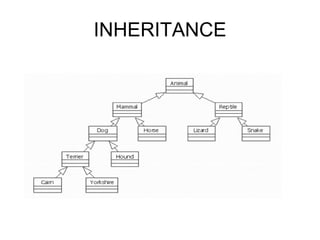
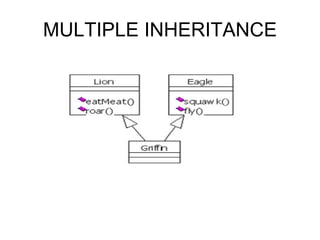
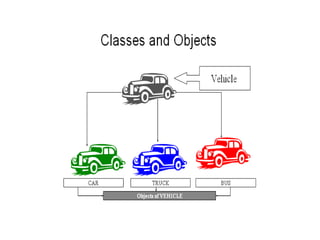
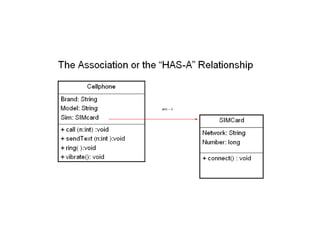
Object-oriented programming uses objects that contain data and methods to design applications. Key concepts include information hiding, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and modularity. Many modern programming languages now support OOP. Objects are instances of classes that define their characteristics and behaviors. Subclasses inherit attributes and behaviors from parent classes and can introduce their own. Polymorphism allows methods to behave differently depending on an object's type.