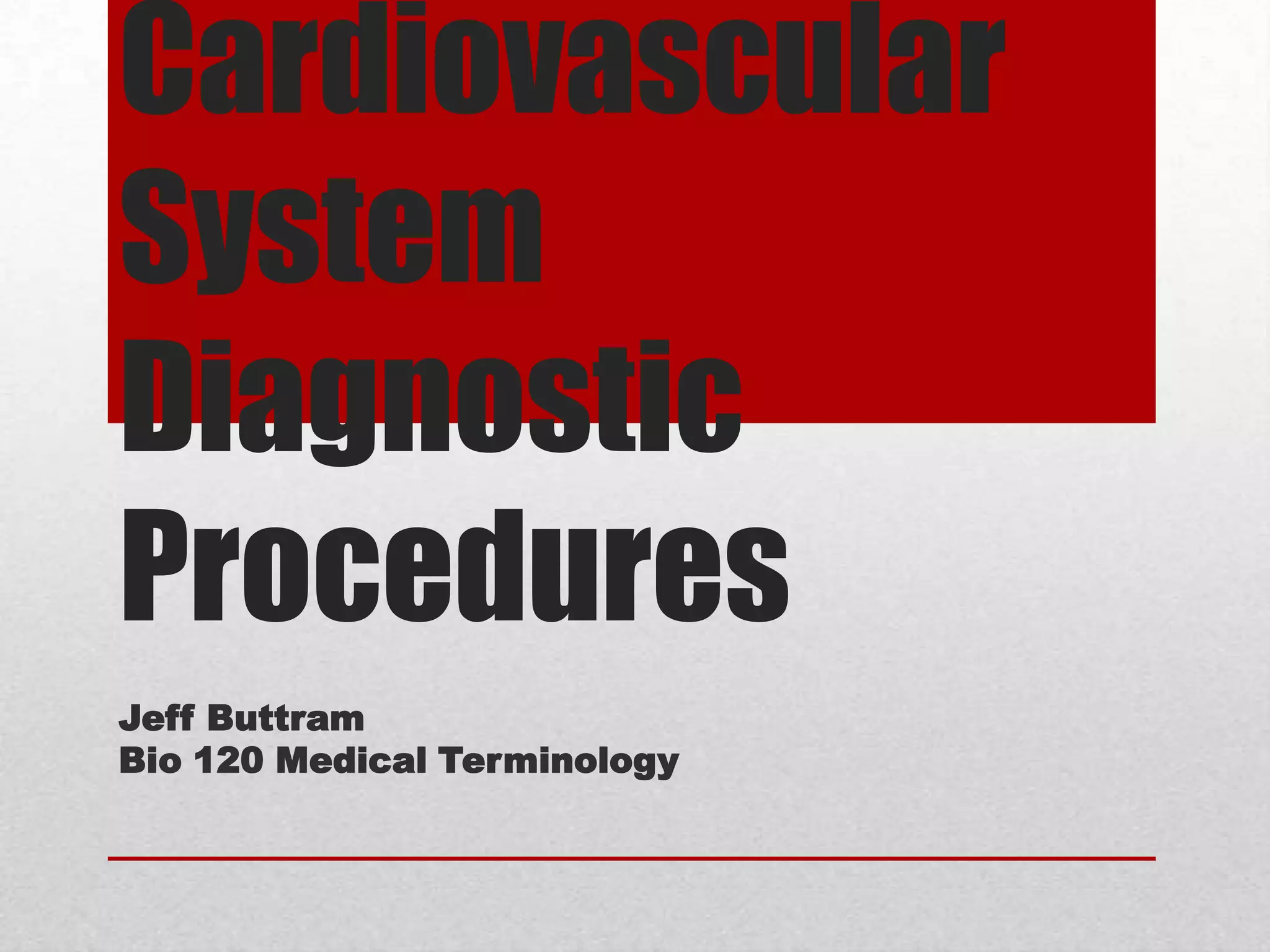
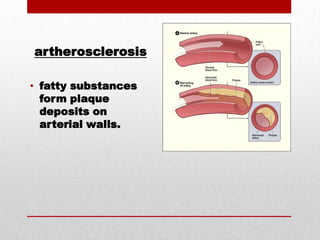
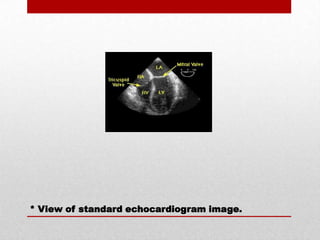
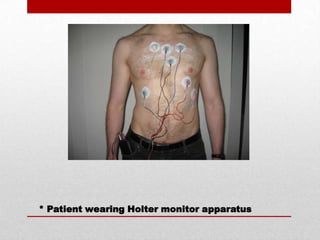
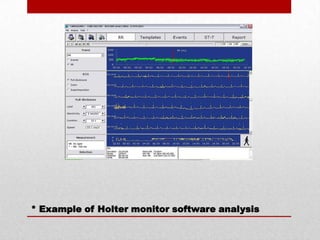
The document discusses three common cardiovascular diagnostic procedures: serum lipoprotein levels tests, echocardiography, and Holter monitor tests. Serum lipoprotein levels tests measure cholesterol and triglyceride levels in blood to determine risk for atherosclerosis. Echocardiography uses ultrasound to visualize the heart's structures and evaluate valves and pumping function. Holter monitors continuously measure heart electrical activity over hours to days to detect arrhythmias.