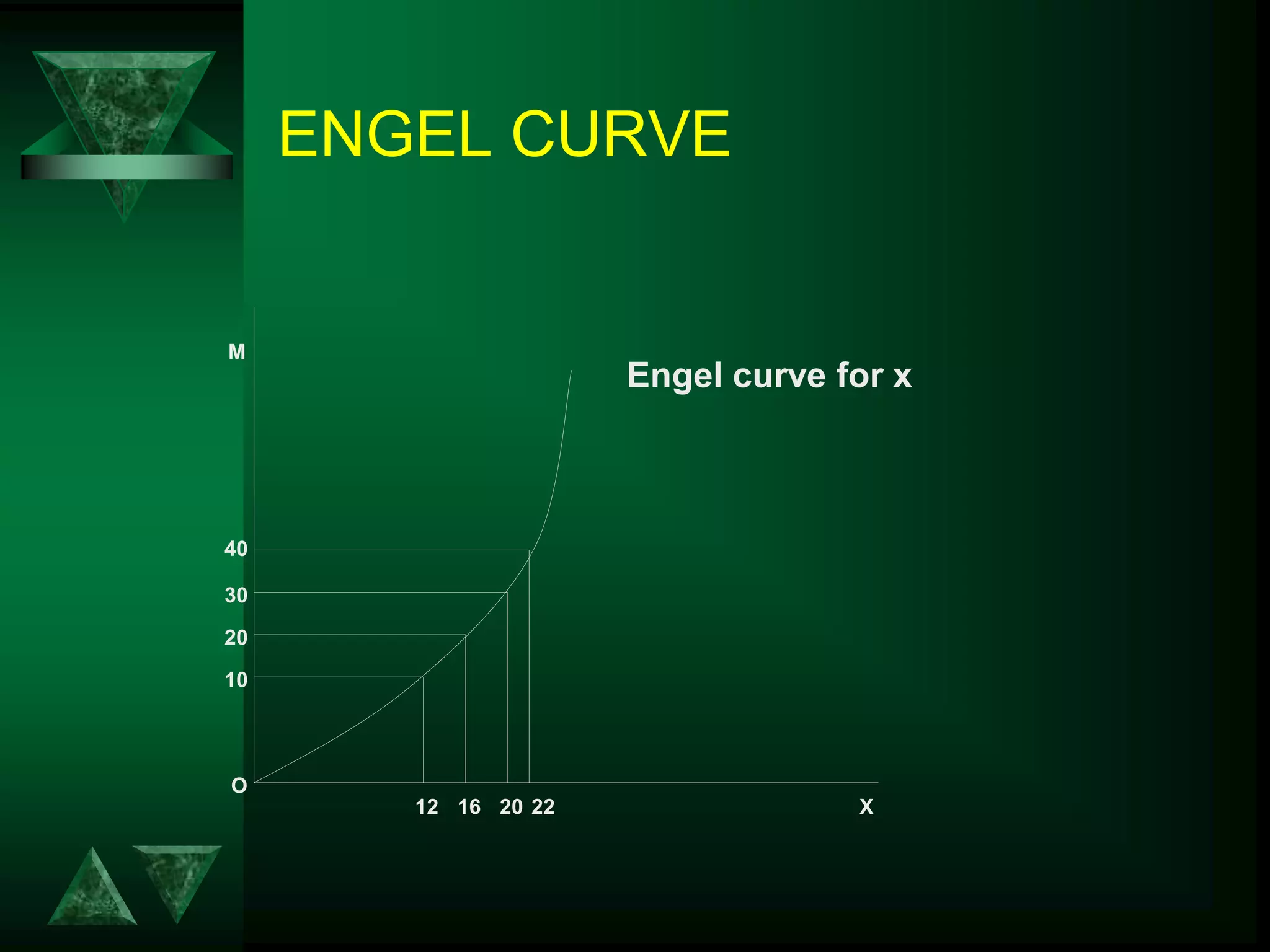
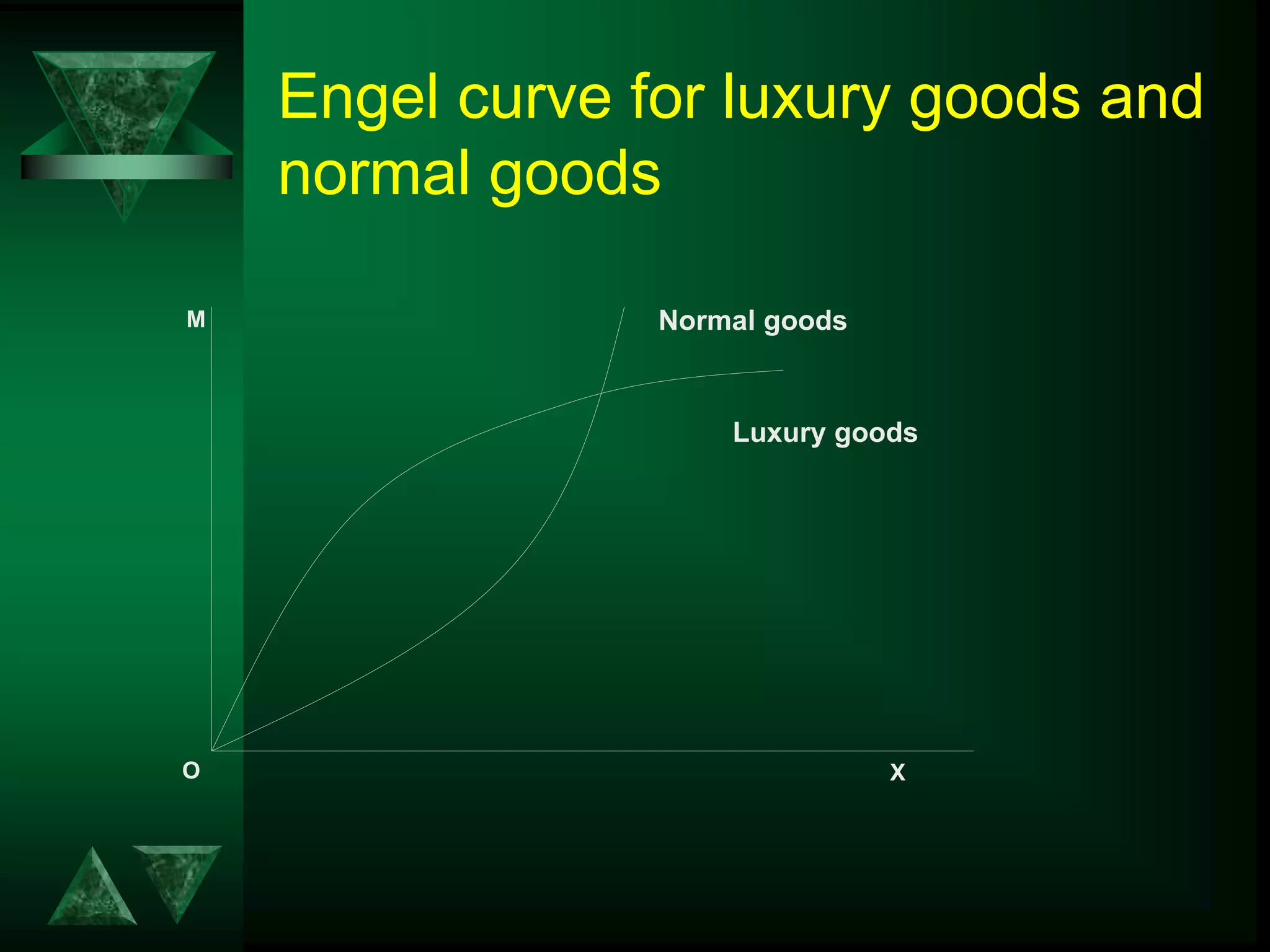
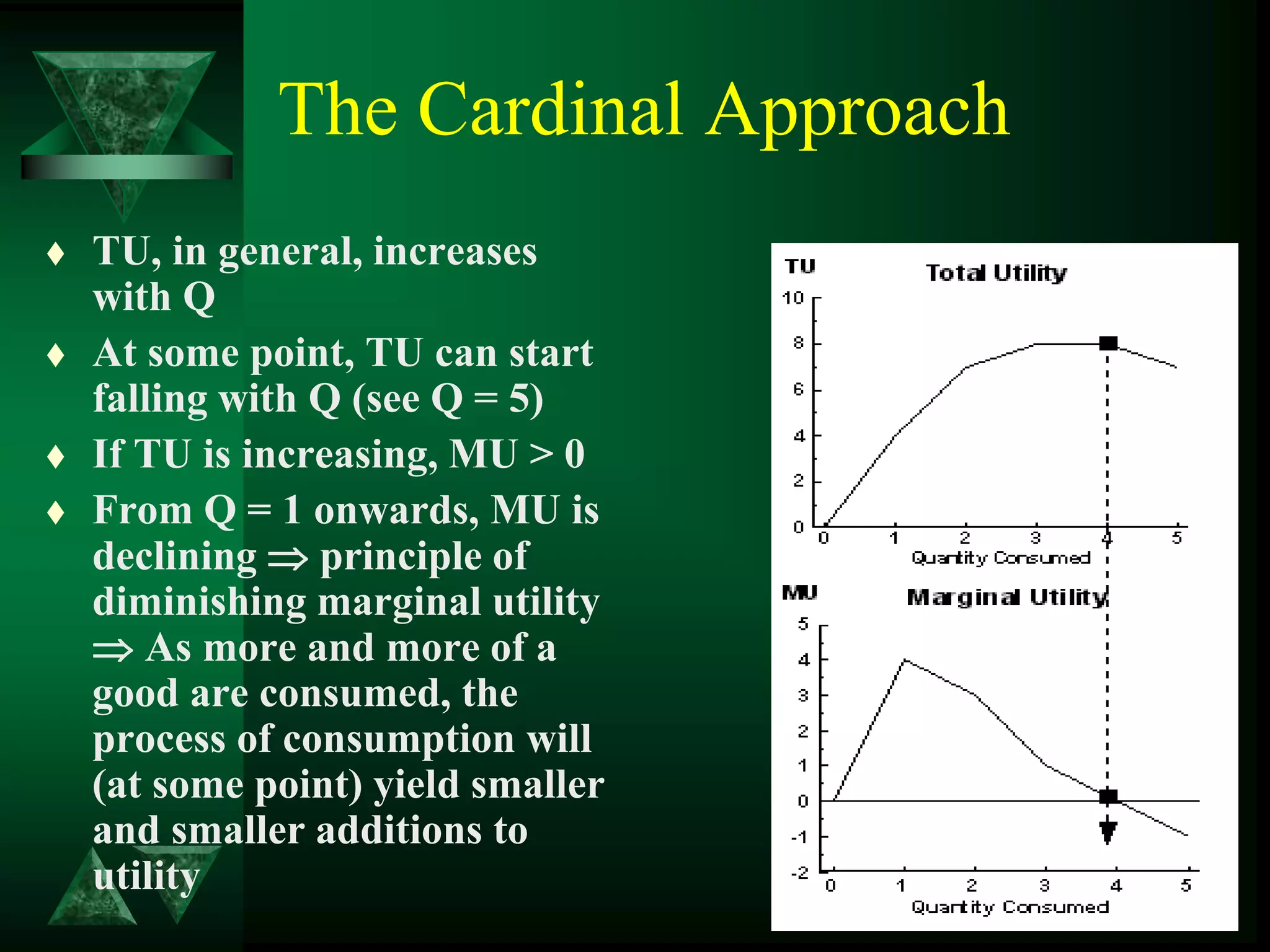
The document discusses theories of consumer behavior, including:
- Consumers attempt to maximize utility given budget constraints by allocating income between goods.
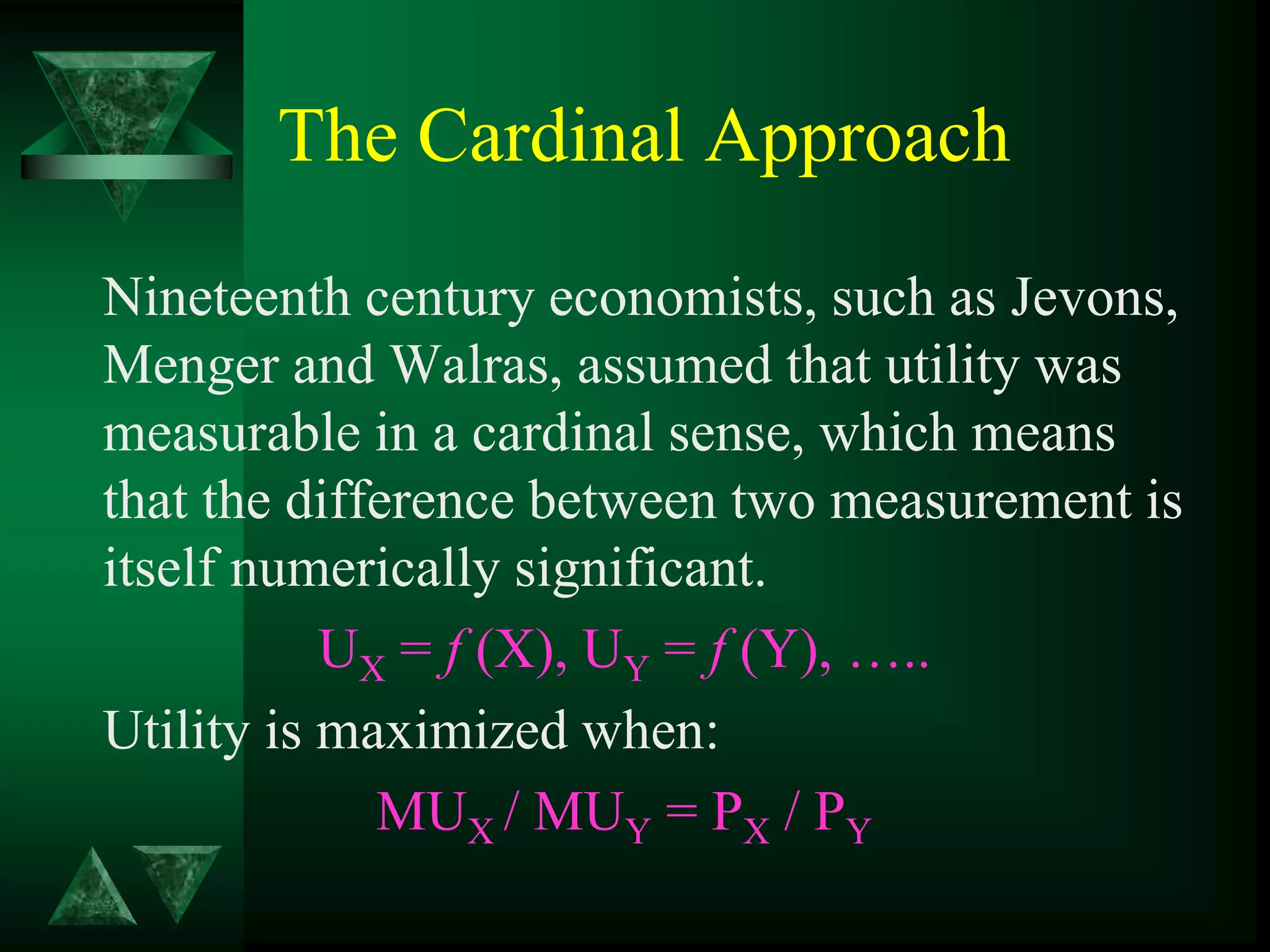
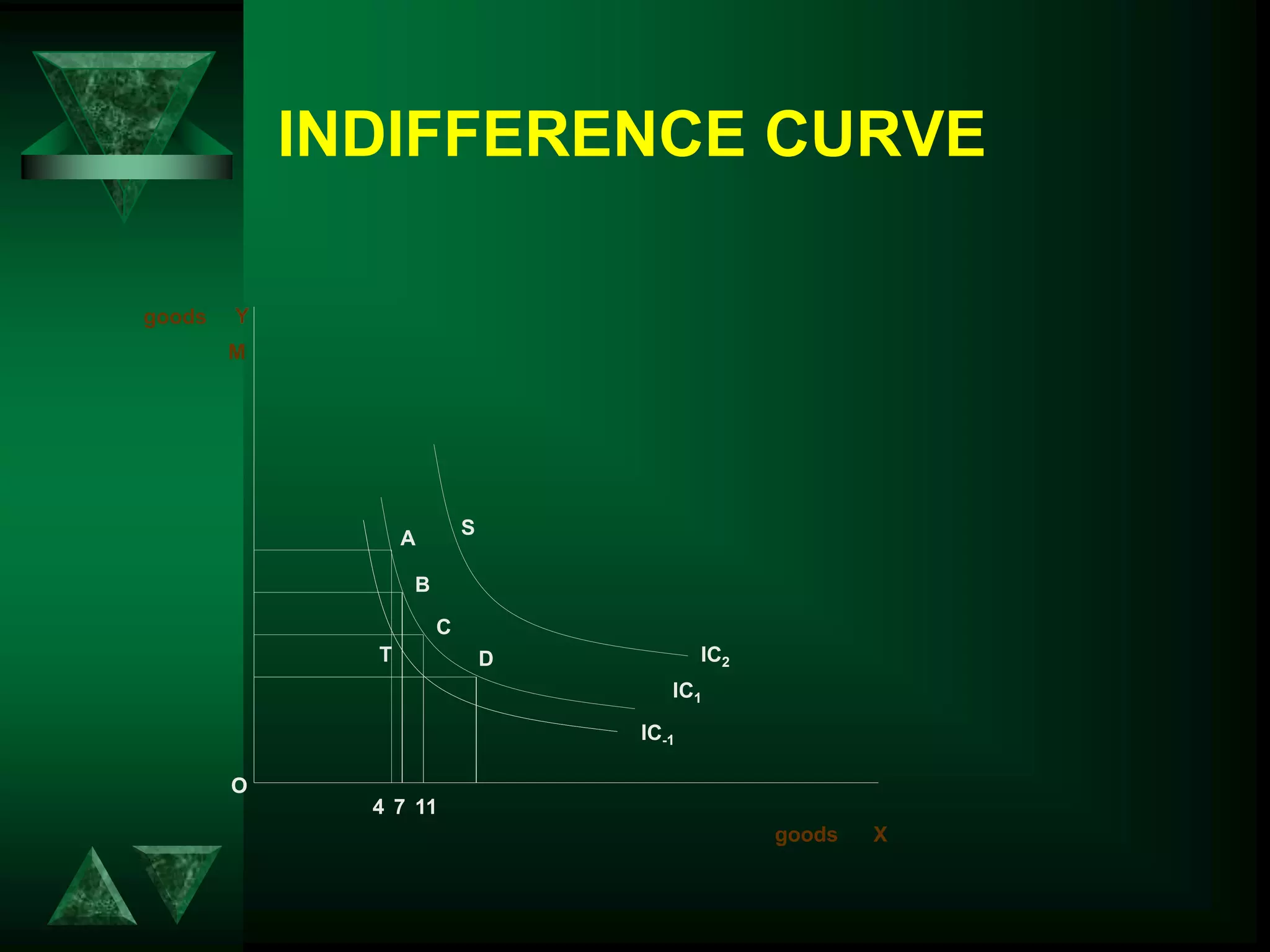
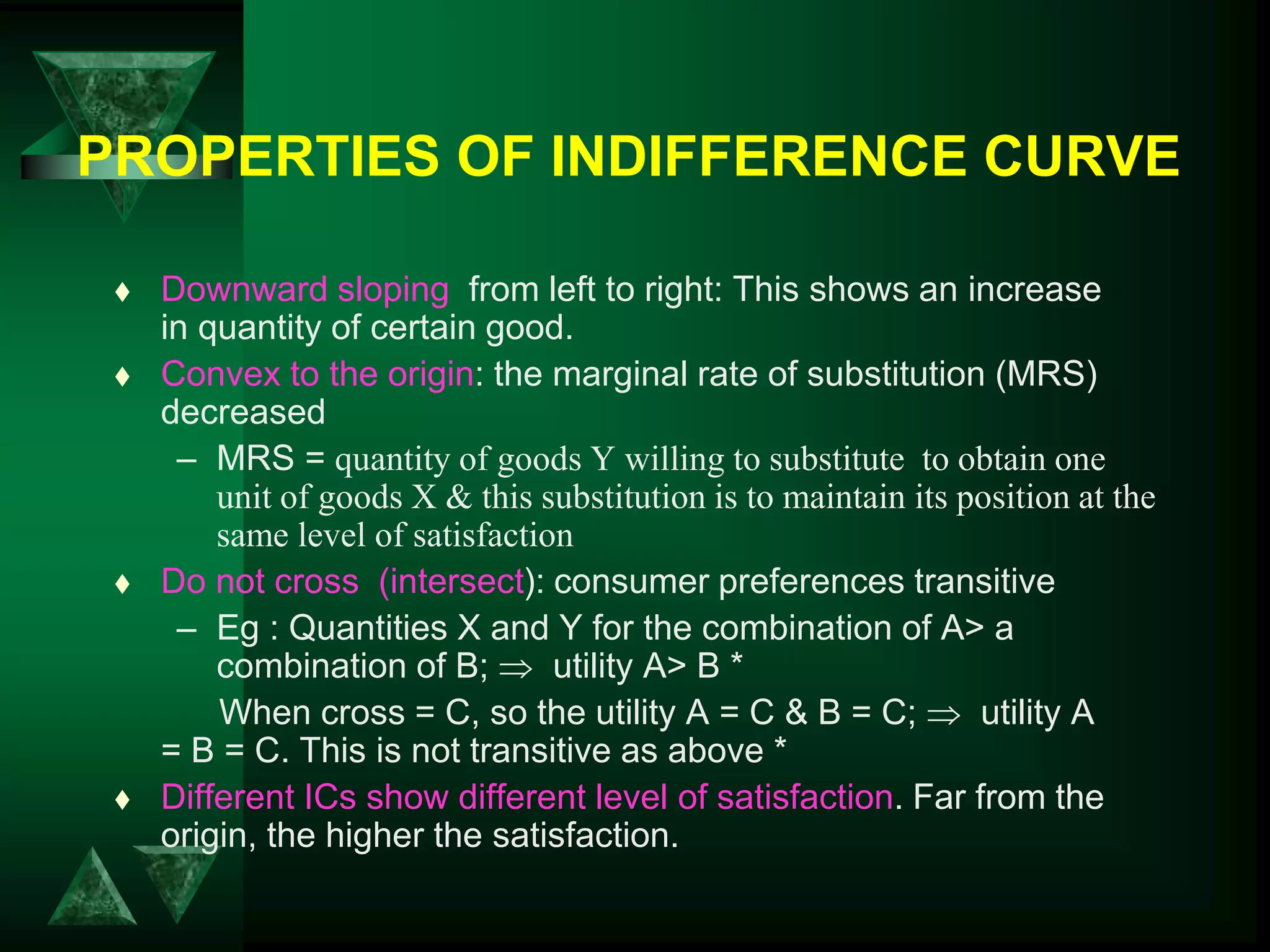
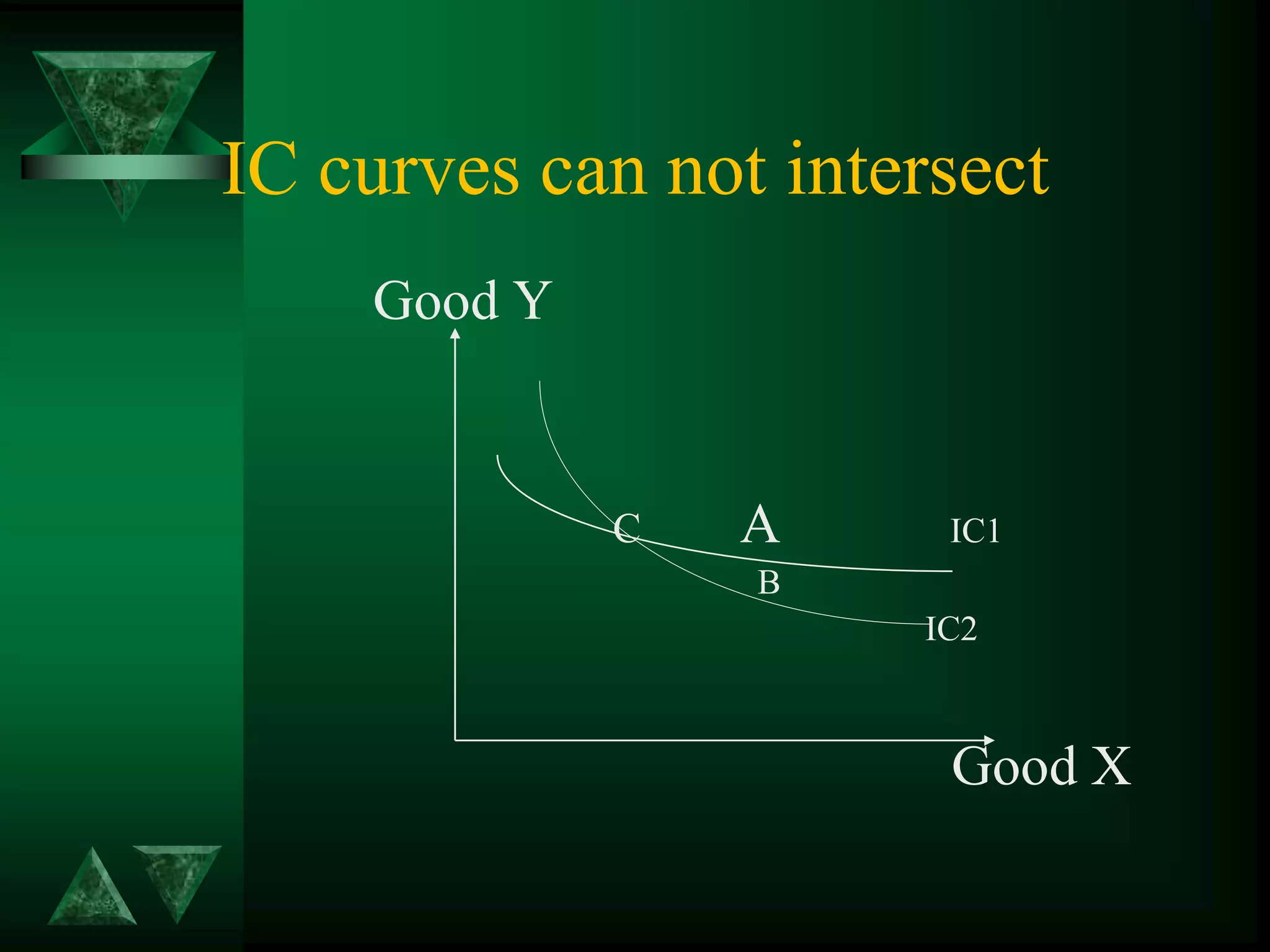
- Utility can be measured cardinally based on total and marginal utility, or ordinally using indifference curves.
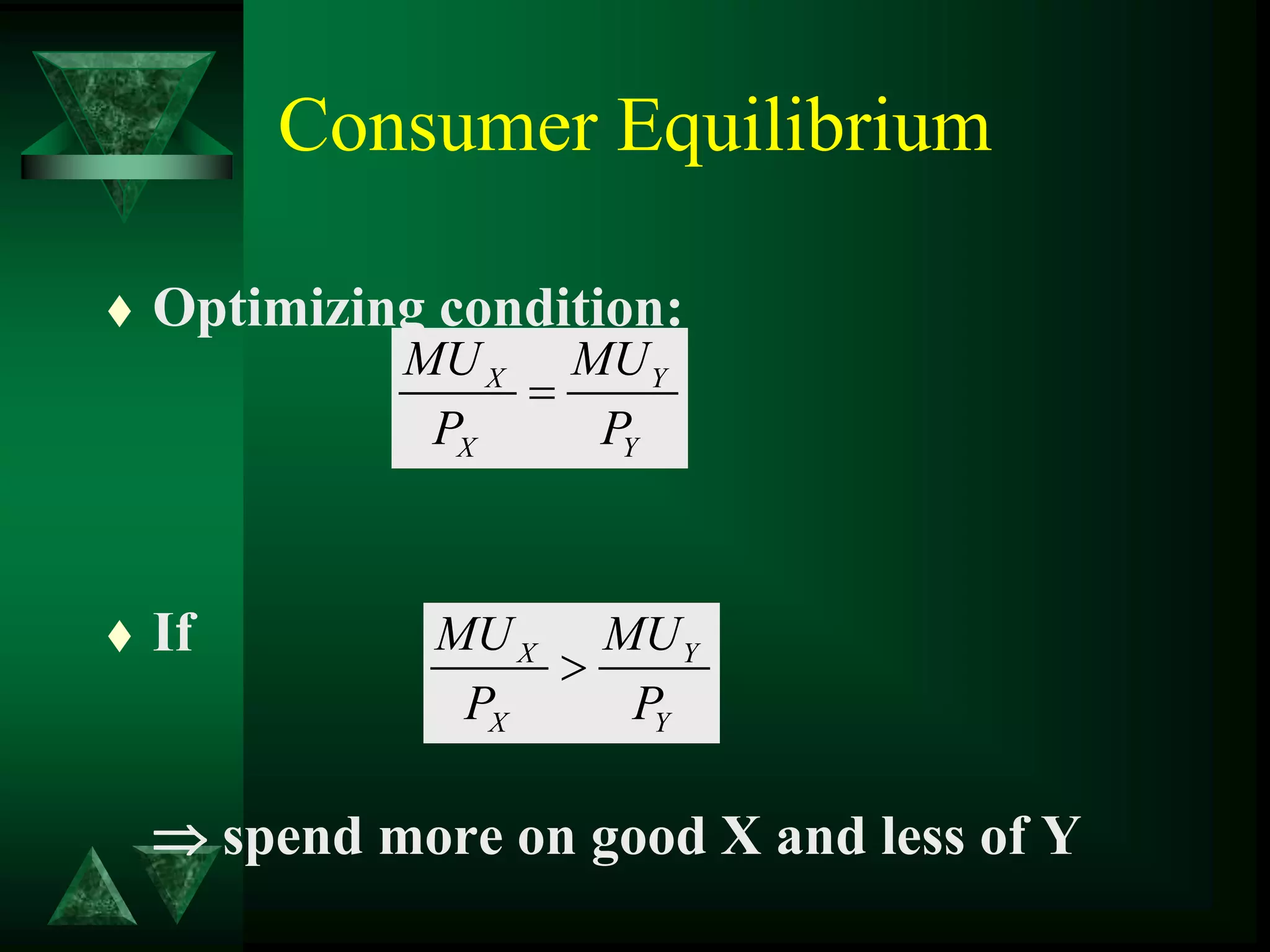
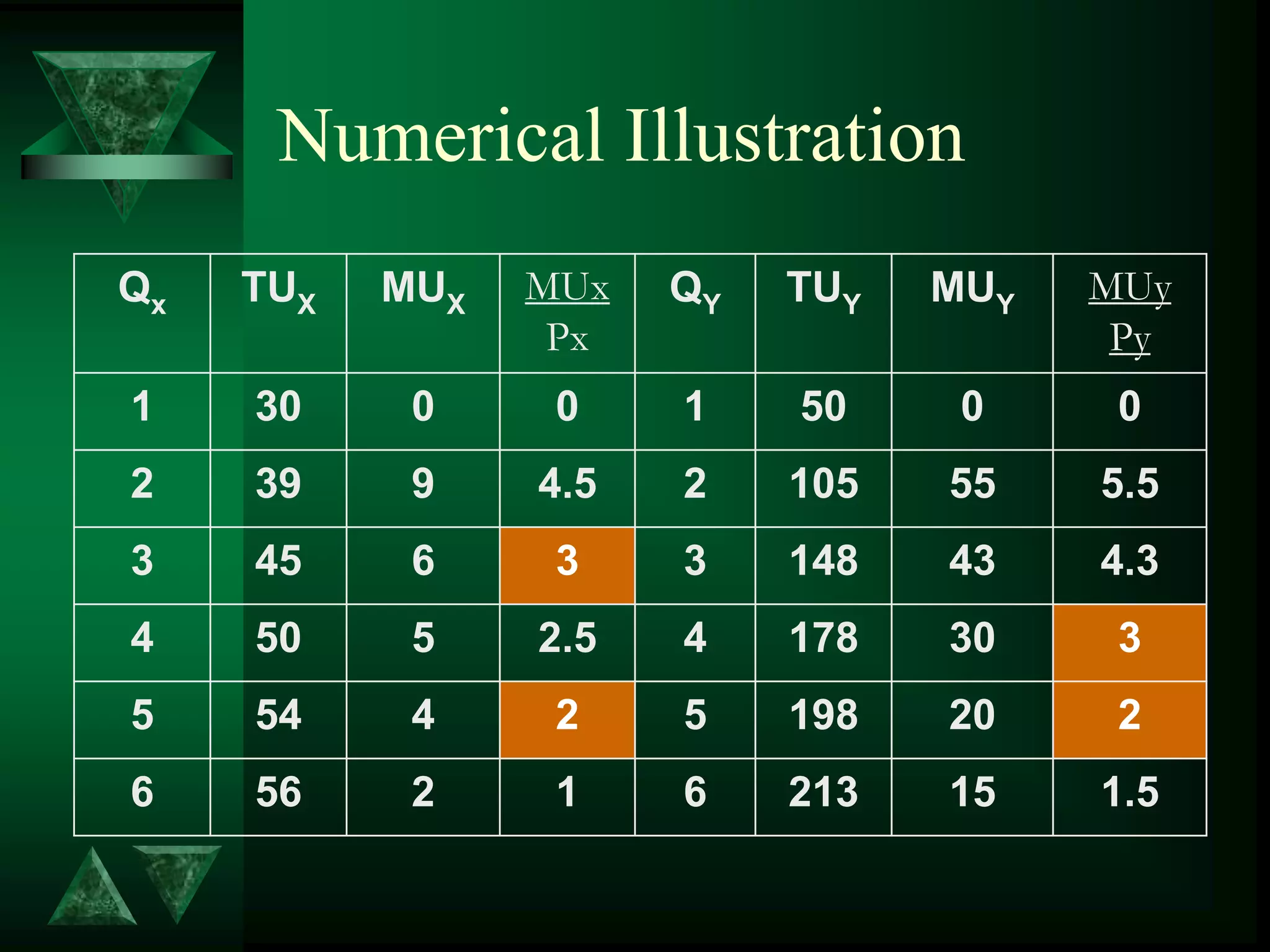
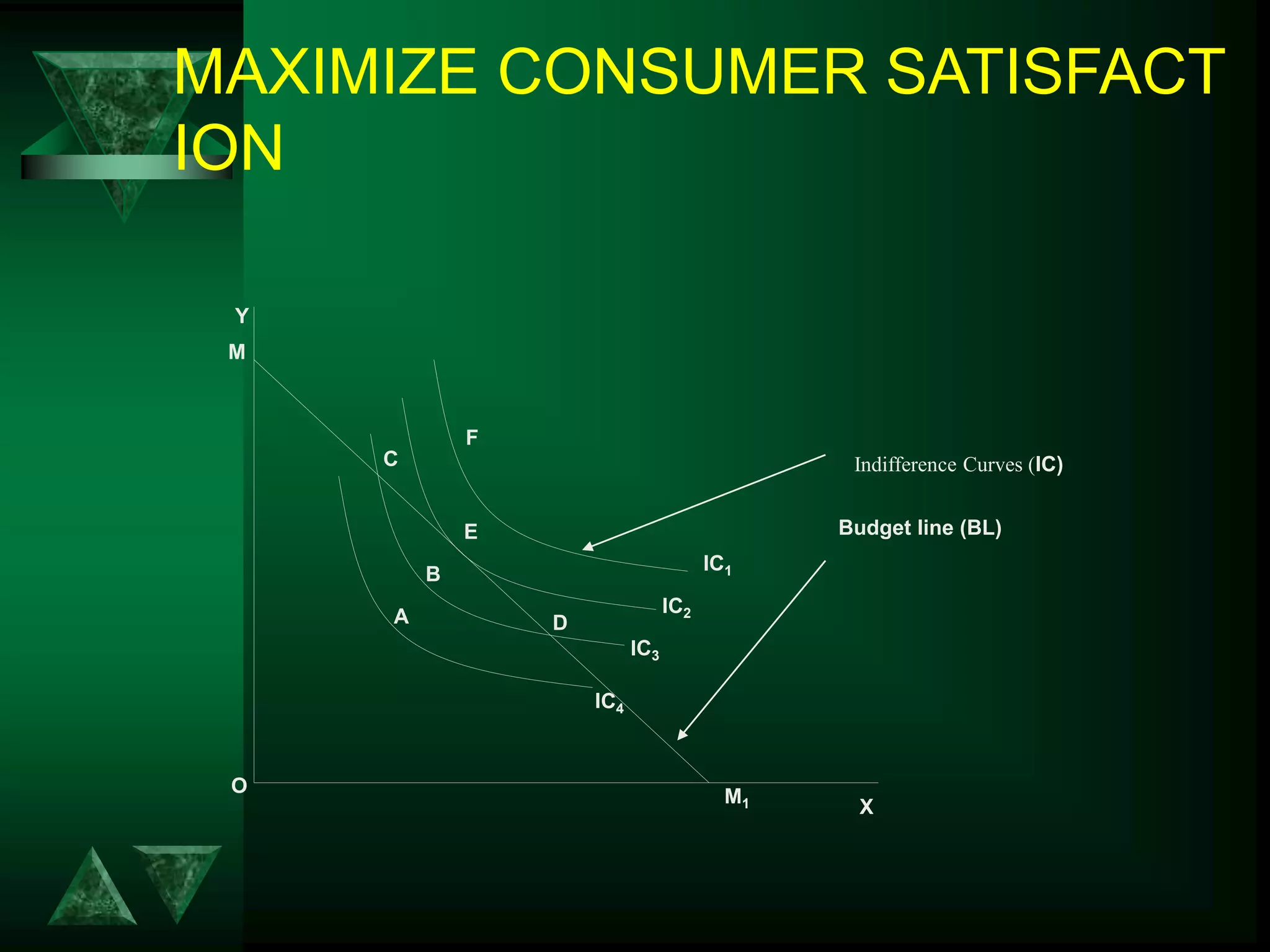
- Consumer equilibrium occurs where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget line, indicating equal marginal utility per dollar spent on each good.
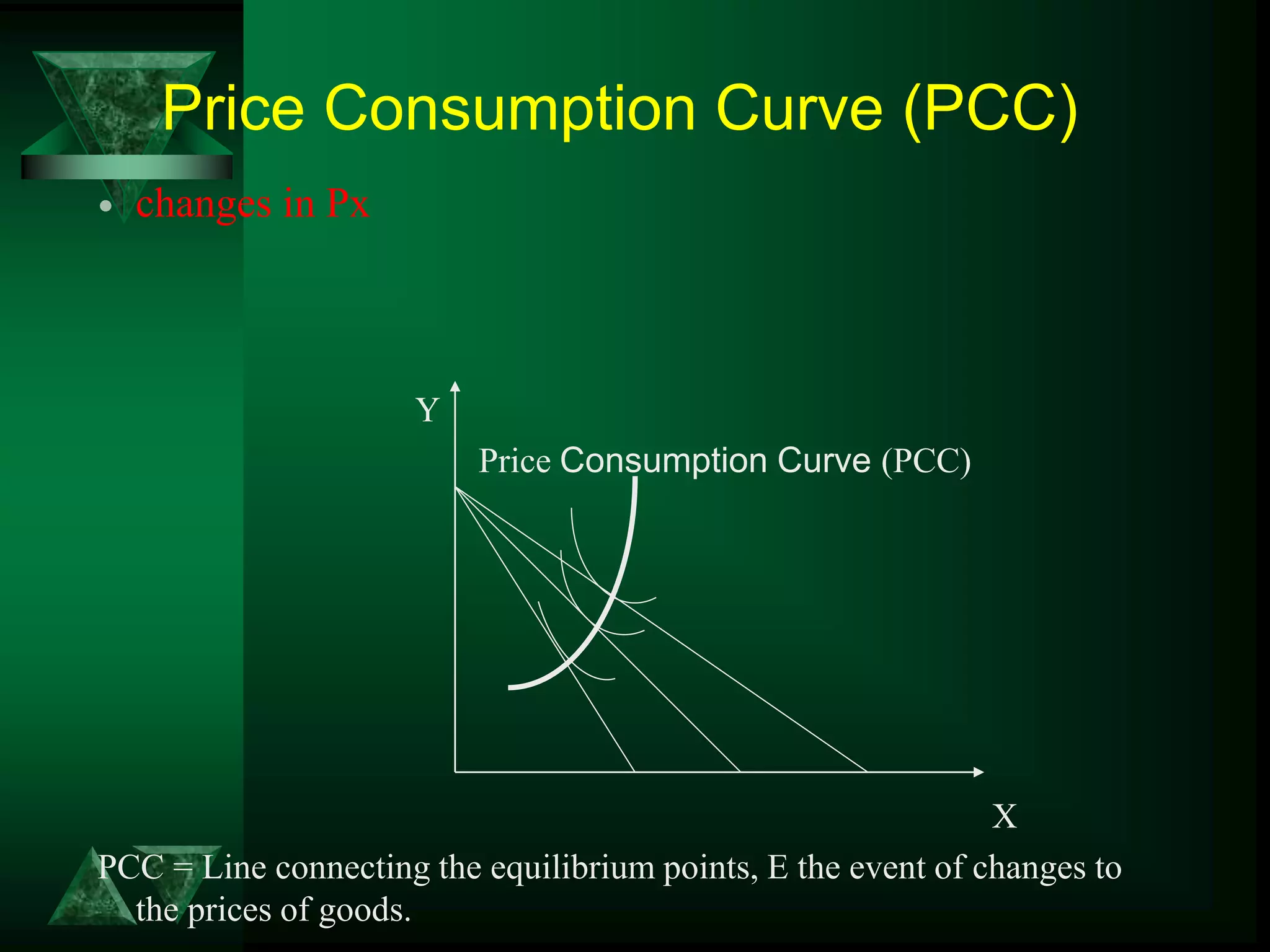
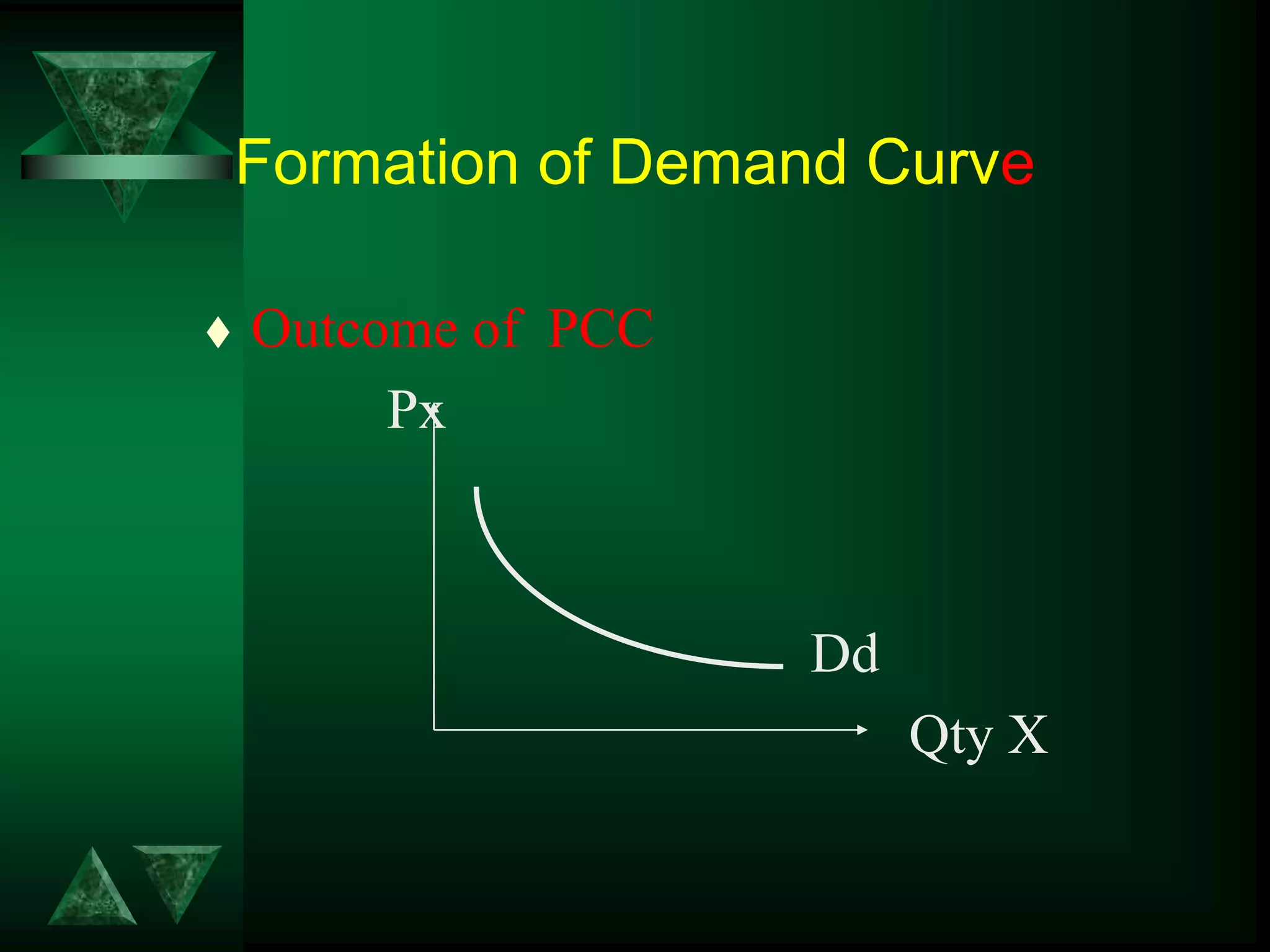
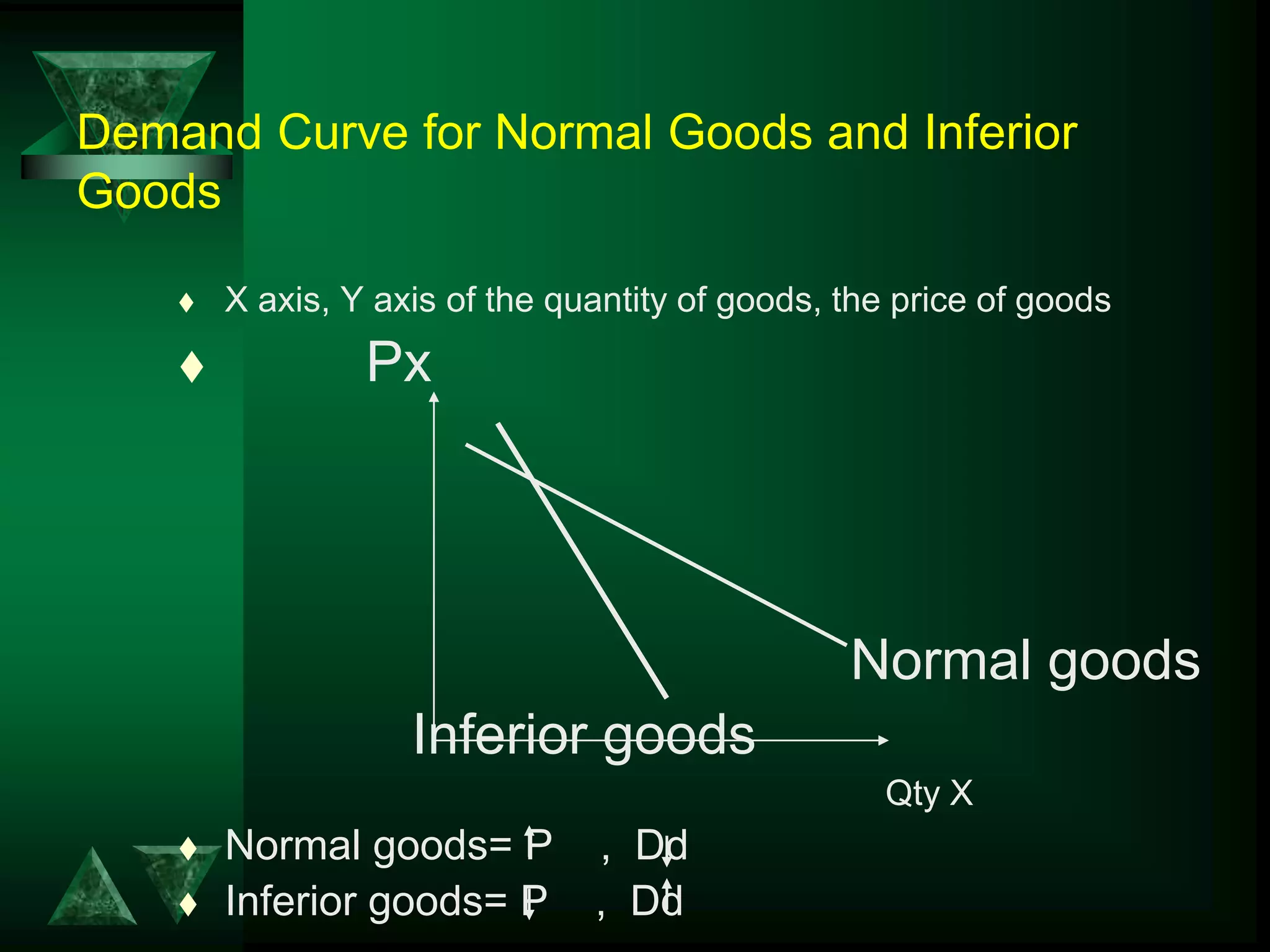
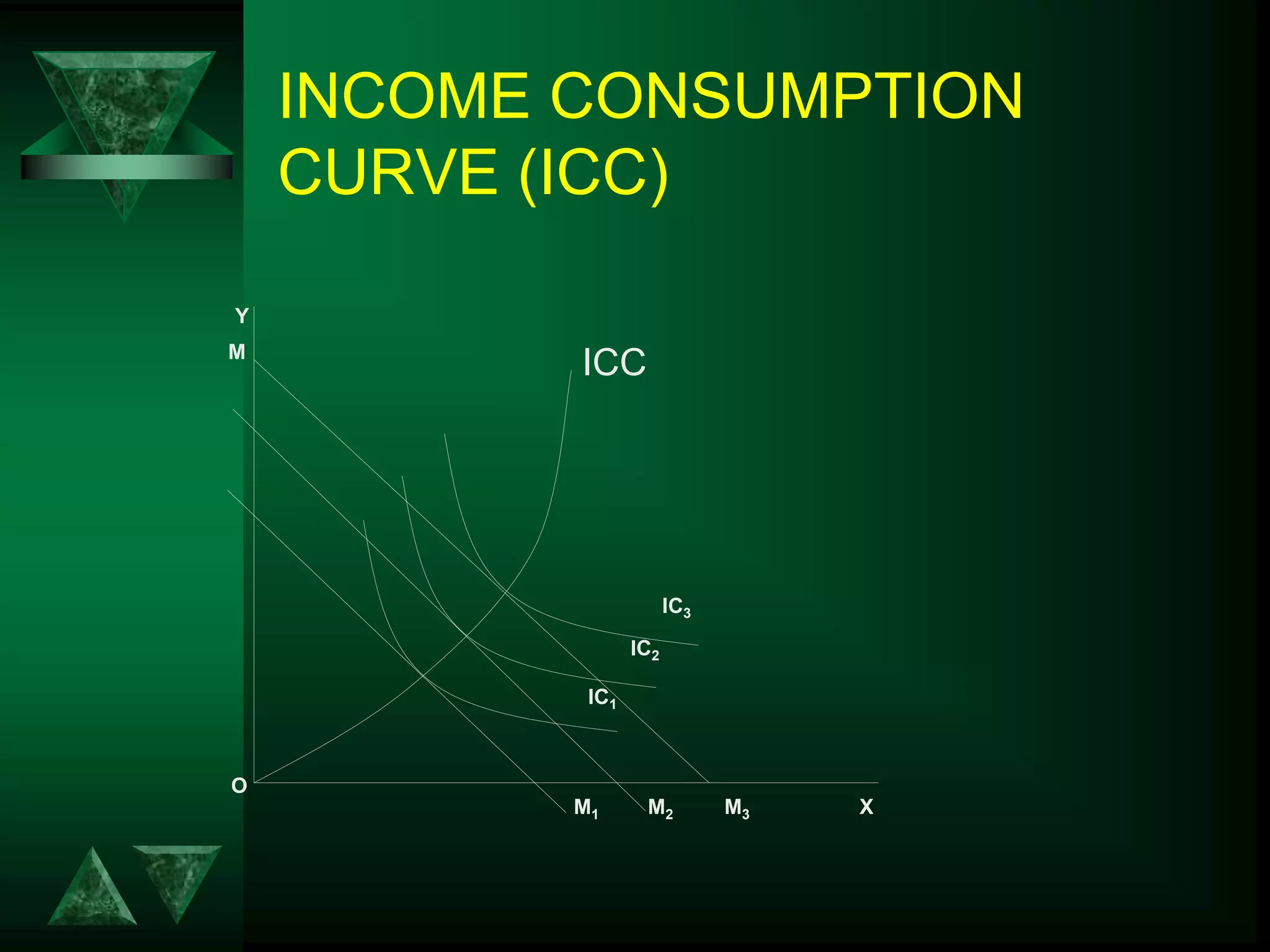
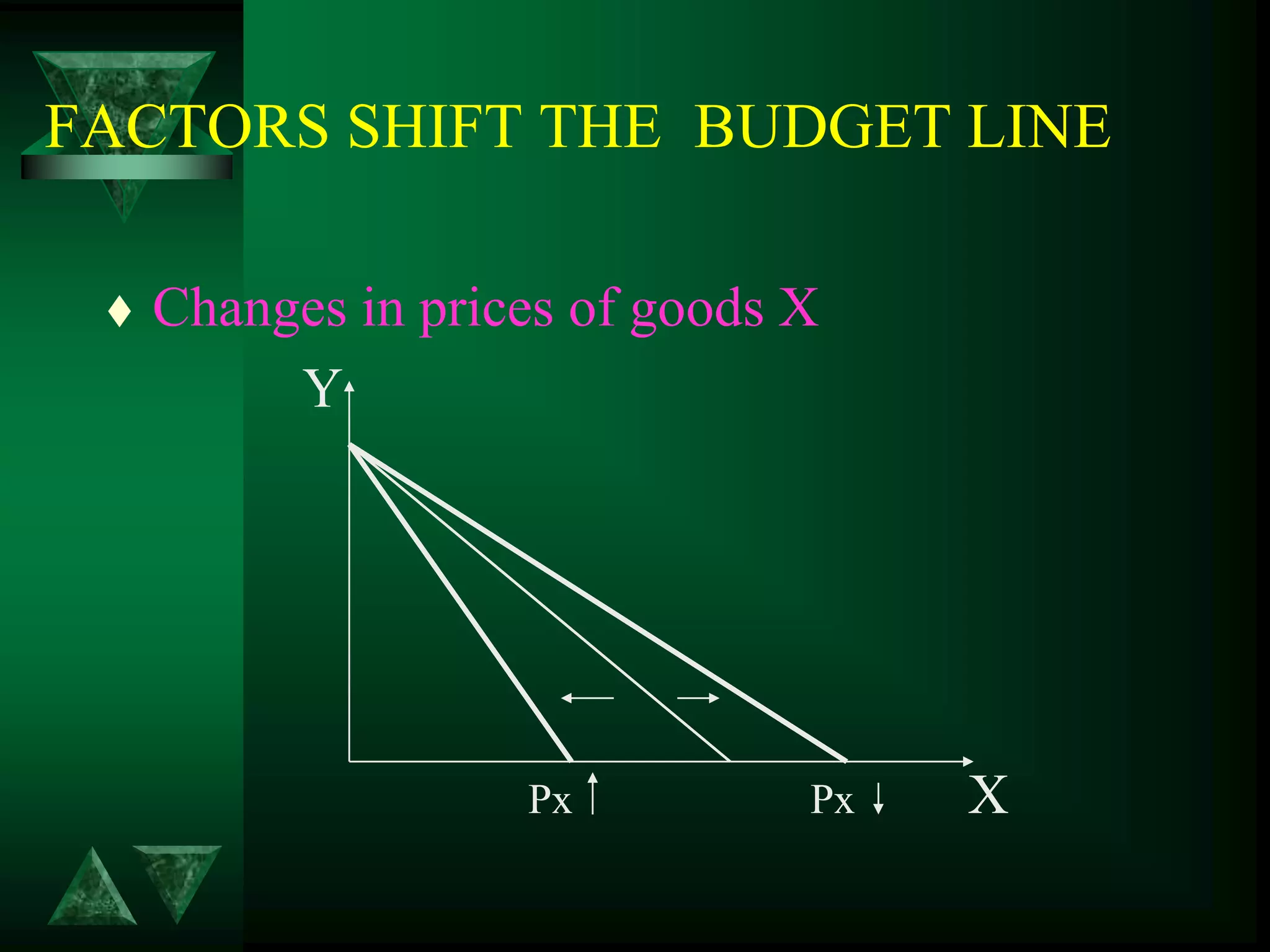
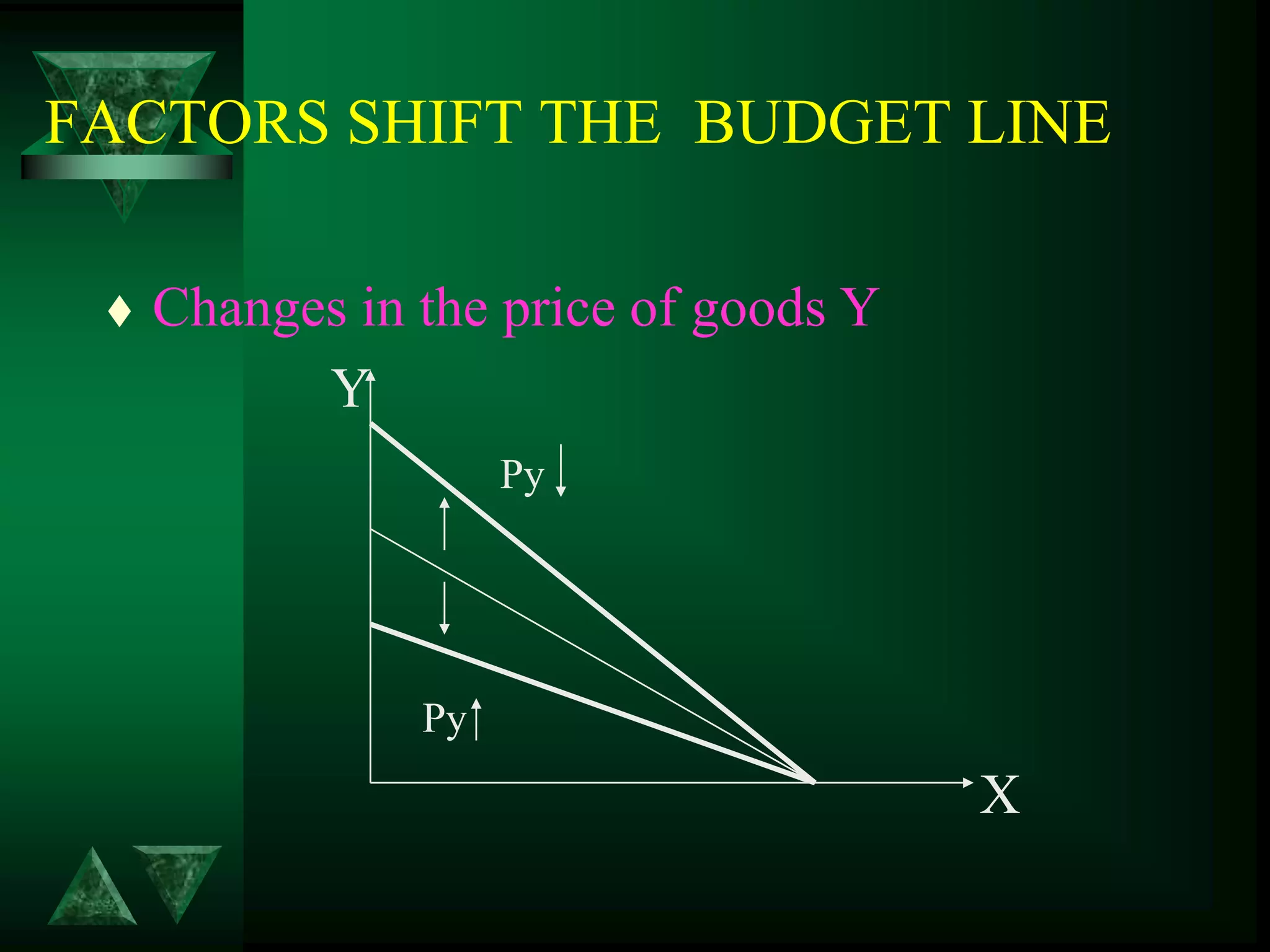
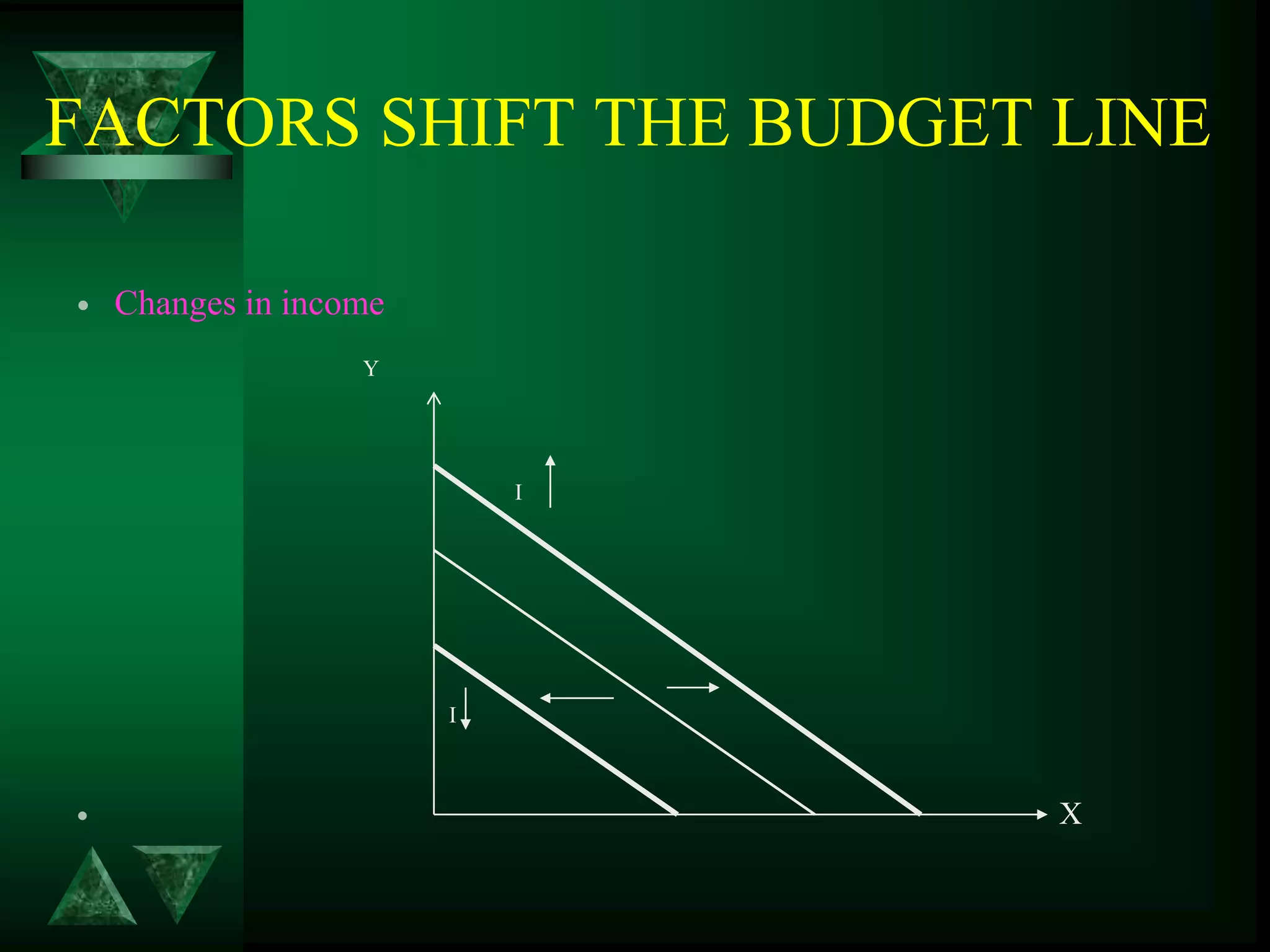
- Changes in prices and income shift budget constraints, changing equilibrium and generating demand and income consumption curves.






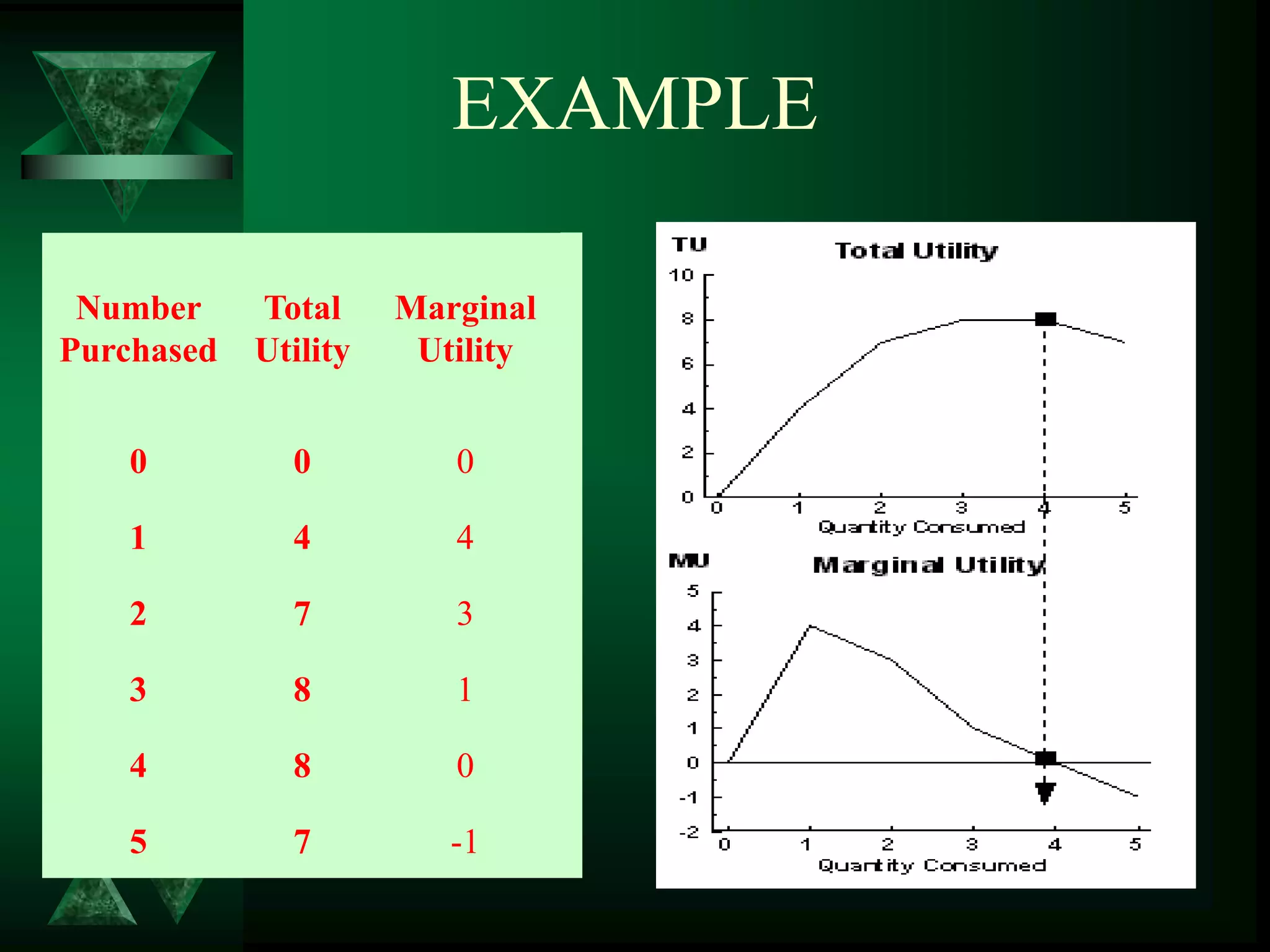














![EXAMPLE
a) A consumer spends all her income on food and
clothing. At the current prices of Pf = K10 and Pc = K5,
she maximized her utility by purchasing 20 units of
food and 50 units of clothing.
i.What is the consumer’s income? [2 marks]
ii.What is the consumer’s marginal rate of substitution
of food for clothing at the equilibrium position? [2
marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1theoryofconsumerbehavior-230321235349-dfbf887e/75/Chapter_1_theory_of_consumer_behavior-ppt-33-2048.jpg)