The document discusses lower bounds for algorithms. It defines lower bounds as estimates of the minimum amount of work needed to solve a problem. It then provides examples of problems and their known lower bounds, such as sorting requiring Ω(nlogn) comparisons. The document outlines several methods for establishing lower bounds, including trivial counting arguments, decision trees, adversary arguments, and reducing other problems. It focuses on using reductions to show that one problem is at least as hard as another known hard problem to prove a new lower bound. The summary concludes by briefly introducing the concept of NP-complete problems.




![A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 3rd ed., Ch. 11 ©2012 Pearson
Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved. 5
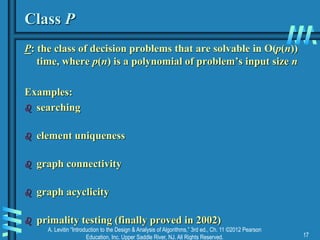
Decision Trees
Decision tree —model algorithms that use comparisons:
internal nodes represent comparisons
leaves represent outcomes
How many orderings of 2 elements? Of 3? Of n?
Tree for 3-element insertion sort [insert b in a, then c into ab]
a < b
b < c a < c
yes
yes no
no
yes
no
a < c b < c
a < b < c
c < a < b
b < a < c
b < c < a
no yes
abc
abc bac
bca
acb
yes
a < c < b c < b < a
no](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch11-04-27-15-230819045747-64d475d2/85/ch11-04-27-15-ppt-5-320.jpg)


![A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 3rd ed., Ch. 11 ©2012 Pearson
Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved. 8
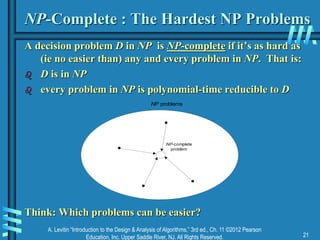
Lower Bounds by Problem Reduction
If we know a LB for alg A, can we use that knowledge to find a
LB for alg B? Remember reduction:
- Minheap reduces to maxheap
- Minimum reduces to sort
- Element uniqueness for pairs reduces to closest pair
Which would be most useful?
A [(f )] reduces to B [(? )]
B [(? )] reduces to A [(f )]
[Assume the reduction itself is fast (ie O(f)) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch11-04-27-15-230819045747-64d475d2/85/ch11-04-27-15-ppt-8-320.jpg)
![A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 3rd ed., Ch. 11 ©2012 Pearson
Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved. 9
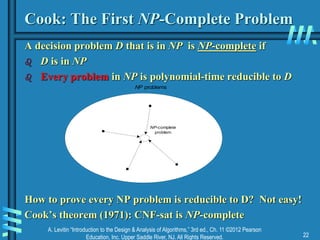
Lower Bounds by Problem Reduction
Which would be most useful?
A [(f )] reduces to B [(? )]
B [(? )] reduces to A [(f )]
Proc A [(f )] Proc B [(? )]
… …
B [(? )] A [(f )]
… …
A= [(? )] => ??? A = [(? )] => ???](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch11-04-27-15-230819045747-64d475d2/85/ch11-04-27-15-ppt-9-320.jpg)
![A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 3rd ed., Ch. 11 ©2012 Pearson
Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved. 10
Lower Bounds by Problem Reduction
Which would be most useful?
A [(f )] reduces to B [(? )]
B [(? )] reduces to A [(f )]
Proc A [(f )] Proc B [(? )]
… …
B [(? )] A [(f )]
… …
A= [(f )] => B = [(f )] A = [(f )] => Nothing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch11-04-27-15-230819045747-64d475d2/85/ch11-04-27-15-ppt-10-320.jpg)

![A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 3rd ed., Ch. 11 ©2012 Pearson
Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved. 12
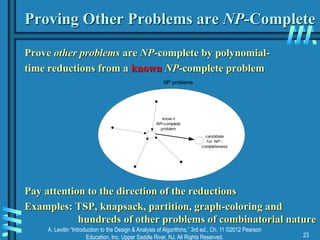
Lower Bounds by Problem Reduction
Example: P is finding MST for n points in Cartesian plane
Q is element uniqueness problem (known to be in (nlogn))
Reduce Element Uniqueness to MST:
Unique (S : IntSet = {x1, x2, …, xn}) [Known (nlogn)]
P : PairSet = {(x1, 0), (x2, 0), …, (xn, 0)}
T : Tree = MST (P)
D : Nat = min_length (edges of T)
return D = 0
Thus, MST is (nlogn)!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch11-04-27-15-230819045747-64d475d2/85/ch11-04-27-15-ppt-12-320.jpg)