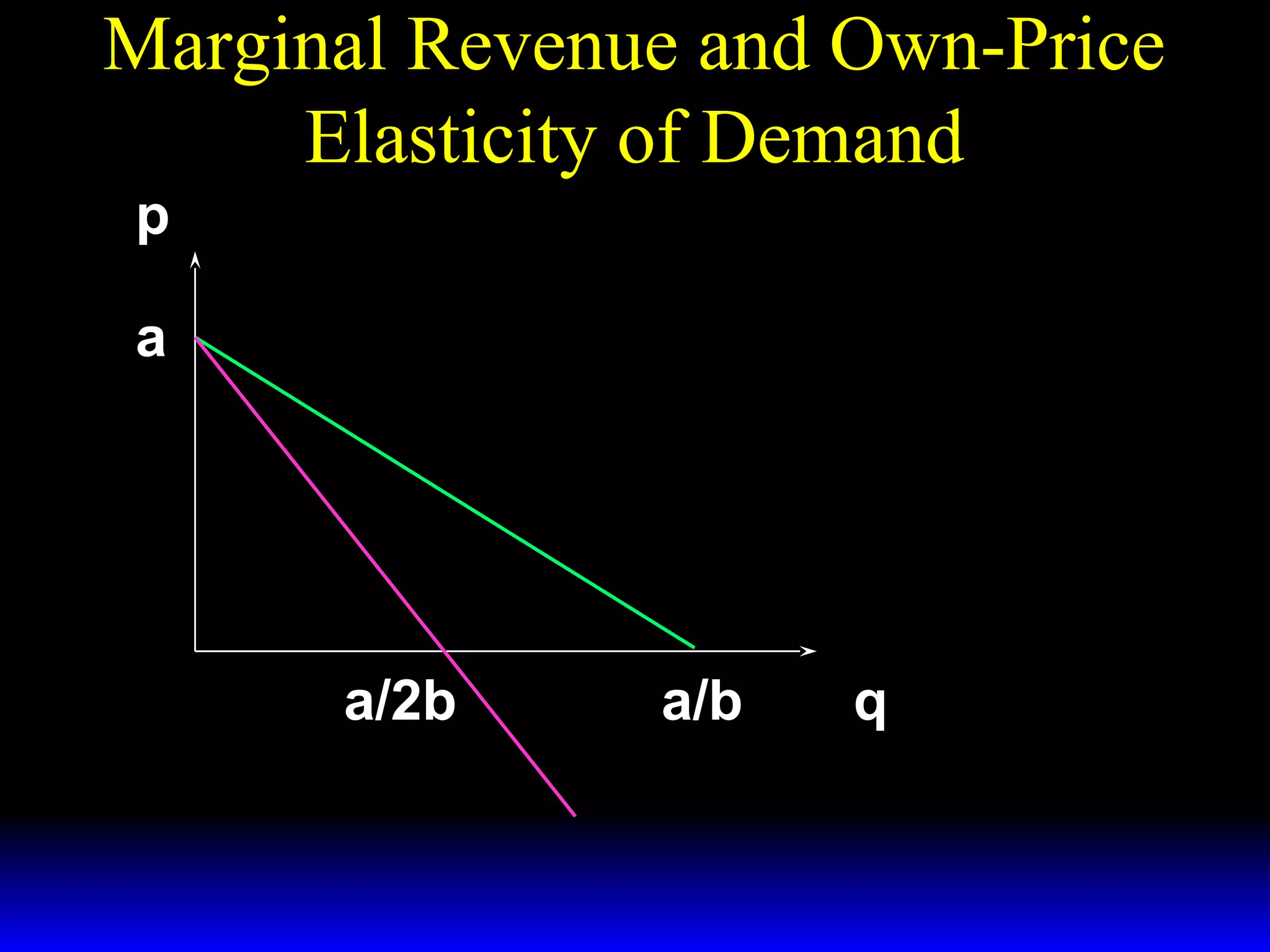
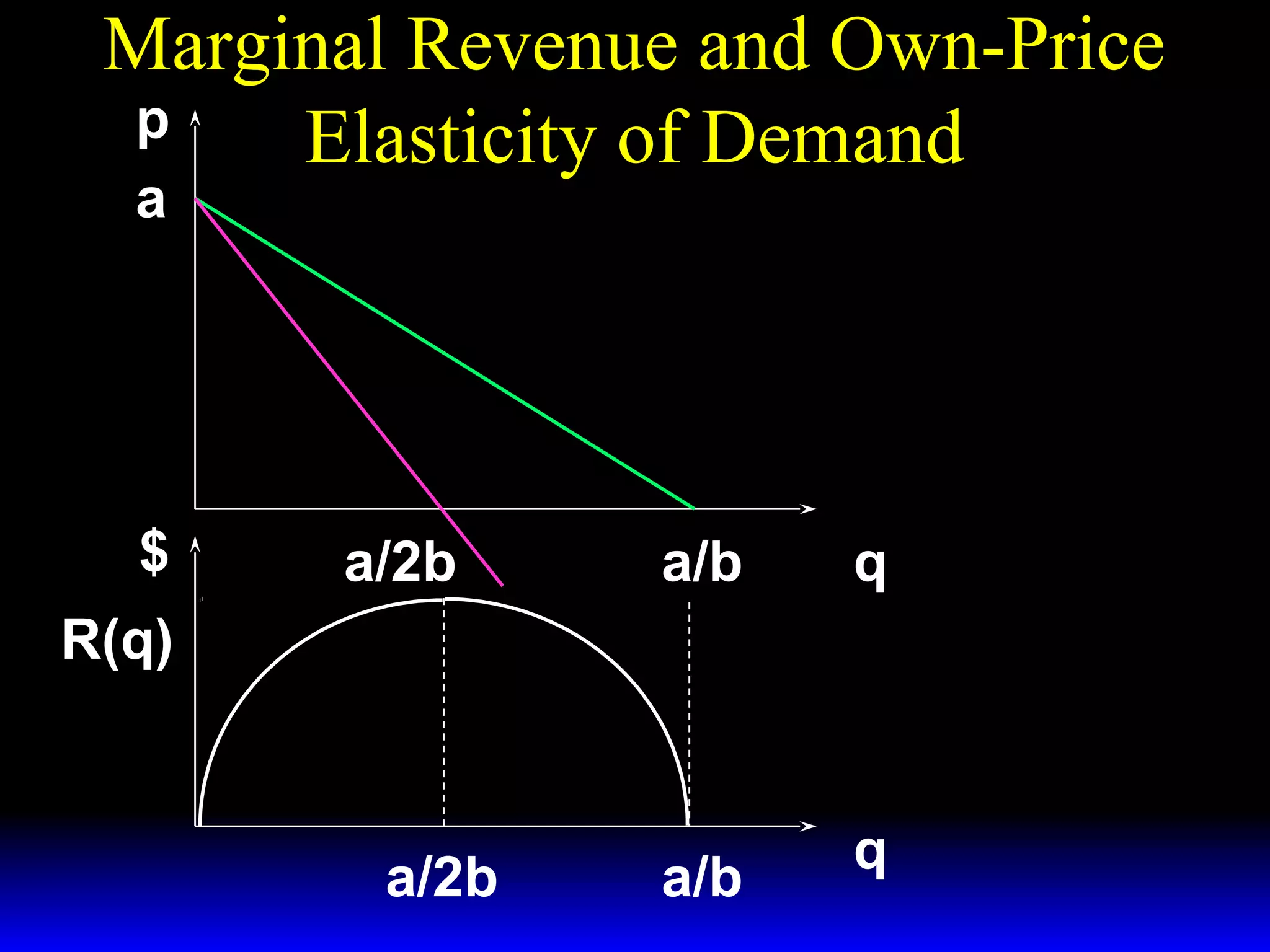
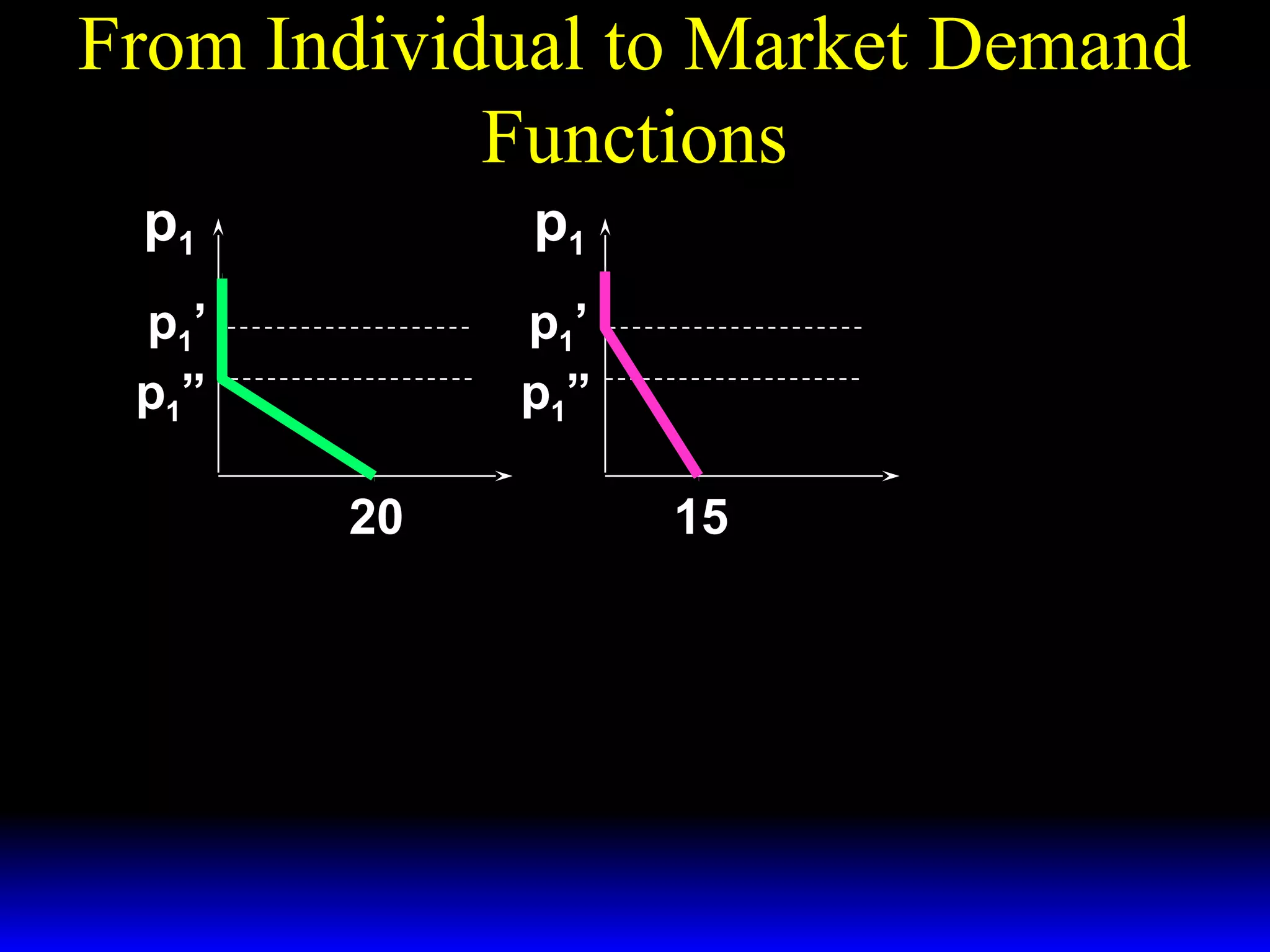
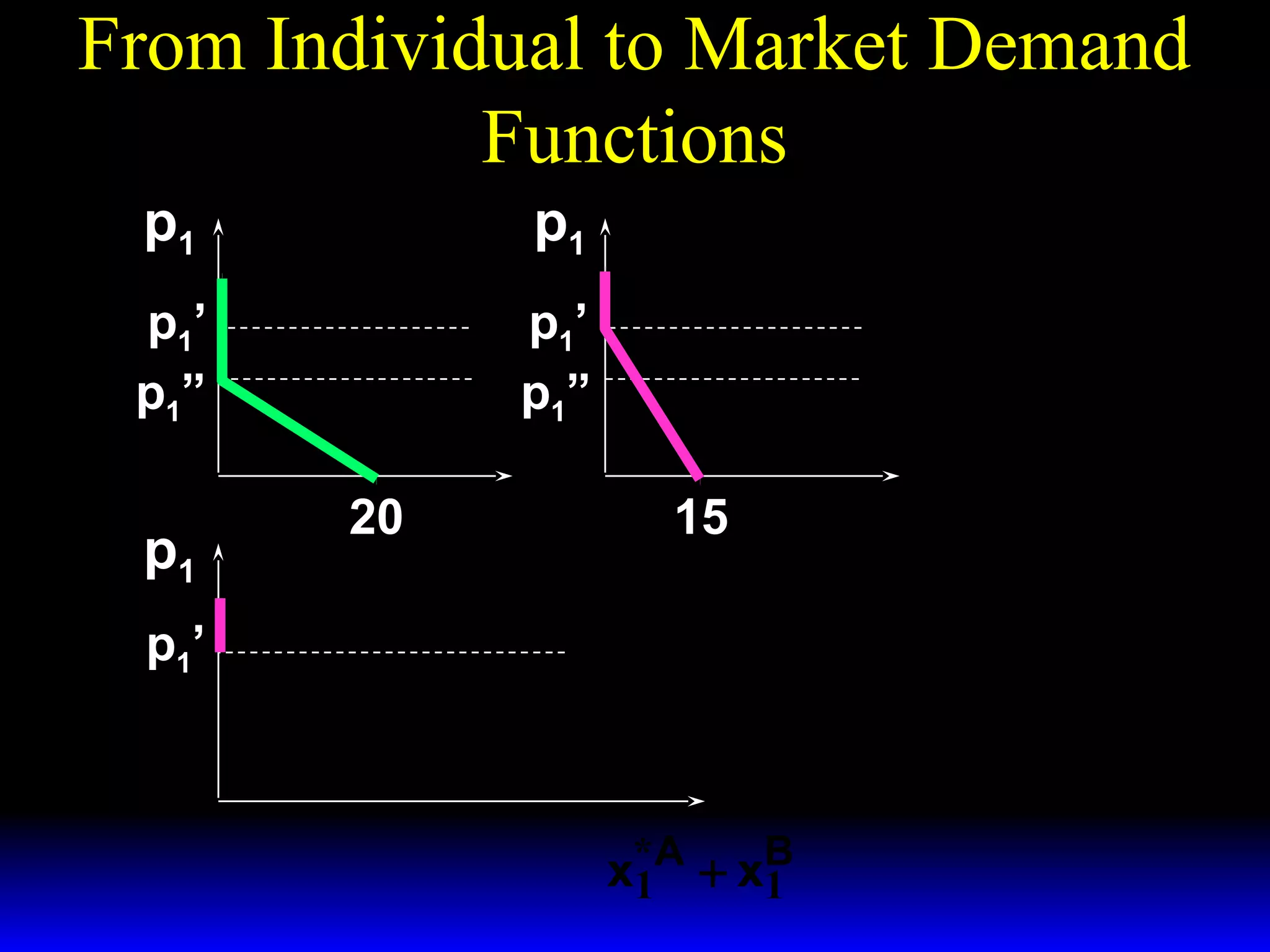
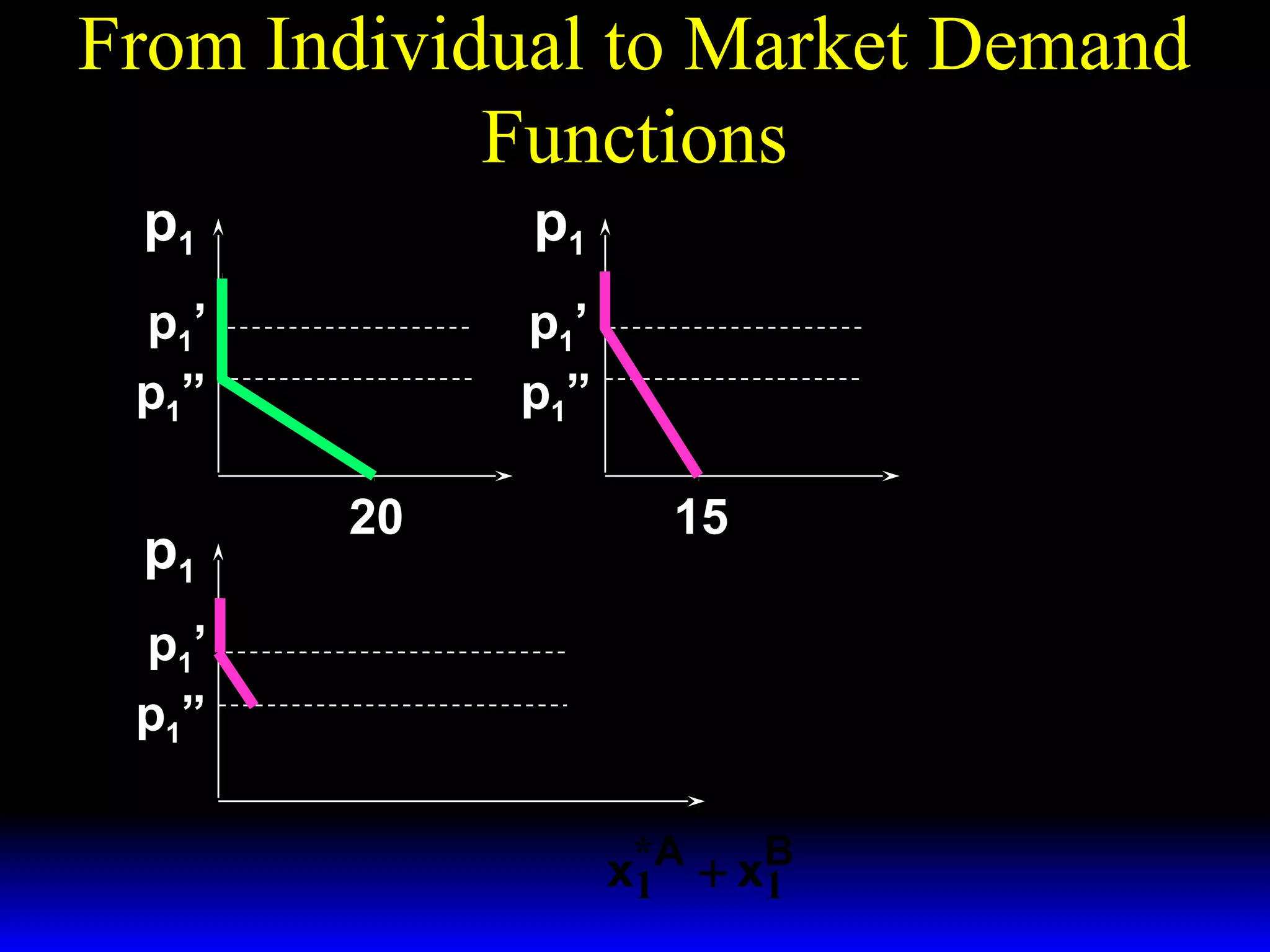
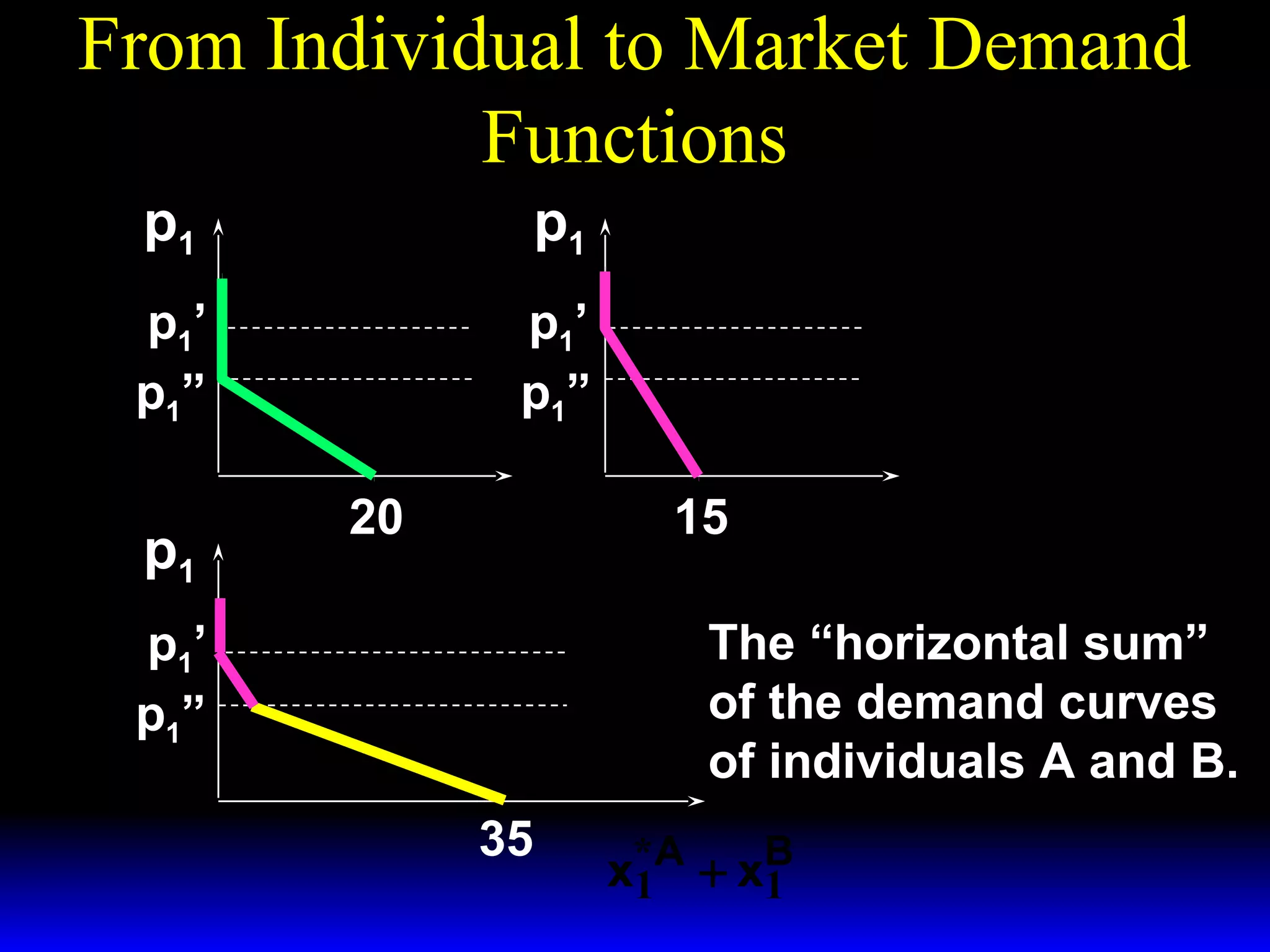
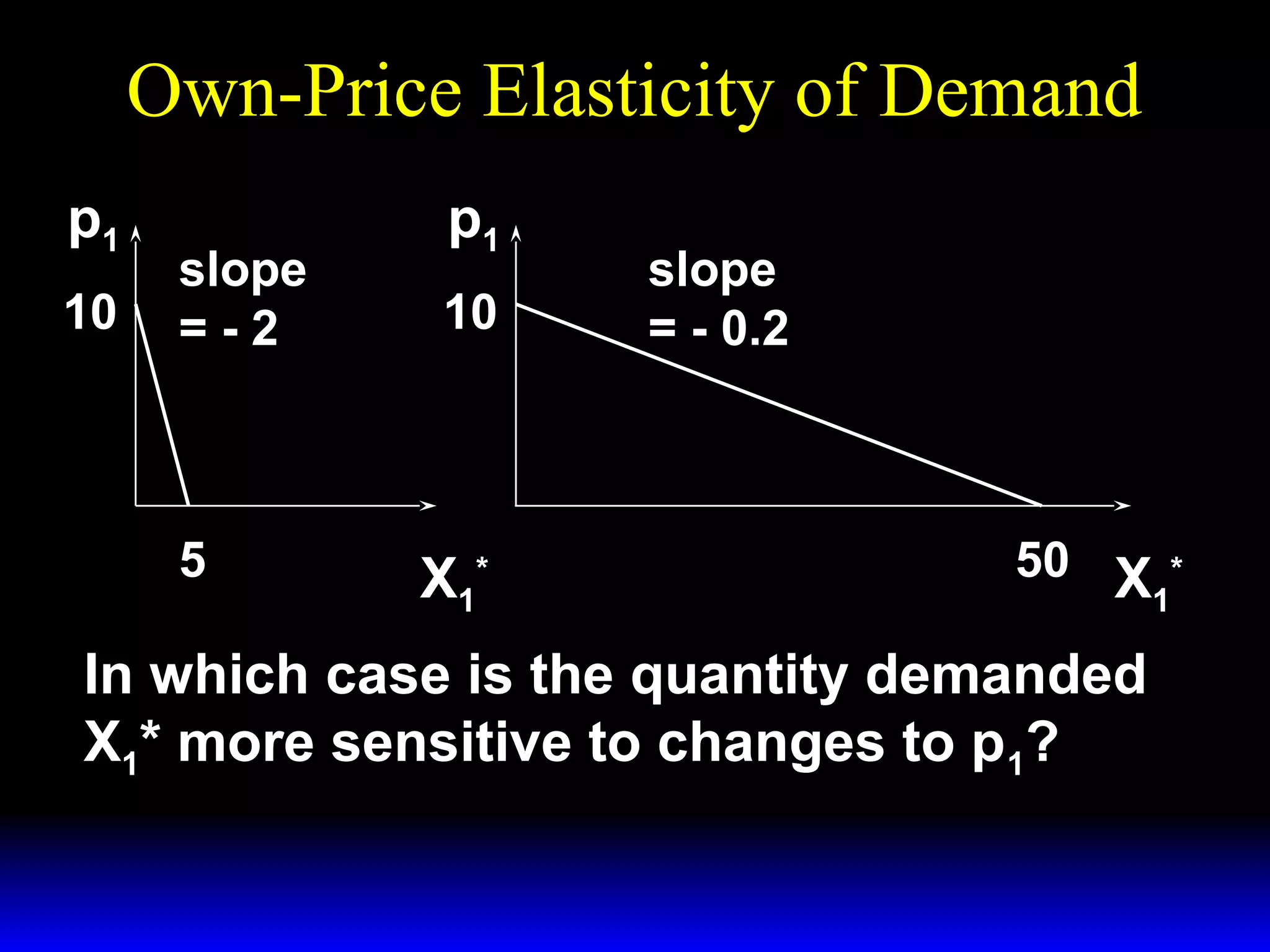
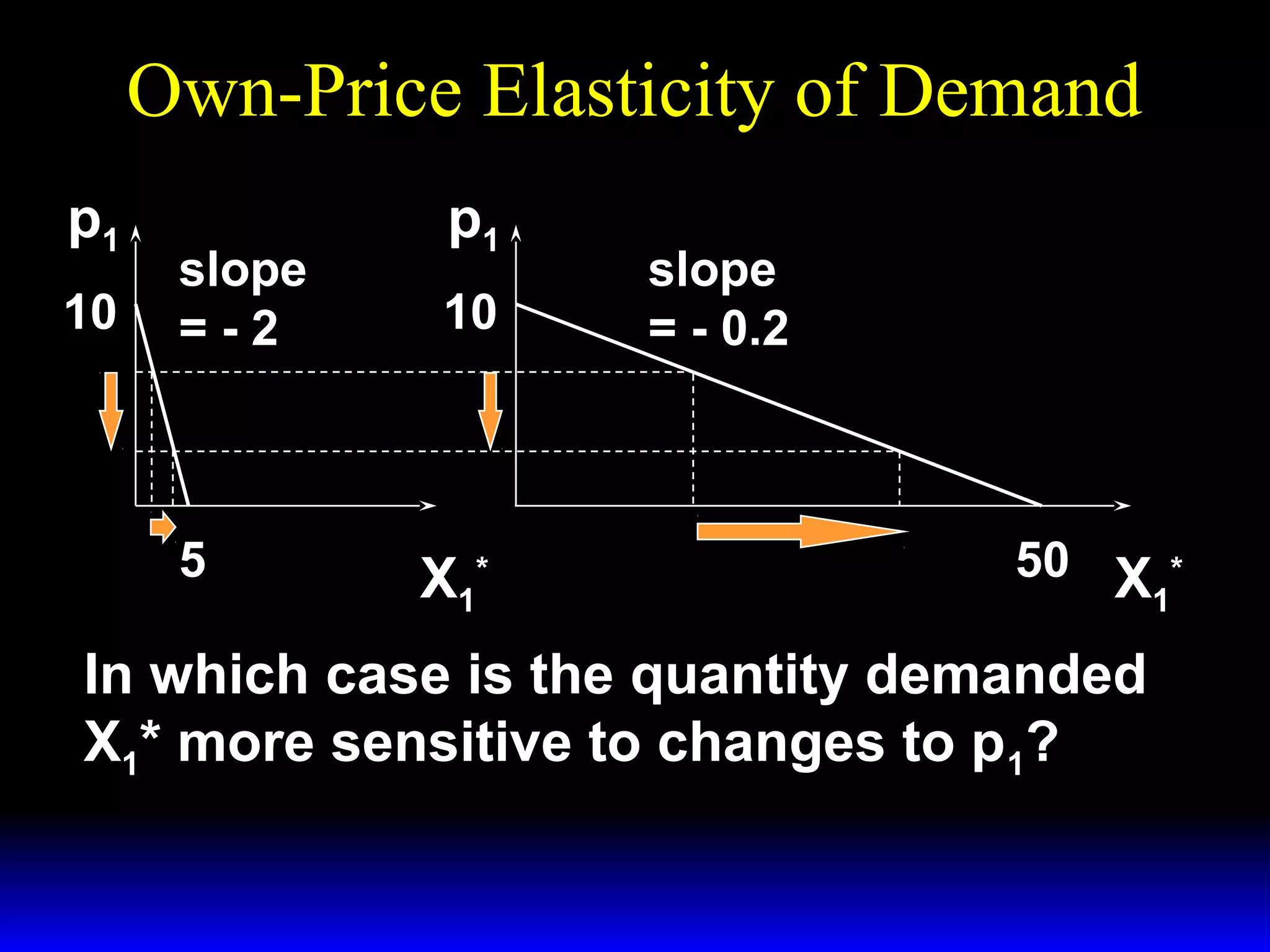
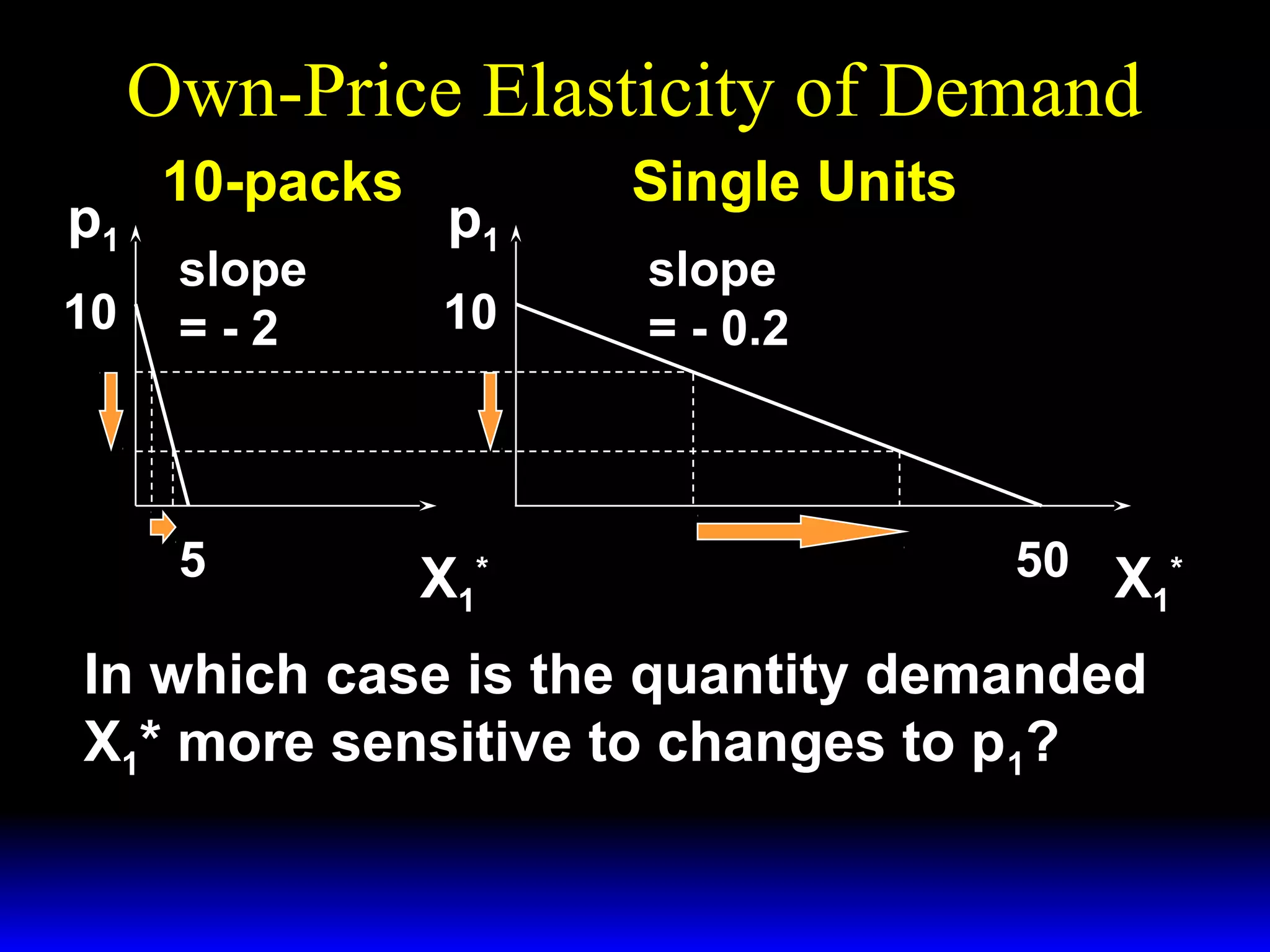
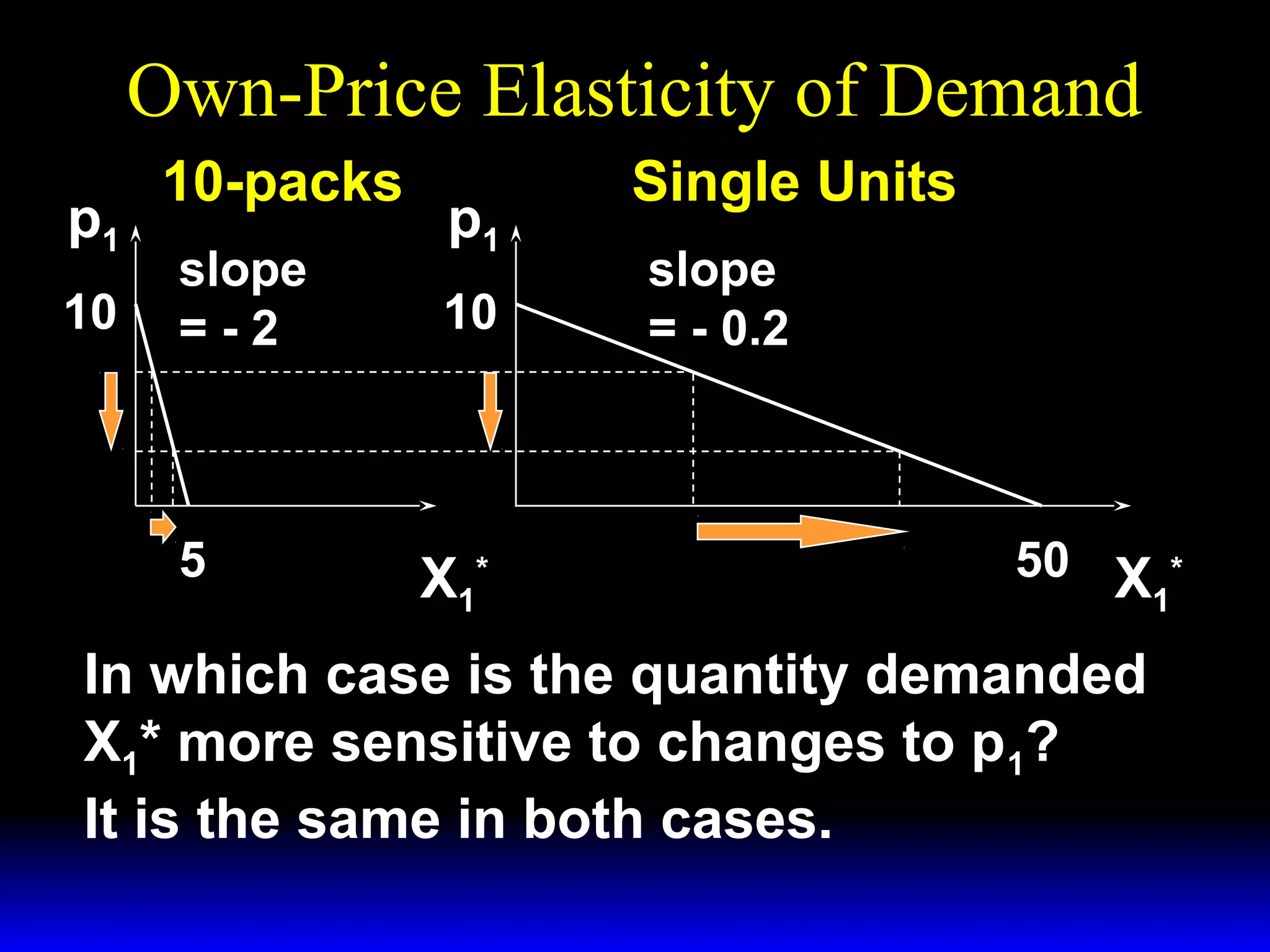
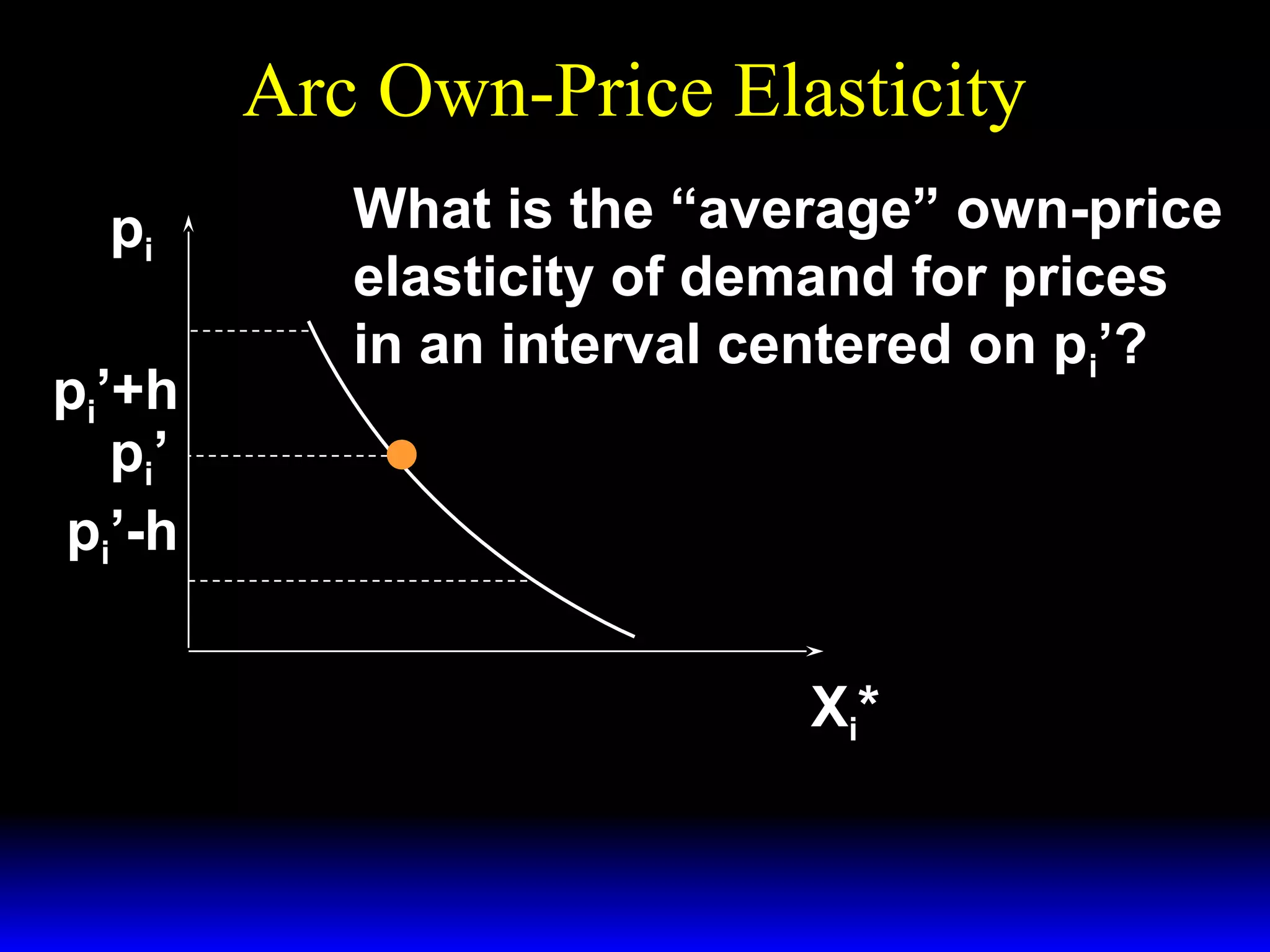
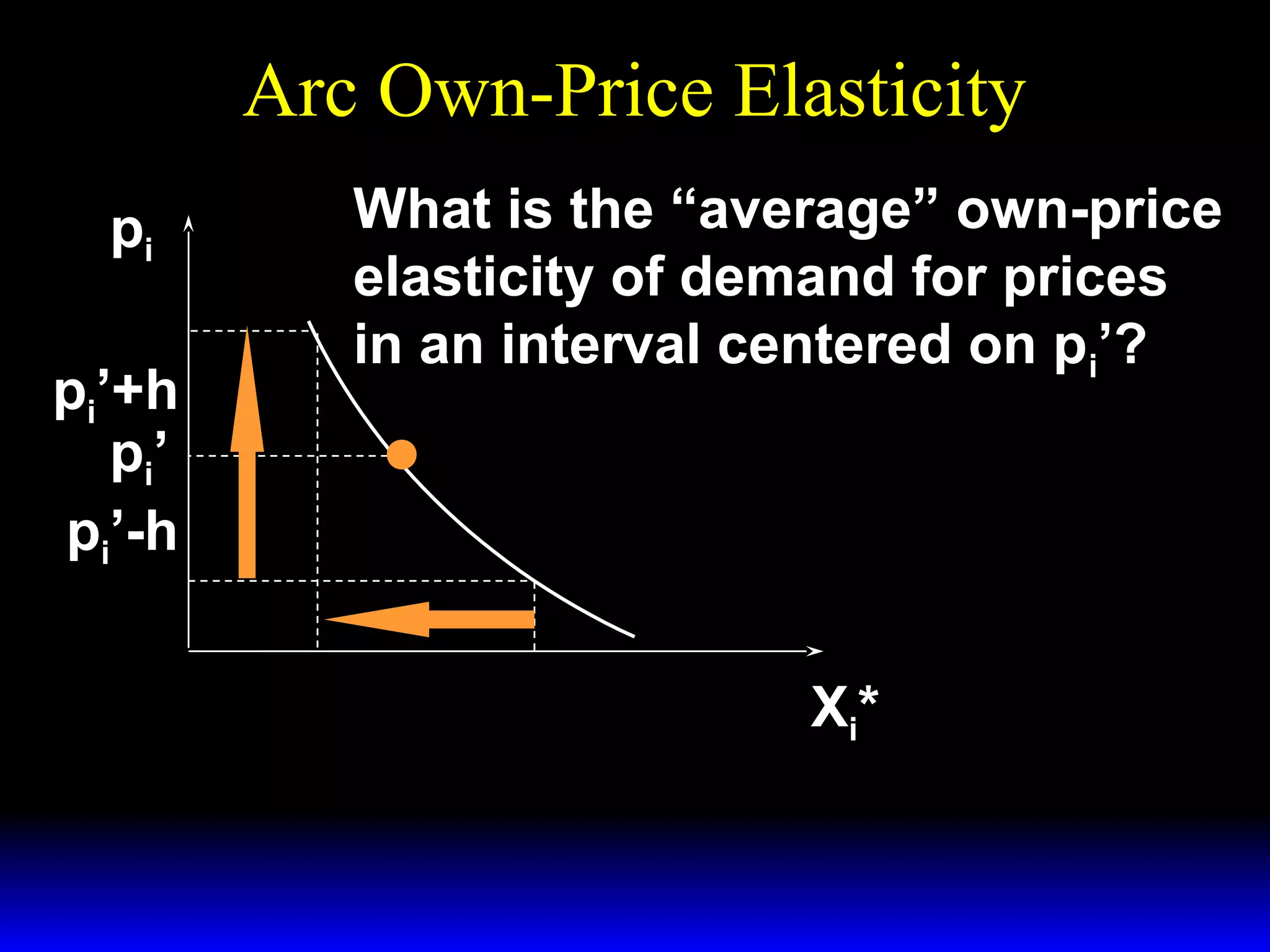
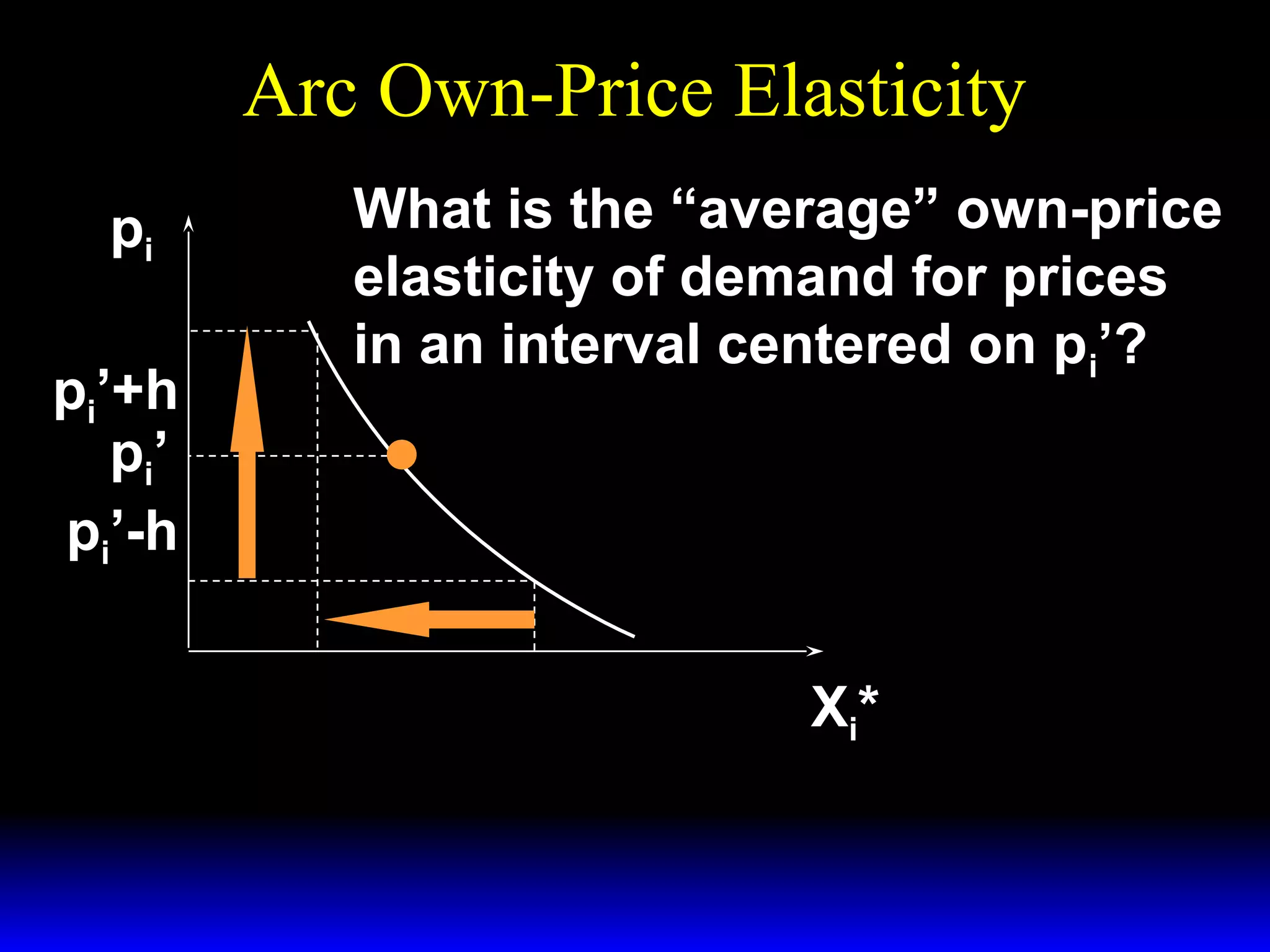
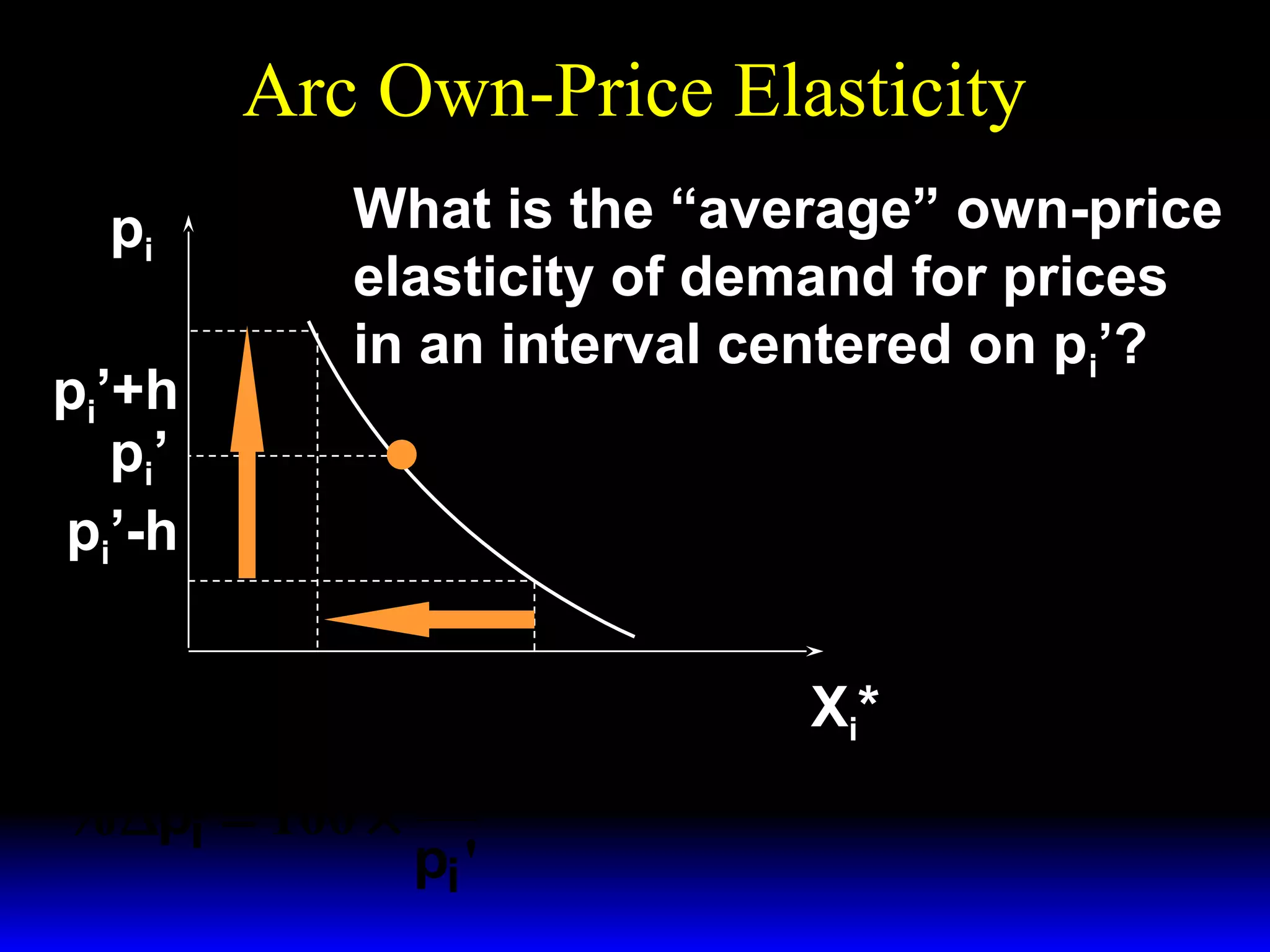
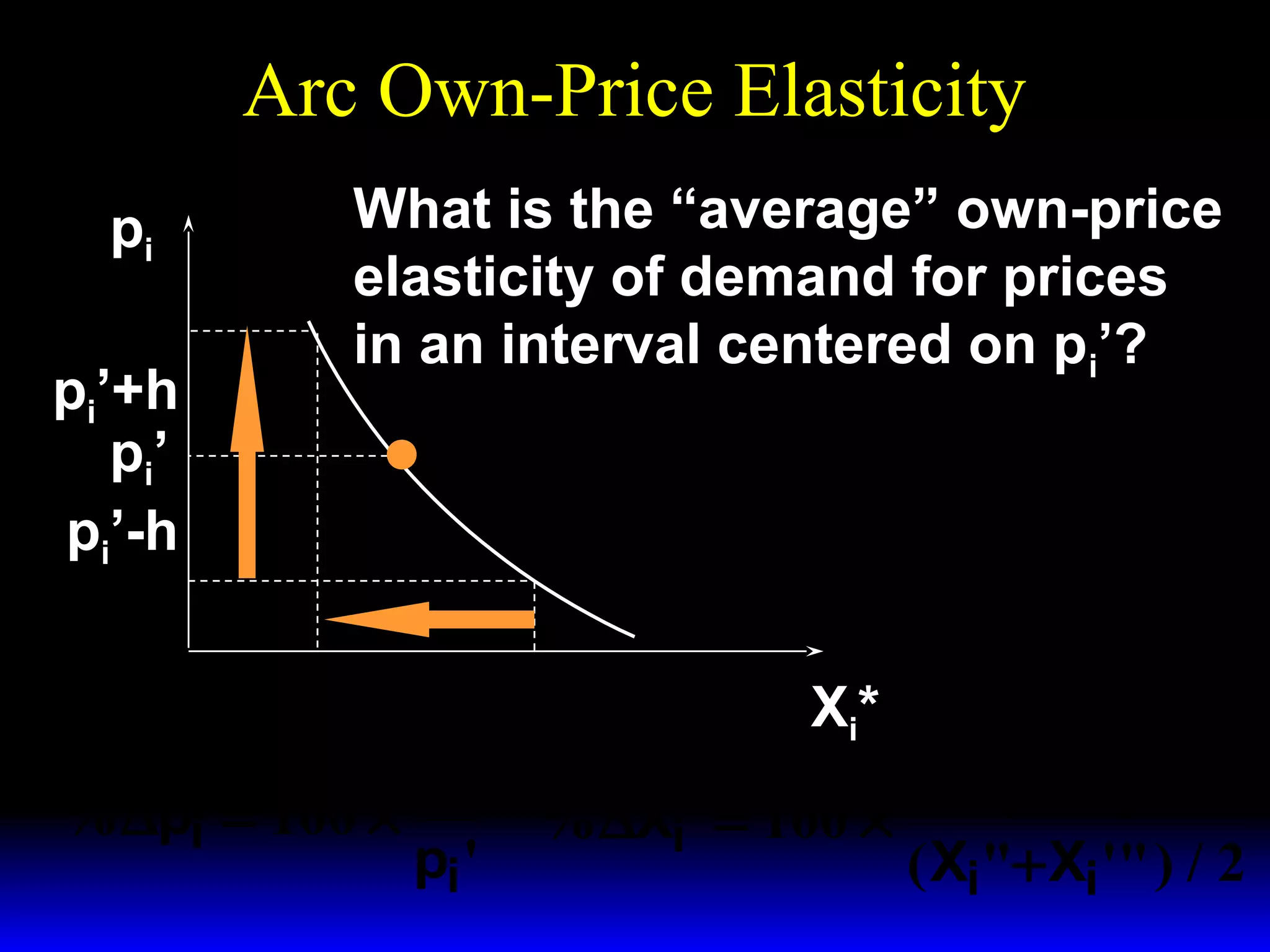
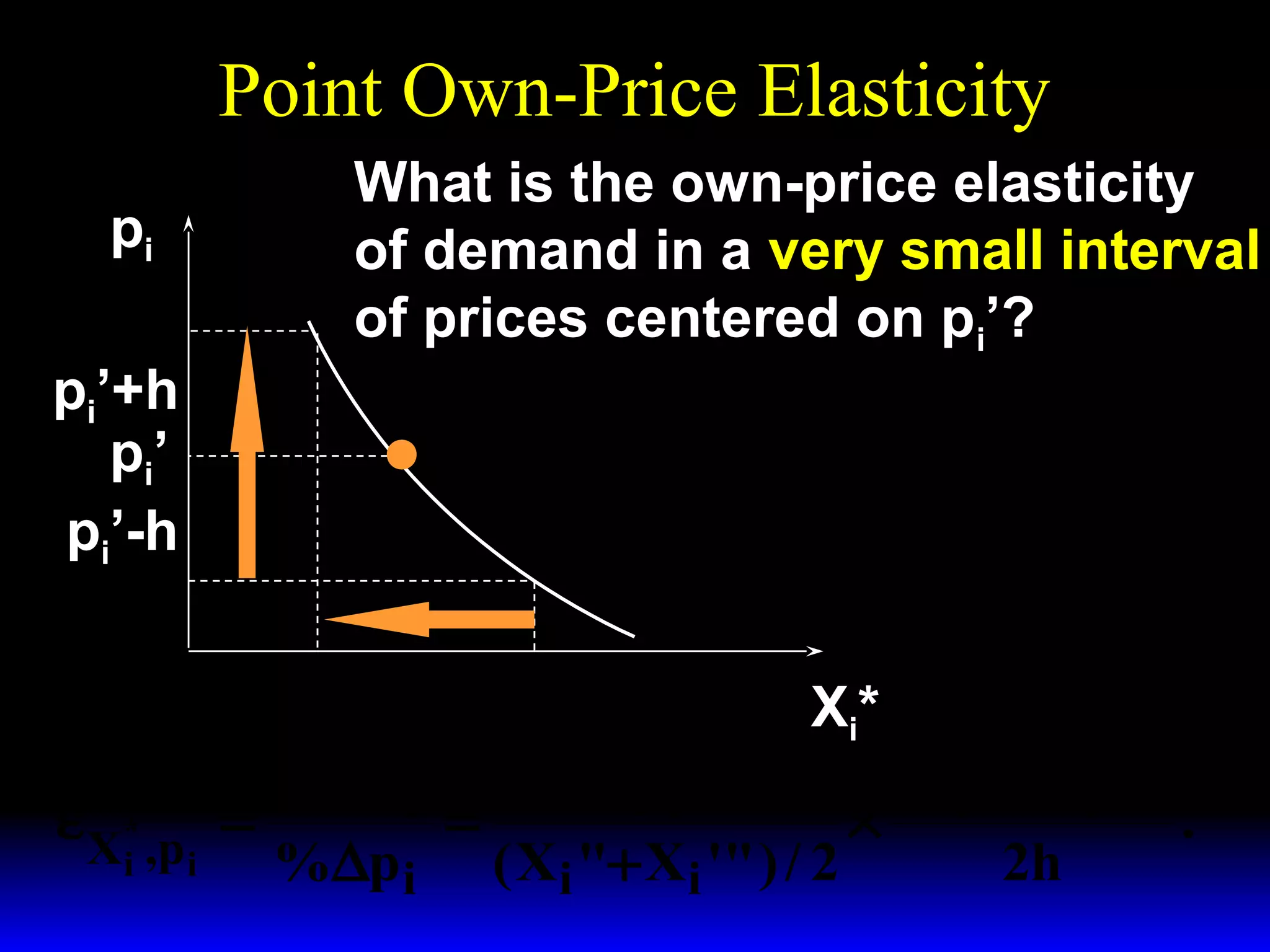
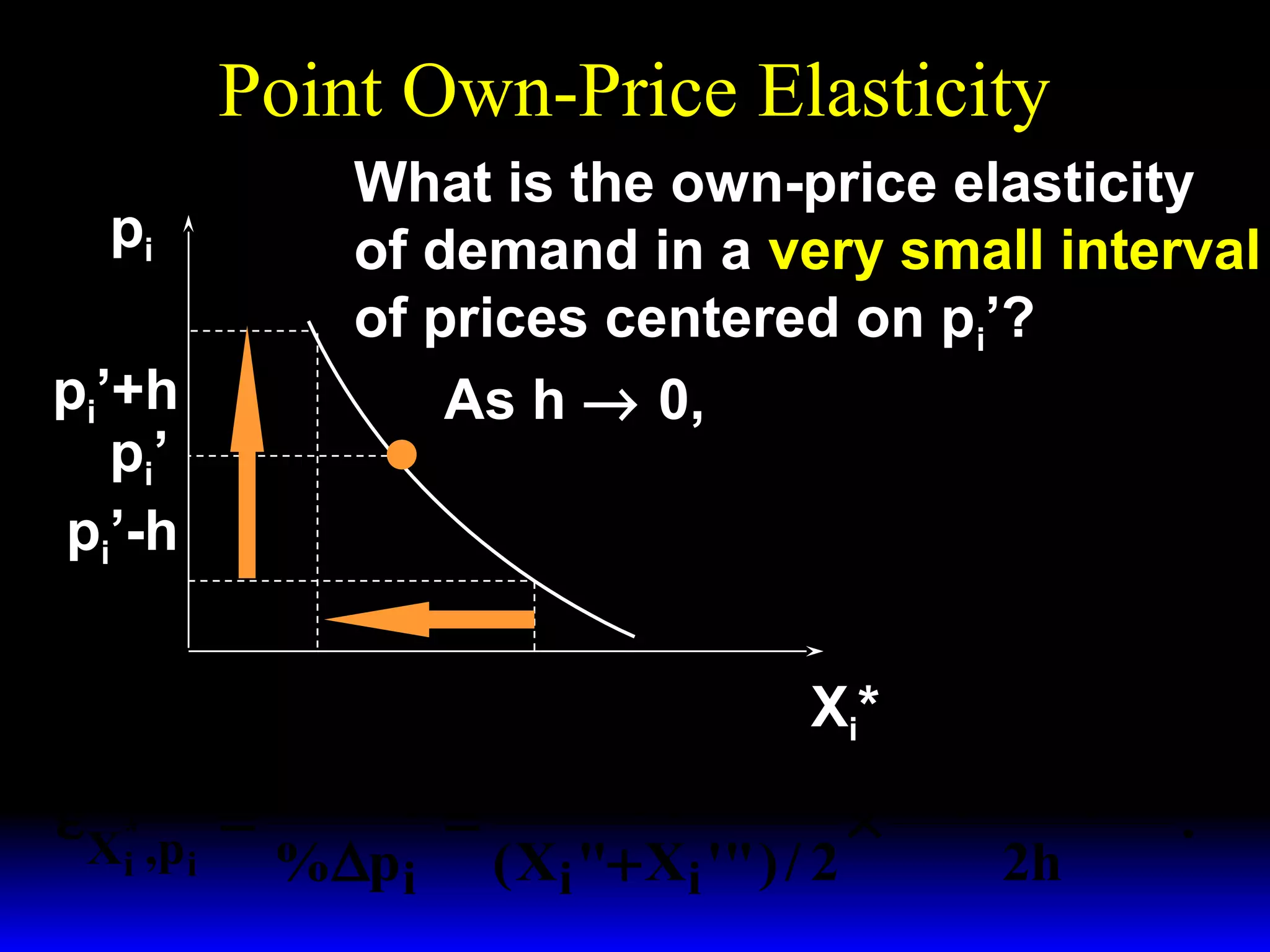
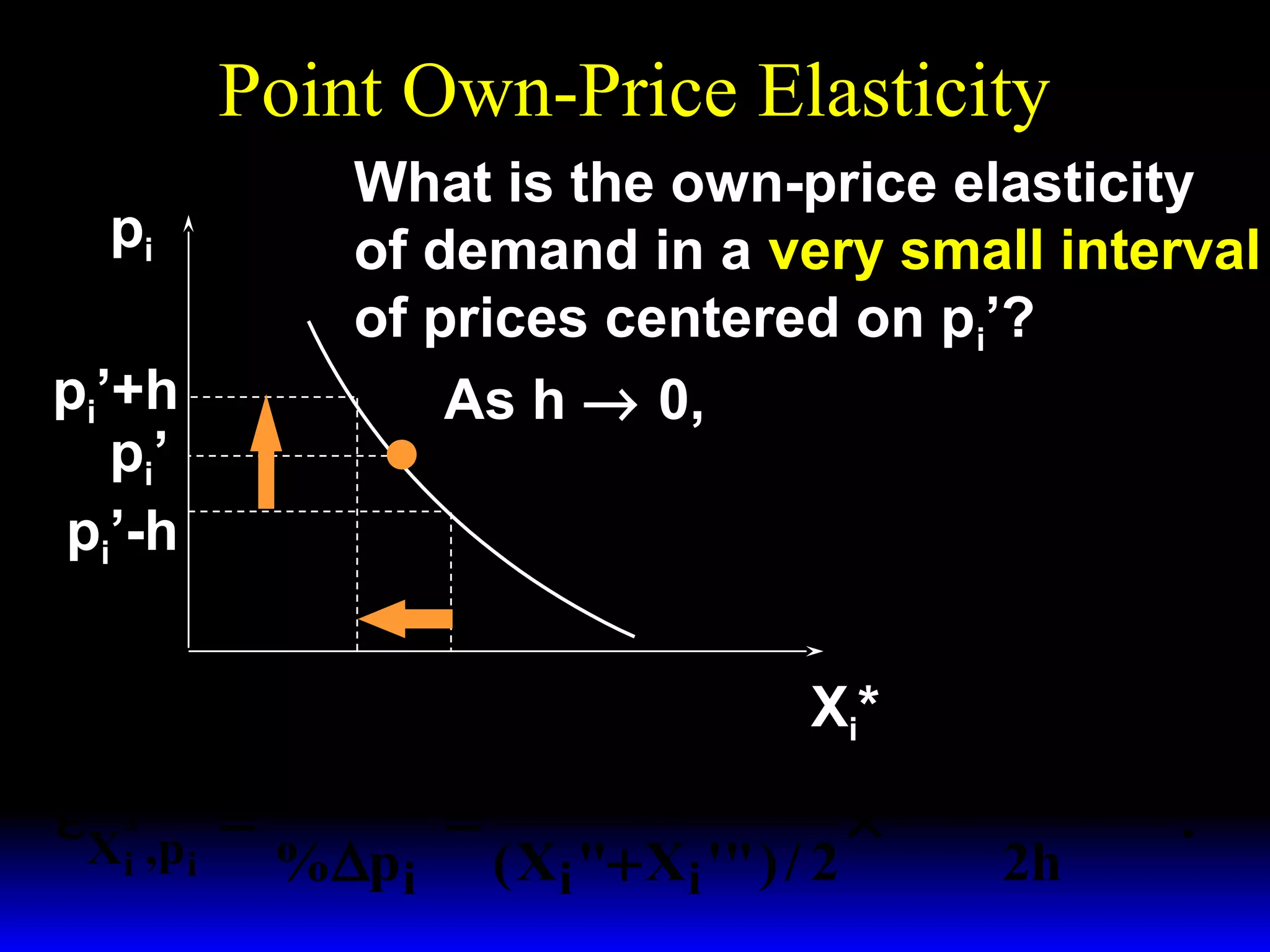
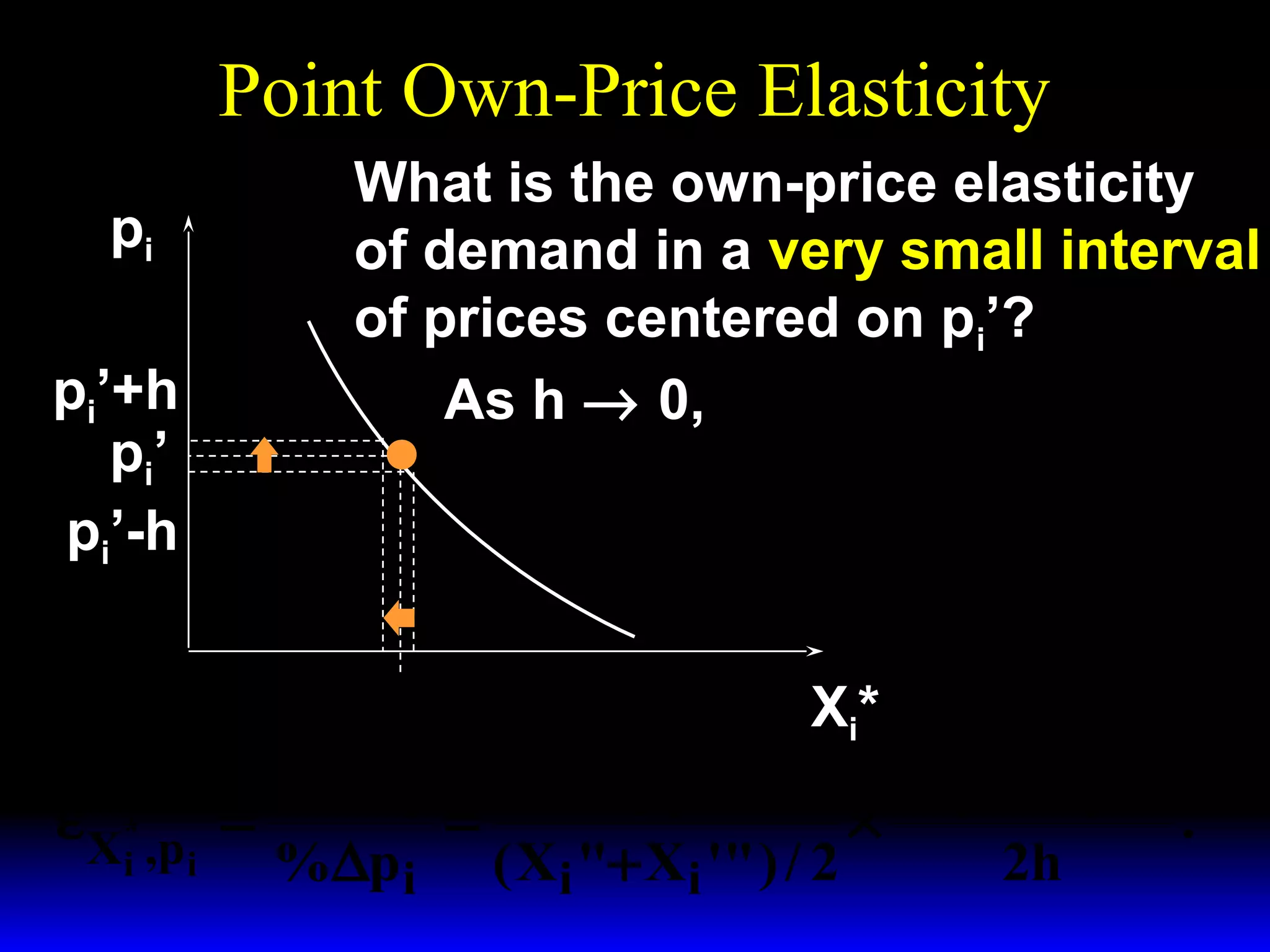
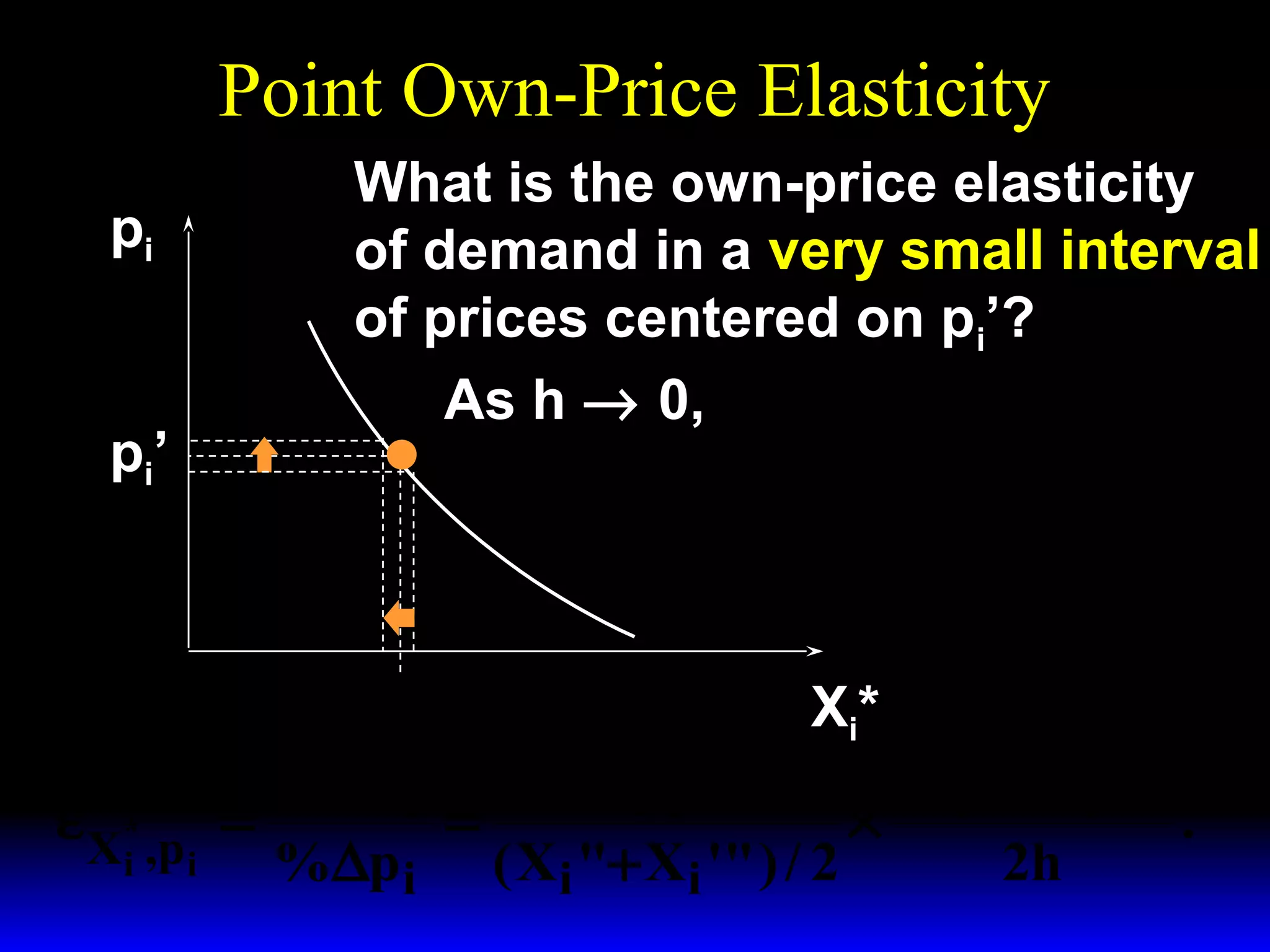
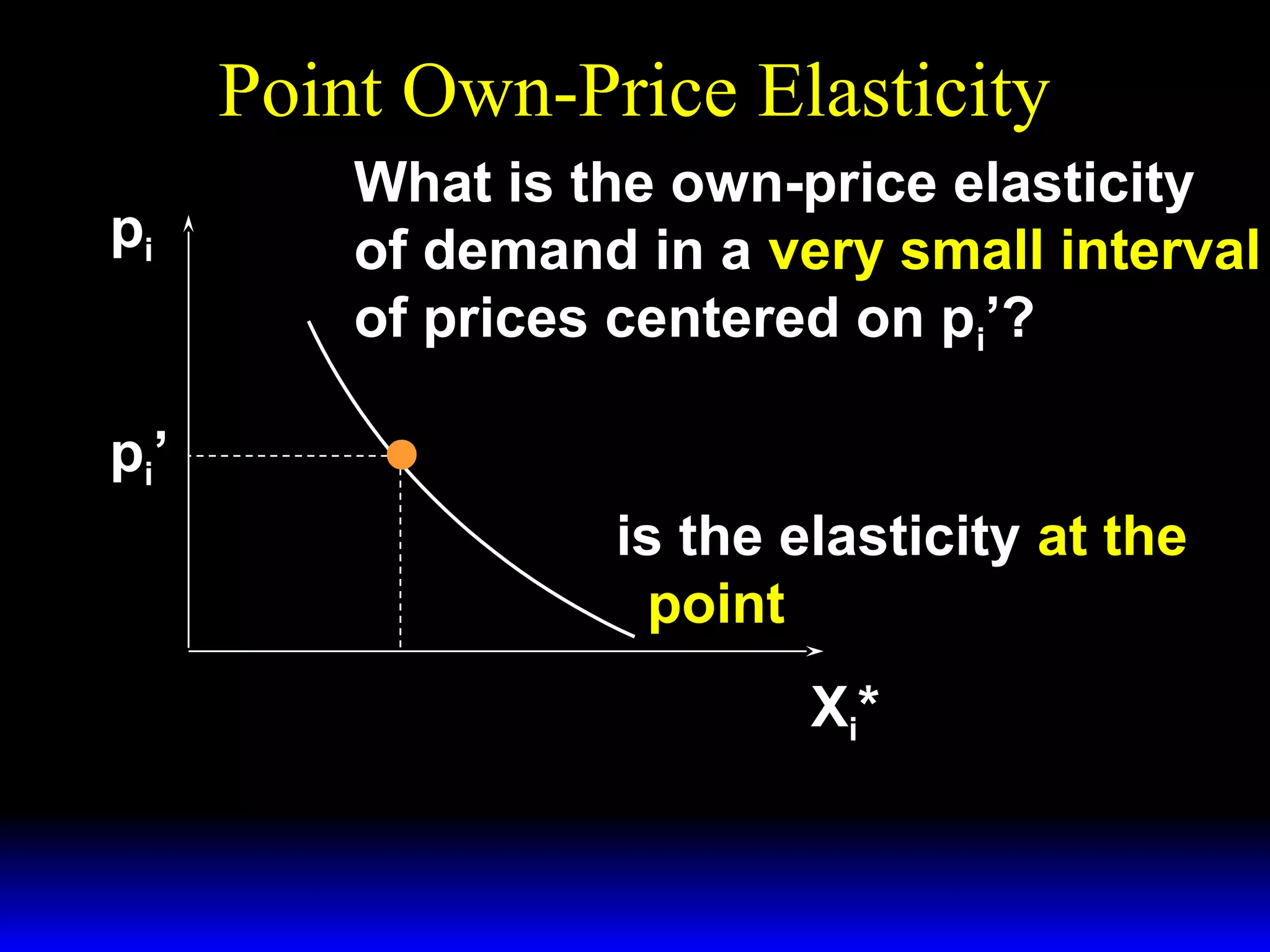
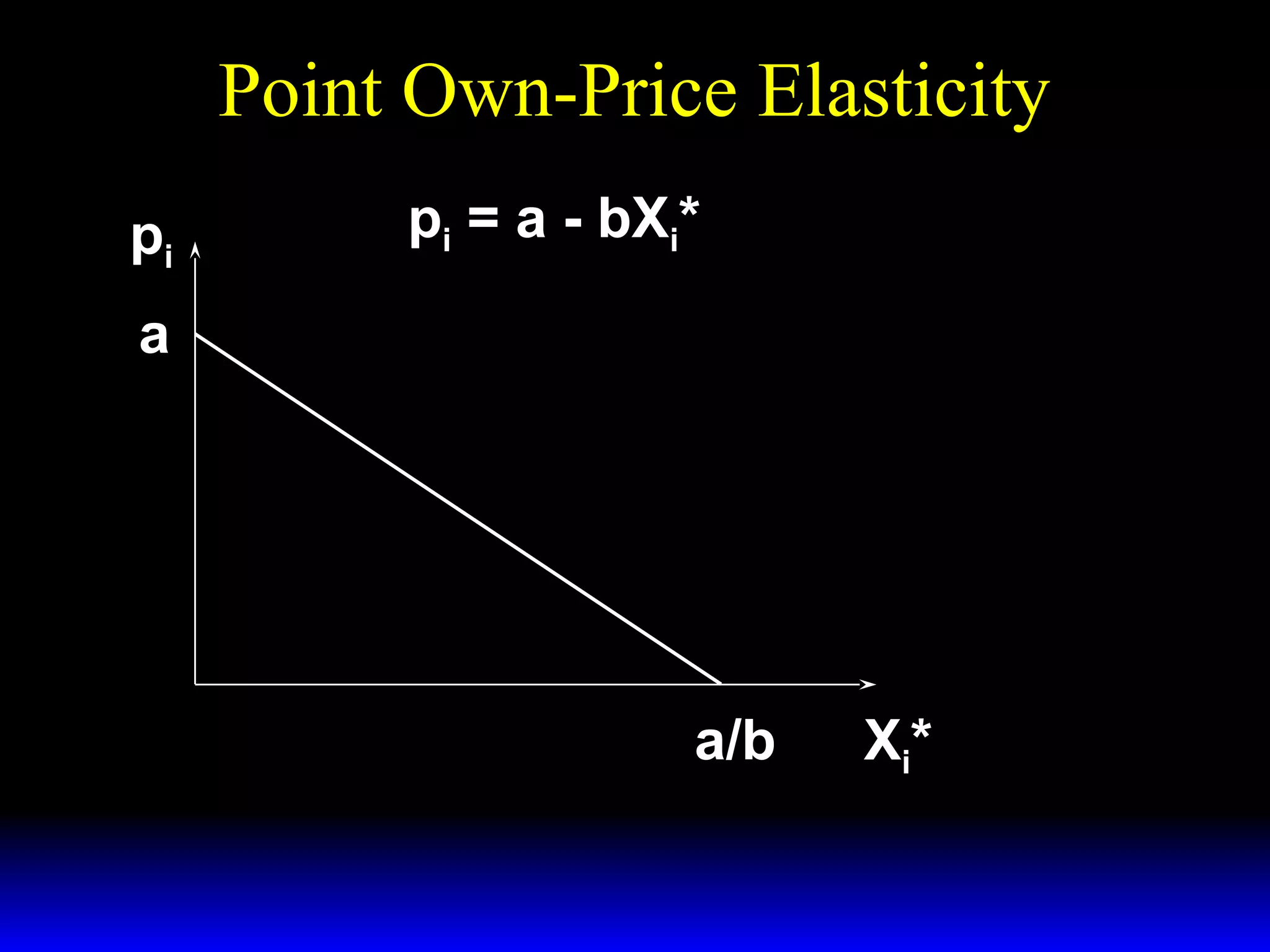
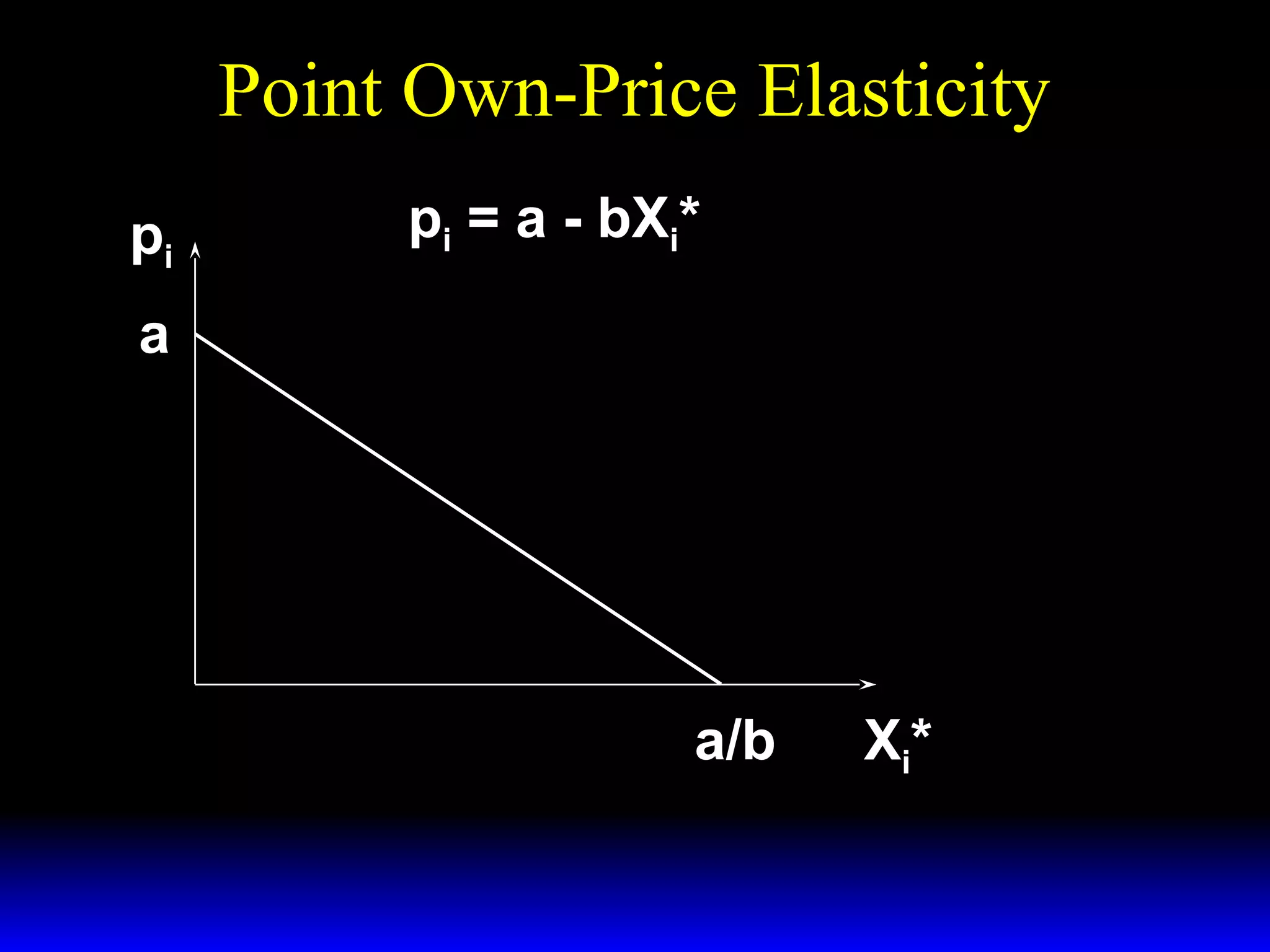
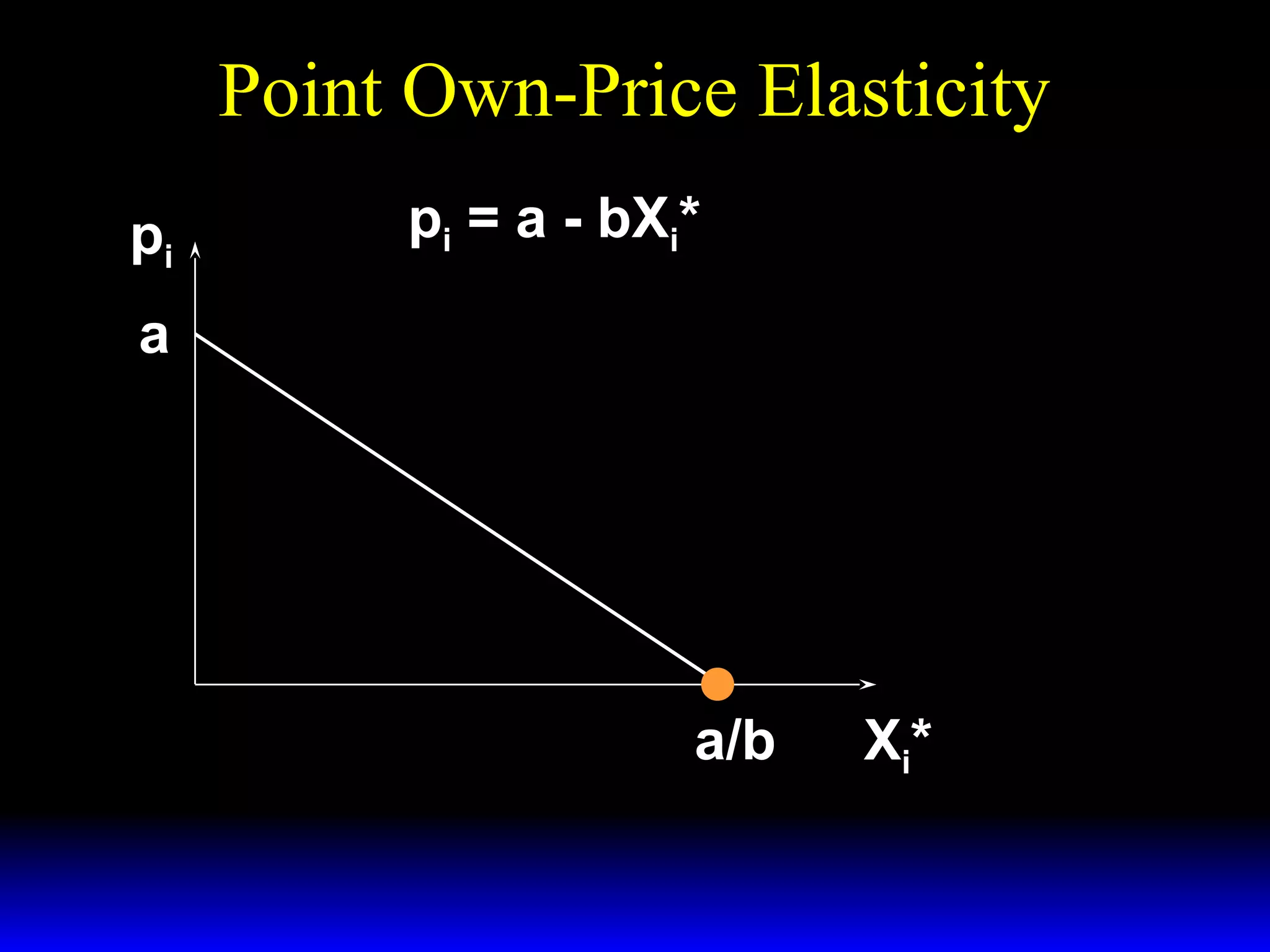
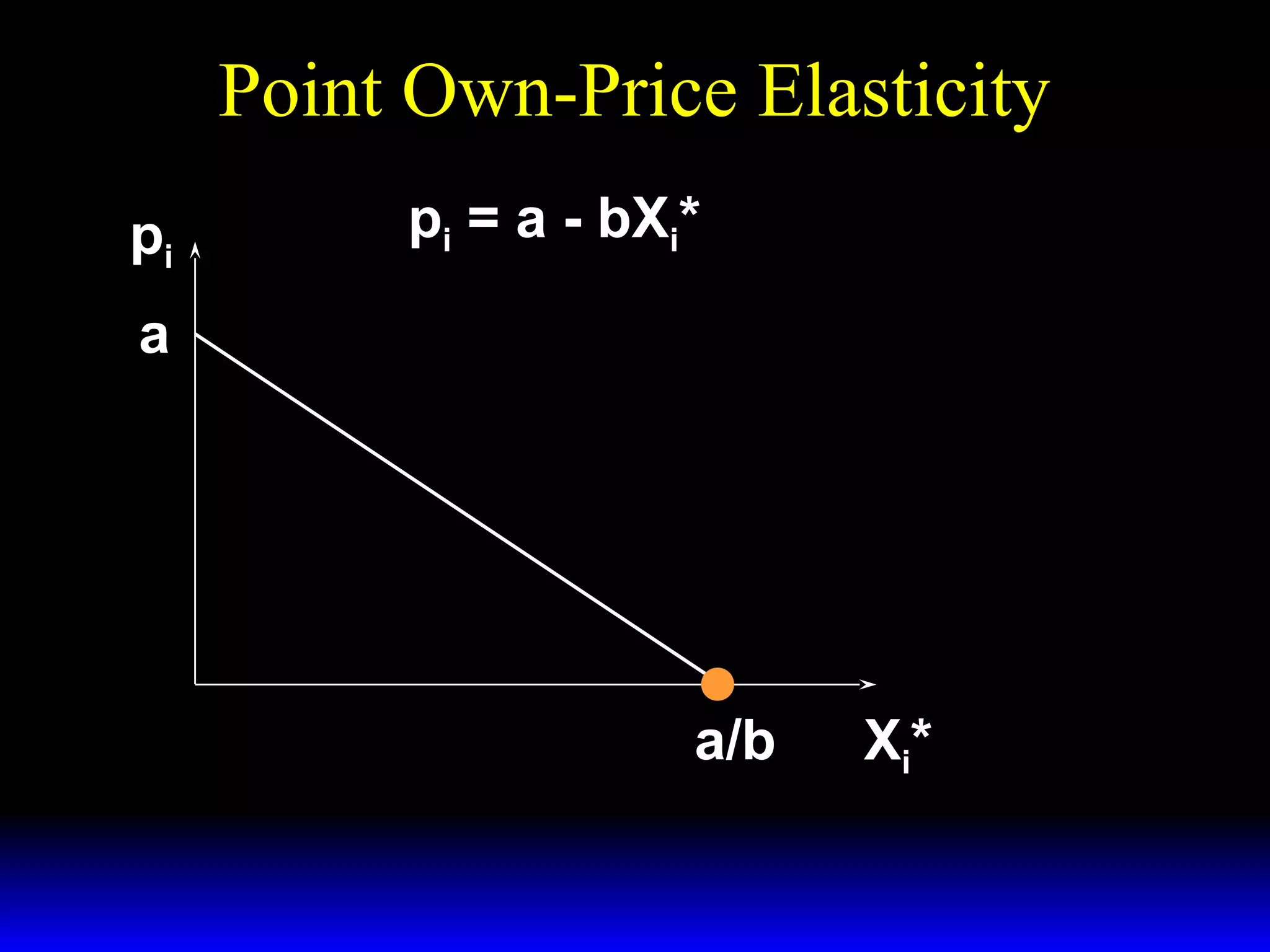
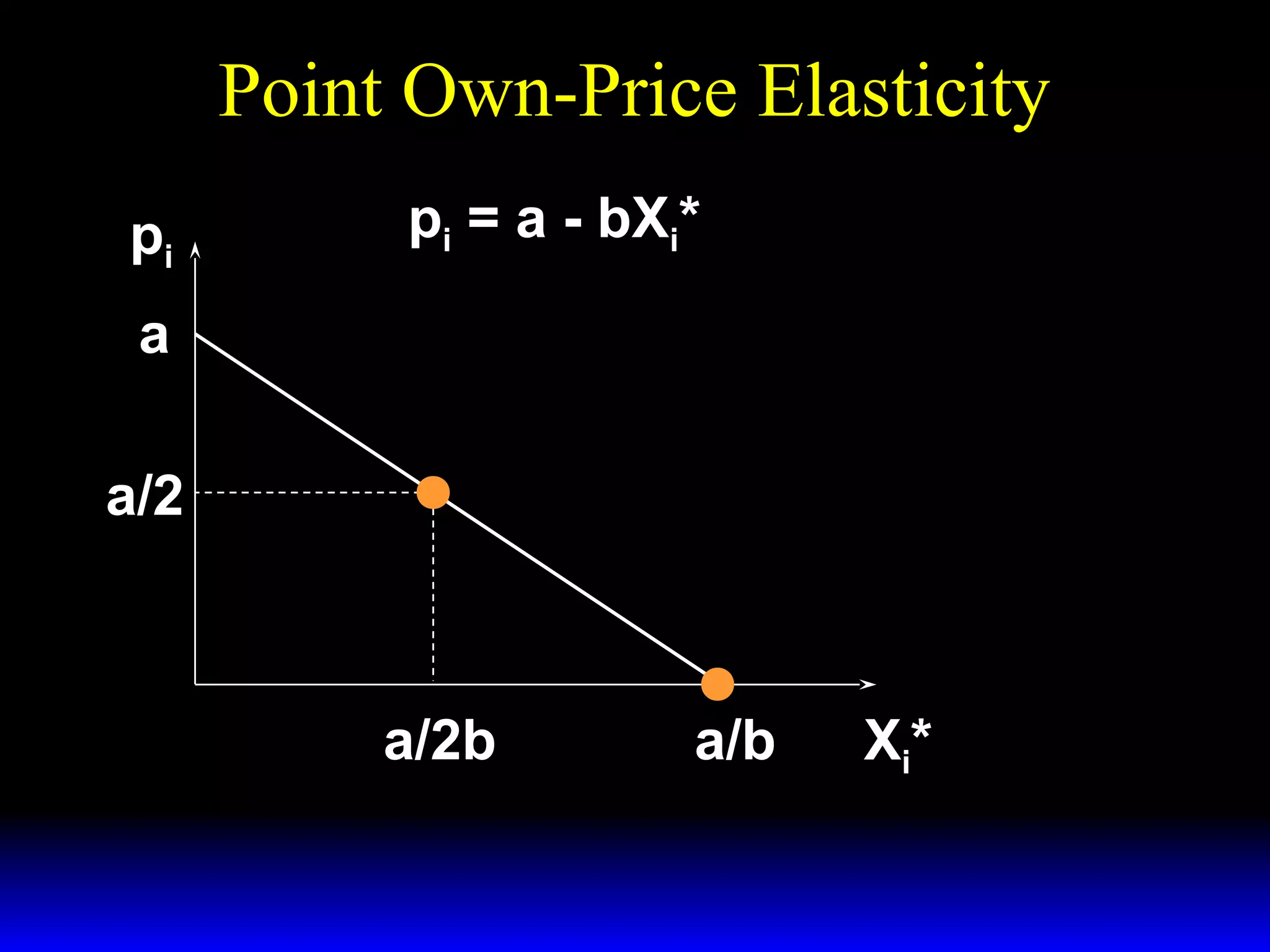
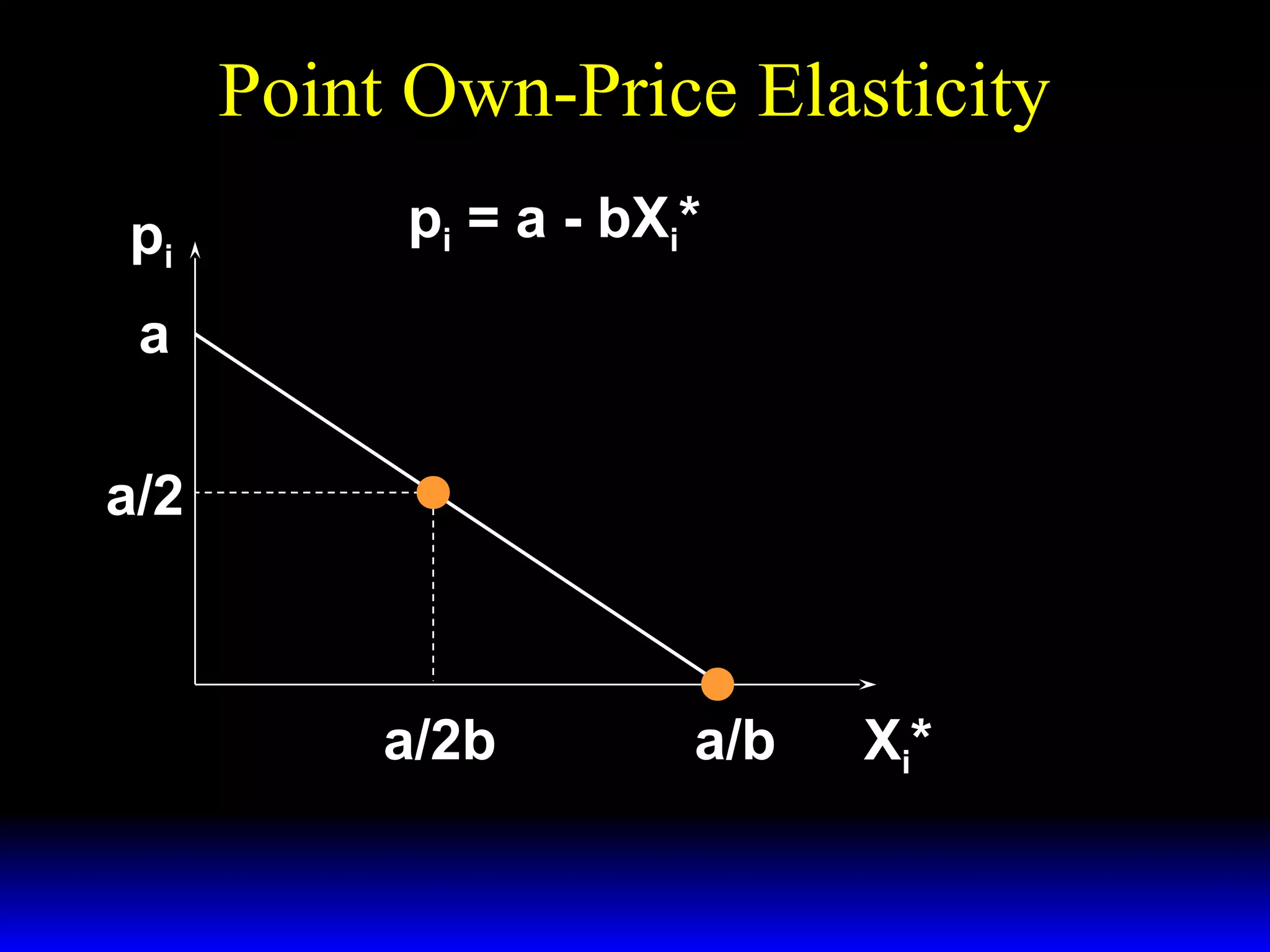
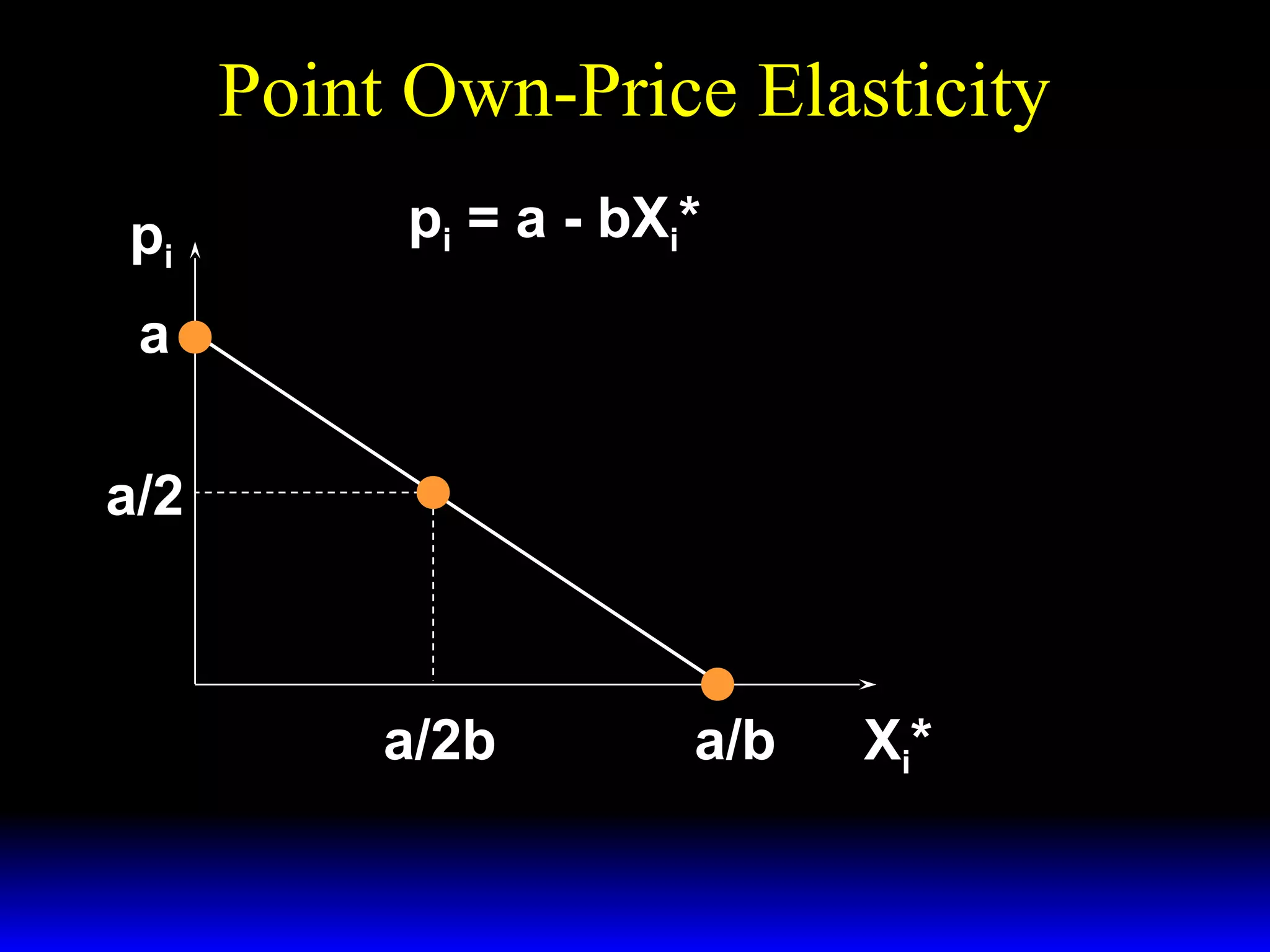
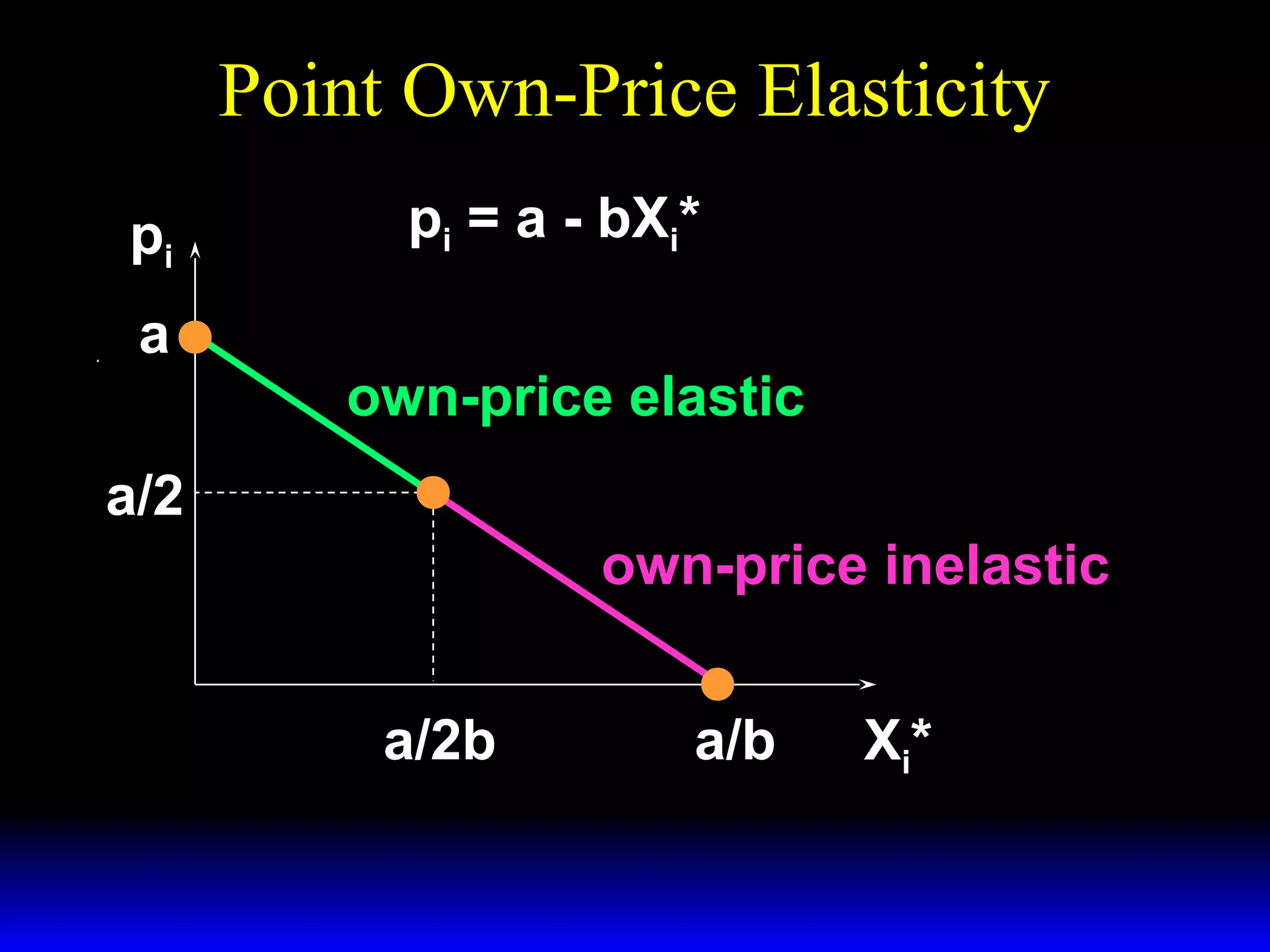
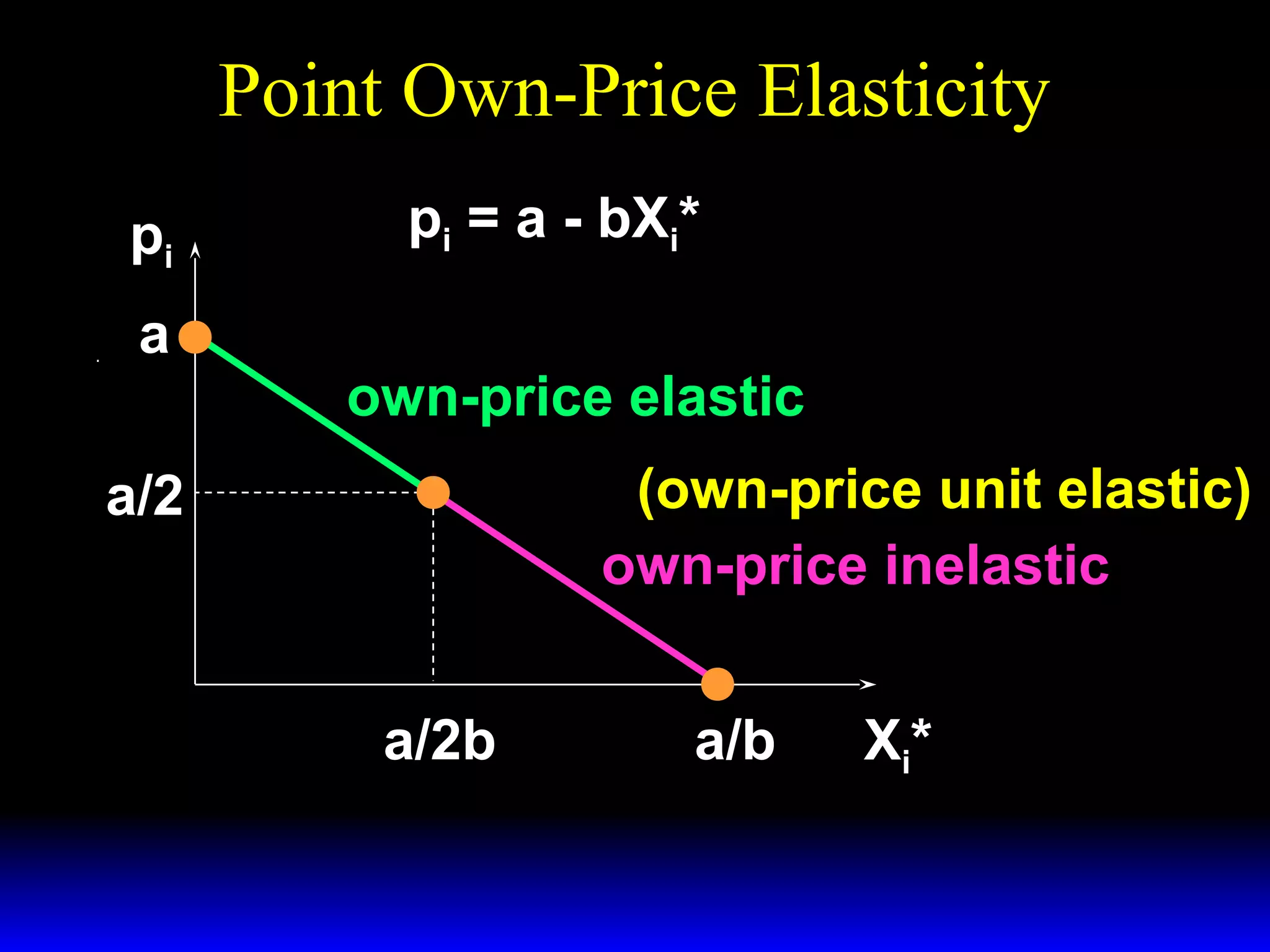
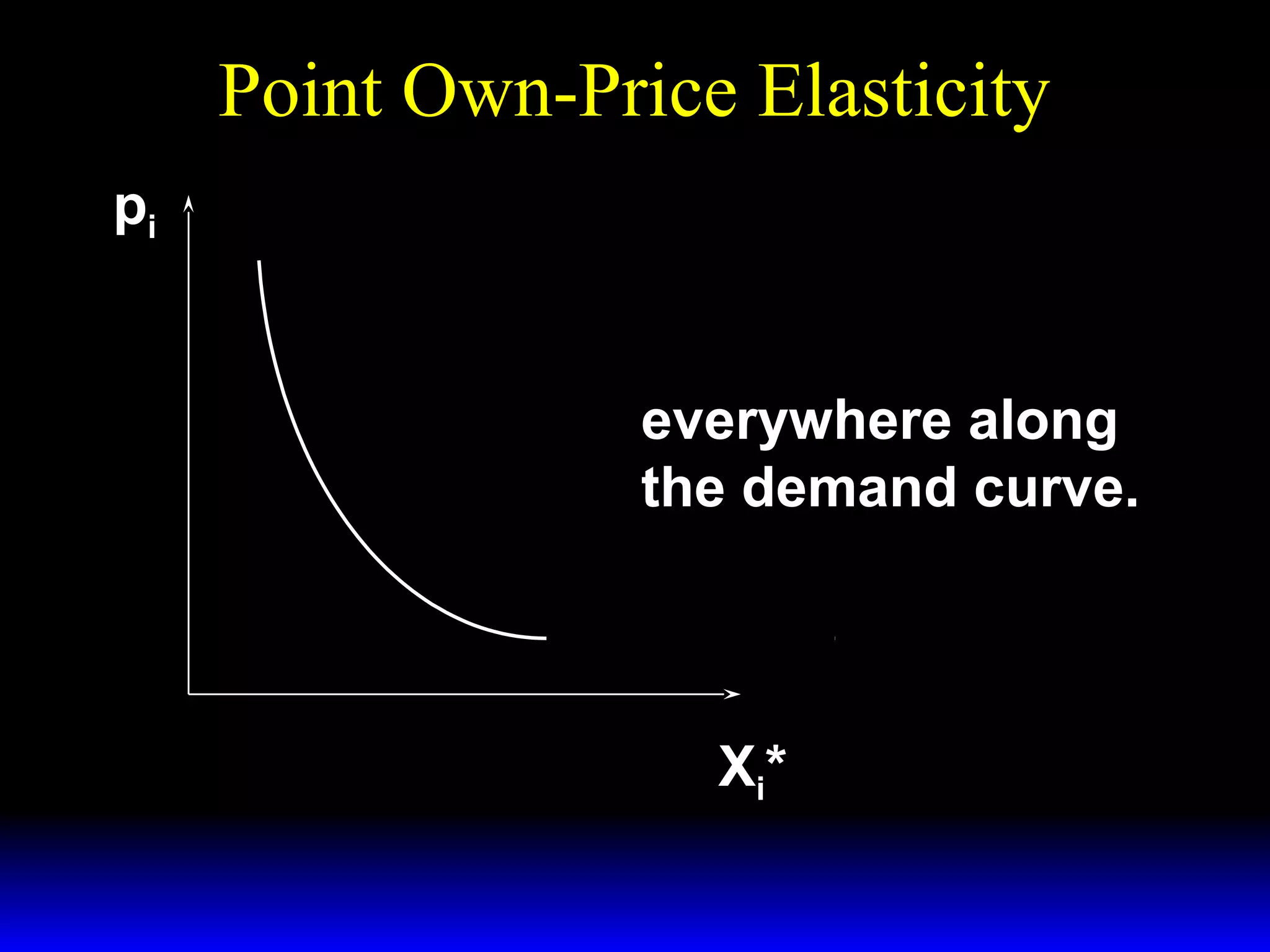
This document discusses the concept of market demand and how it relates to individual consumer demand. It explains that the market demand curve is the horizontal sum of individual demand curves. It then discusses the concept of elasticity, including own-price elasticity of demand and how elasticity measures the sensitivity of one variable to changes in another. It provides examples of how own-price elasticity can be calculated using demand curves and formulas. It also discusses how the elasticity measurement relates to whether raising price will increase or decrease seller revenue.






















![Revenue and Own-Price Elasticity of
Demand
R( p ) = p × X* (p ).
Sellers’ revenue is
dR
dX*
So
= X* (p ) + p
dp
dp
*
p dX
*
= X (p )1 +
*
X (p ) dp
= X* (p )[ 1 + ε ] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15-140131134447-phpapp01/75/Ch15-52-2048.jpg)
![Revenue and Own-Price Elasticity of
Demand
dR
= X* (p )[ 1 + ε ]
dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15-140131134447-phpapp01/75/Ch15-53-2048.jpg)
![Revenue and Own-Price Elasticity of
Demand
dR
= X* (p )[ 1 + ε ]
dp
so if ε = −1
then
dR
=0
dp
and a change to price does not alter
sellers’ revenue.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15-140131134447-phpapp01/75/Ch15-54-2048.jpg)
![Revenue and Own-Price Elasticity of
Demand
dR
= X* (p )[ 1 + ε ]
dp
dR
>0
but if − 1 < ε ≤ 0 then
dp
and a price increase raises sellers’
revenue.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15-140131134447-phpapp01/75/Ch15-55-2048.jpg)
![Revenue and Own-Price Elasticity of
Demand
dR
= X* (p )[ 1 + ε ]
dp
And if
ε < −1
dR
<0
then
dp
and a price increase reduces sellers’
revenue.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15-140131134447-phpapp01/75/Ch15-56-2048.jpg)