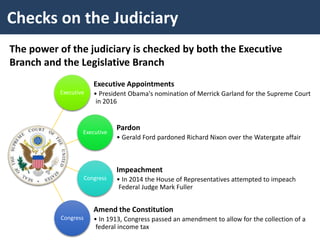
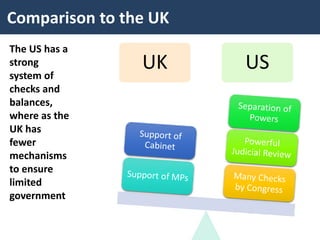
The document discusses checks and balances in the US government. It outlines the checks that each branch of government (Congress, the presidency, and the judiciary) has on the others, such as congressional oversight of the presidency and judicial review. Potential threats to checks and balances are also examined, like executive orders and signing statements. Finally, it notes that the US has a stronger system of checks and balances than the UK to limit government power.