOGY
Renal vasoconstriction Arteriolar ↓ functions damaged tisue
constriction of nephrons cells and RBC’s
↓ GFR
HTN failure of excretion disturbance of
Na+ and water of H2 ions Na+and K+
retension ↑circulatory exchange
overload ↑production of
EDEMA and Na + acids ↑ extracellular
retention K+ overload
metabolic acidosis [HYPERKALEMIA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-13-320.jpg)





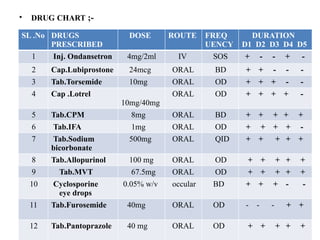
![• DRUG INFORMATION ;-
• Inj.Ondansetron ;- {BRAND NAME :- ZOFRAN}
Dose ;- 4mg/2ml
Category ;- 5HT3 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST
MOA ;- Inhibition of seratonin receptor to reduce the vomiting sensation by
inhibit chemoreceptor trigger zone.
ADR’s;- Headache,Drowsiness,Constipation
Uses ;- To treat the Nausesa , Vomiting
• Cap.Lubiprostone ;- {BRAND NAME :-AMITIZA}
Dose ;- 24mcg
Category ;- LAXATIVE[CHLORIDE CHANNEL
ACTIVATOR]
MOA ;- Lubiprostone works by activating chloride channels in the intestinal
epithelium, leading to increased fluid secretion into the lumen of the intestines.
This helps soften stools and promotes bowel movements
ADR’s ;- Nausea,Diarrhea,Abdominal pain,Headache,Vomiting
Uses ;- Mainly used in the treatment of Constipation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-19-320.jpg)

![• Cap. Lotrel {AMLODIPINE+BENZAPRIL} ;-
Dose ;- 10mg/40mg [Amlodepine/Benazepril]
Category ;- CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKER/ACE INHIBITOR
• MOA ;-Amlodipine:
• Action: Amlodipine works by blocking calcium channels in the smooth muscle
cells of the blood vessels. This prevents calcium from entering these cells, leading
to relaxation of the vascular smooth muscle. As a result, there is vasodilation
(widening) of the blood vessels, which reduces blood pressure and decreases the
workload on the heart.
• MOA ;- Benzapril :-
Benazepril is a prodrug, meaning it's converted into its active form, benazeprilat, in
the liver.
Benazeprilat inhibits the enzyme ACE, which is responsible for converting
angiotensin I into angiotensin II.
ADRs ;- cough,.dizziness,headache, vomiting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-21-320.jpg)


![• SOAP NOTES;-
• SUBJECTIVE ;- A 65 years old male patient admitted in male medical ward with vomiting,
edema, constipation , shortness of breath.
• OBJECTIVE ;- The abnormal lab findings are –
1
PARAMETER LAB
FINDING
PARAMETER LAB
FINDING
URINALYSIS
HB 09 Na+ 150 PROTEIN levels are
increase in urine
DC-B 01 K+ 7.0
ESR 23 Cl 109 Presence of BLOOD
in urine
BUN 20 Uric Acid 08
Sr.Creat 4.1 Creatinine 0.5 Urine pH is
decreased[acidic]
IMAGING STUDIES :- CT SCAN ;- 8cm of kidney length [10-12 cm]
STAGE 3A OF CKD*
{GFR RATE ;- 45-59 mL/min}
[Moderate to severe cause to kidney]
CKD*= CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
STAGE 3 of CKD = 30-59 mL/min](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-24-320.jpg)

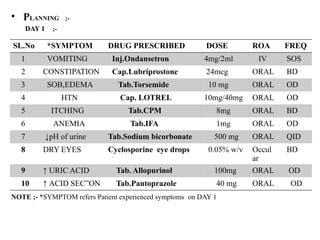

![• PATIENT COUNSELLING ;-
[TO PATIENT REPRESENTATIVE because patient is not able to conselled]
- Maintain regular diet
- Avoid sugar containing foods
- Followup medicines regularly
- Restrict electrolyte containing foods like ORS
- Sessation alcohol and smoking intake
- Make low protein diet
- Maintain physical exercise
• REFERANCE ;-
CLINICAL PHARMACY andTHERAPEUTICS TEXTBOOK
[ROGER WALKER and CATE WHITTLSEA] Pg.No ;- 272
PHARMACOTHERAPY [A Pathophysiologic Approch] Pg.No ;-765](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dilipsckdppt2-250905014241-3052d824/85/CHRONIC-KIDNEY-DISEASE-CASE-PRESENTATION-28-320.jpg)
