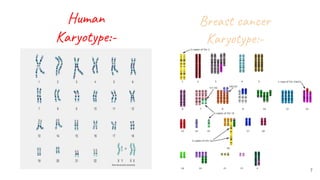
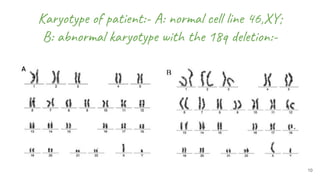
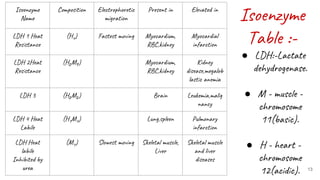
This document discusses techniques for characterizing cell lines, including karyotyping and isozyme analysis. Karyotyping allows visualization of chromosome number and structure to identify genetic abnormalities. It provides information on species identification, genome stability, and numerical chromosome abnormalities. Isozyme analysis examines differences in enzyme structure and mobility between species using electrophoretic banding patterns. This can determine species identity and detect contamination. Common isozymes analyzed include LDH, MD, G6PD and NP. Both techniques are used to accurately characterize cell lines.