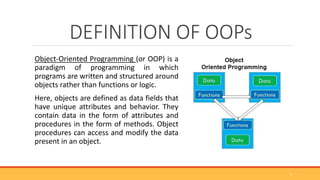
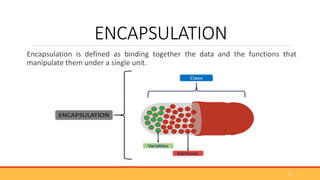
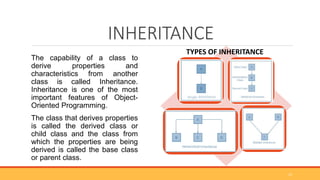
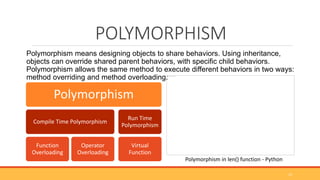
This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP). It defines OOP as a programming paradigm centered around objects rather than functions. The key building blocks are classes, which provide blueprints for objects, and objects, which are instances of classes. Classes contain attributes to store data and methods to define behaviors. The four main principles of OOP are encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, and polymorphism. Popular OOP languages include Java, C++, Python, and C#. OOP offers benefits like reusability, easier debugging, and security through encapsulation.