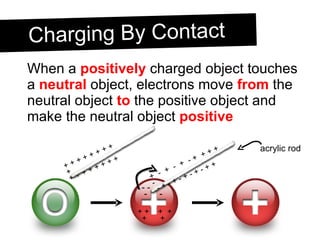
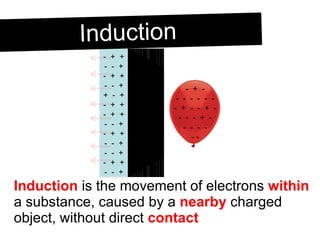
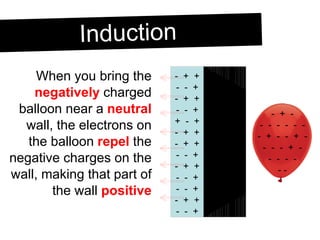
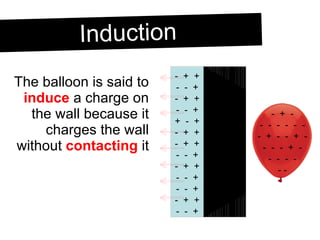
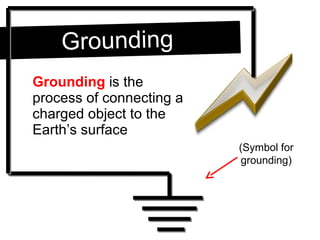
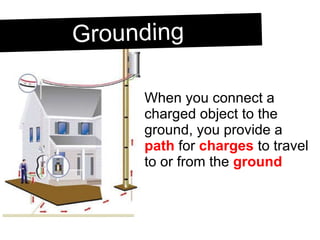
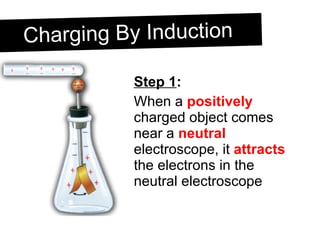
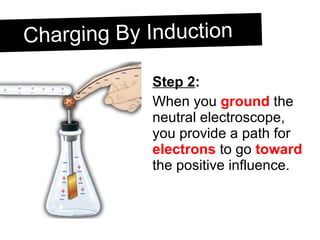
An electroscope is a device used to test if an object is charged. It consists of a metal ball, rod and leaves. When neutral, the leaves stay together, but when charged, they repel each other. Charging can occur through contact or induction. Induction involves charging an object without direct contact by using a nearby charged object to move its electrons. Grounding provides a path for charges to travel to or from the ground.