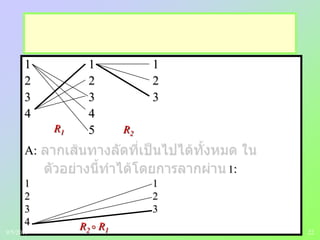
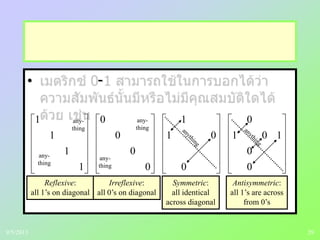
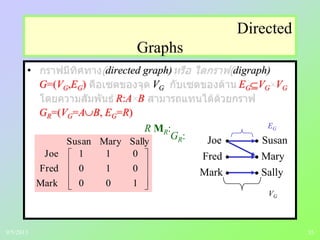
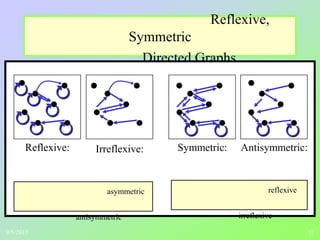
(1) The document discusses binary relations and concepts such as ordered pairs, reflexive relations, symmetric relations, inverse relations, and representing relations using matrices.
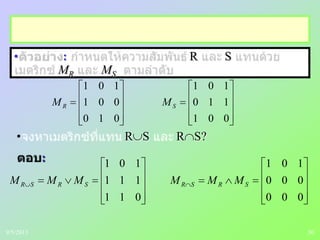
(2) It also covers topics like equivalence relations, equivalence classes, and partitioning a set based on an equivalence relation.
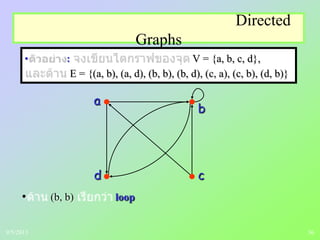
(3) Examples are provided to illustrate key concepts like inverse relations, representing relations as directed graphs, and determining equivalence classes.













![25
Representing
Relations)
• :
- Zero-one matrices
Directed graphs
• R
A = {a1, a2, …, am} B ={b1, b2, …, bn}, R
MR = [mij]
mij = 1, (ai, bj) R,
mij = 0, (ai, bj) R
•
9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-25-320.jpg)



![31
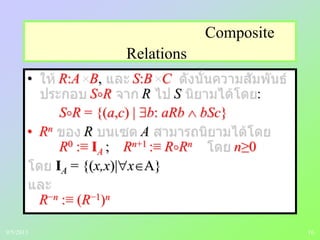
• A = [aij] - m k
B = [bij] - k n
• Boolean product A B,
AB m n
i j [cij]
cij = (ai1 b1j) (ai2 b2j) … (aik bkj)
cij = 1 (ain bnj) = 1 n
(ain bnj) cij
= 09/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-31-320.jpg)
![32
• - MA = [aij], MB = [bij] MC = [cij]
A, B, C,
• MC = MAMB
cij = 1 (ain bnj) = 1
n
(ain bnj) cij = 0
C (xi, zj) yn
(xi, yn) A (yn, zj)
B
• C = B A (C A9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-32-320.jpg)
![33
• B A
:
MB A = MAMB
•
A B
A Boolean product
B
•
:
[n]
9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-33-320.jpg)
![34
• : R2
R
001
110
010
RM
: R2
010
111
110
]2[
2 RR
MM
9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-34-320.jpg)


![40
Equivalence Classes
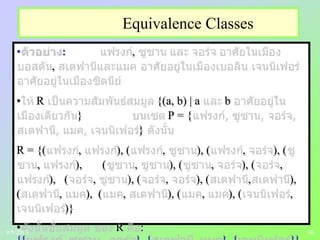
• : R A
a
A a
• a R
[a]R [a]R :≡ { b | aRb }
•
a [a]
• b [a]R, b representative
9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-40-320.jpg)
![41
Equivalence Classes
:
mouse,
[mouse] ?
: [mouse]
[mouse] ={horse, table, white,…}
„horse‟
9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-41-320.jpg)
![42
Equivalence
Classes
• “ a b ”
– [a] =
a
• “ a b ”
– [a] = {a, −a}
• “ a b (
, a − b Z)”
– [a] = {…, a−2, a−1, a, a+1, a+2, …}
• “ a b
m ” ( m>1)
– [a] = {…, a−2m, a−m, a, a+m, a+2m, …}9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-42-320.jpg)
![43
Equivalence Classes
: R A
:
• aRb
• [a] = [b]
• [a] [b]
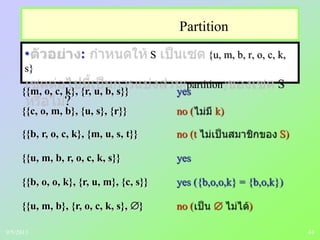
: partition S
S
union
S Ai i I
S
(i) Ai i I
(ii) Ai Aj = , i j
(iii) A = S9/5/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4relationsth01-130905111137-/85/Relations-43-320.jpg)