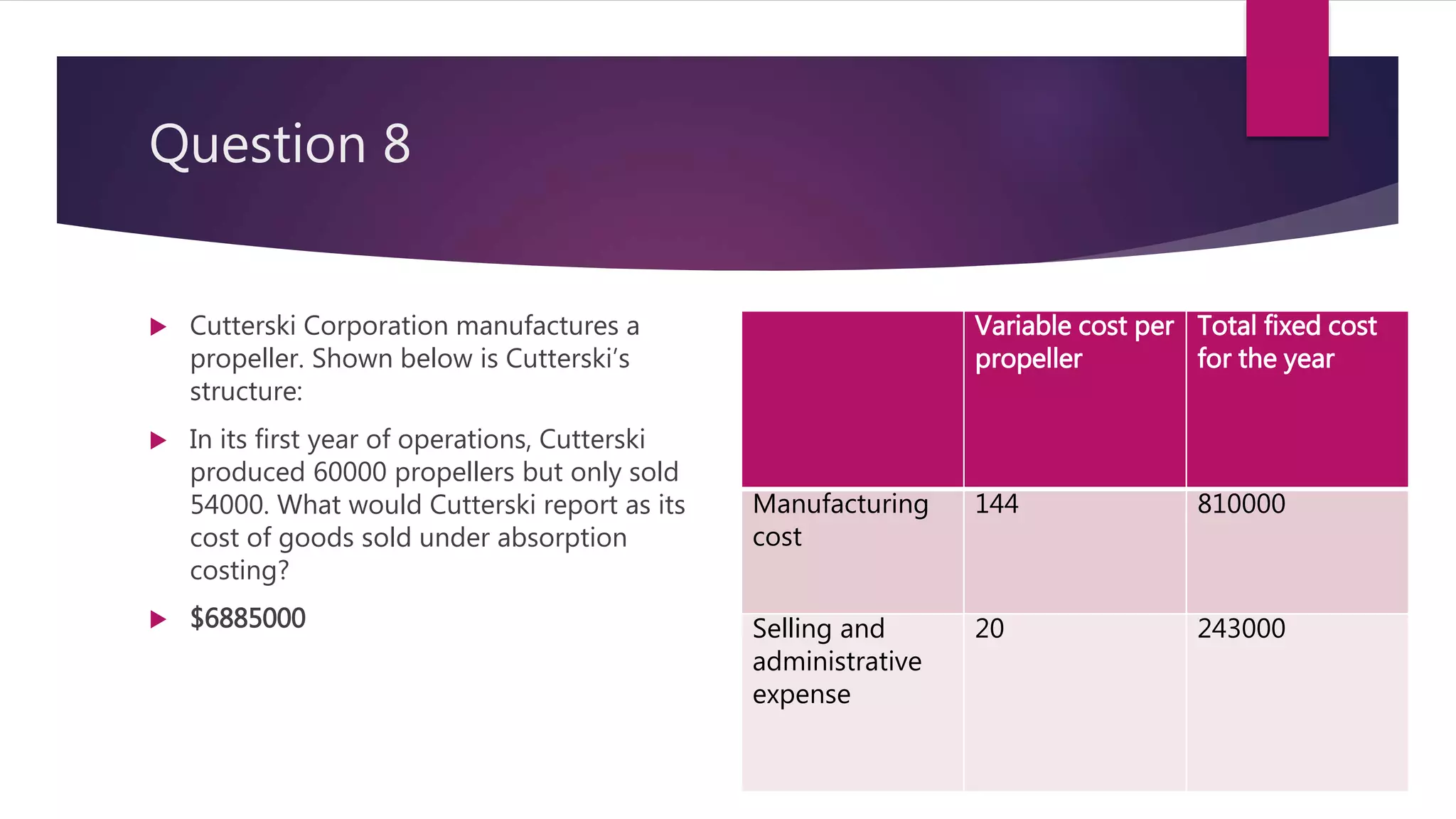
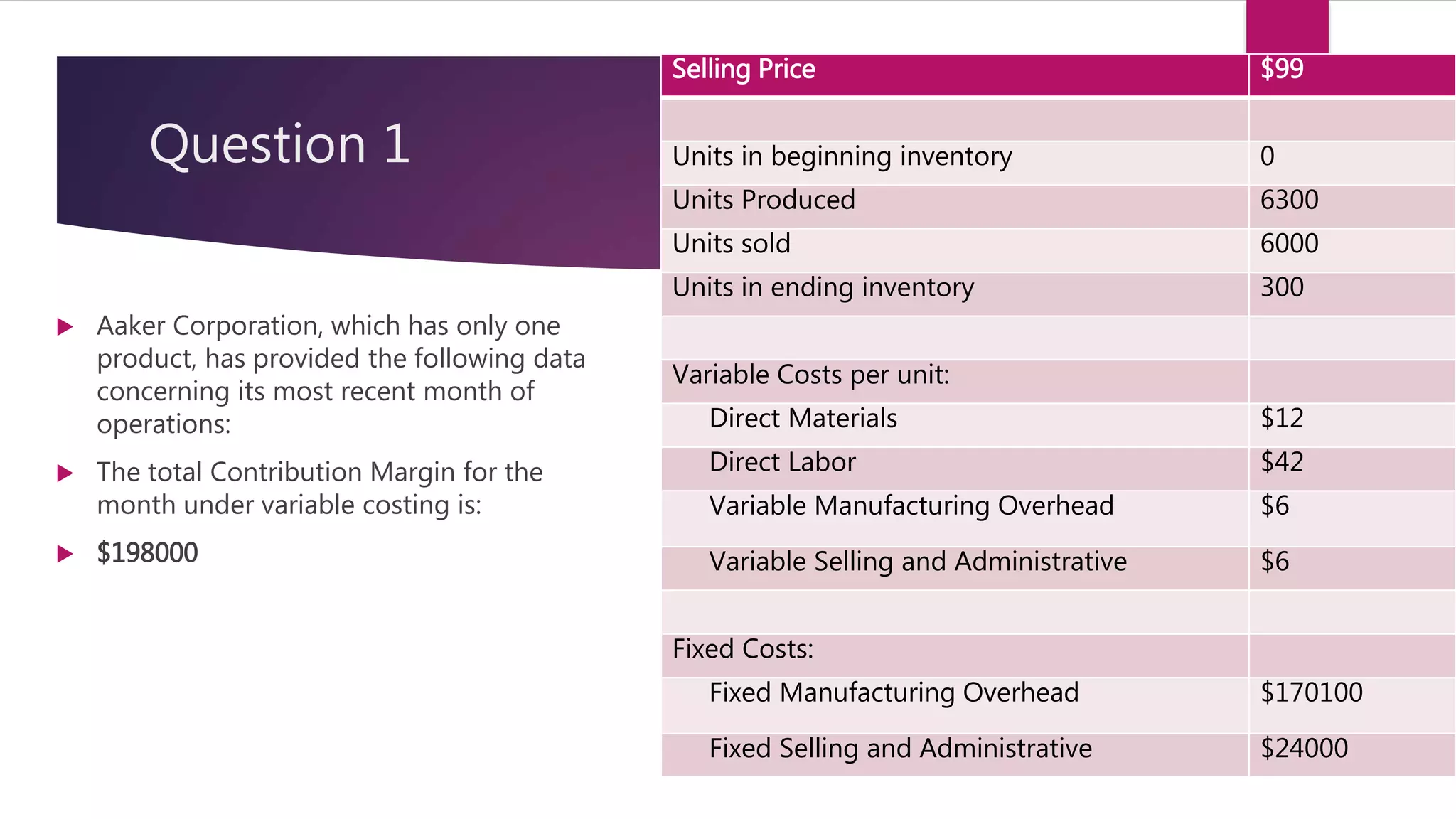
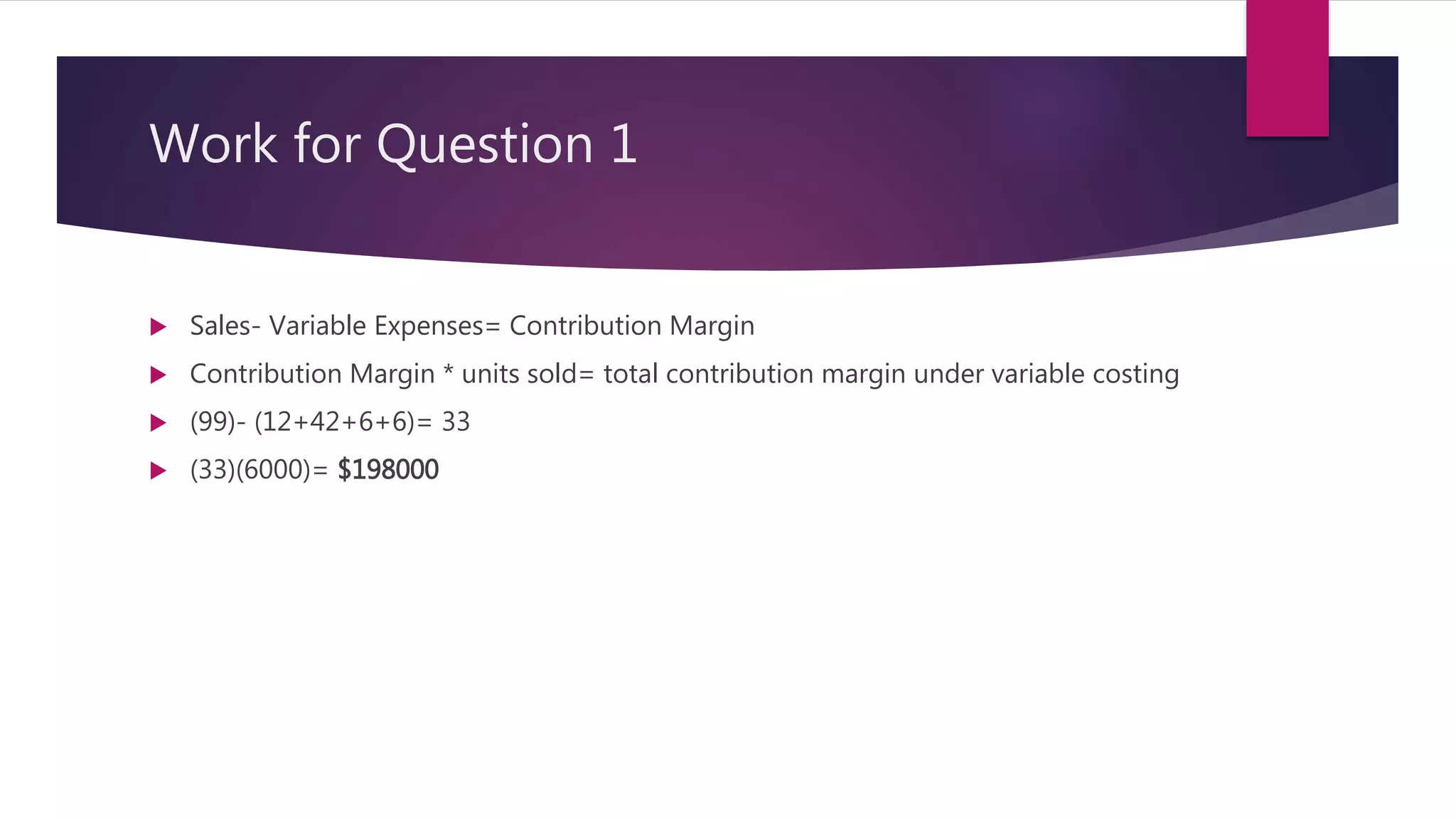
1. Aaker Corporation reported a total contribution margin of $198,000 for the most recent month. The contribution margin was calculated as (Selling Price - Variable Costs) x Units Sold.
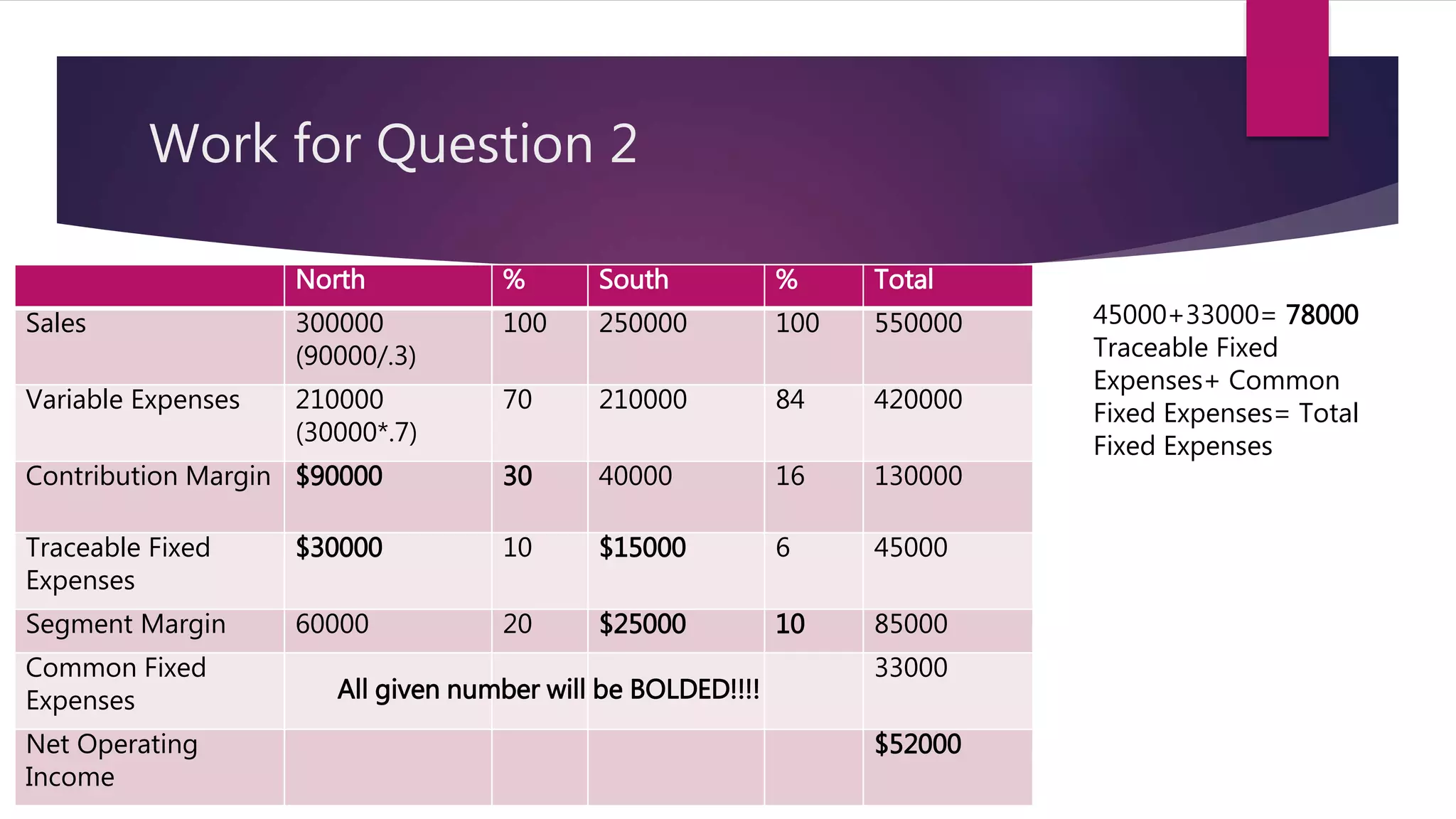
2. Meyer Corporation reported total fixed expenses of $78,000. This was calculated by adding the traceable fixed expenses of $45,000 and the common fixed expenses of $33,000.
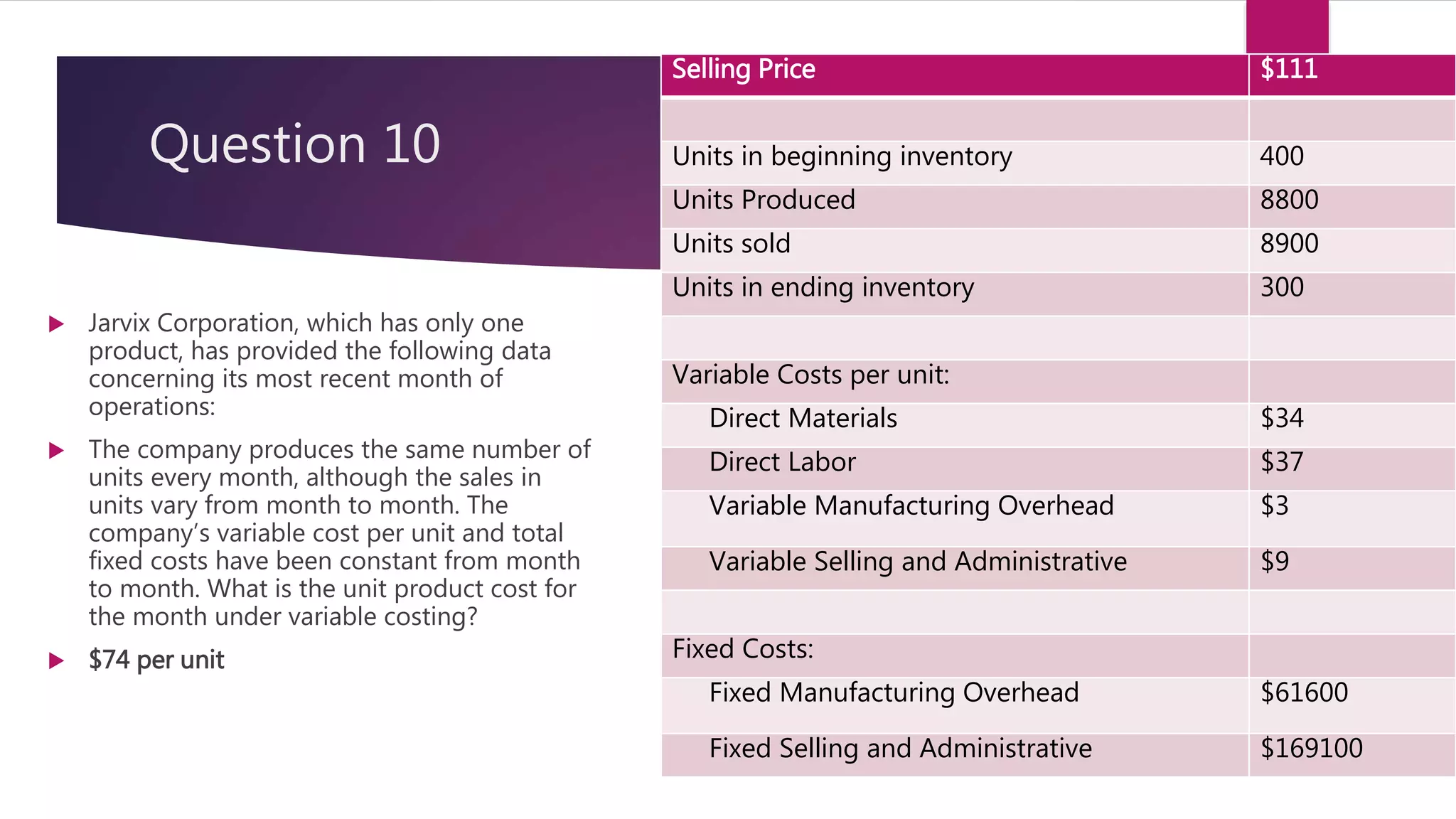
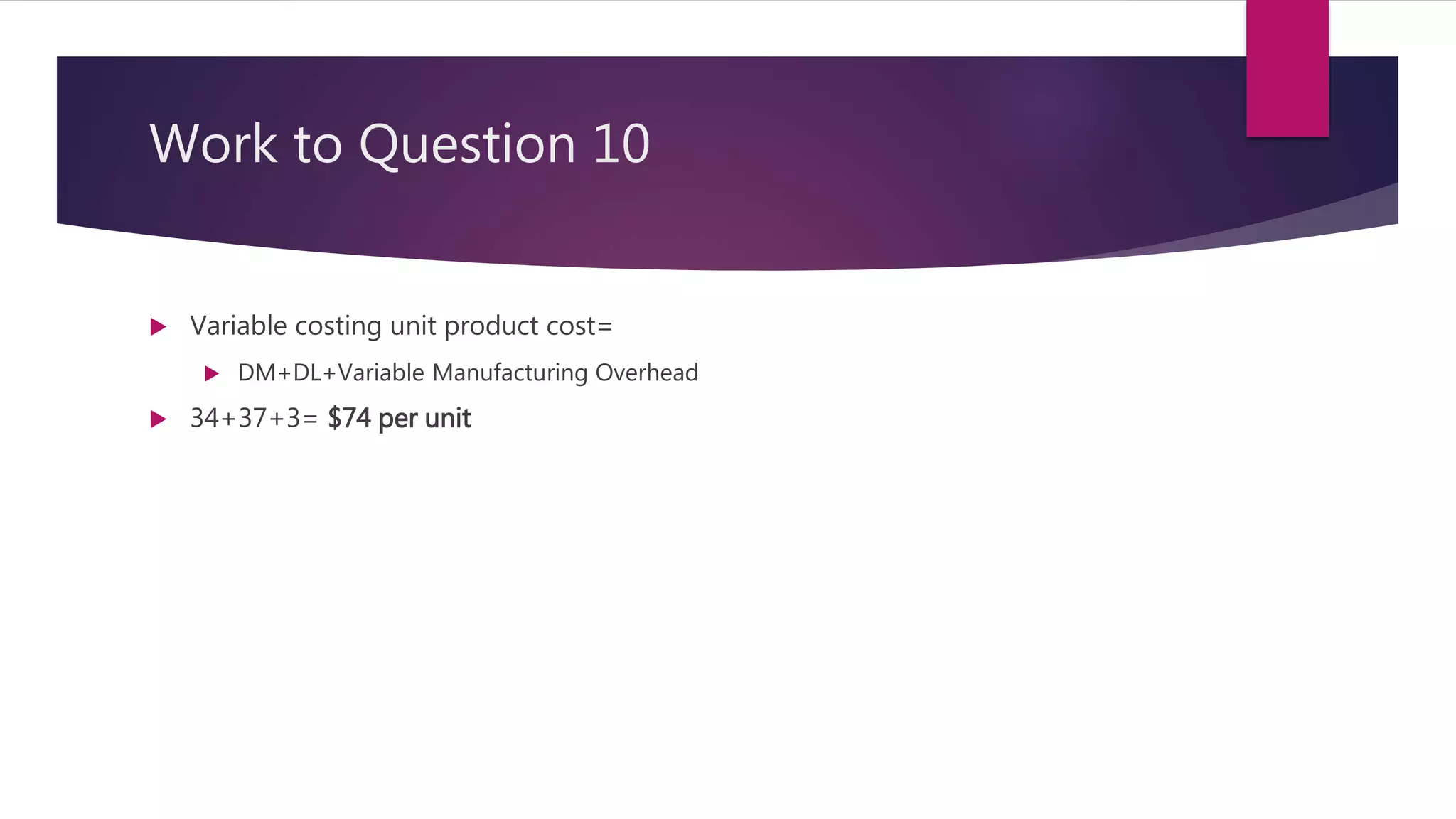
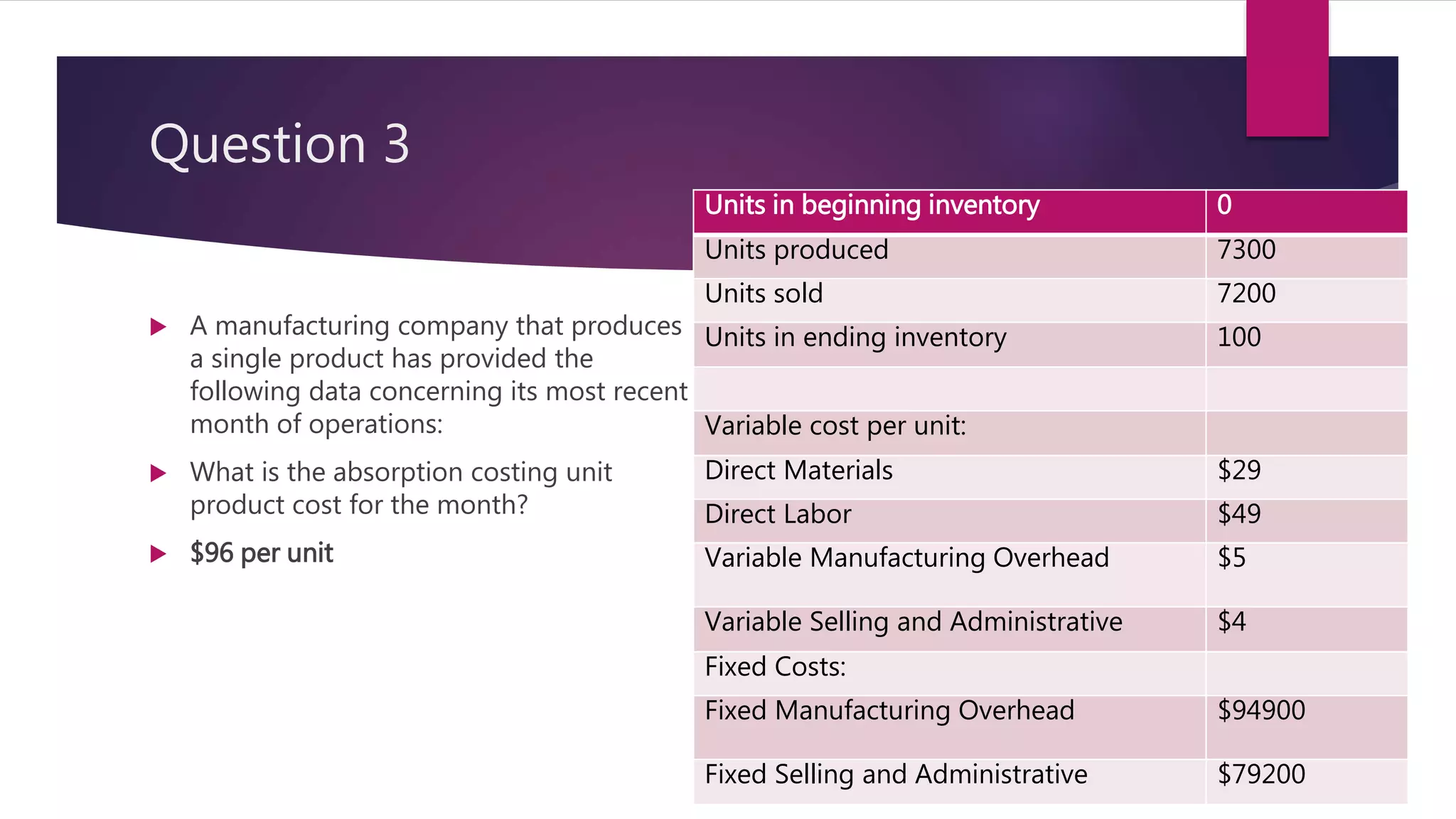
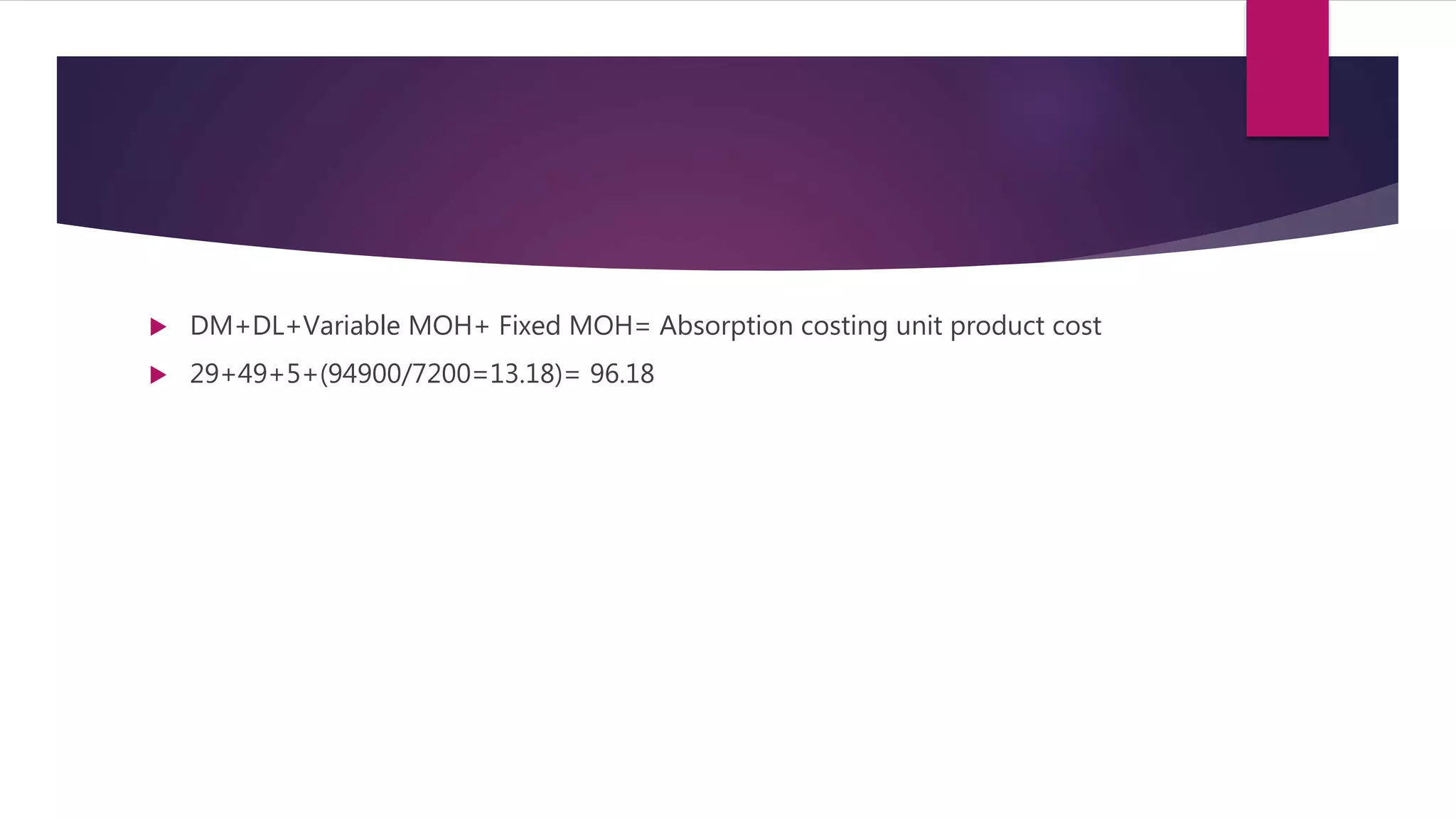
3. For a manufacturing company, the absorption costing unit product cost for the month was $96 per unit. This was calculated by taking the variable costs per unit plus the fixed manufacturing overhead costs allocated on a per unit basis.



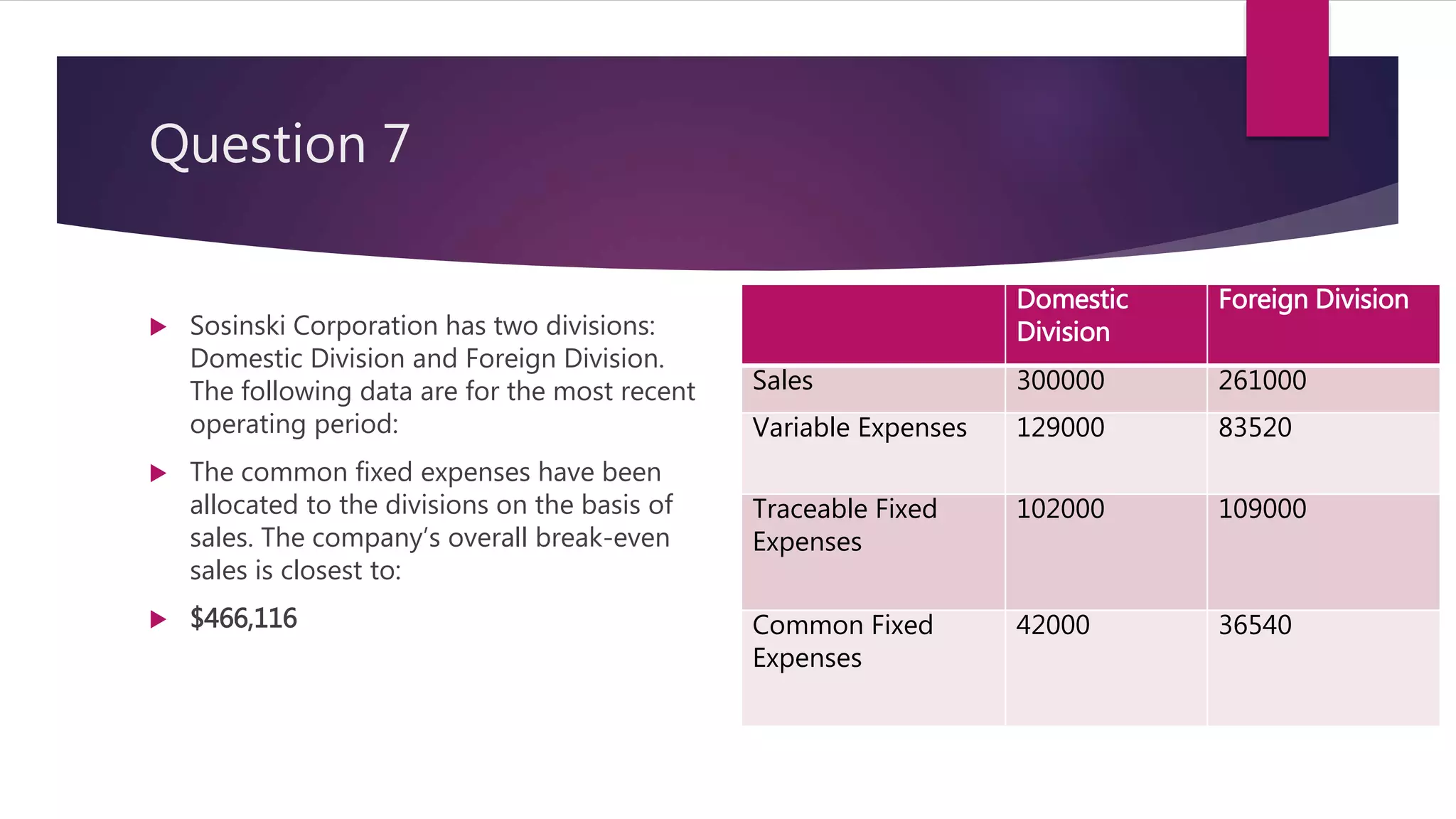
![Work to Question 7
Dollar sales for company to Break Even=
(Traceable Fixed Costs+ Common Fixed Costs)/Overall CM Ratio
Overall CM Ratio= (Sales- Variable Expenses)/Sales
Overall CM Ratio= [(300000+261000)-(129000+83520)]/(300000+261000)
(561000-212520)/561000
.62
Break Even= [(102000+1090000)+(42000+36540)]/.62
(211000+78540)/.62
$466116](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6connectquiz-160316000730/75/Chapter-6-Connect-Quiz-Variable-Costing-and-Segment-Reporting-Tools-for-Management-14-2048.jpg)