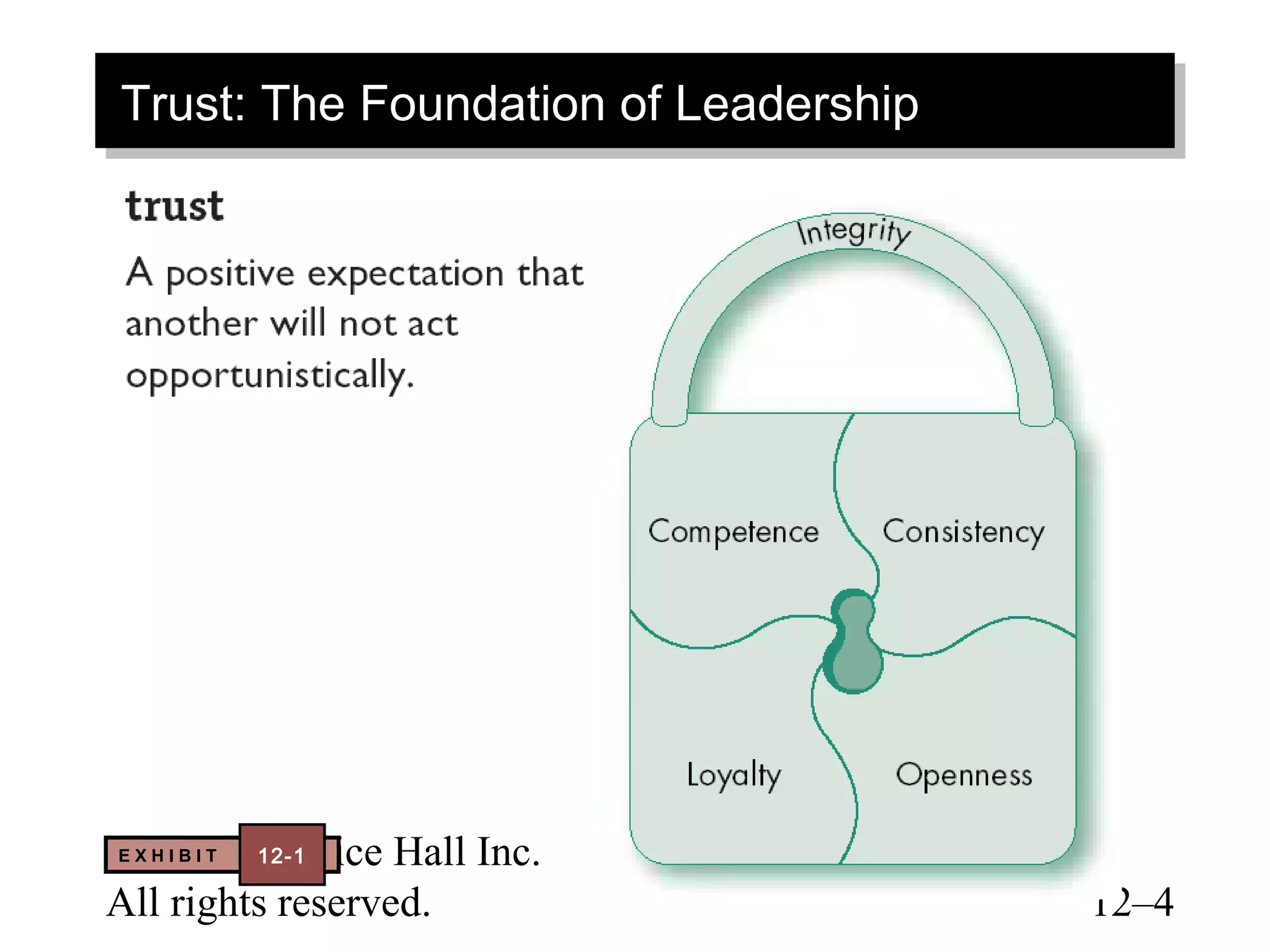
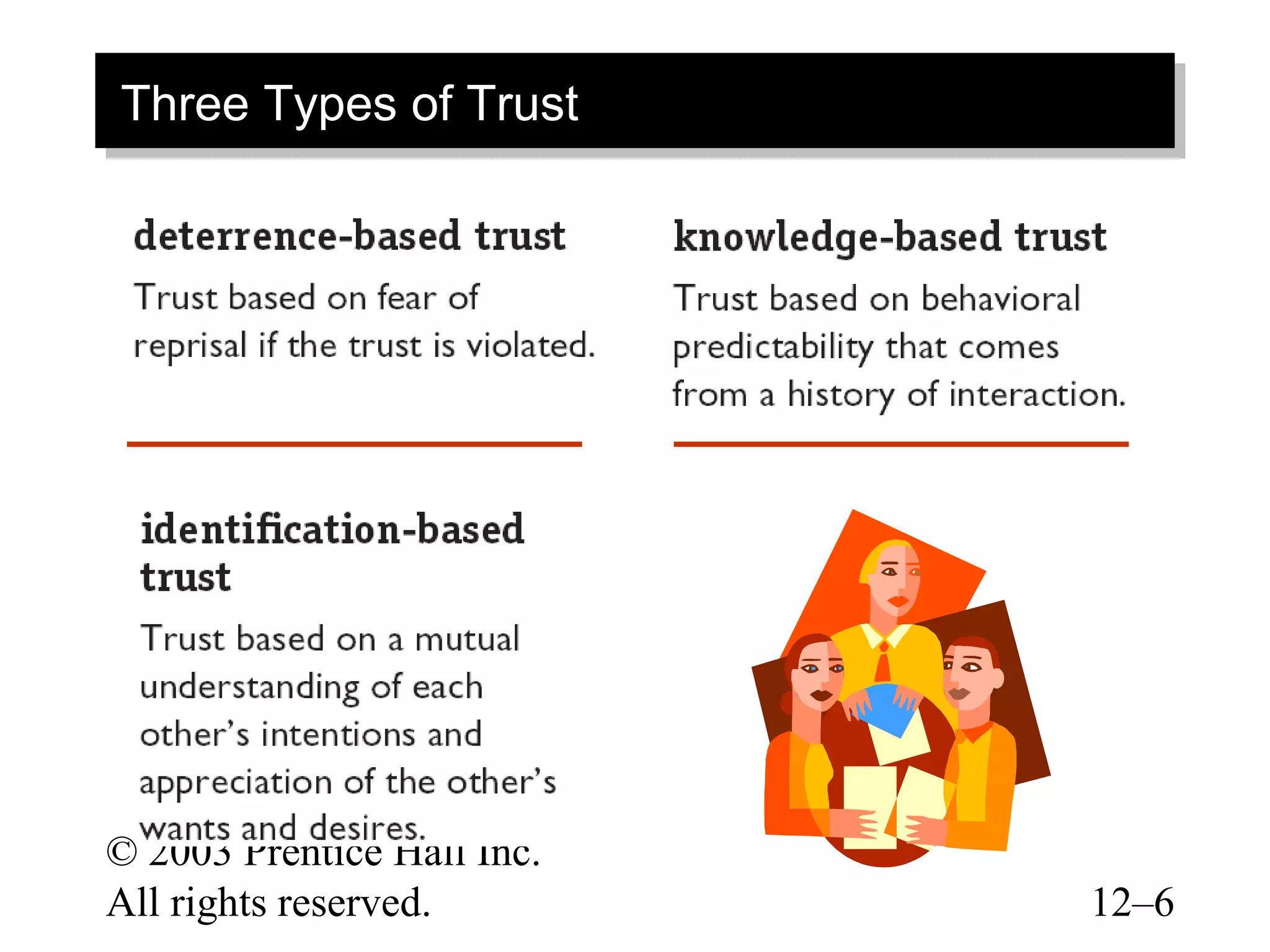
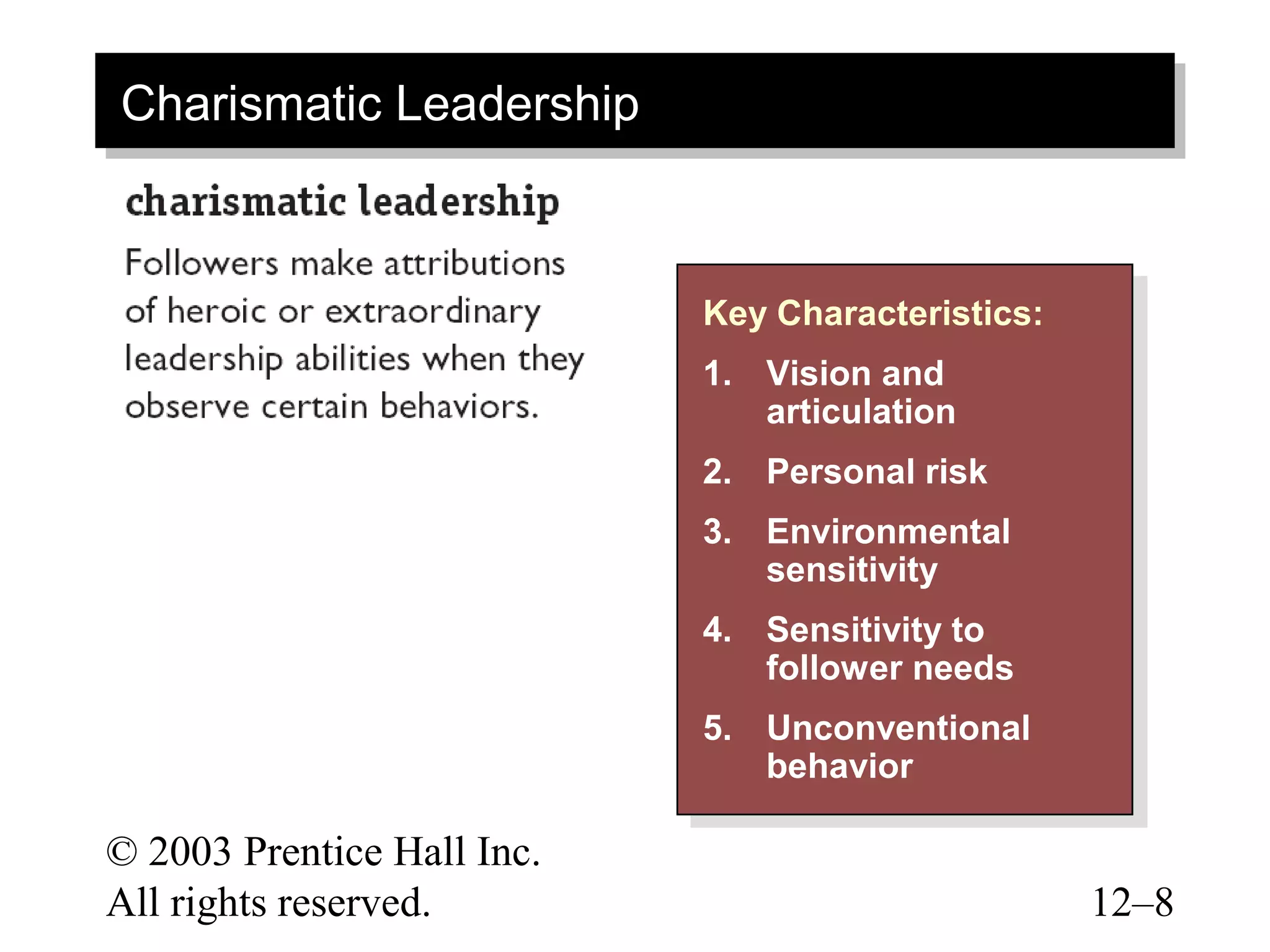
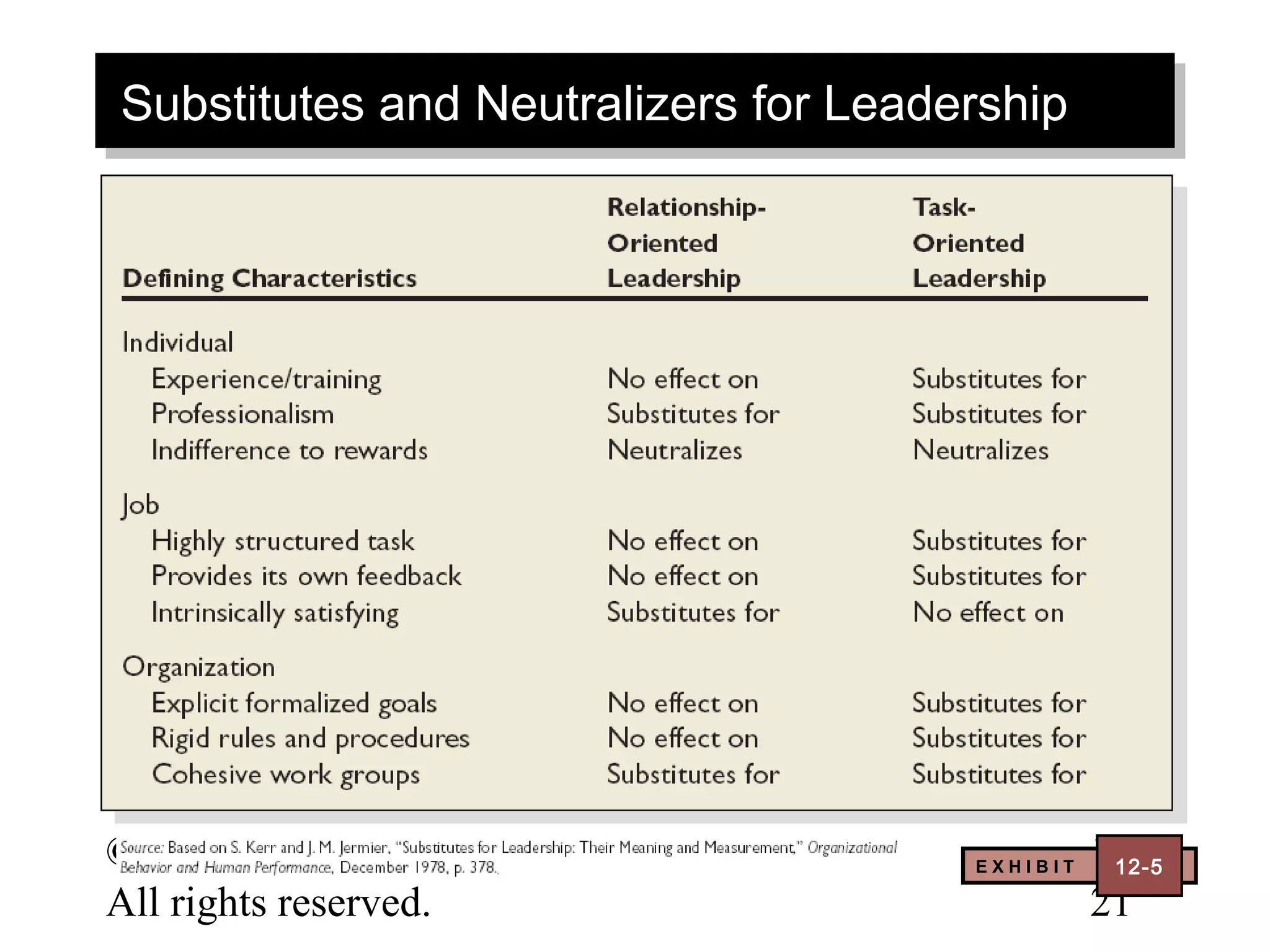
This document discusses leadership concepts from a textbook on organizational behavior. It covers dimensions of trust, characteristics of charismatic and transformational leaders, qualities of visionary leadership, roles of team leaders and mentors, and creating self-leadership. The objectives are to understand key leadership theories and apply them to analyze leadership effectiveness.