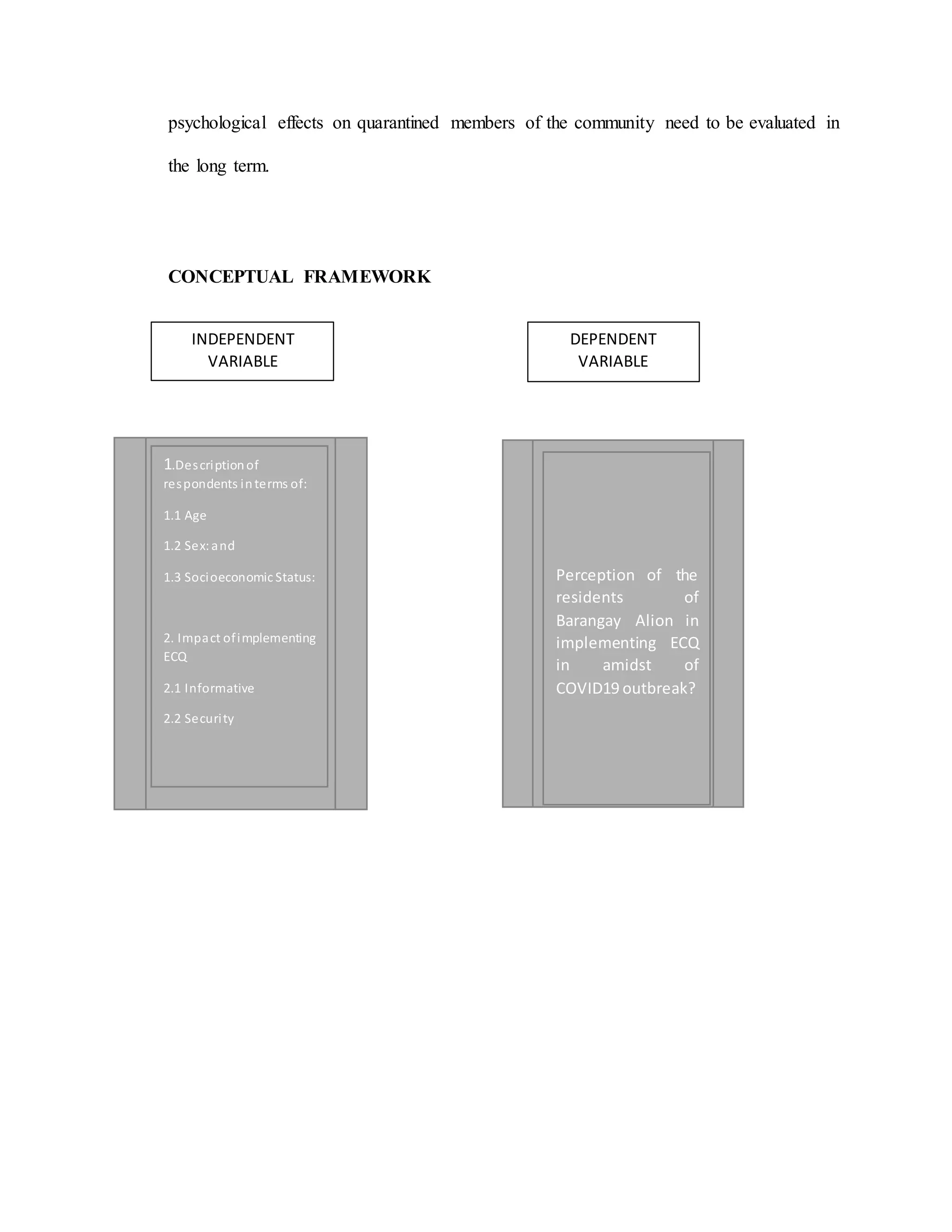
The document discusses the theoretical framework for understanding the impact of implementing Enhanced Community Quarantine (ECQ) in preventing the spread of COVID-19 in Alion, Mariveles. It reviews relevant theories and literature on quarantine and pandemics. Studies show that quarantine can effectively reduce transmission by isolating cases, but it also has economic and psychological costs. The conceptual framework identifies independent variables like age, sex, and socioeconomic status, and dependent variables like perception of the quarantine's informativeness and security. The hypothesis is that these factors may influence perceptions of the quarantine's effectiveness.