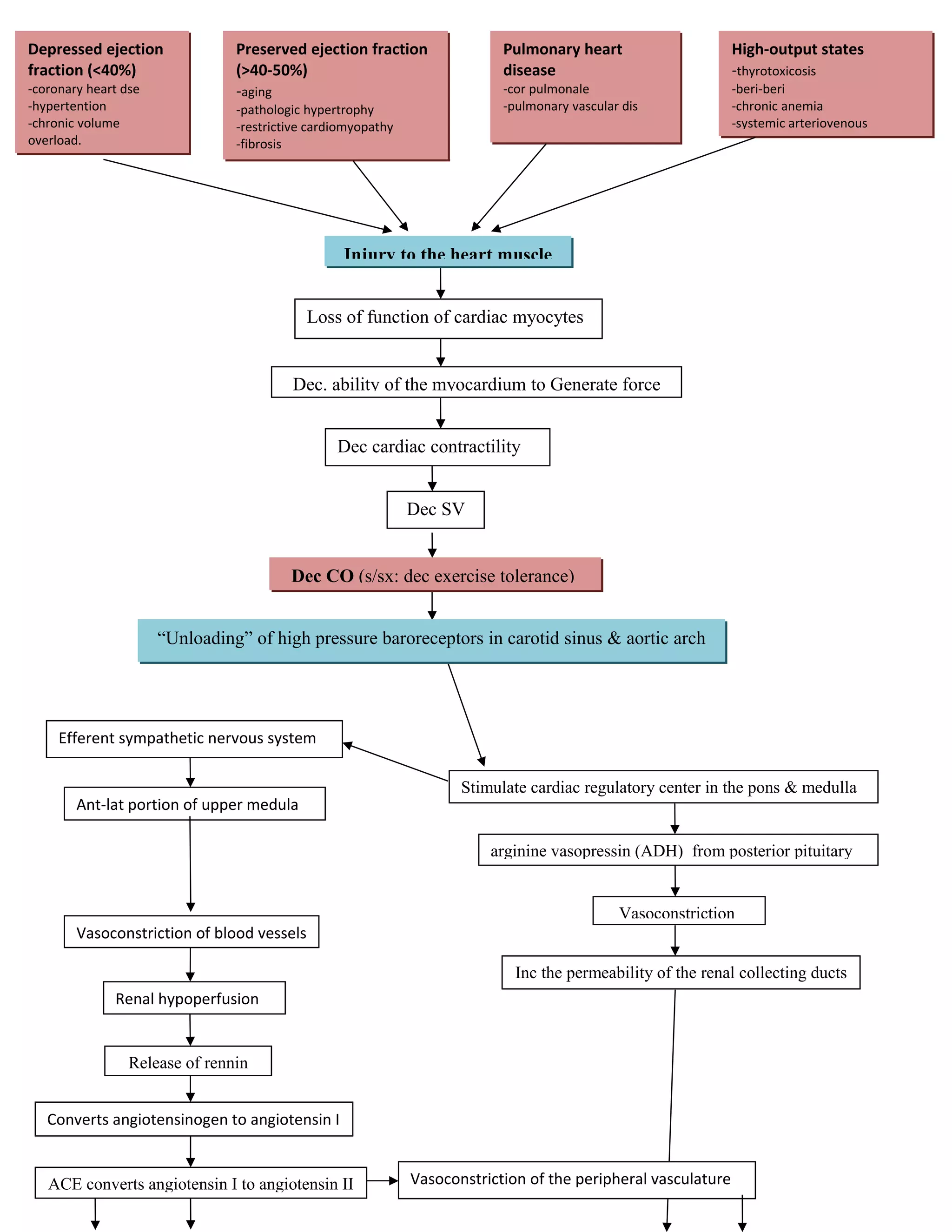
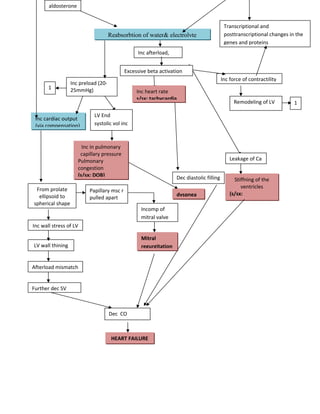
The document discusses the pathophysiology of heart failure, including causes such as coronary heart disease, hypertension, and pulmonary heart disease. It describes how injury to the heart muscle leads to a loss of cardiac myocyte function and decreased contractility, stroke volume, and cardiac output. As a compensatory response, the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system are activated to increase preload and afterload. Over time, this leads to left ventricular remodeling and further worsening of cardiac function, resulting in the symptoms of heart failure.