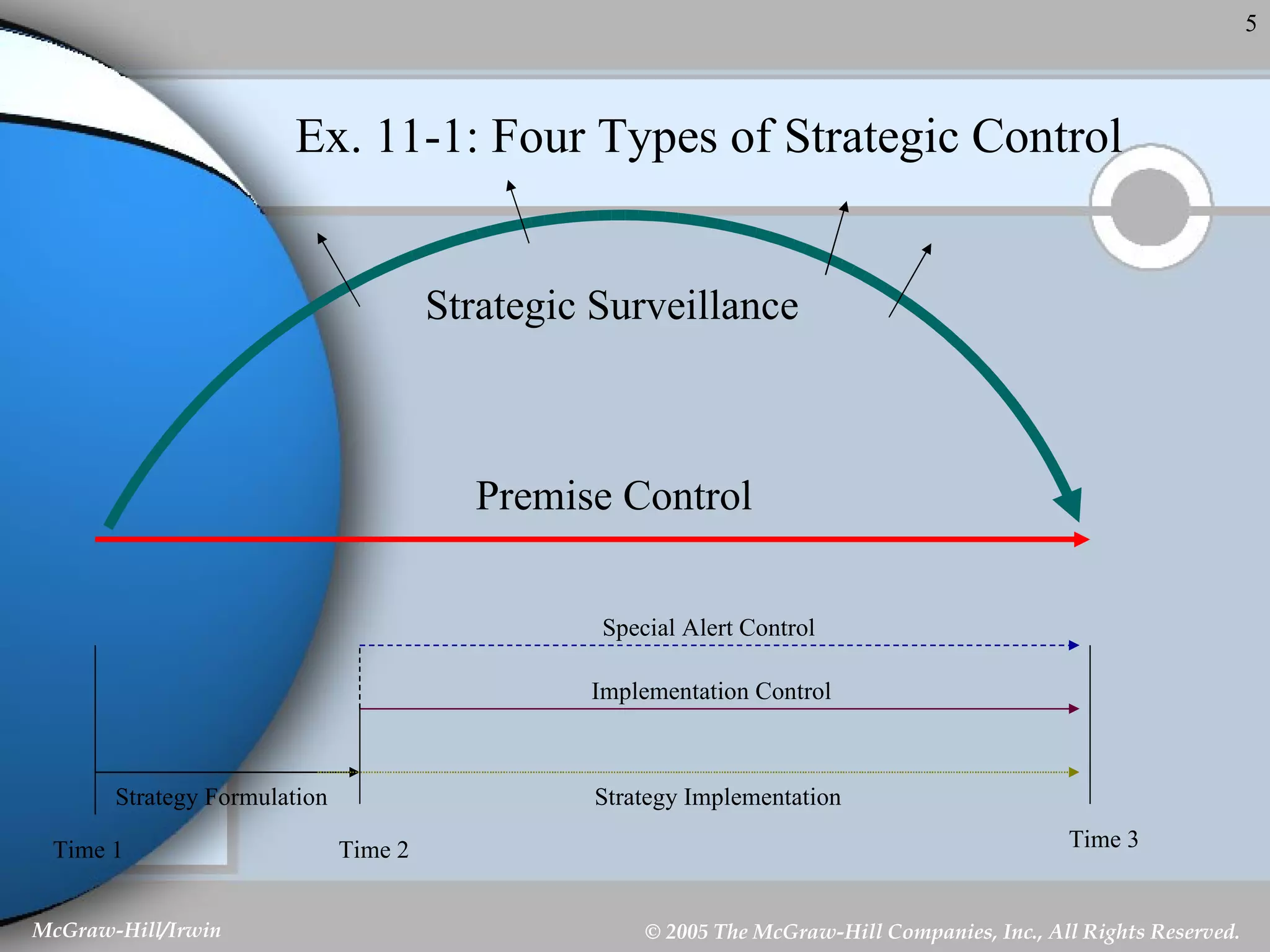
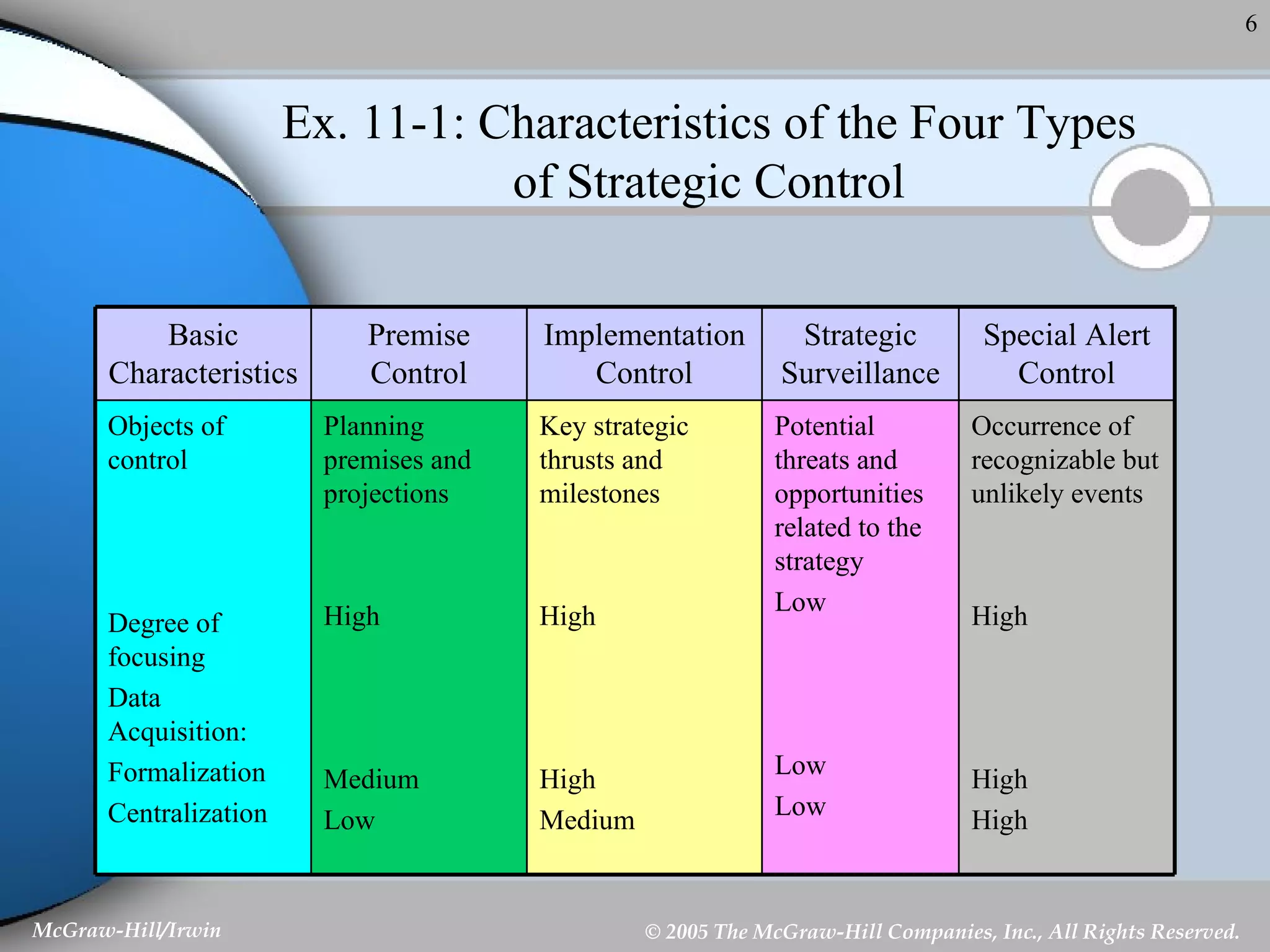
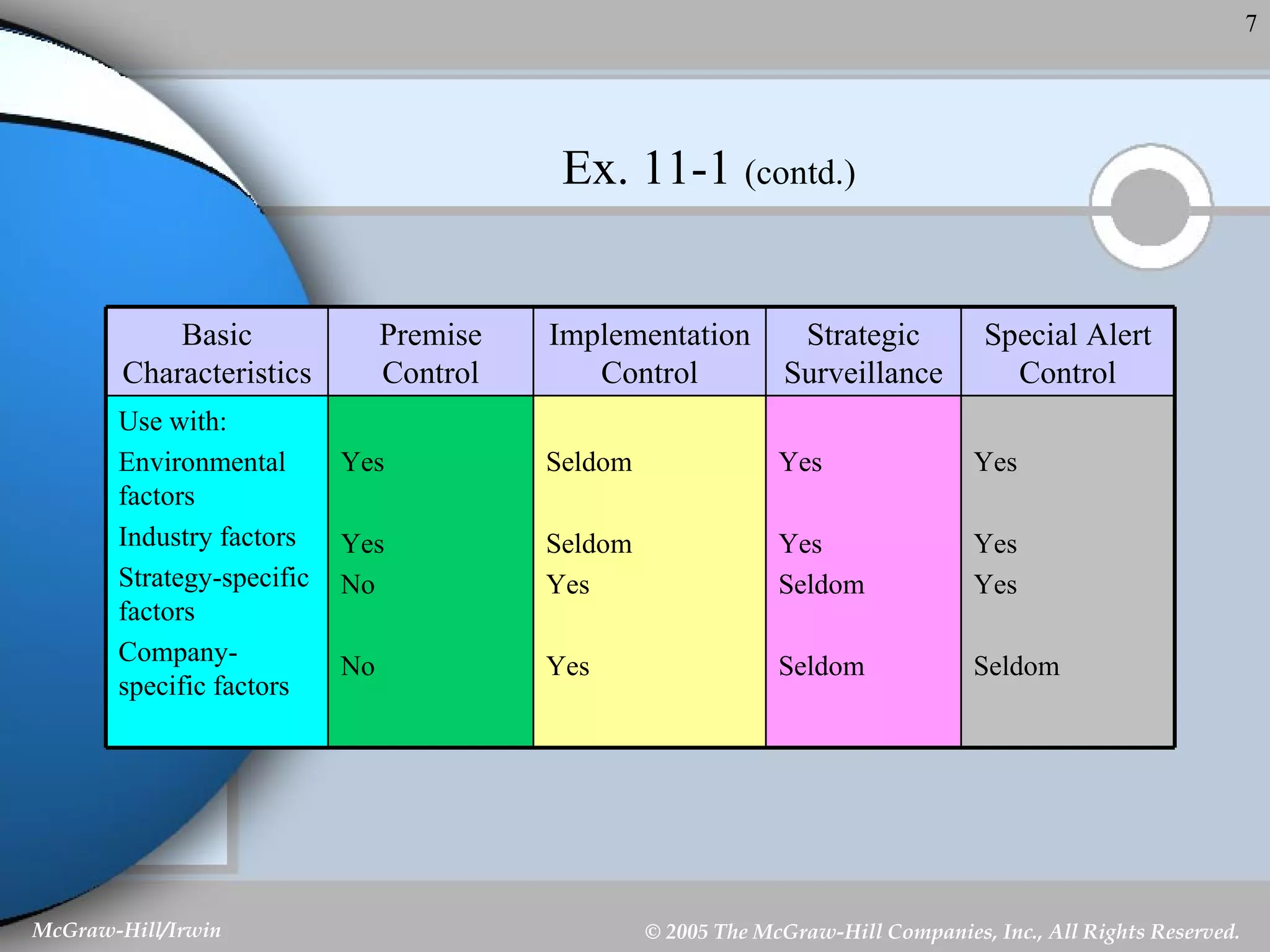
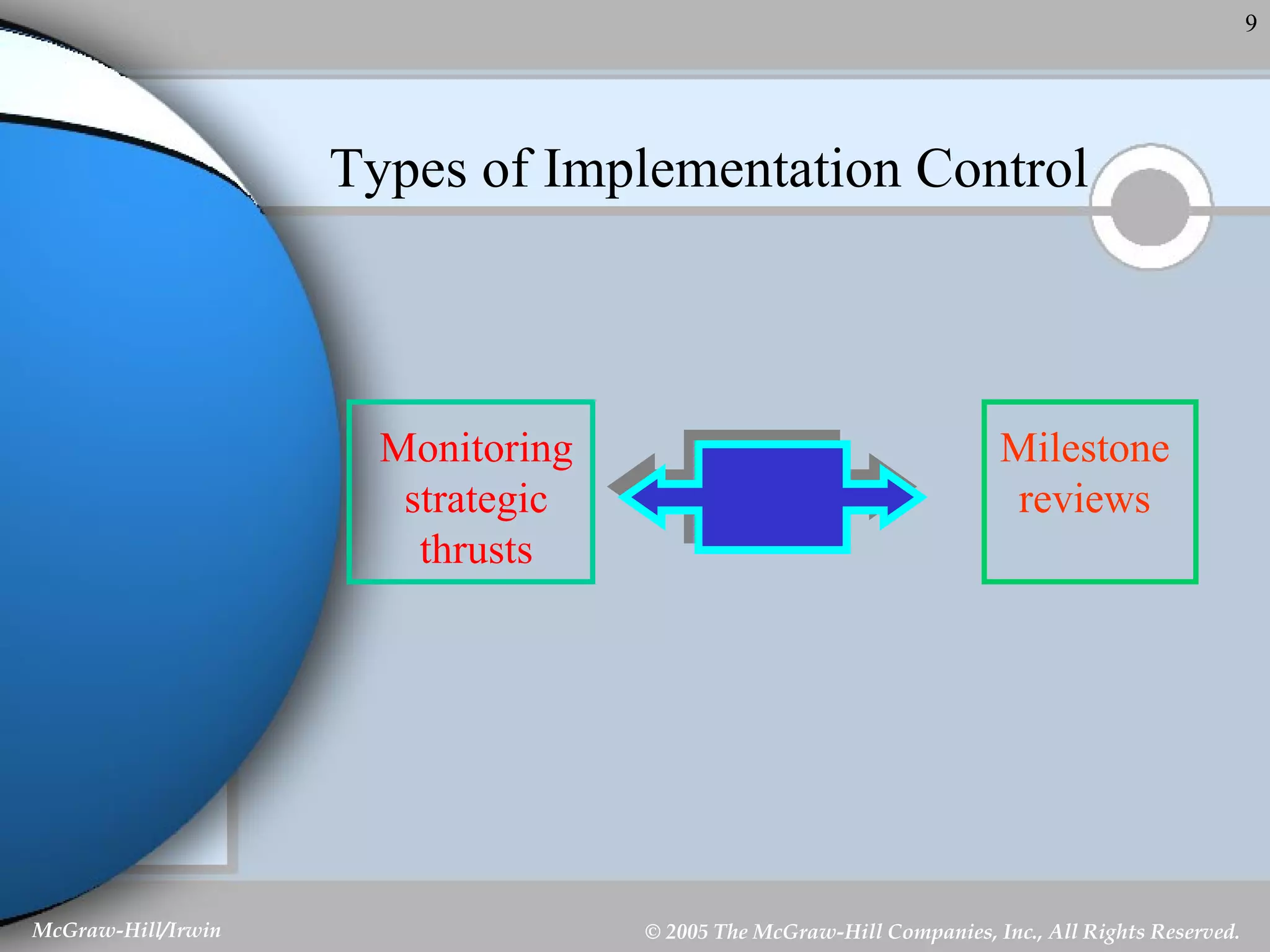
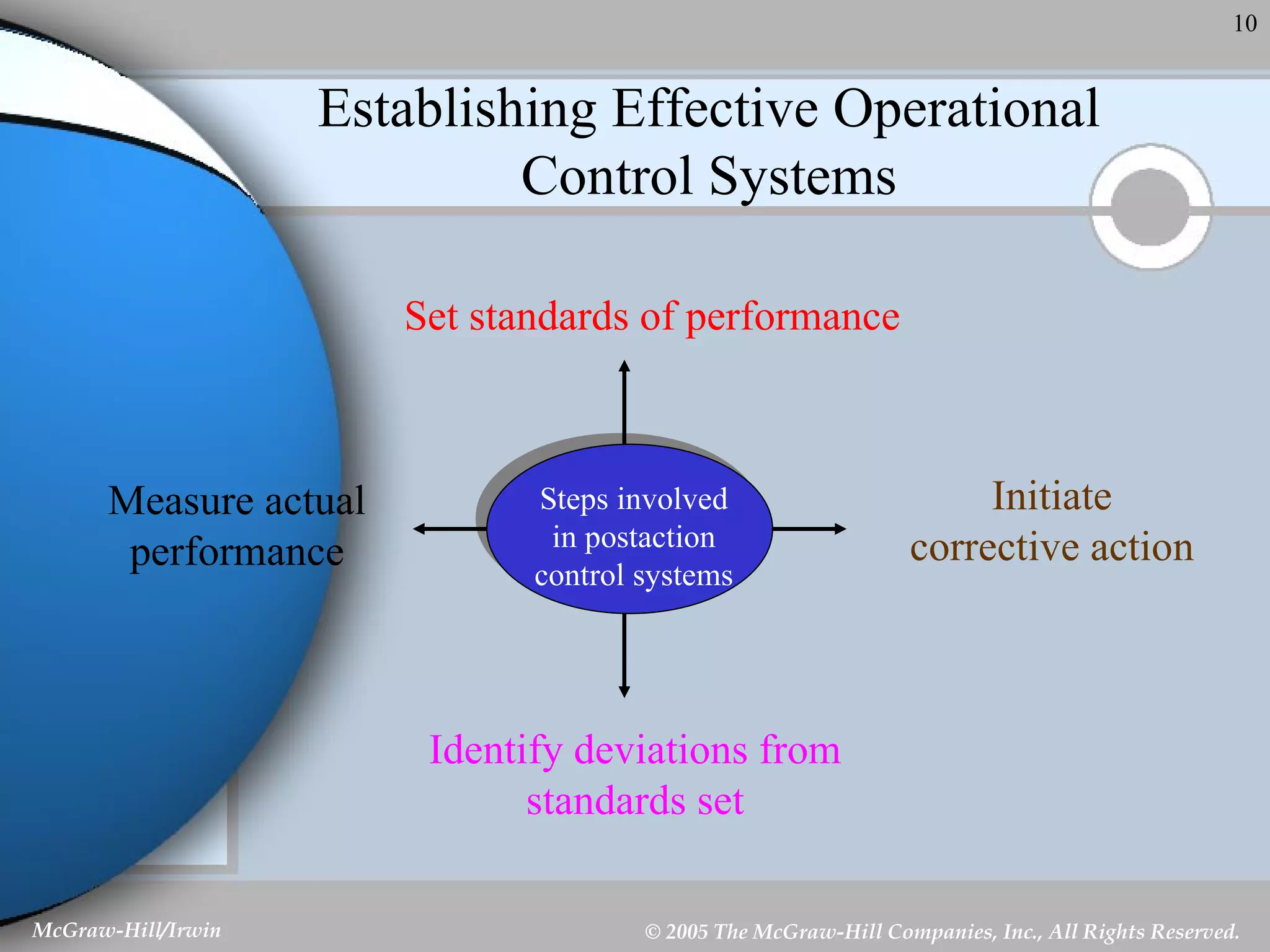
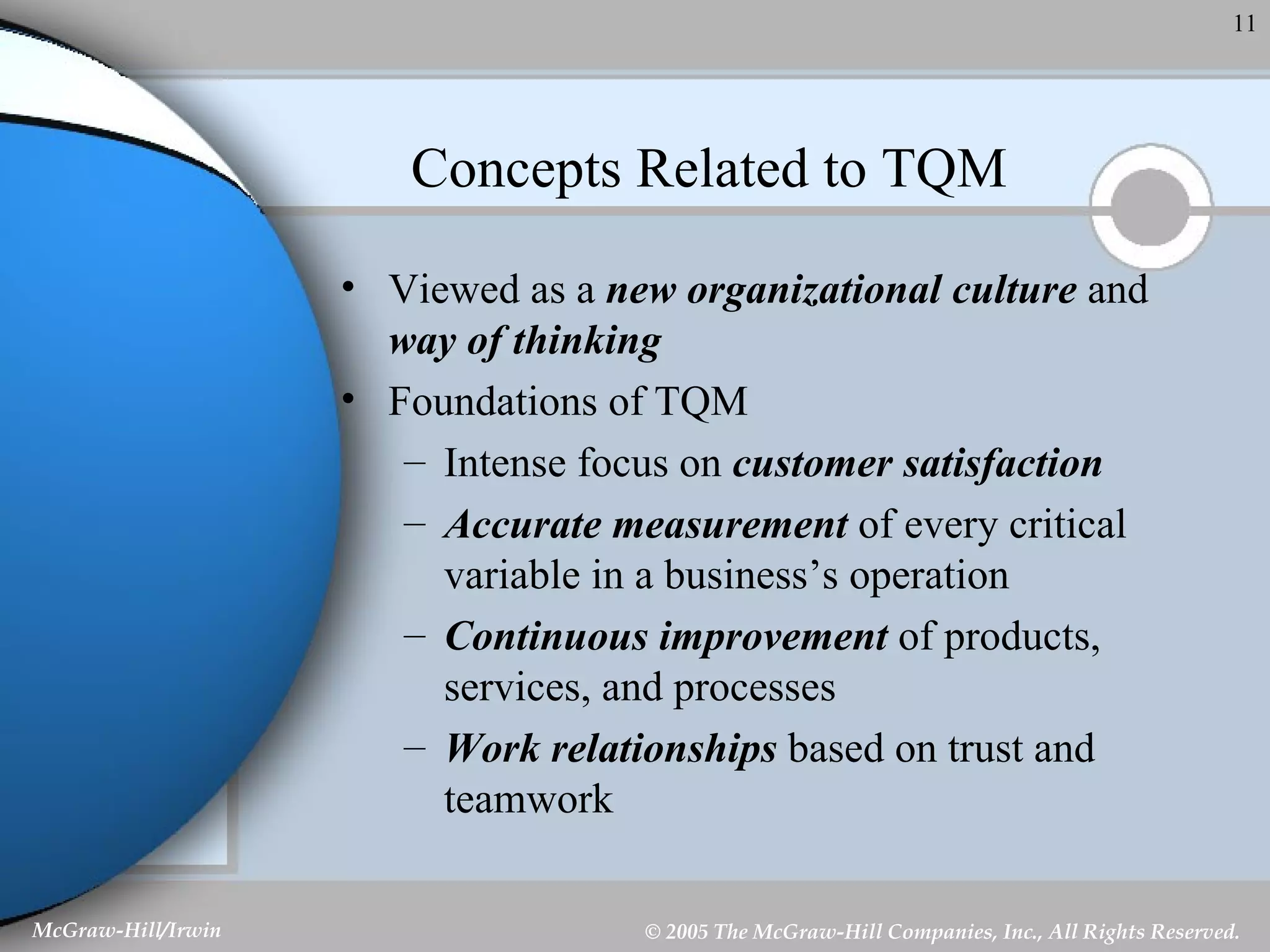
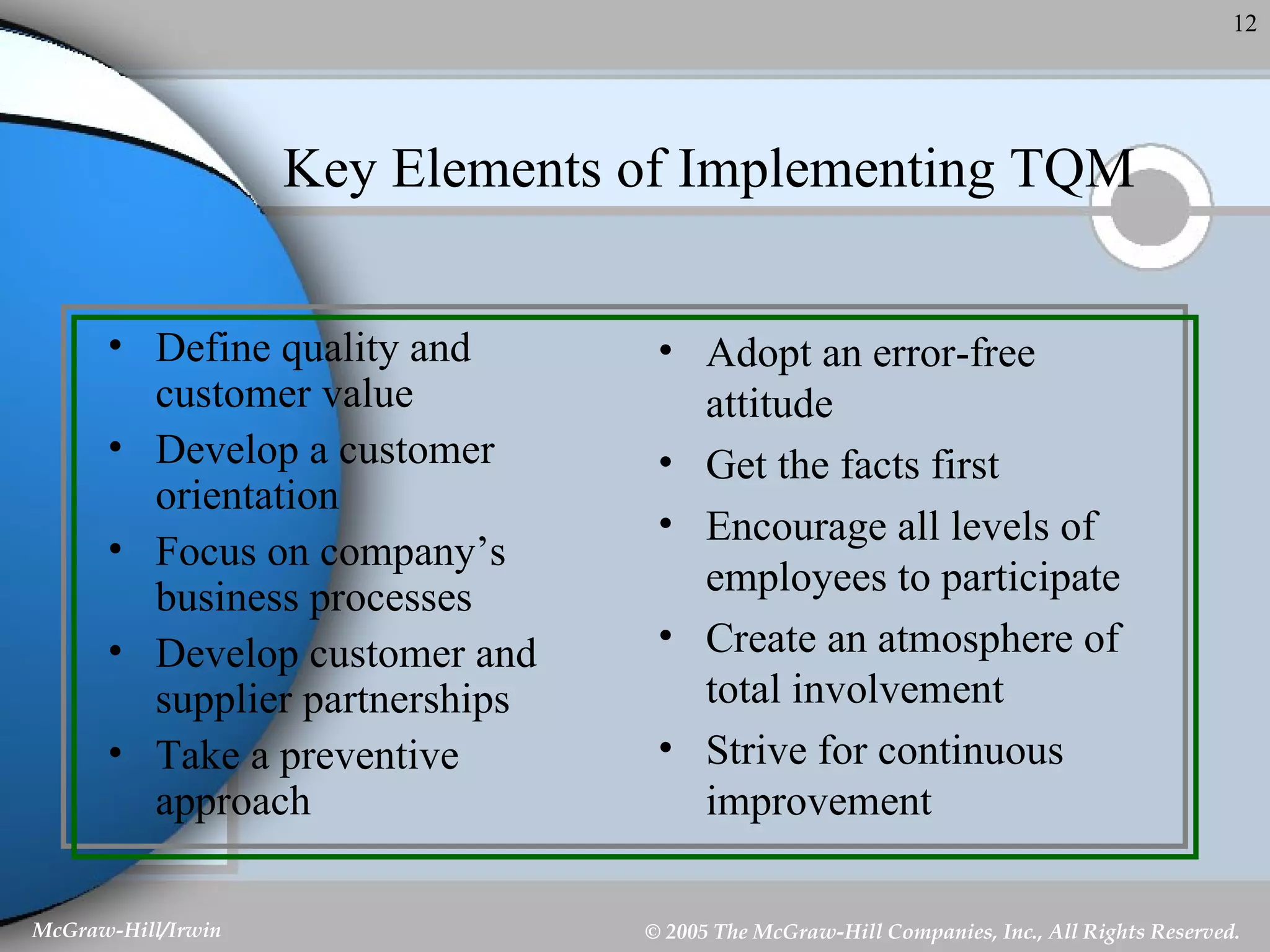
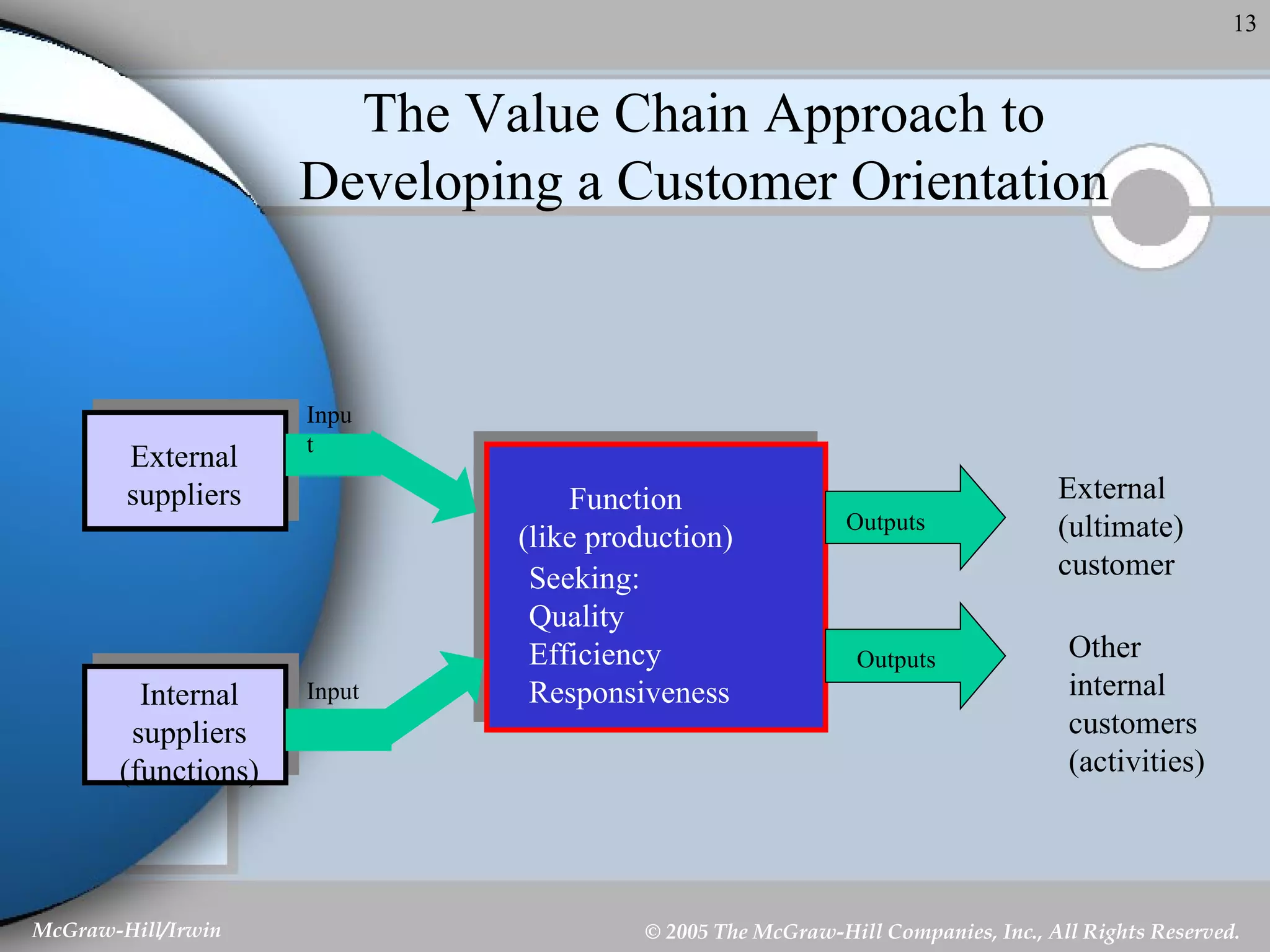
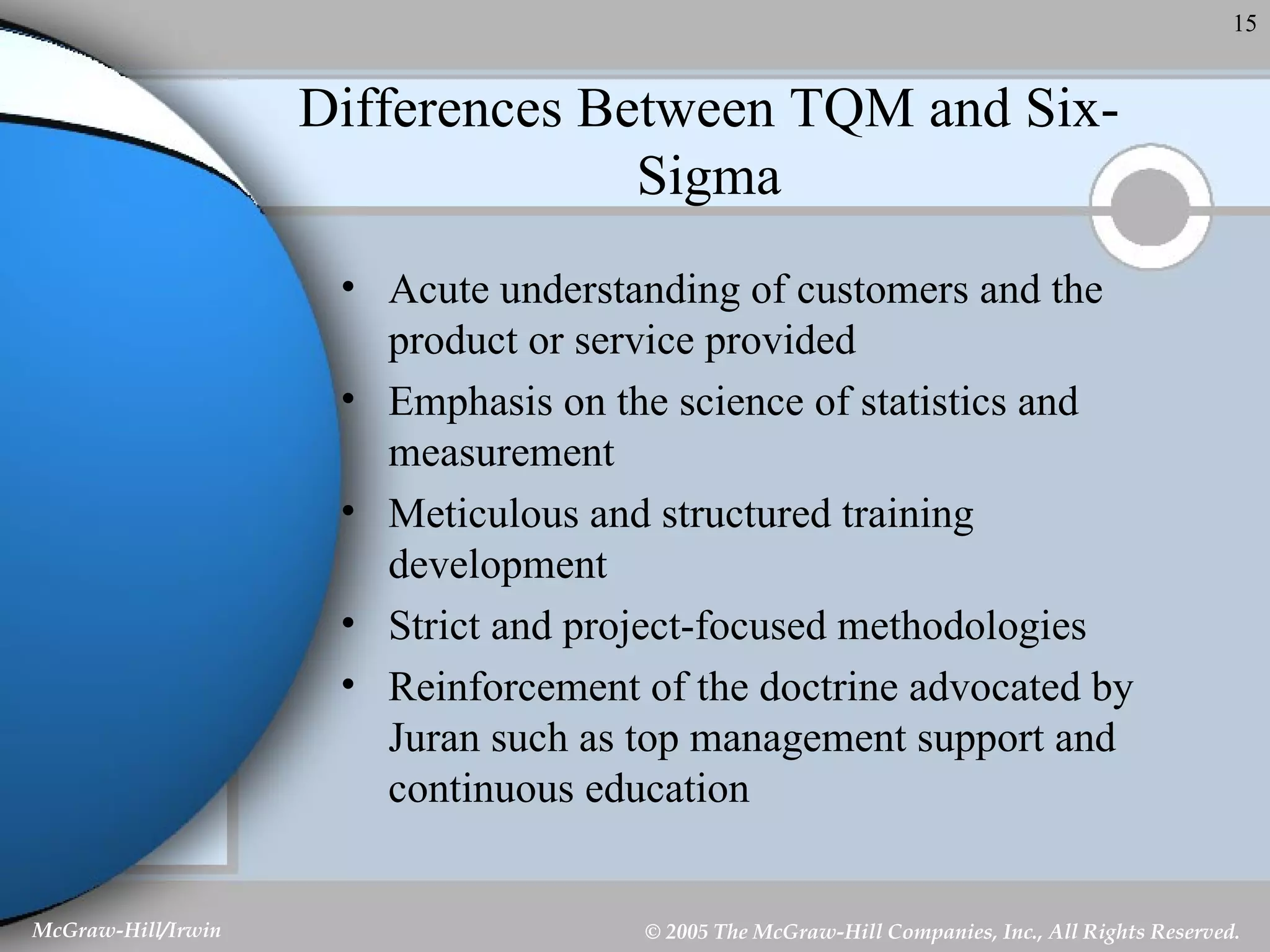
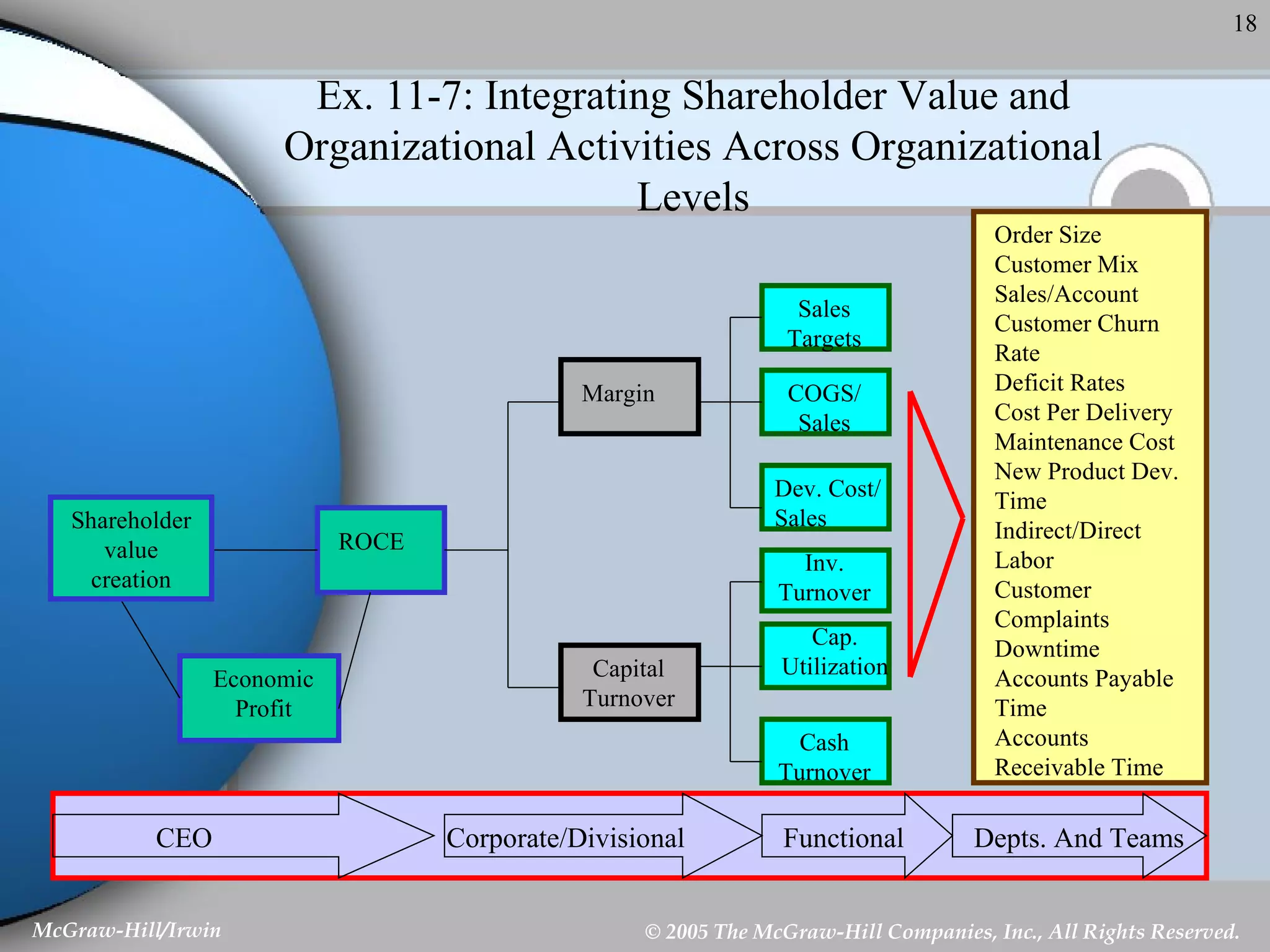
This document discusses strategic control and continuous improvement. It defines strategic control as tracking strategy implementation, detecting changes, and making adjustments. There are four types of strategic control: premise control checks strategy assumptions; strategic surveillance monitors internal/external events; special alert control reconsiders strategy due to unexpected events; and implementation control assesses strategy changes based on incremental actions. Continuous improvement focuses on customer satisfaction, measurement, and process improvement through techniques like total quality management (TQM), six sigma, ISO 9001, and balanced scorecards.