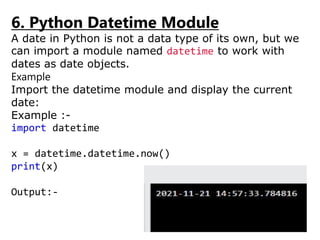
1. Modules allow the user to organize Python code into reusable files called modules and then import and use functionalities from those modules in other Python scripts and files.
2. Core Python modules like math, random, datetime etc. are bundled with the Python interpreter while third party modules need to be installed separately.
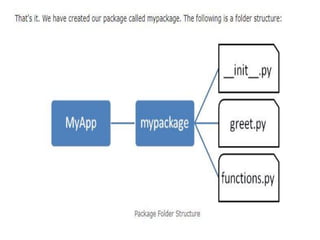
3. Packages are a way to group related modules together and avoid naming collisions, they create a hierarchical namespace and allow modules to be logically organized.




















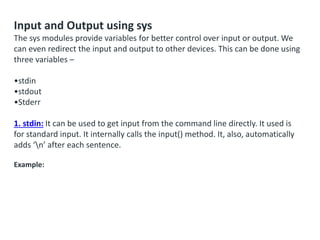
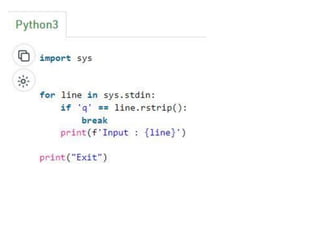
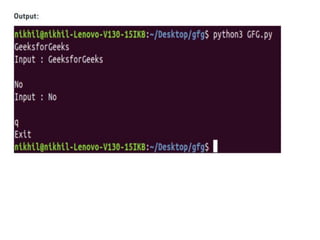

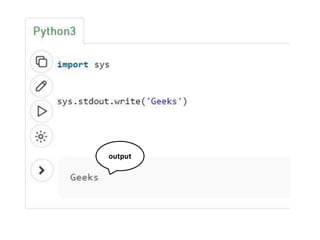









![Create a NumPy ndarray Object
NumPy is used to work with arrays. The array object in NumPy is
called ndarray.
We can create a NumPy ndarray object by using the array() function.
Example
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(arr)
print(type(arr))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonmodule-converted-220124041845/85/ch-2-Python-module-53-320.jpg)



