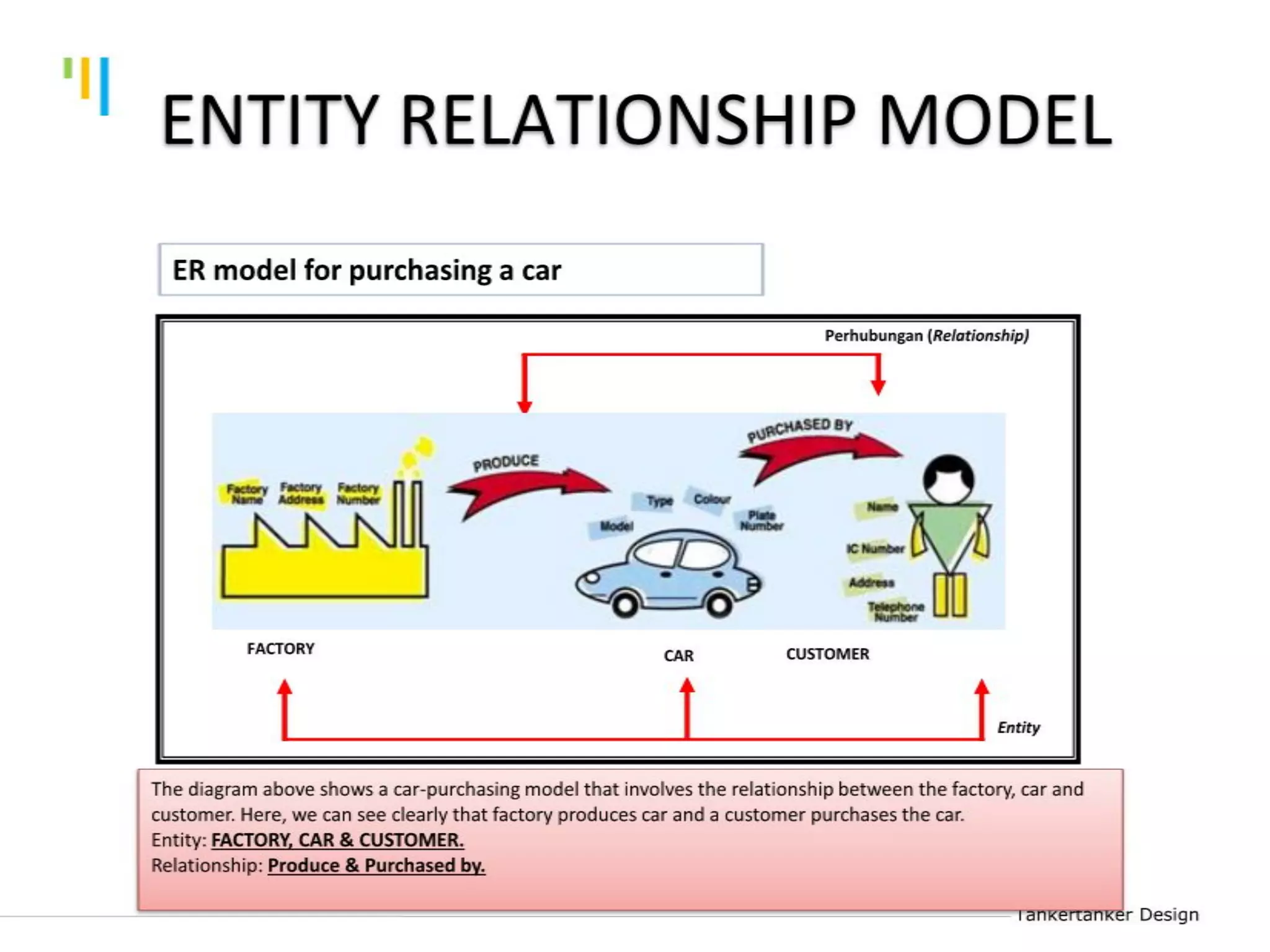
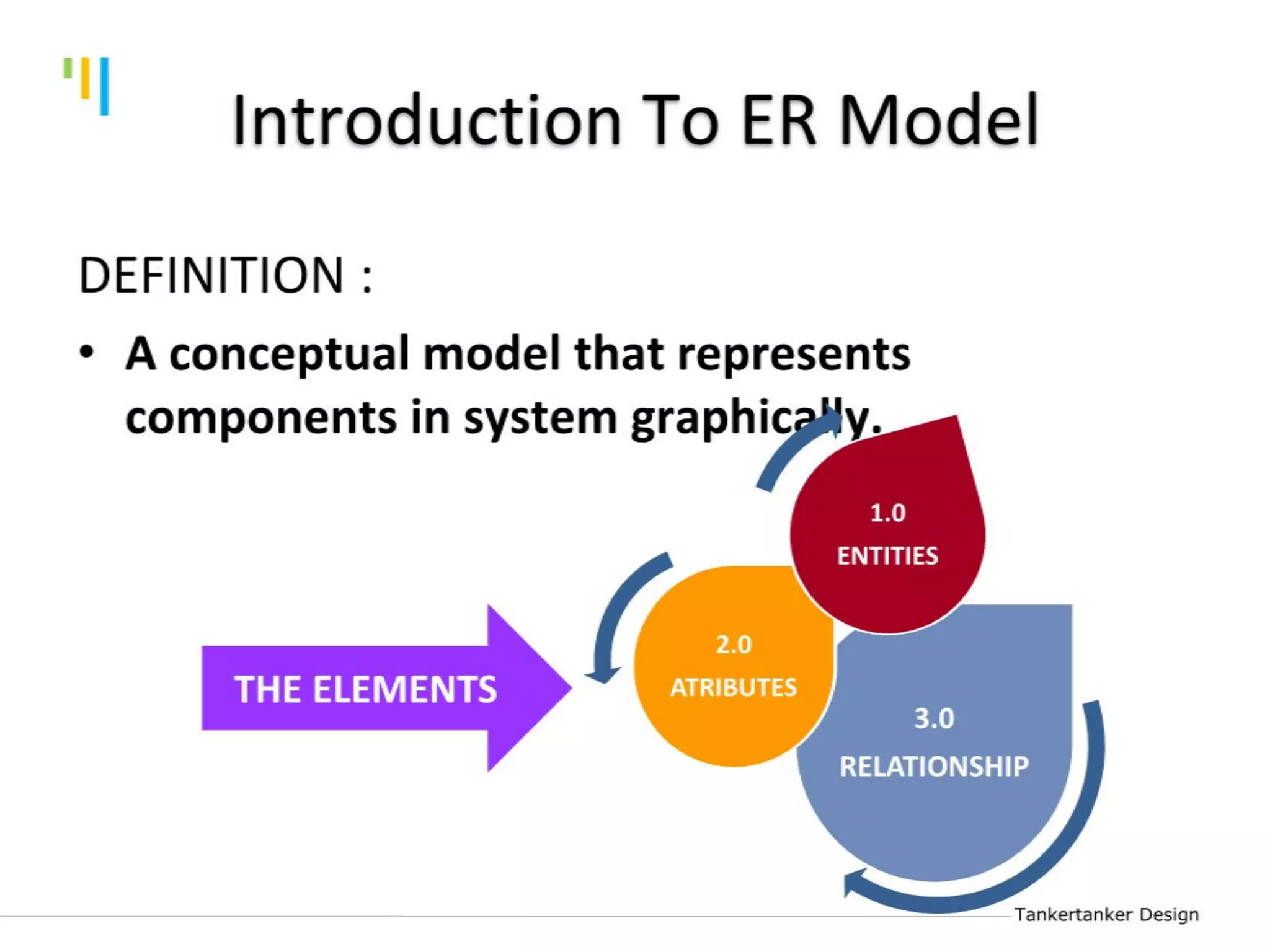
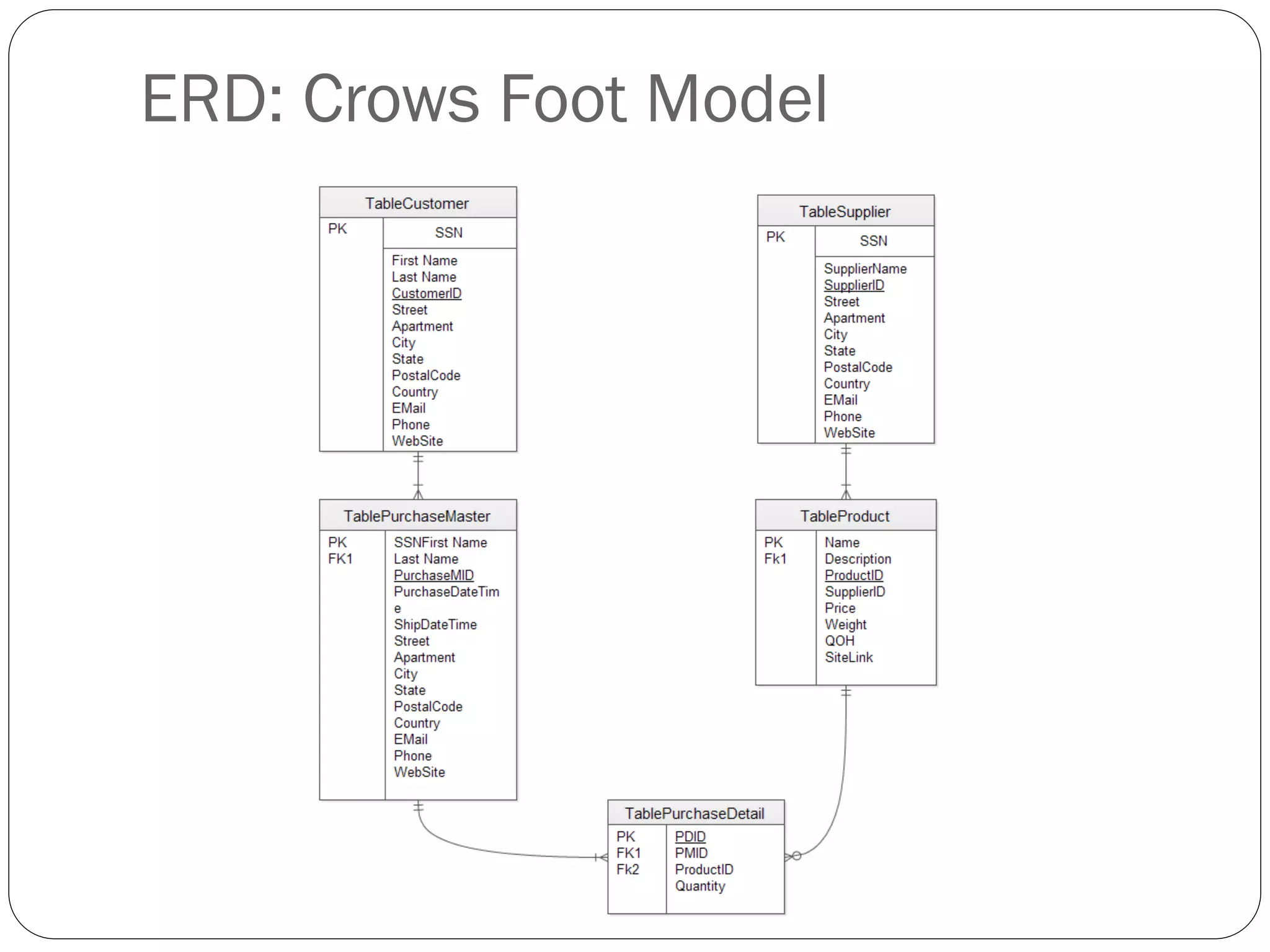
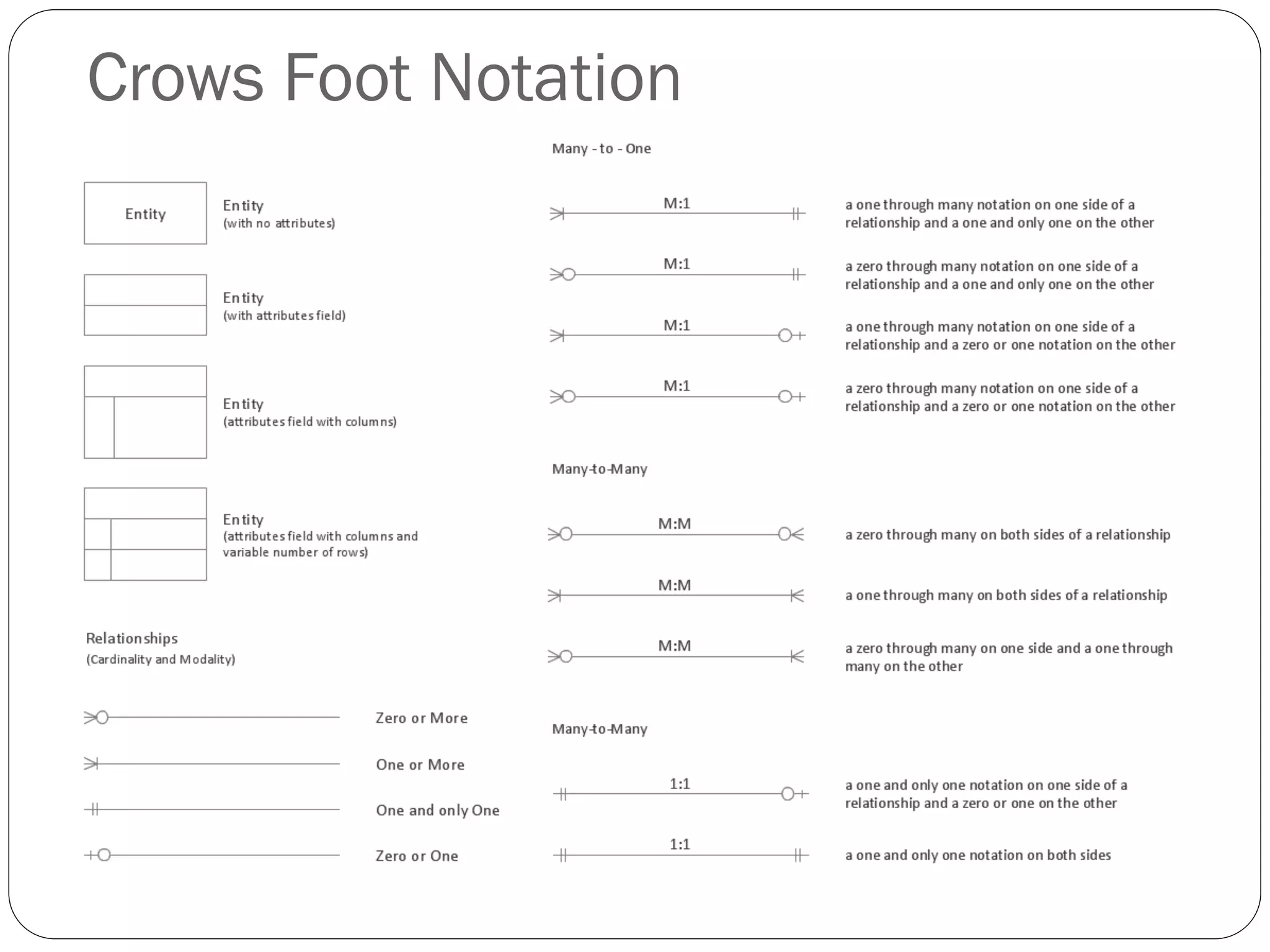
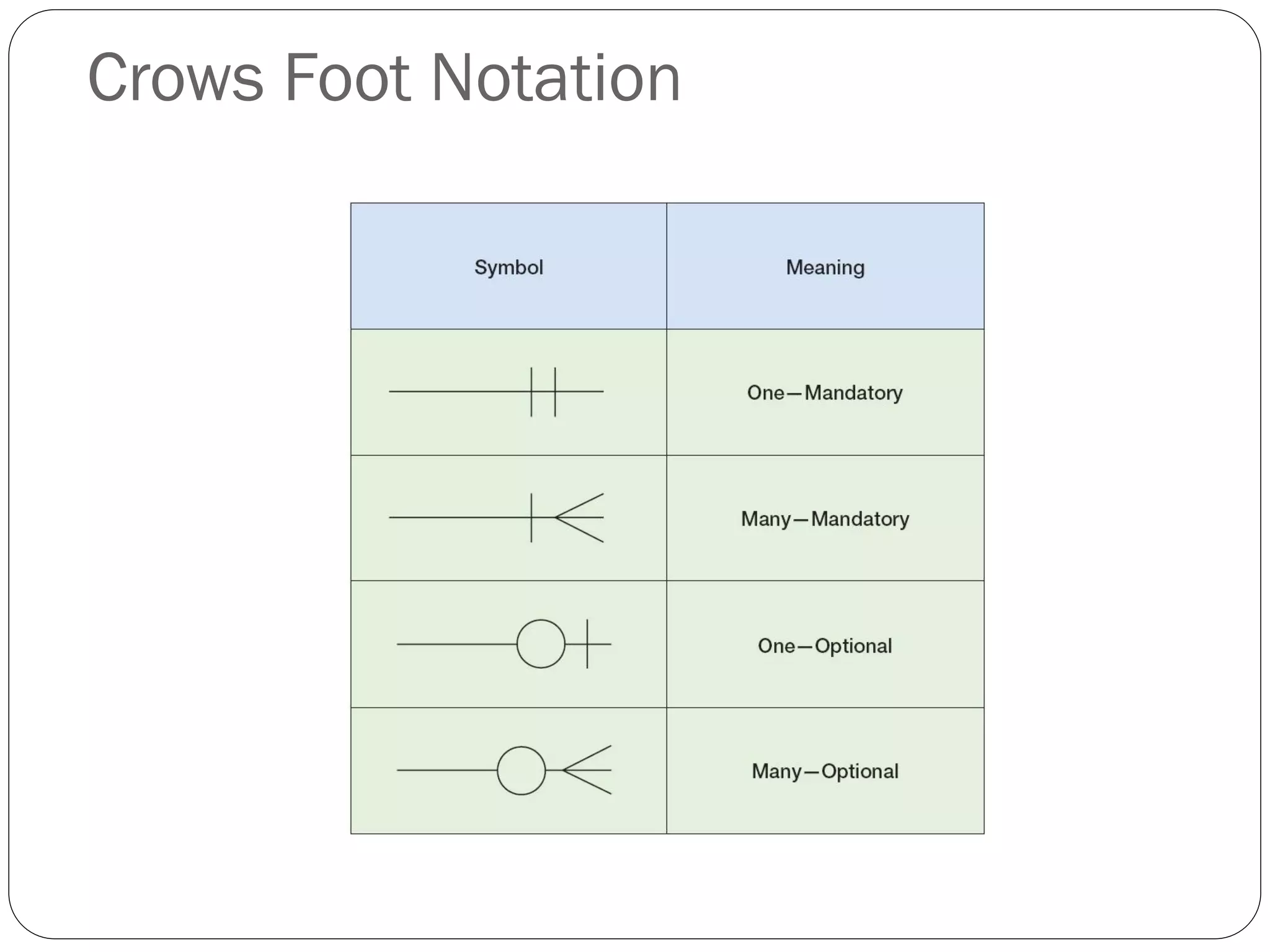
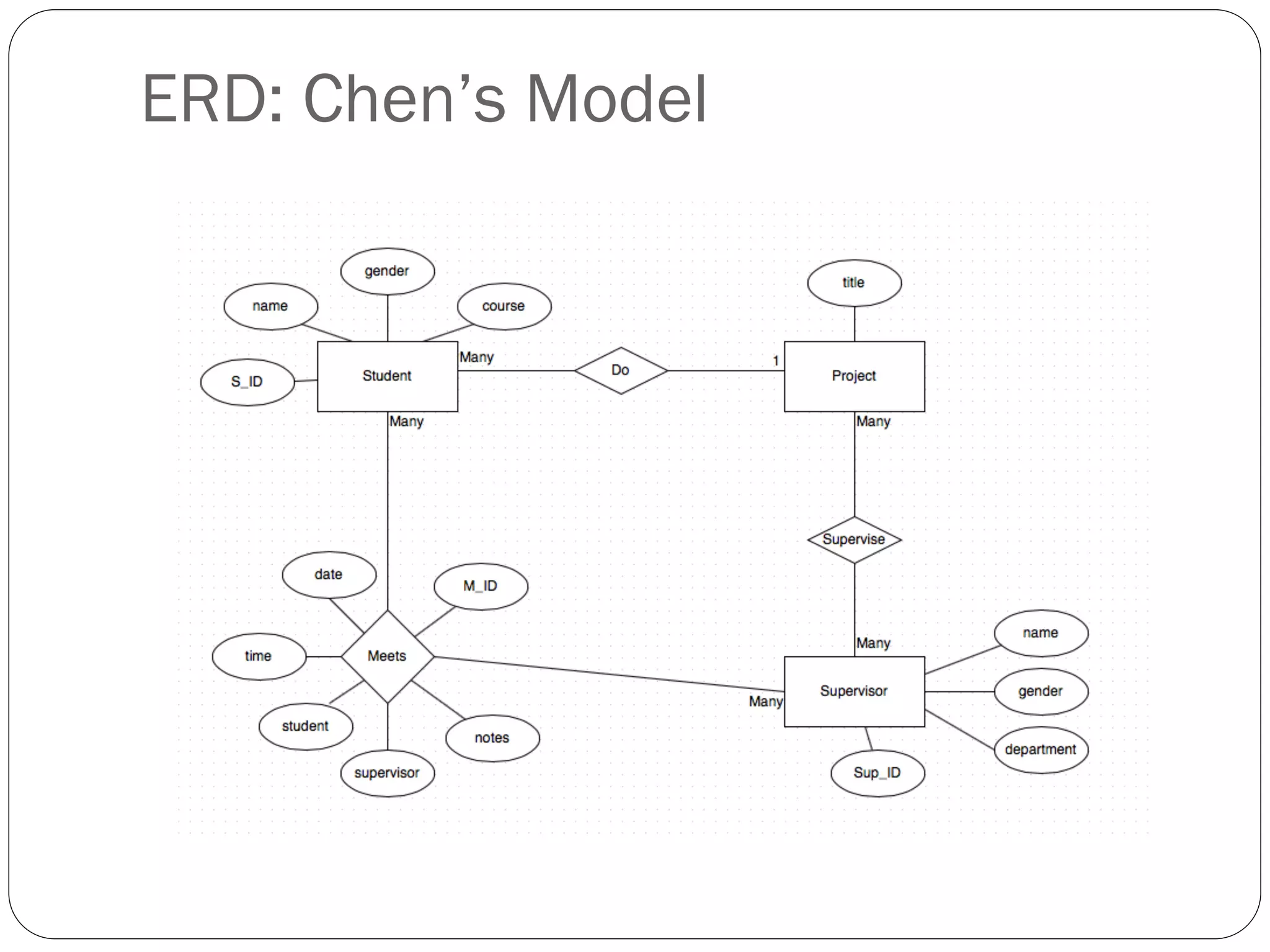
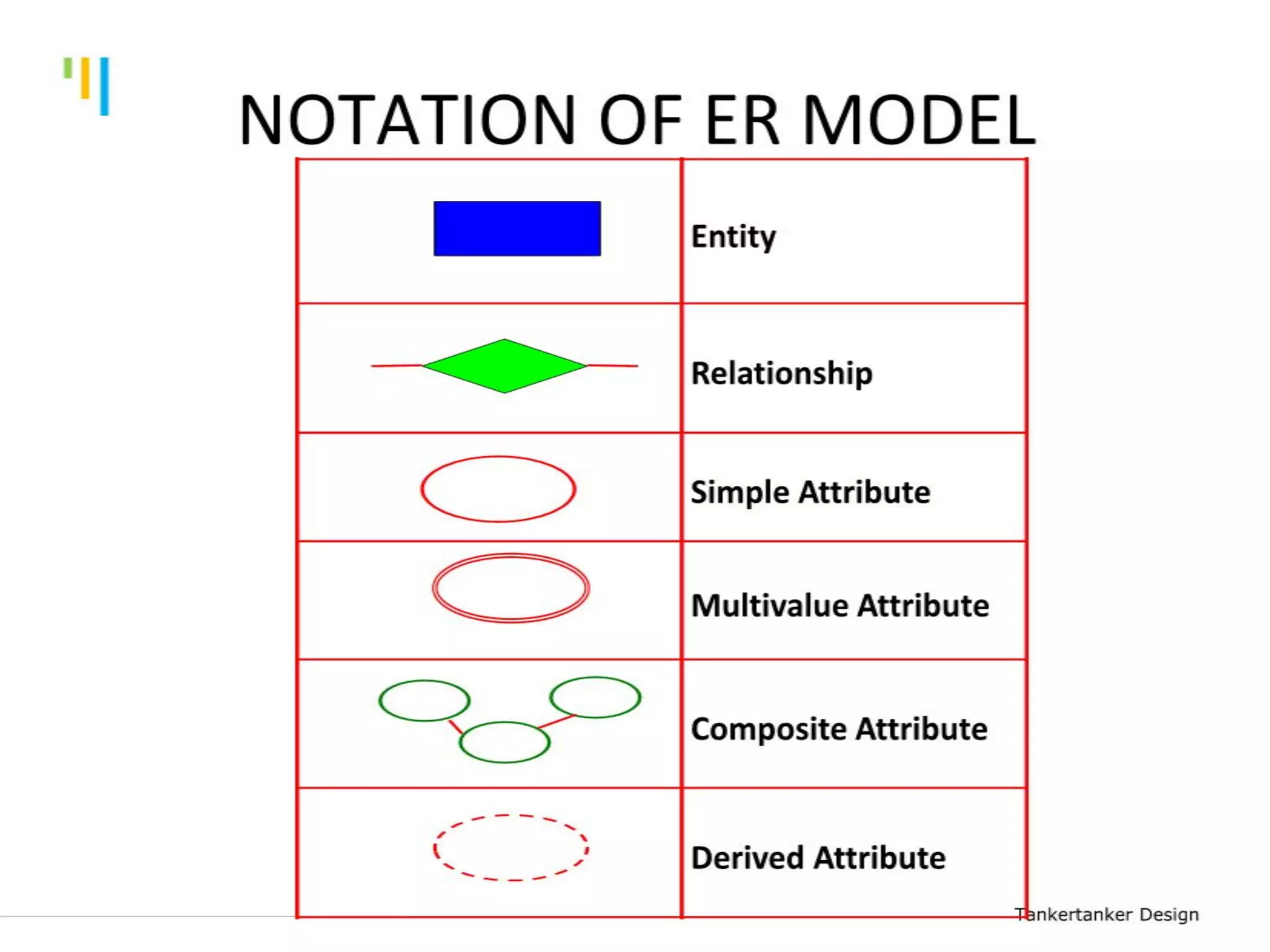
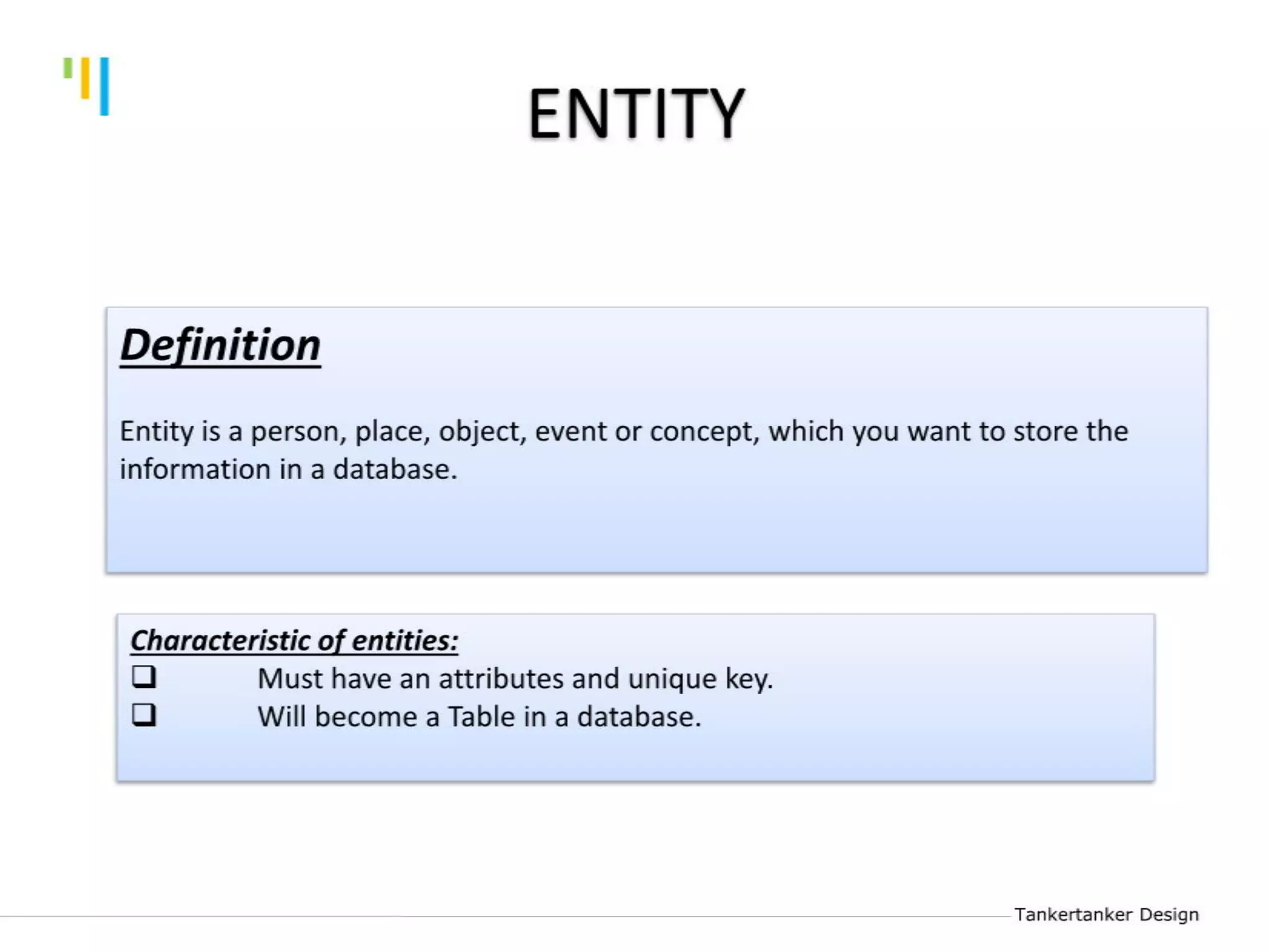
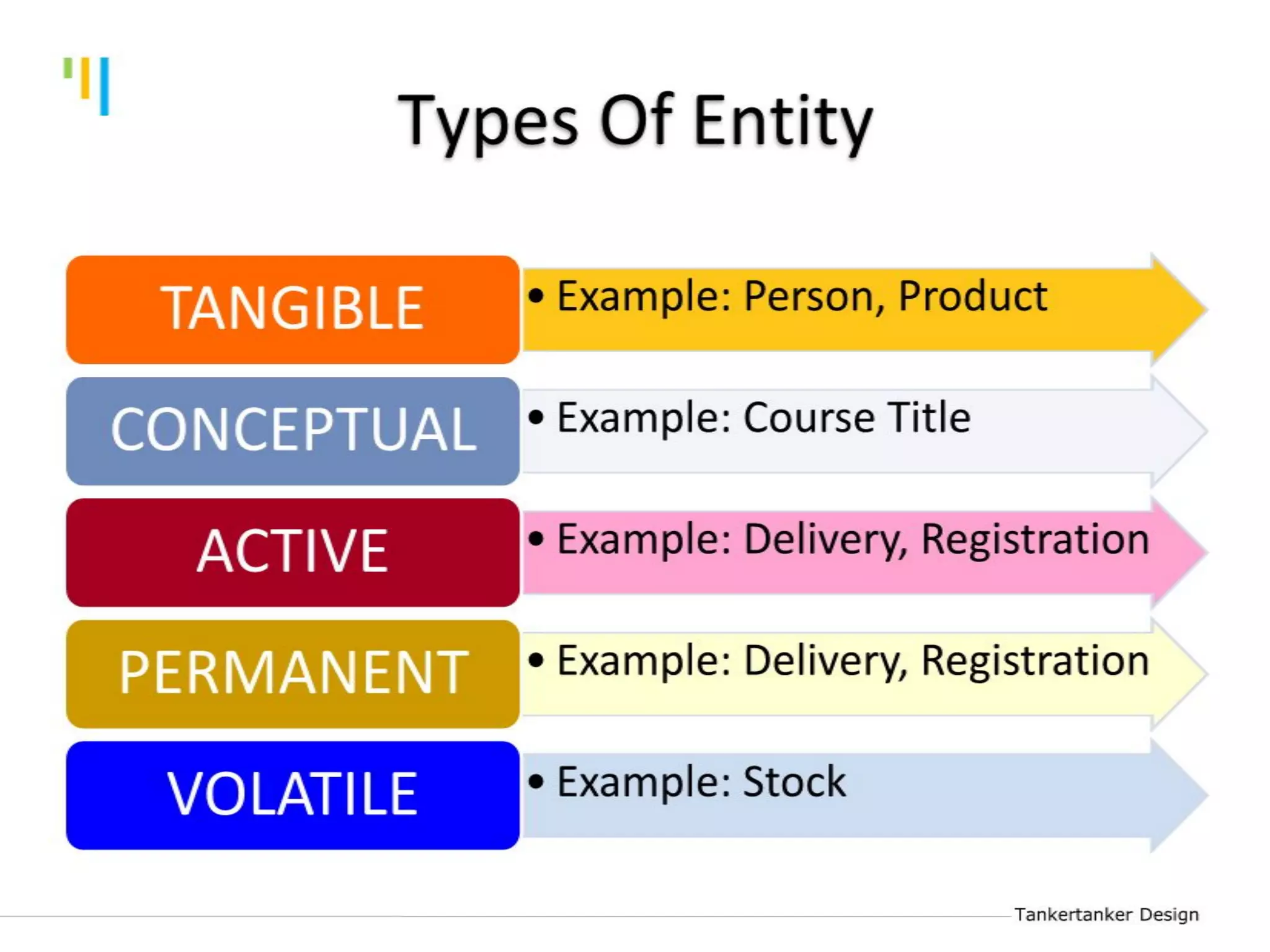
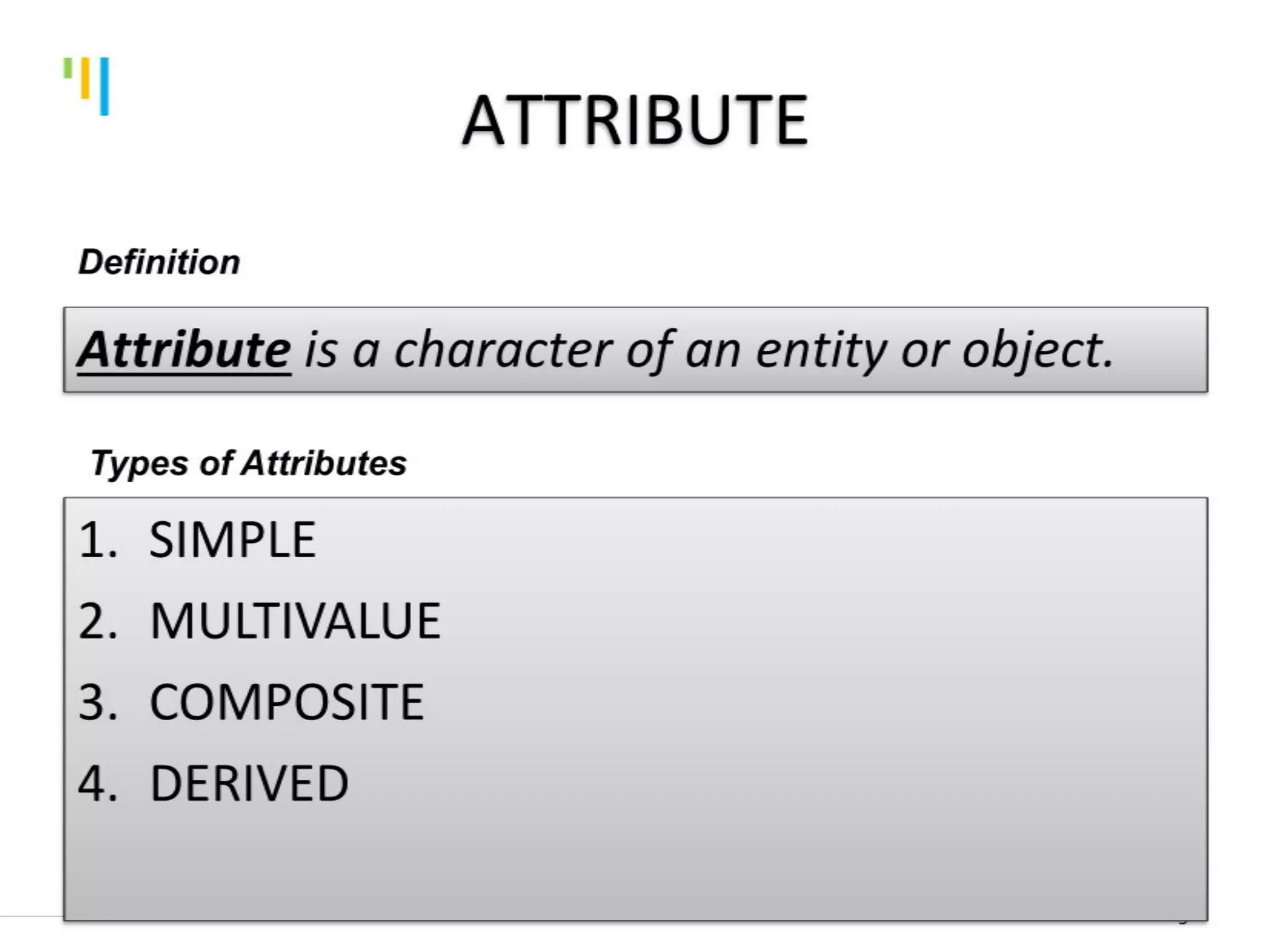
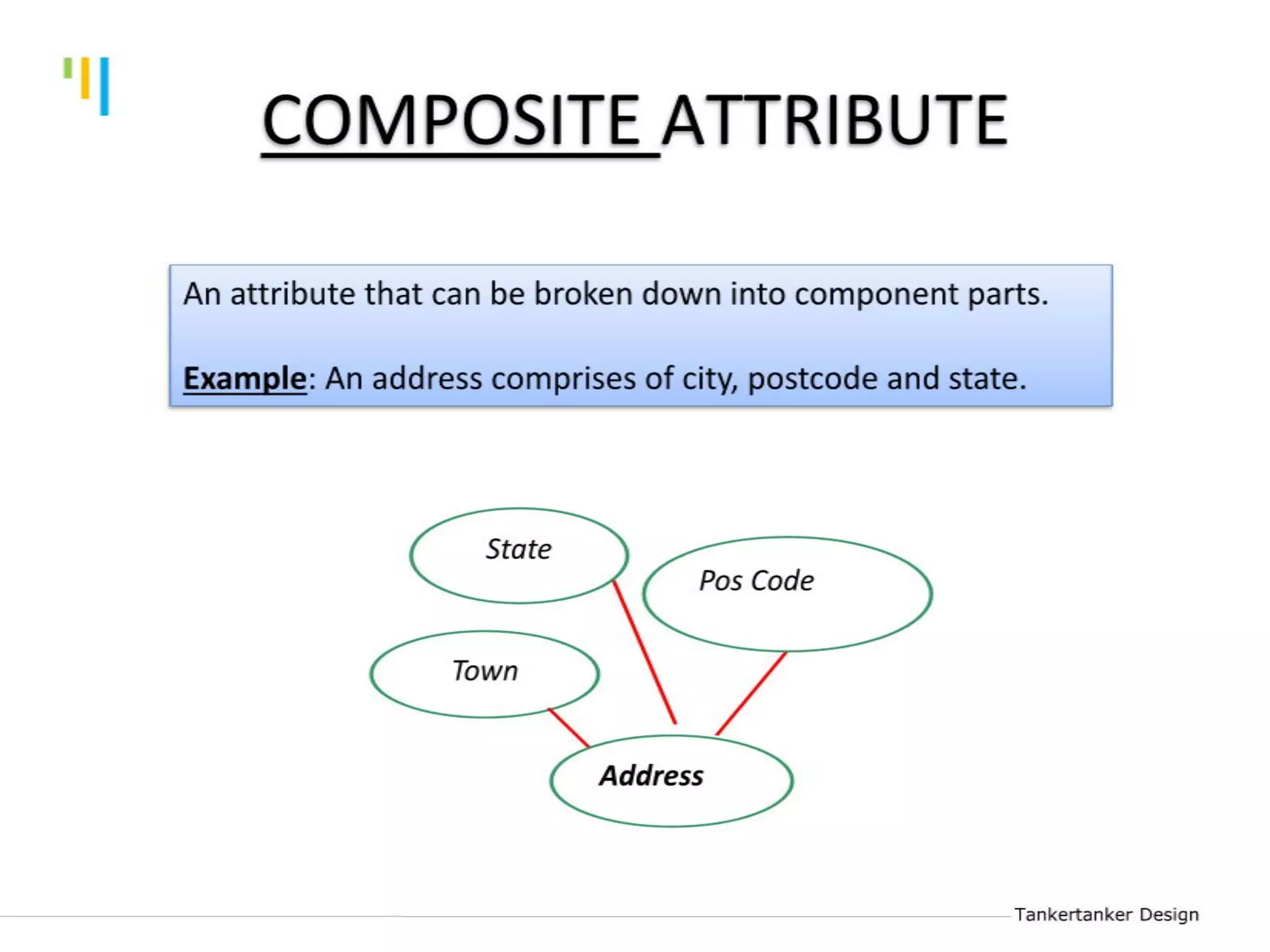
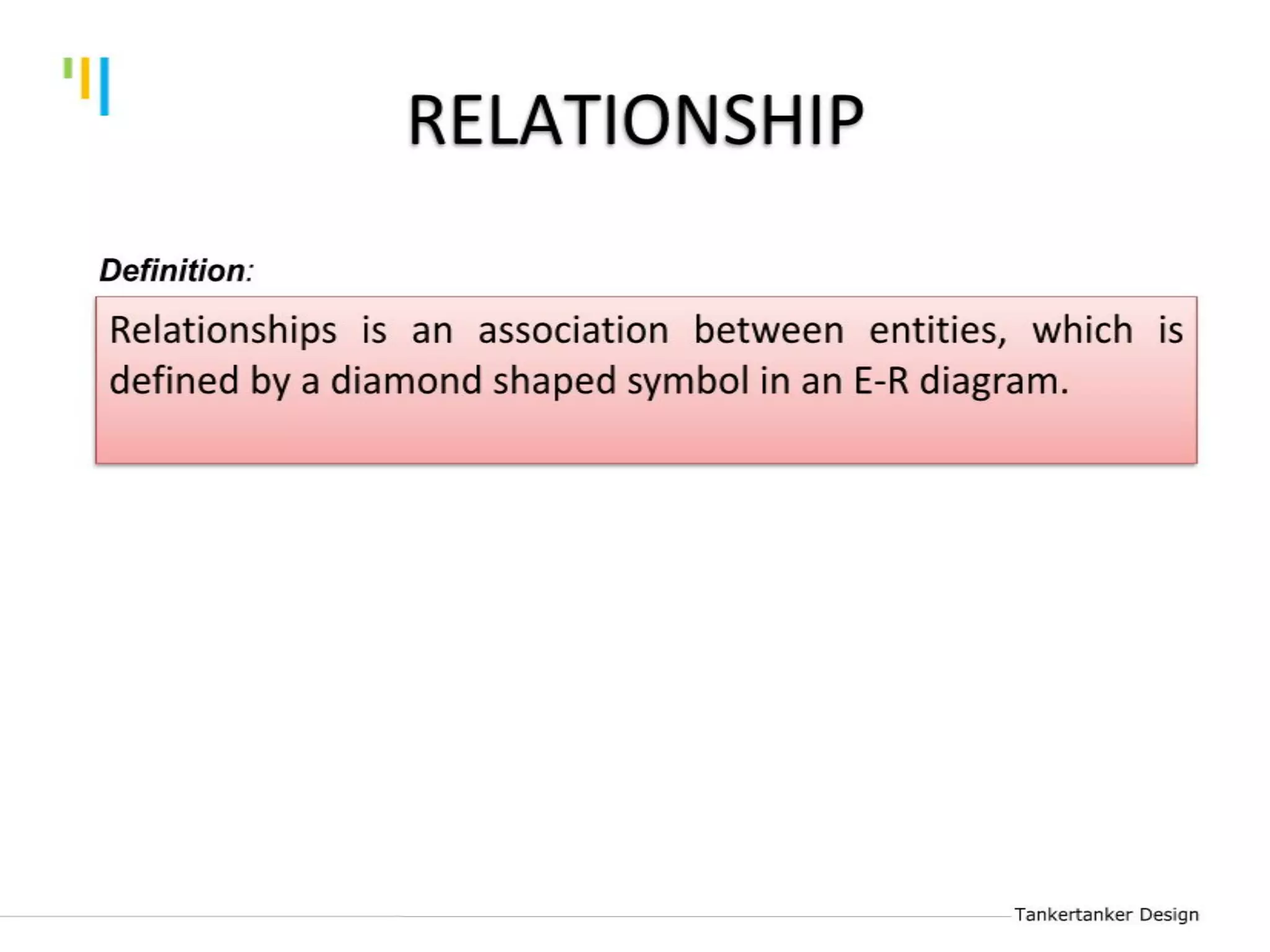
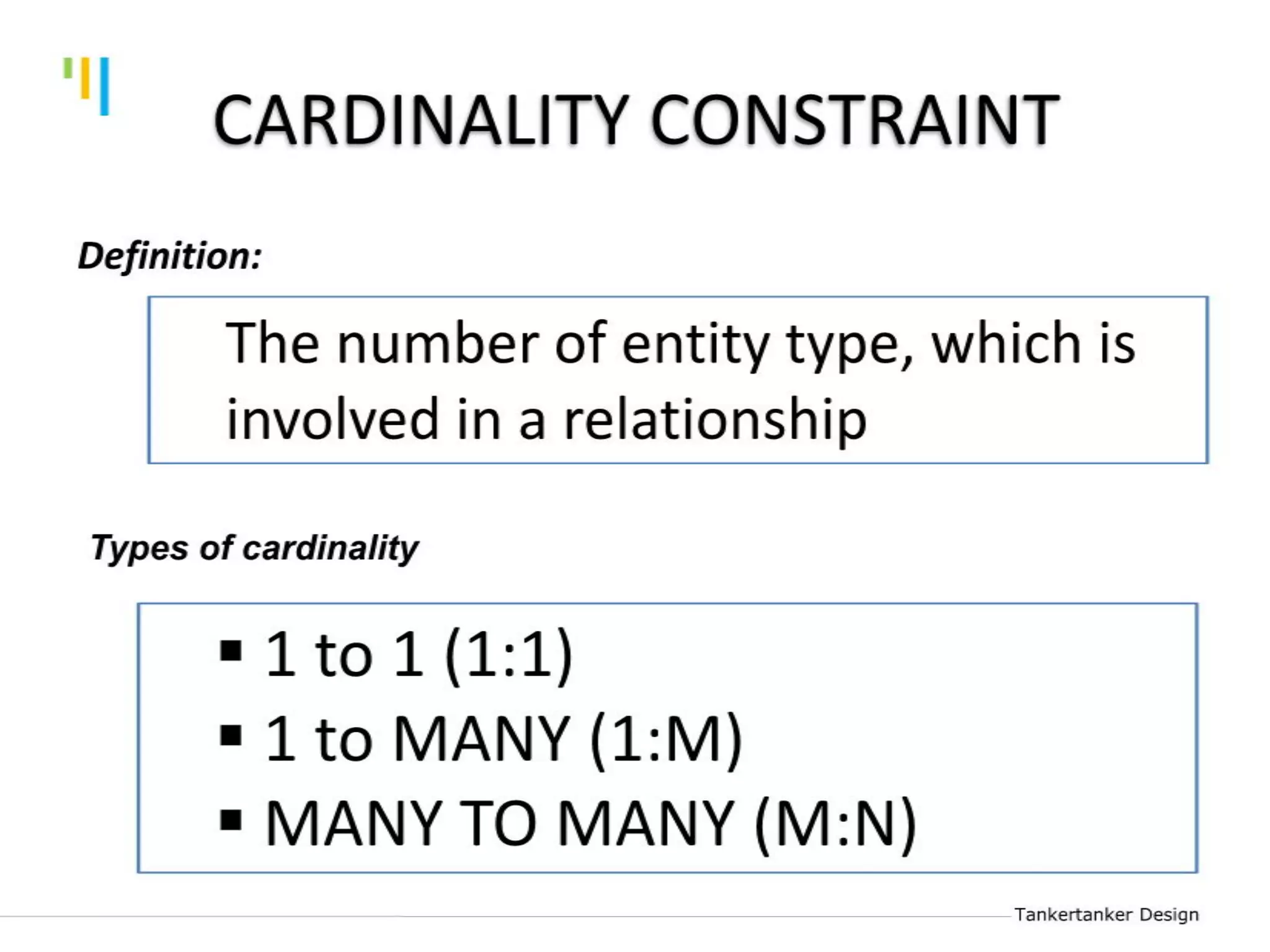
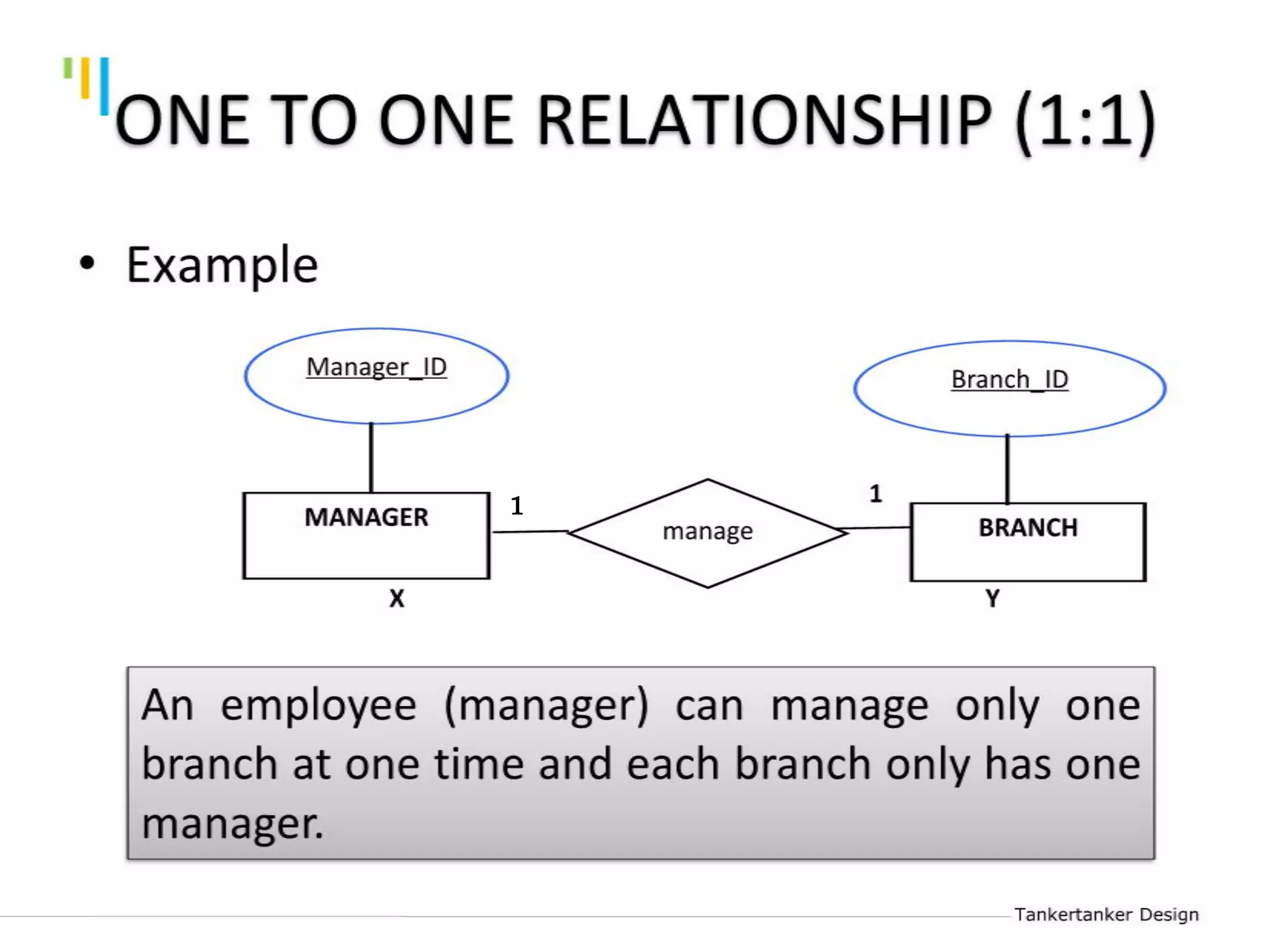
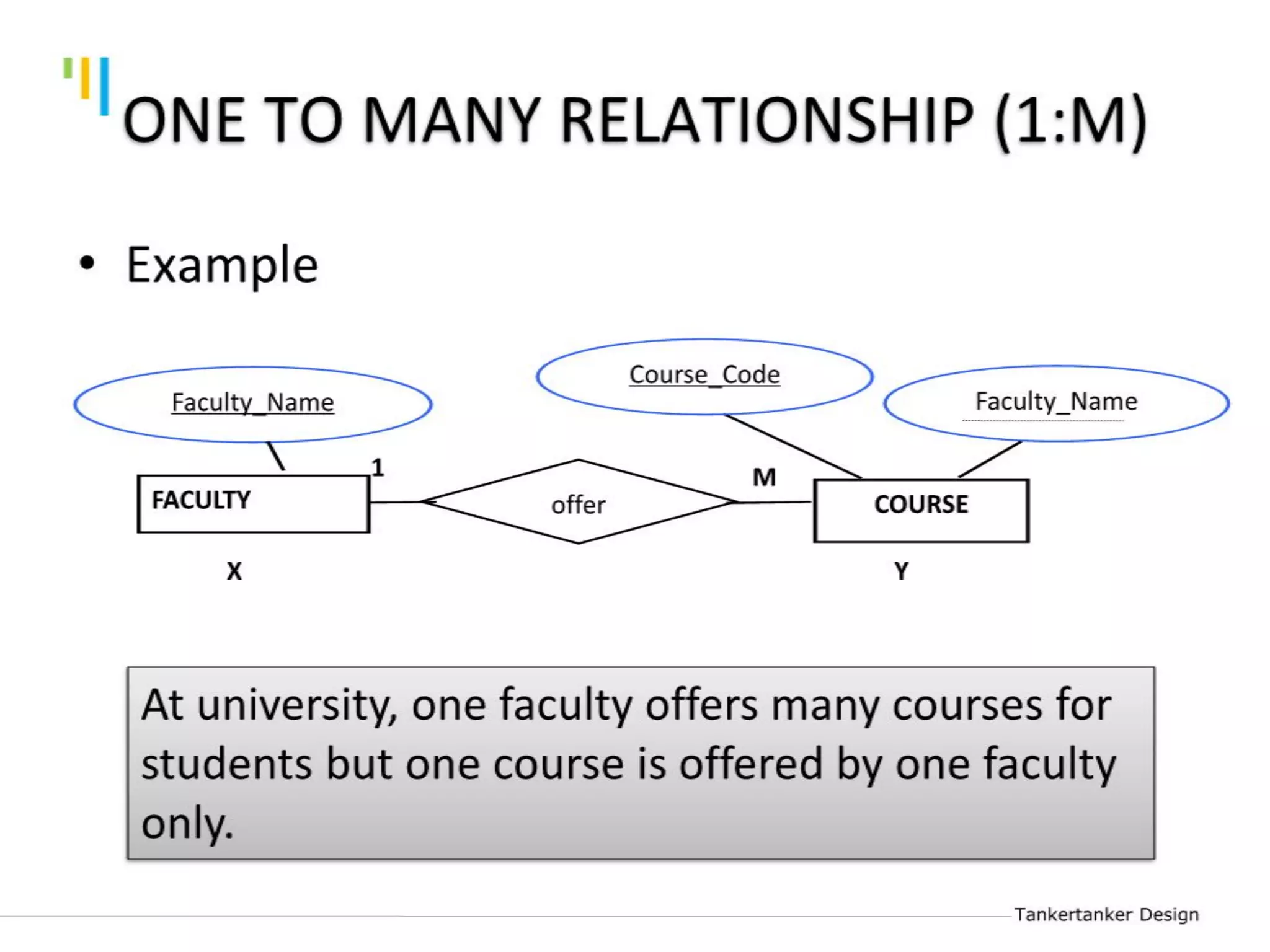
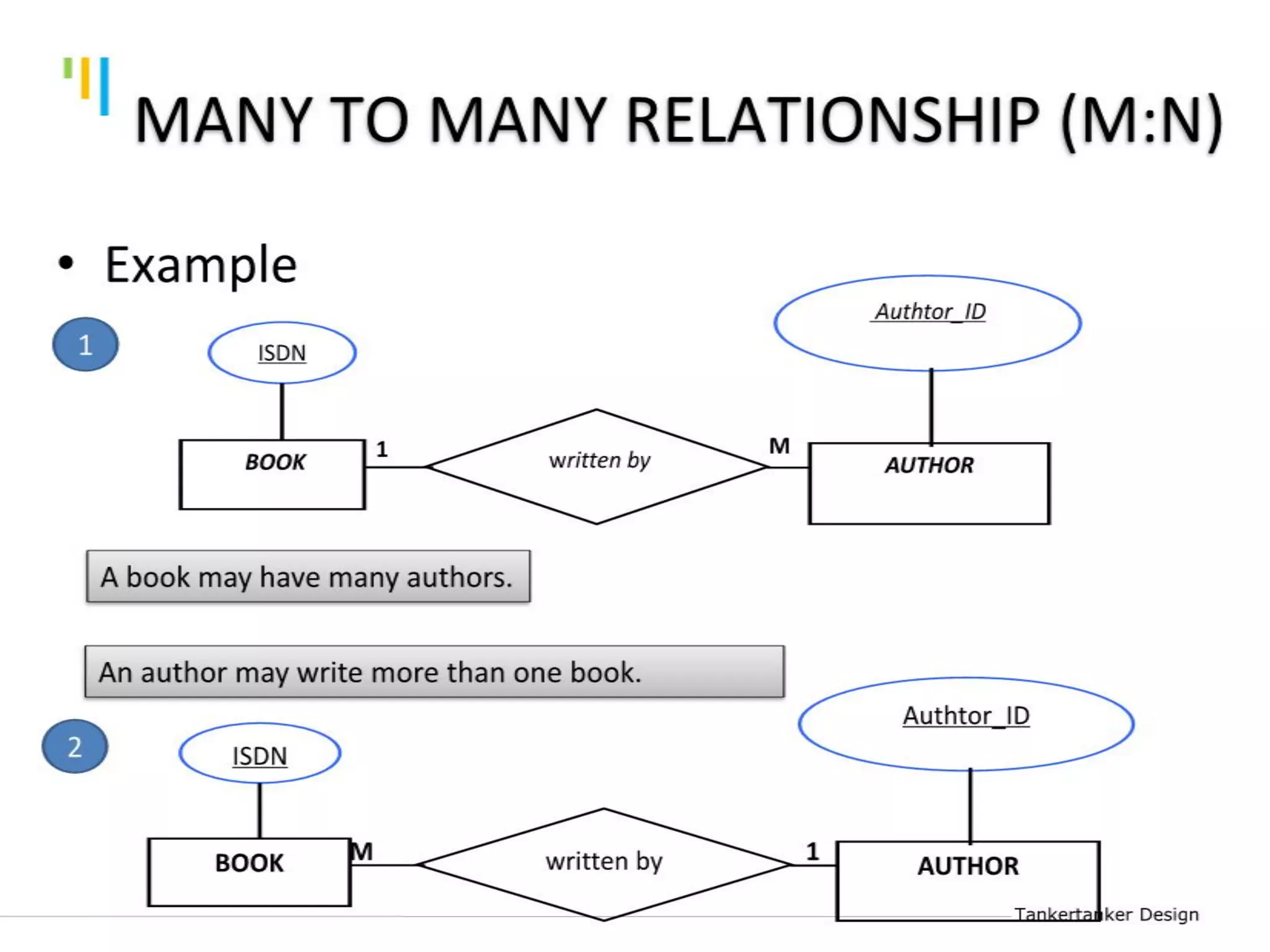
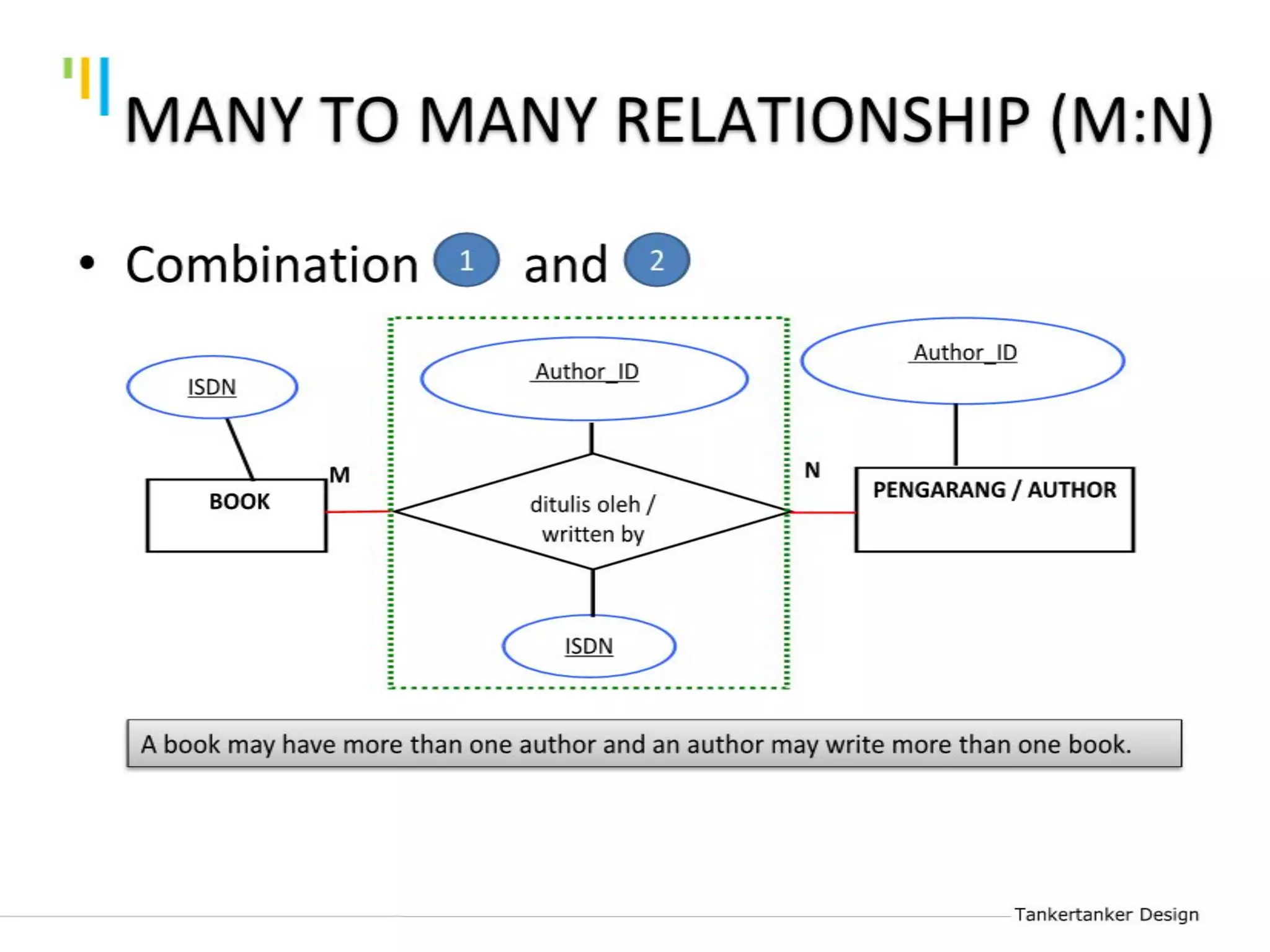
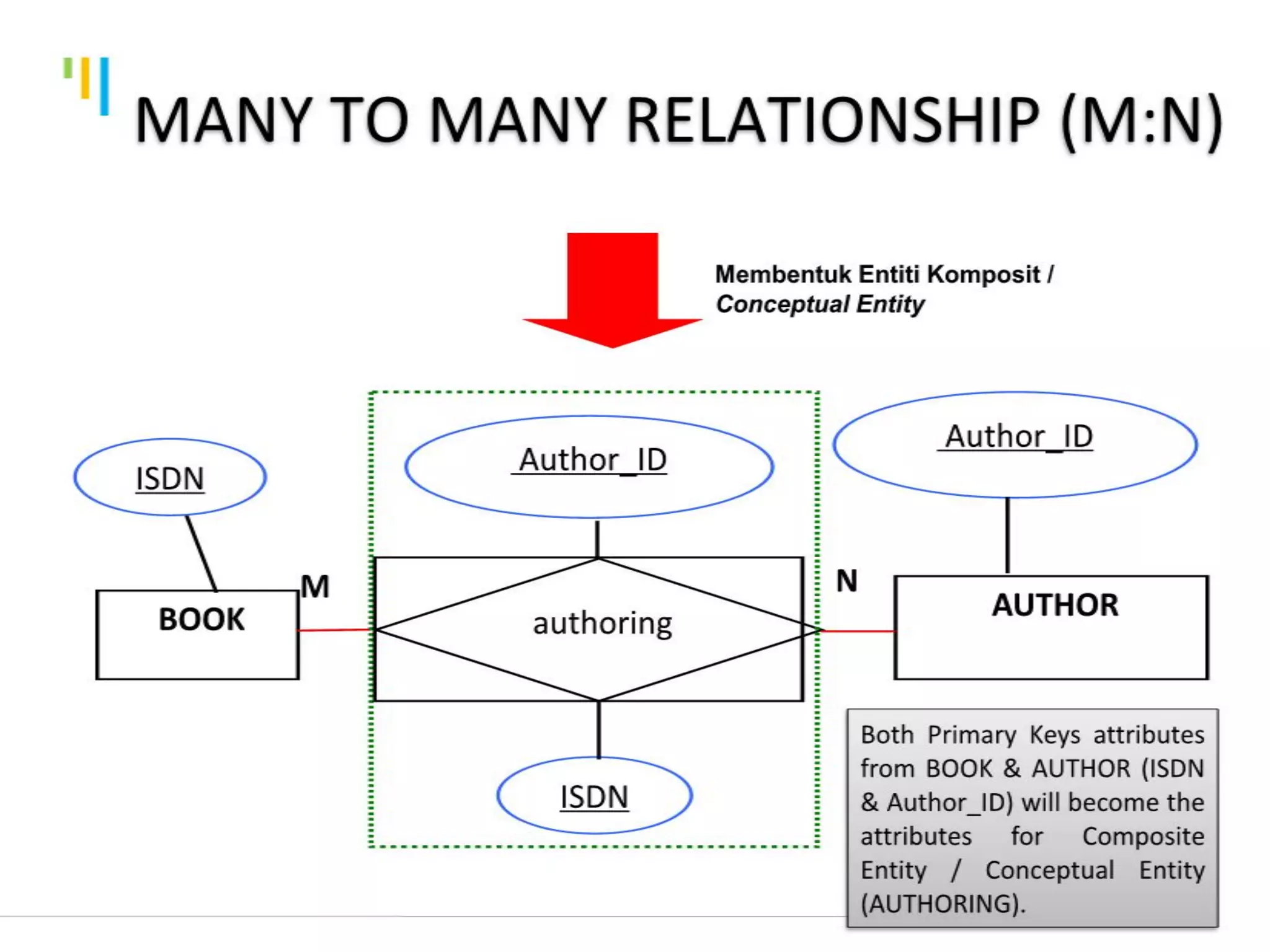
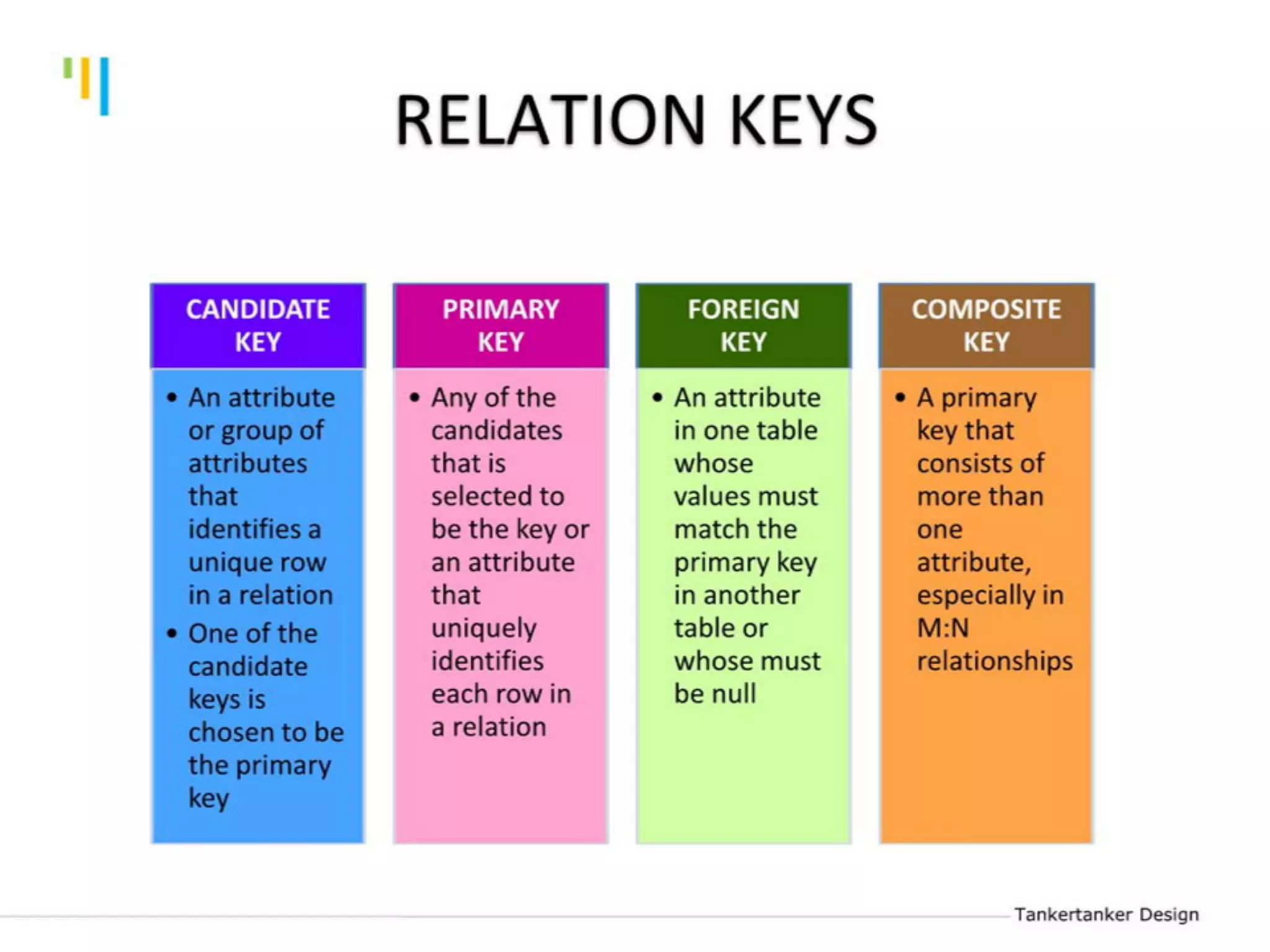
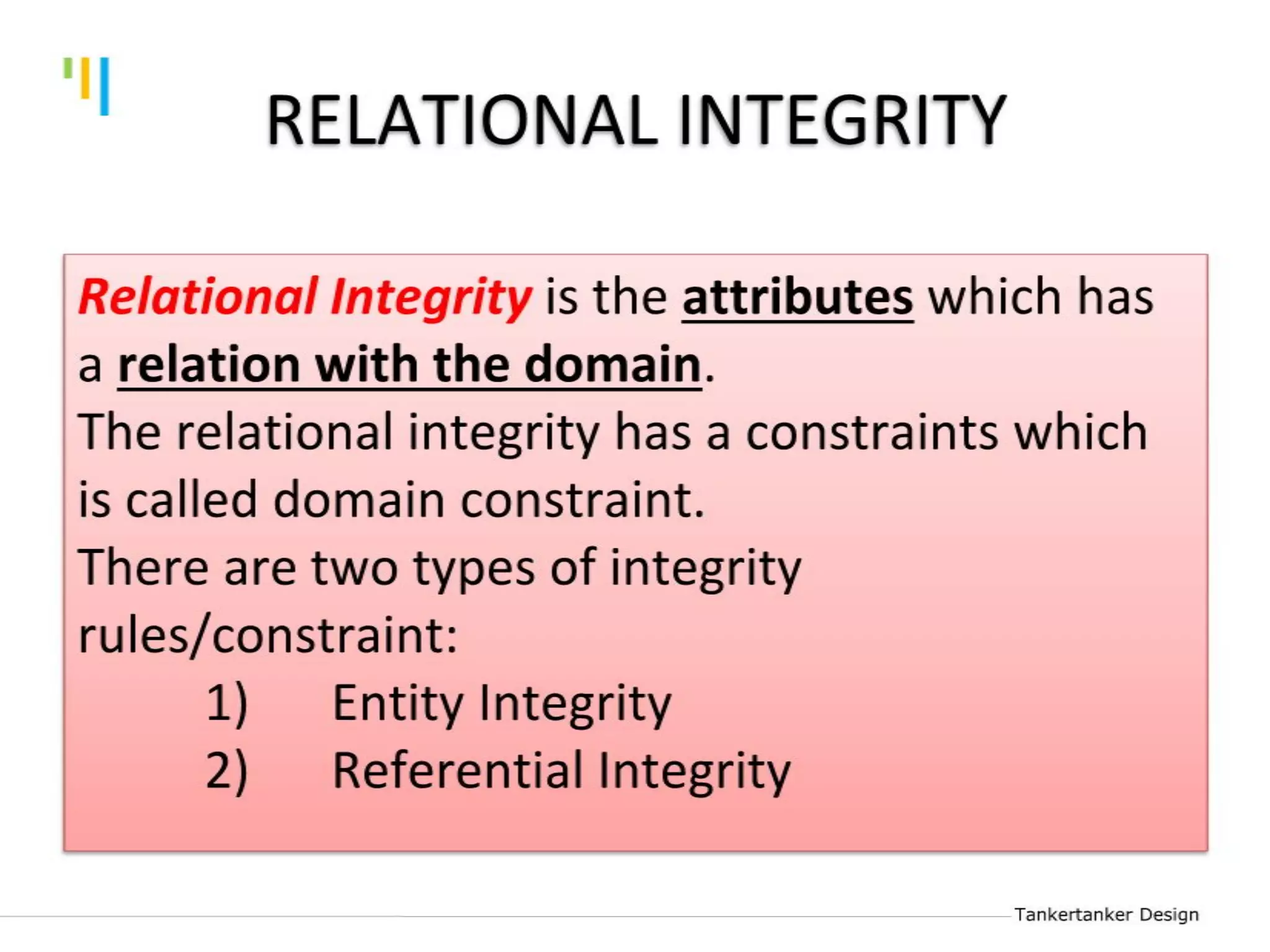
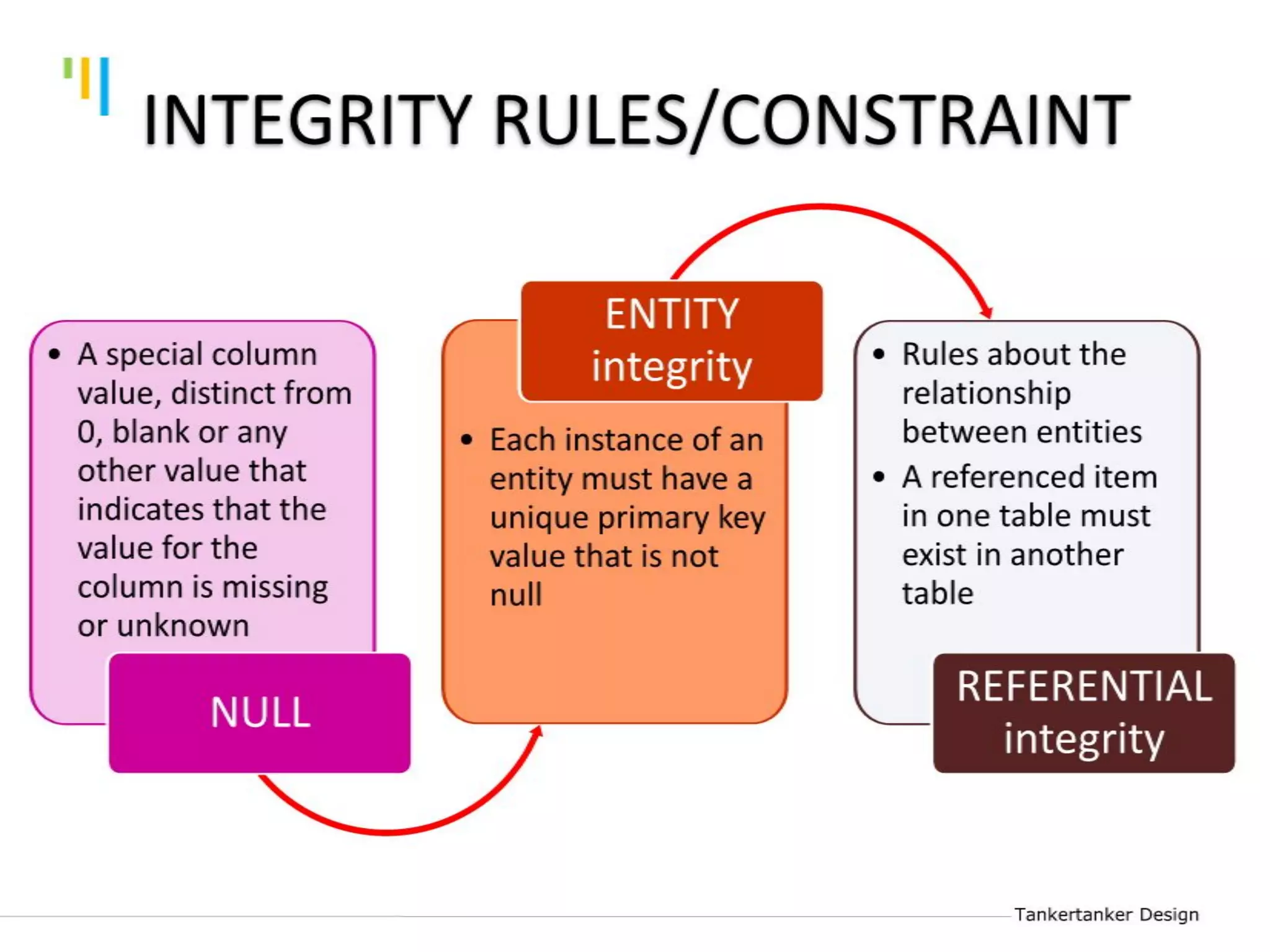
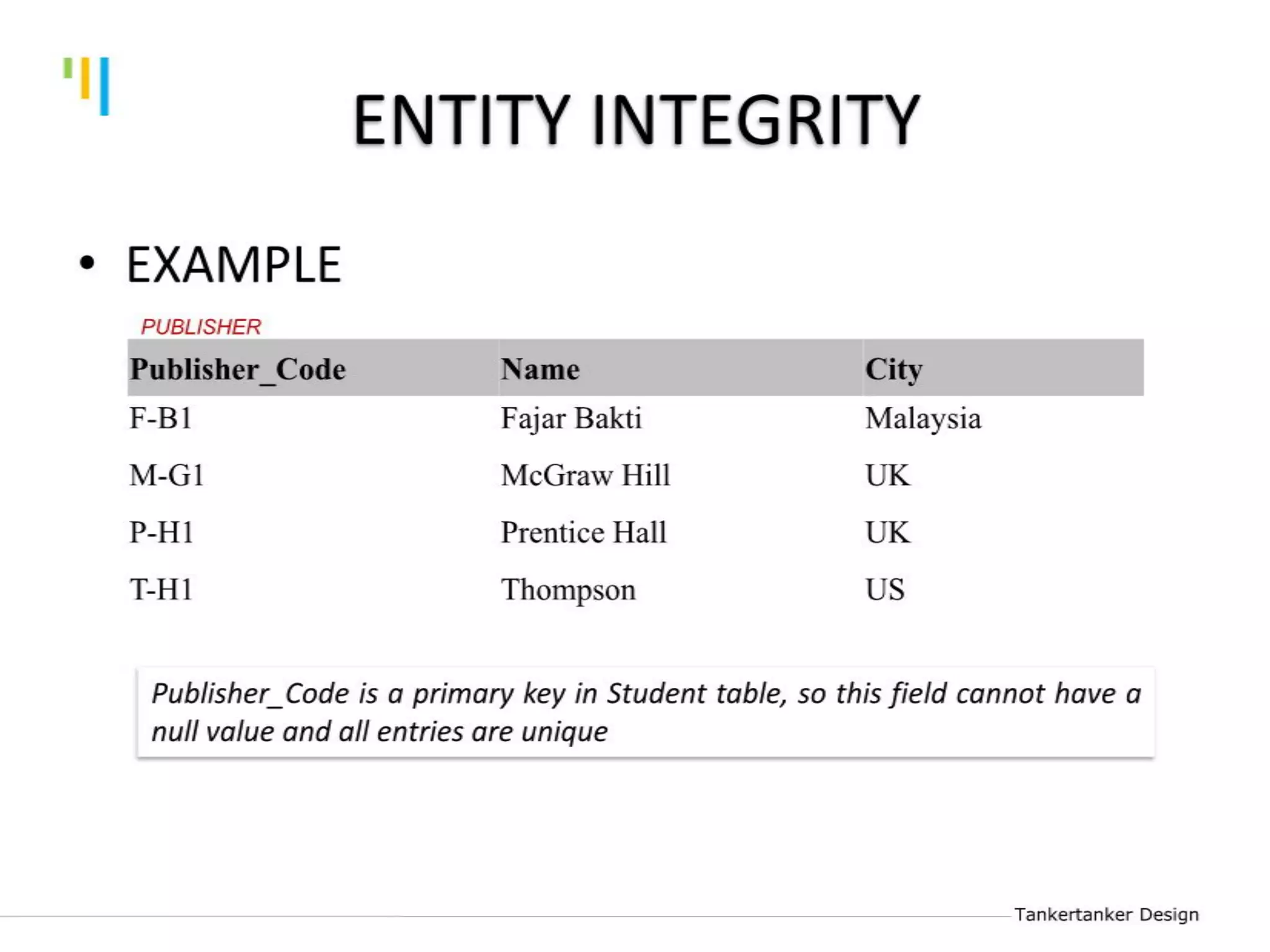
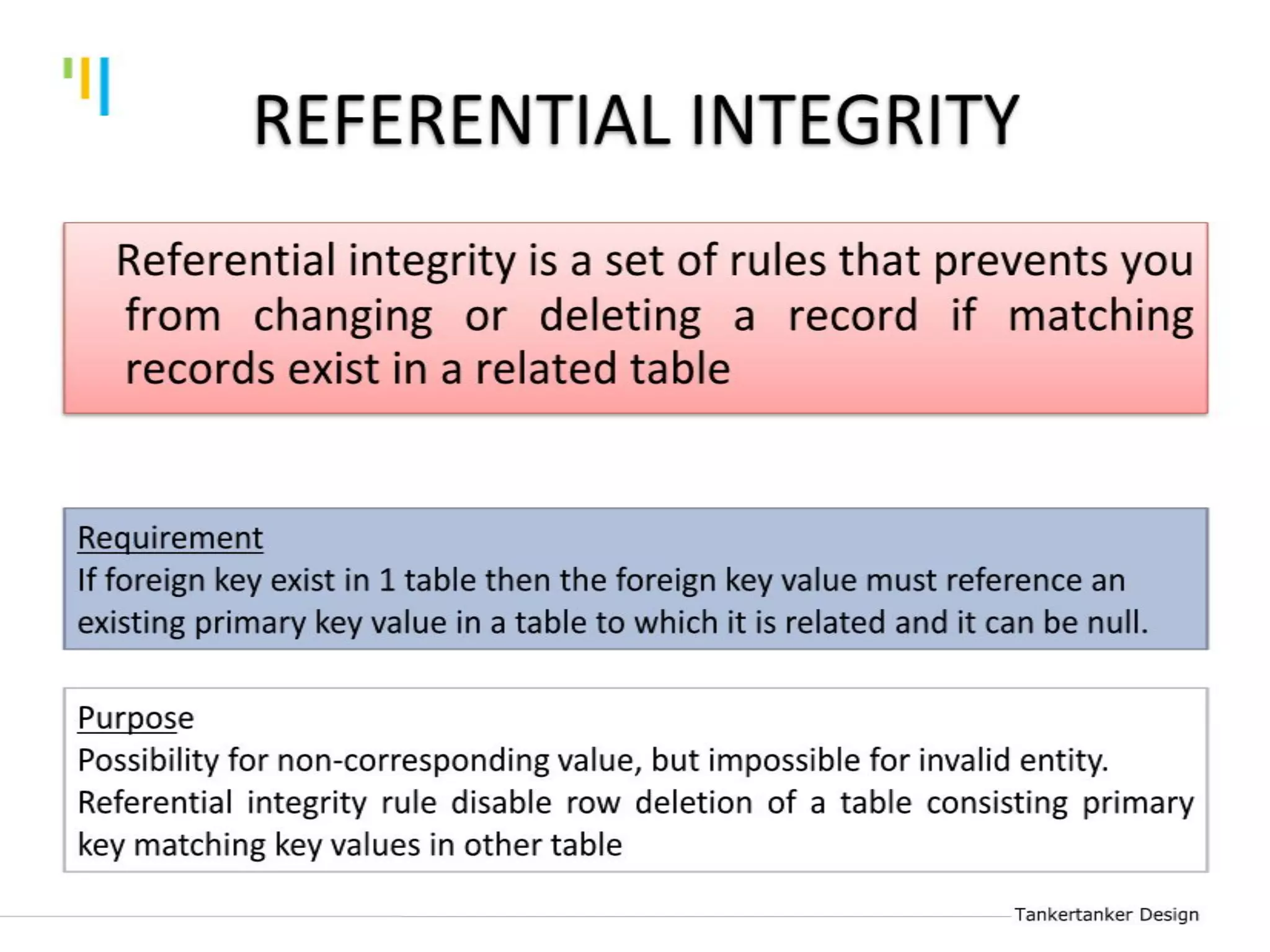
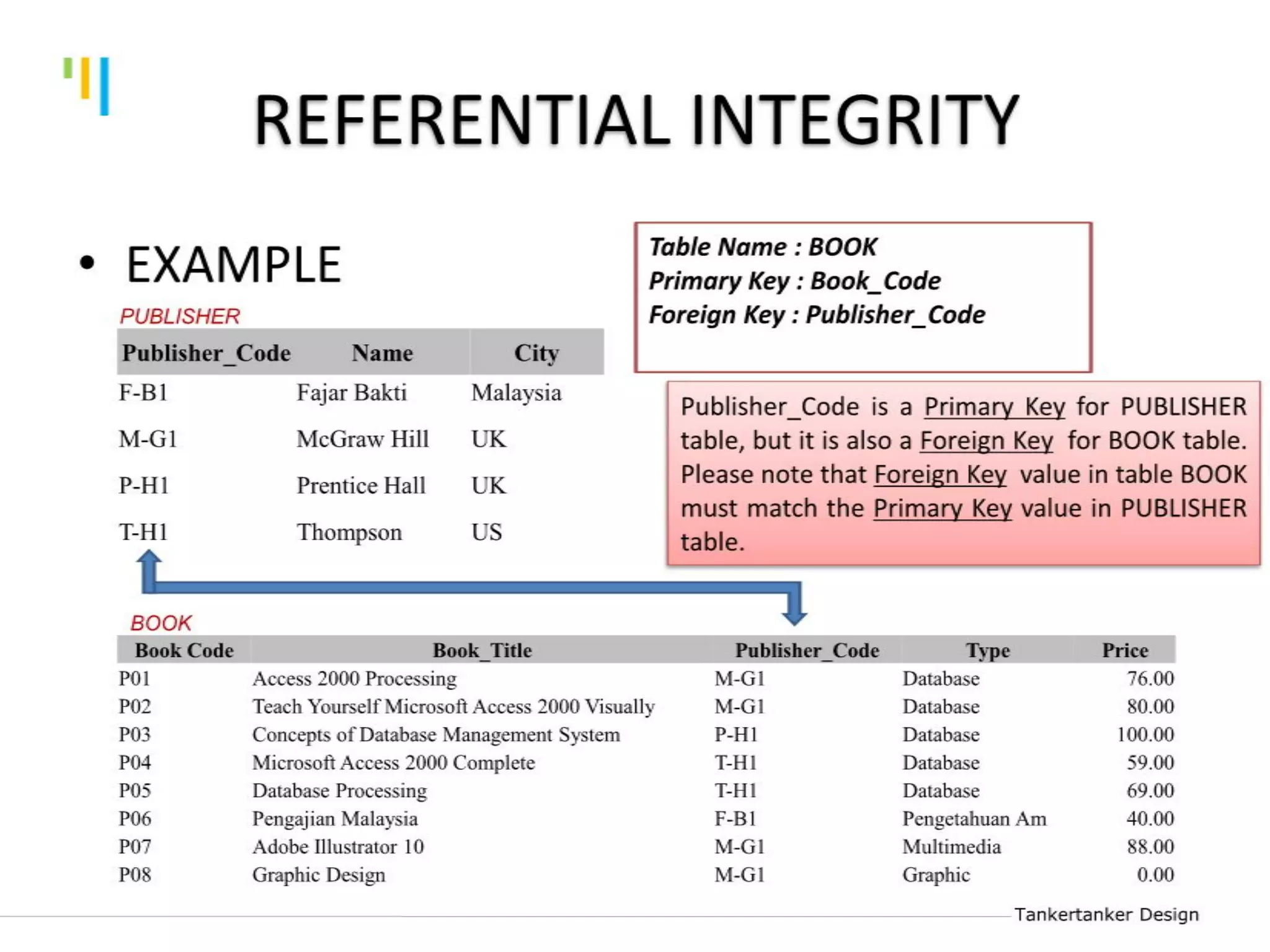
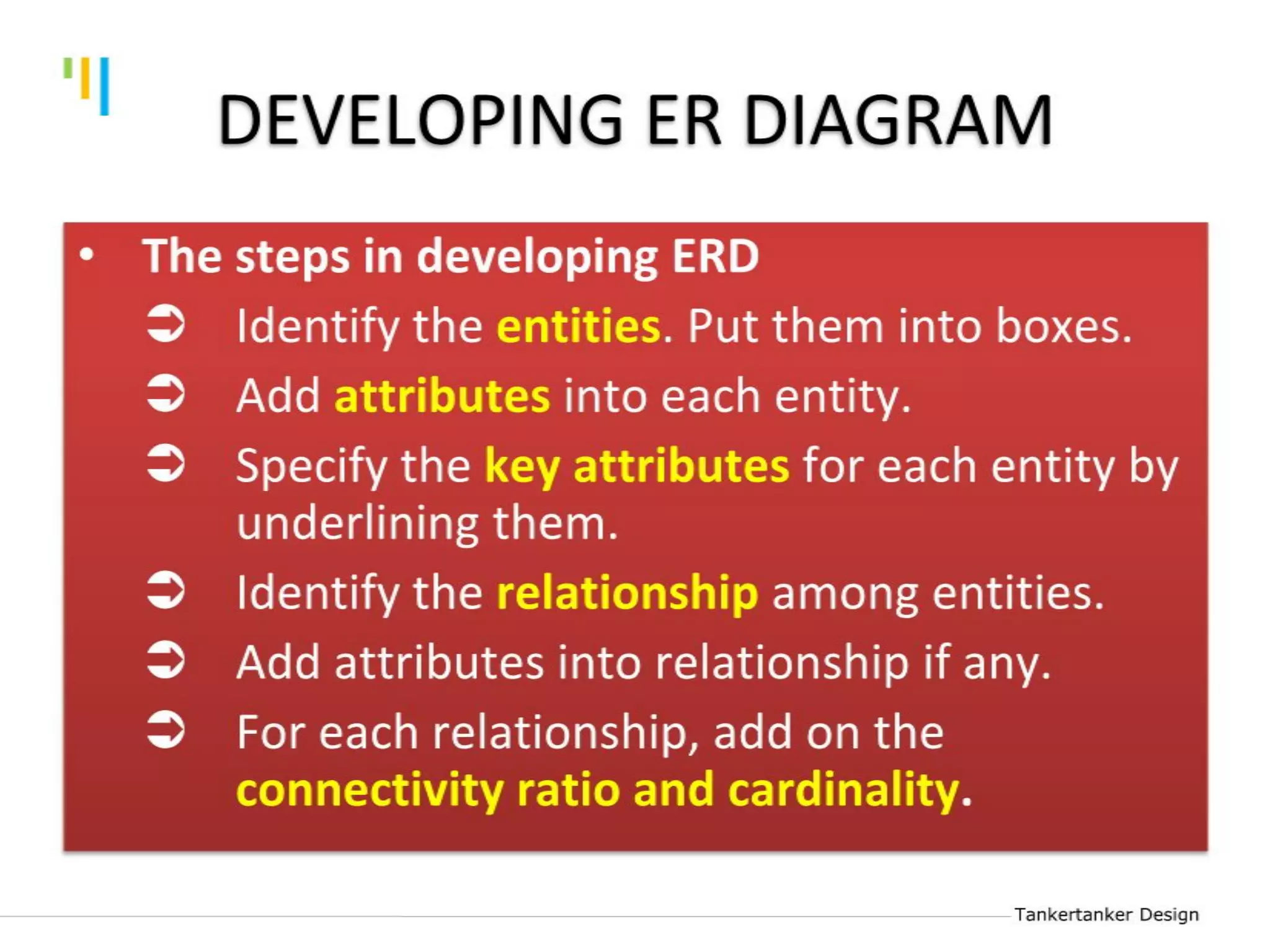
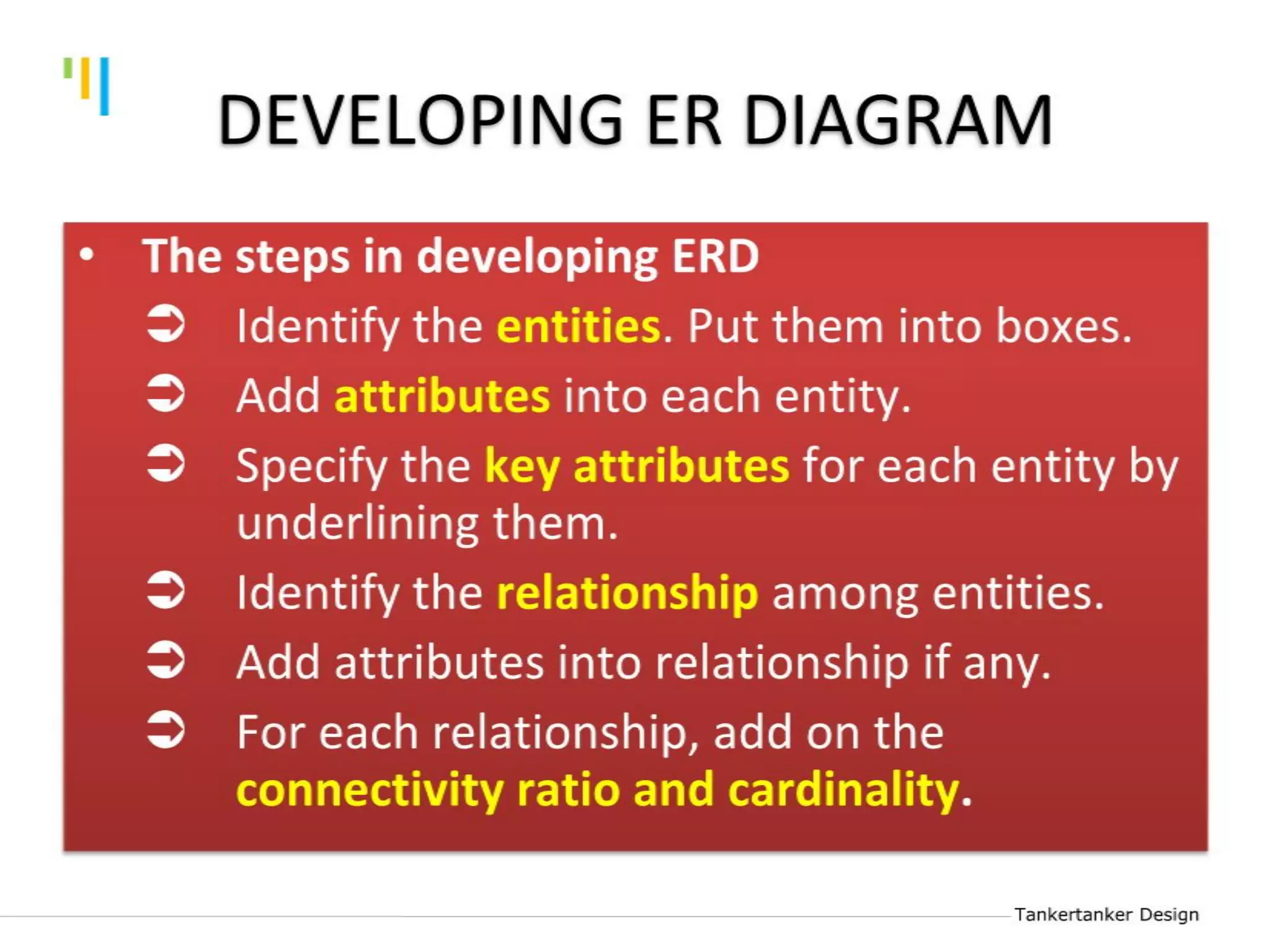
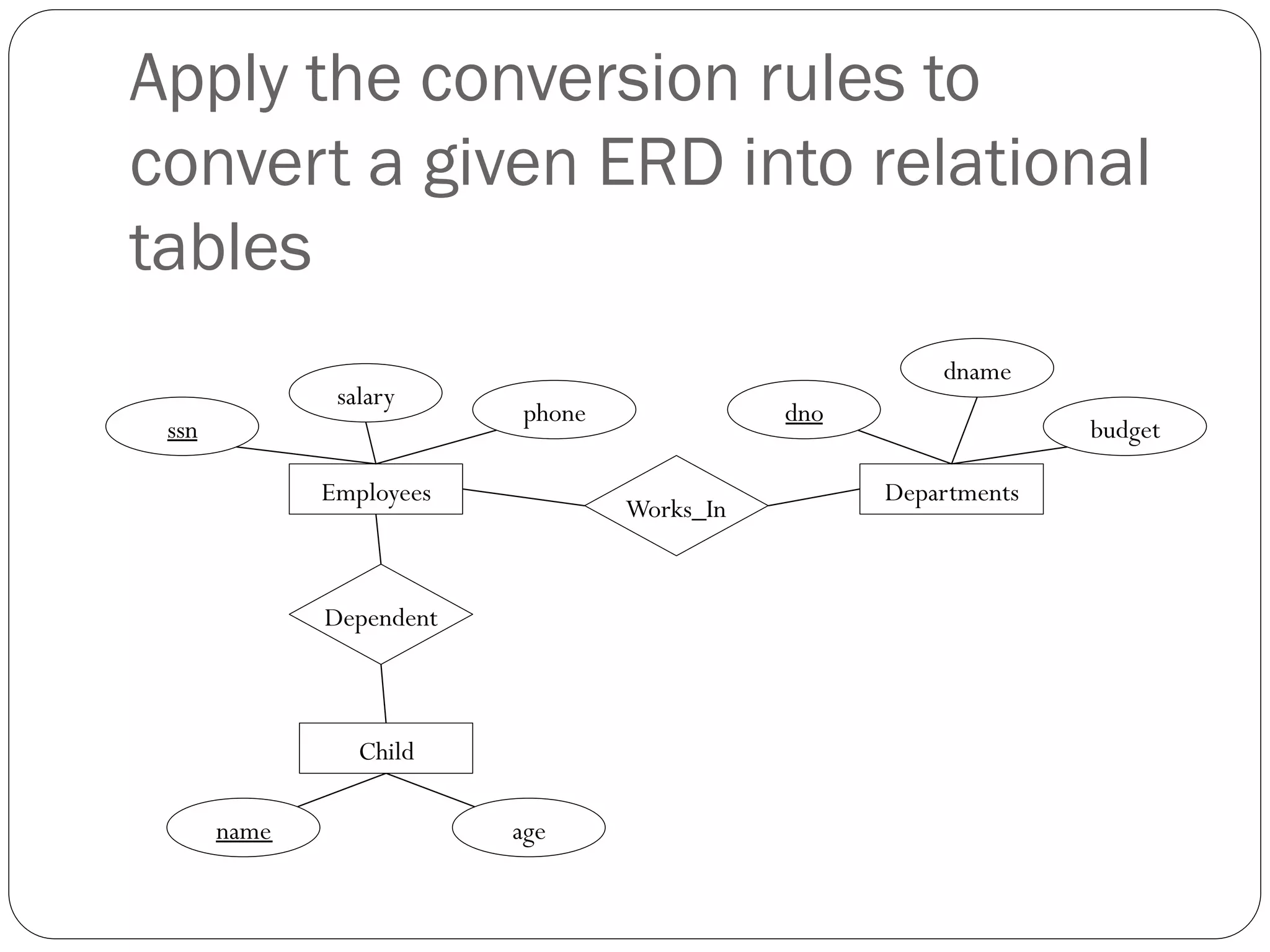
This document discusses database design using Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs). It covers how to draw ERDs using Chen's Model and Crow's Foot notations and define the basic elements of ERDs. Conversion rules are presented to convert ERDs into relational tables for one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships. An example is given to demonstrate drawing an ERD for a company database and converting it into relational tables.