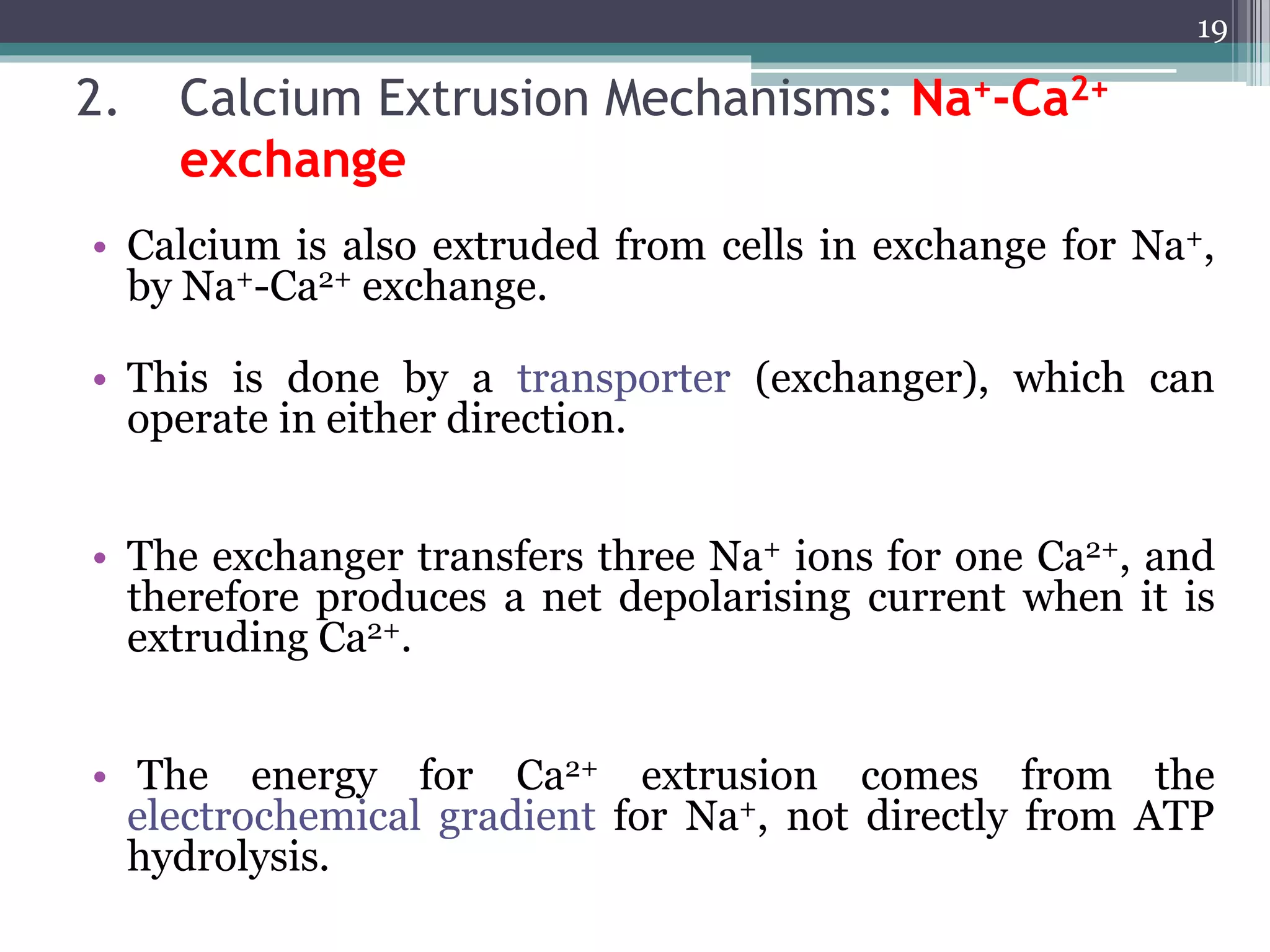
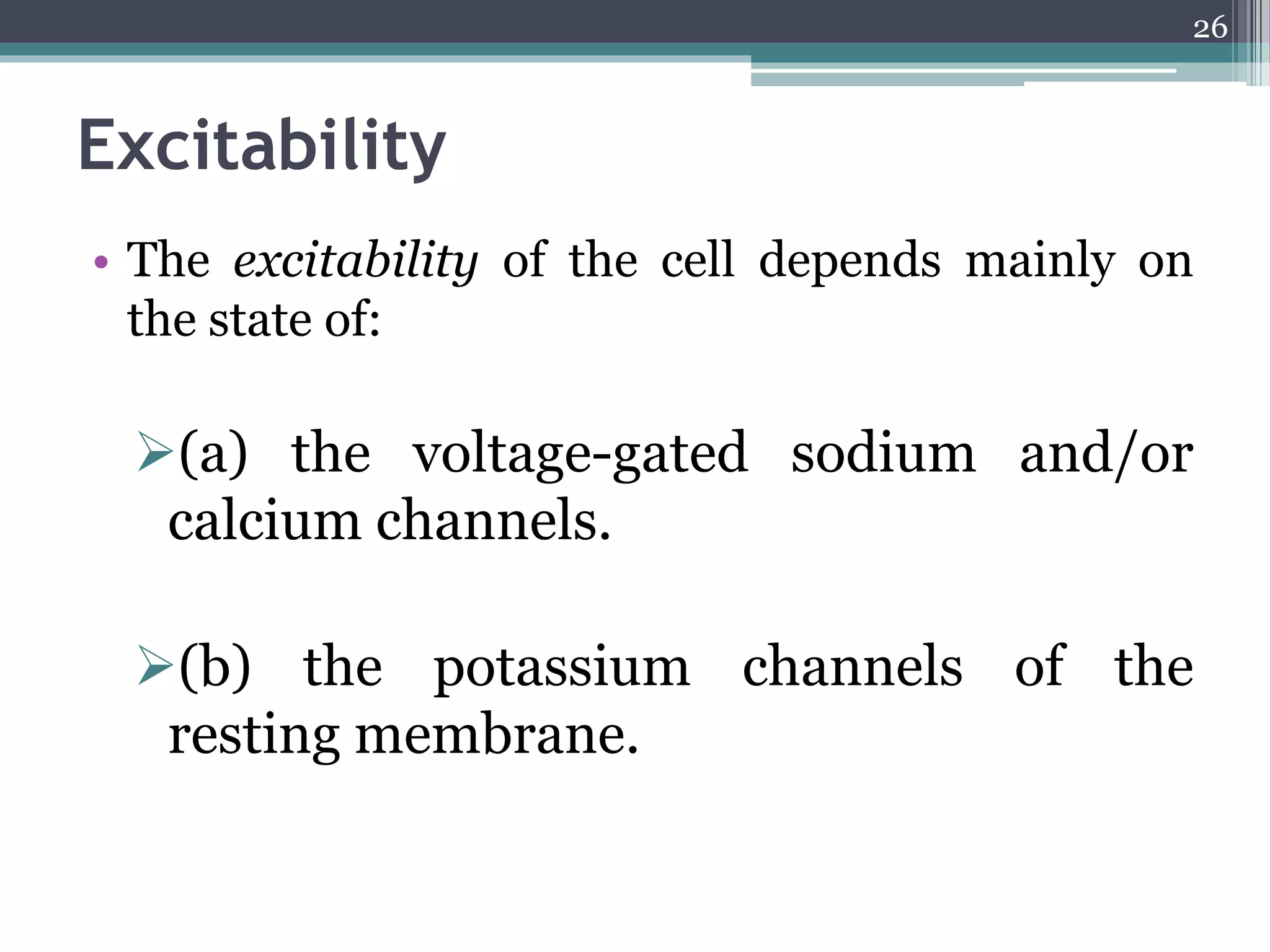
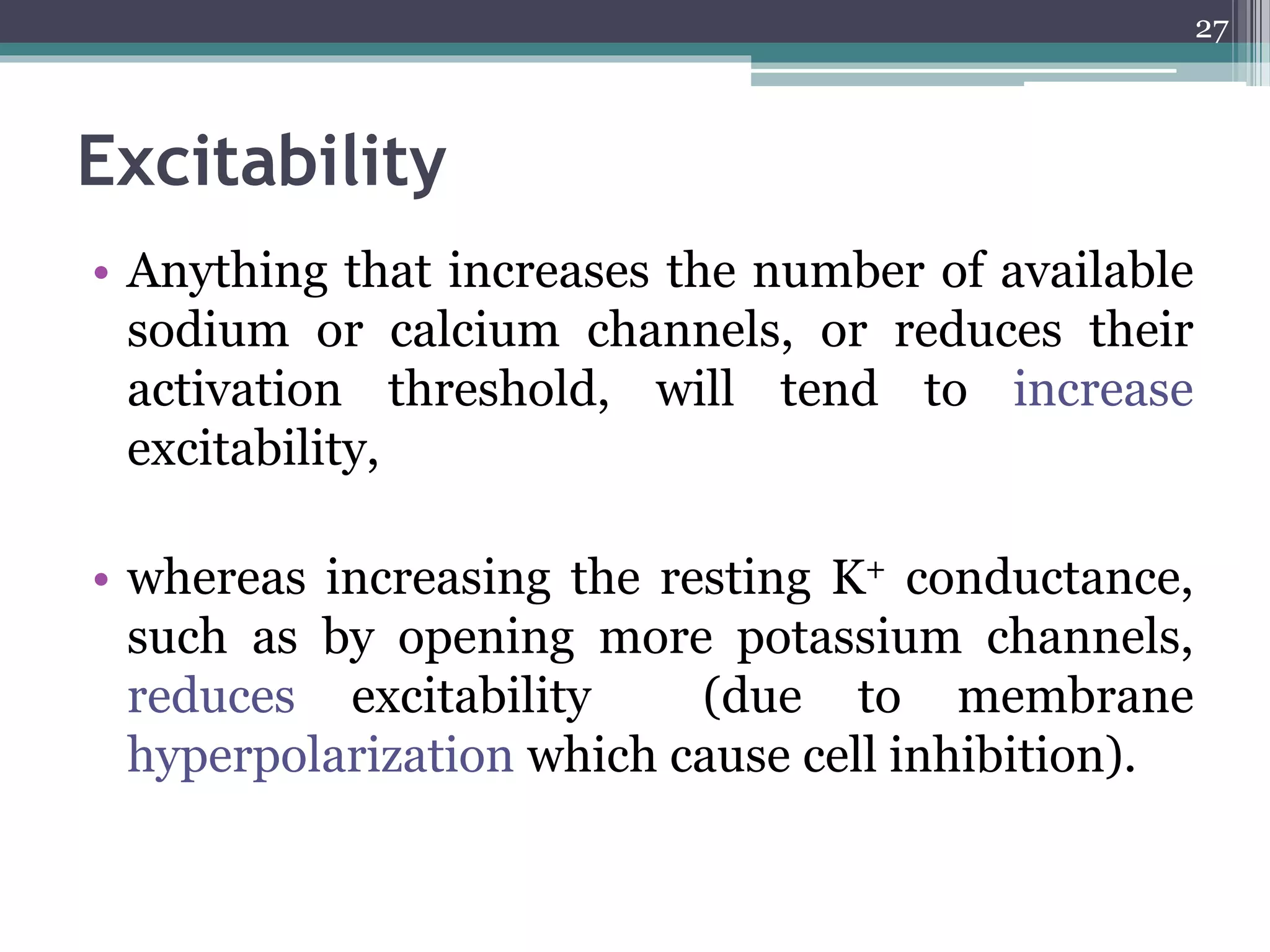
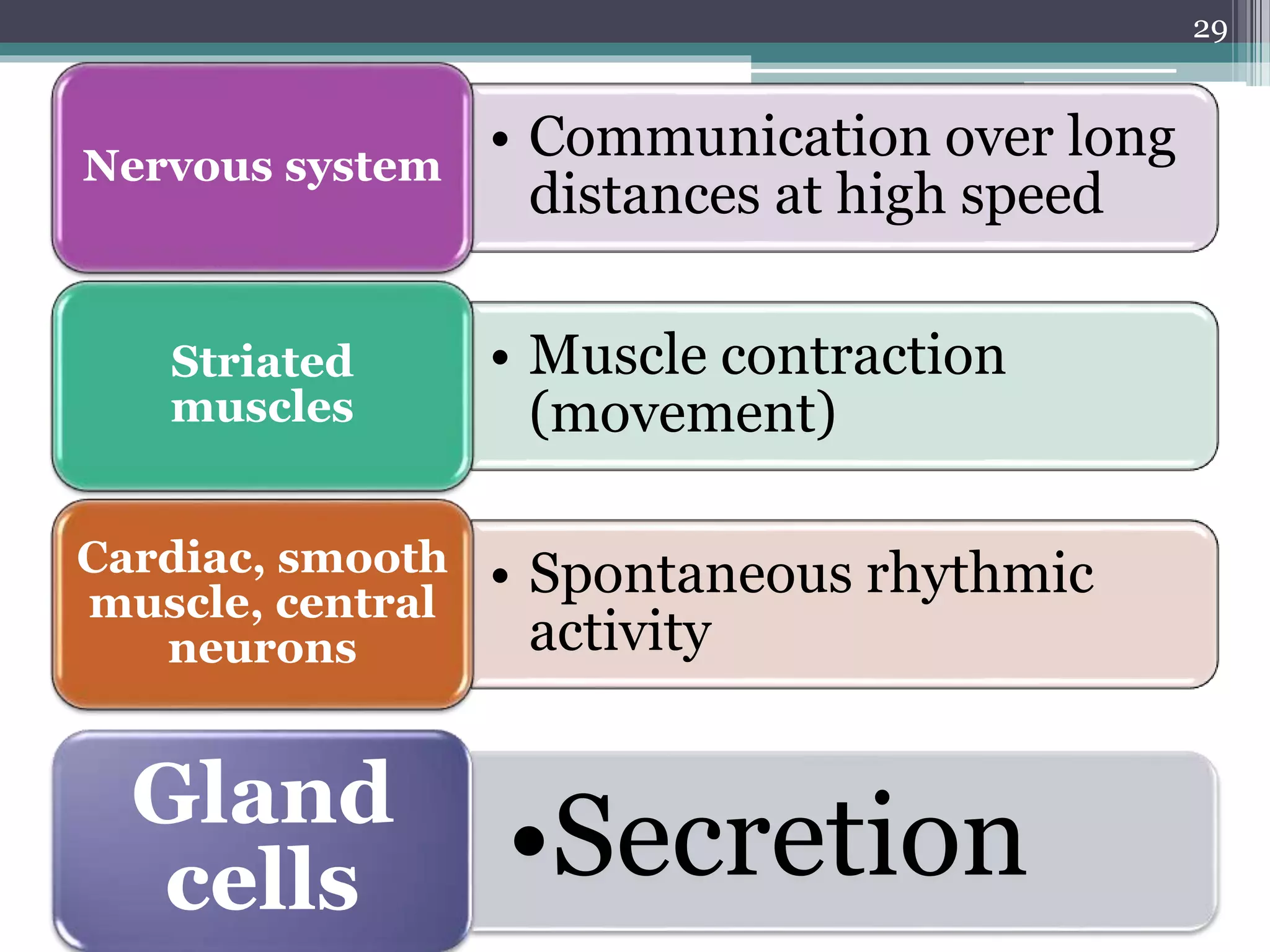
1) The document discusses how drugs act at the cellular level, focusing on calcium regulation and its role in excitation, muscle contraction, and chemical mediator release.
2) Intracellular calcium levels are tightly regulated by calcium entry through channels in the plasma membrane, calcium extrusion via pumps and exchangers, and calcium release from intracellular stores like the endoplasmic reticulum.
3) Changes in calcium levels influence a variety of cellular functions by regulating enzymes and ion channels. Calcium signaling underlies important physiological processes like excitation, contraction of cardiac and smooth muscle, and neurotransmitter release.



![Con.
• The short-term regulation of cell function depends
mainly on the free concentration of Ca2+ in the cytosol,
[Ca2+]i.
• Ca2+ is the most important regulator of cell function.
• Many drugs and physiological mechanisms operate,
directly or indirectly, by influencing [Ca2+]i. [Ca2+]i is
regulated by:
• ion channels and transporters in the plasma membrane.
• the storage and release of Ca2+ by intracellular
organelles.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-4-2048.jpg)
![Con.
• In turn [Ca2+]i regulates a variety of functional
proteins, including:
Enzymes (particularly kinases and
phosphatases),
channels,
transporters,
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-5-2048.jpg)

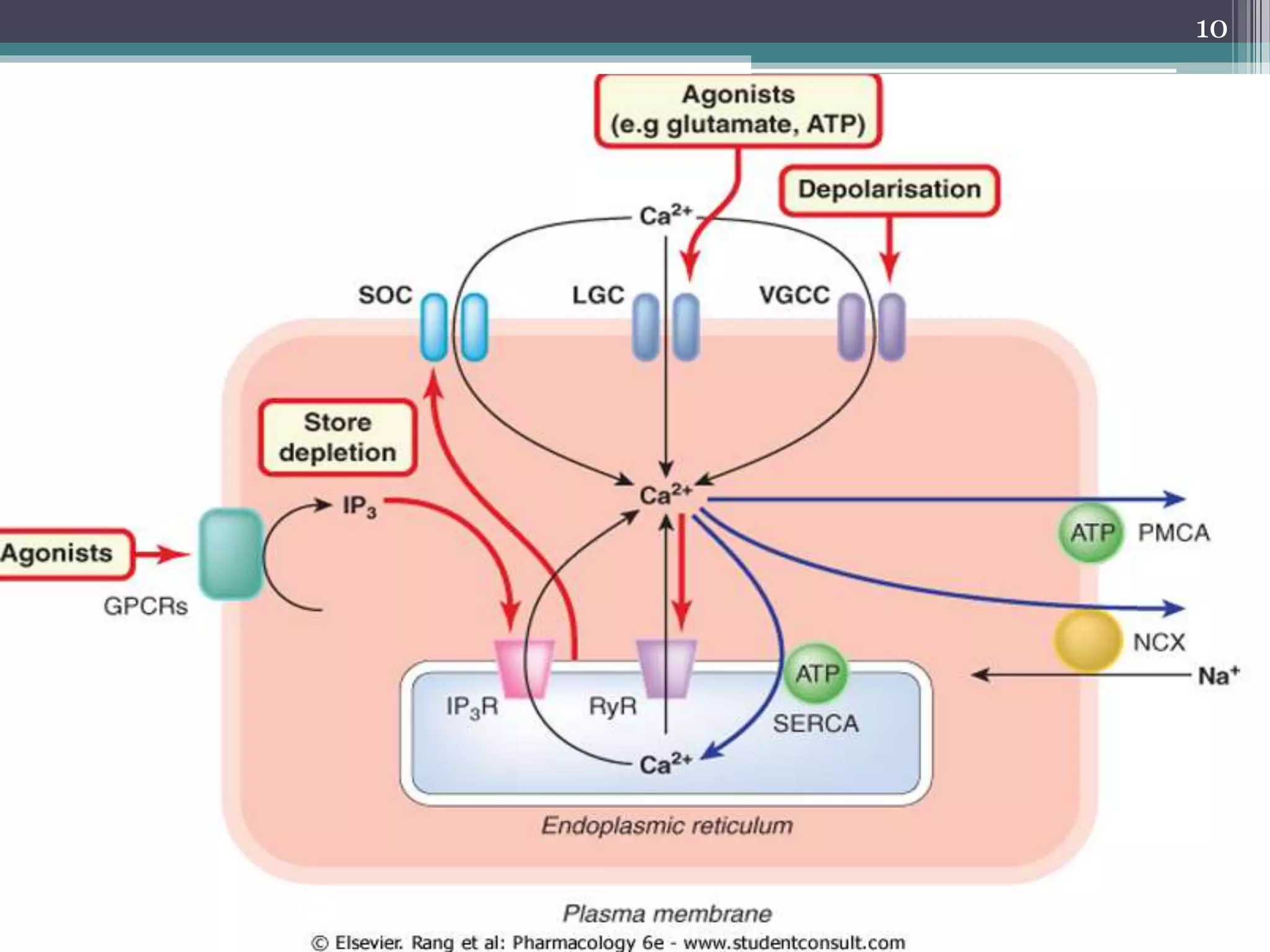
![Regulation Of Intracellular Calcium Levels
• Most of the Ca2+ in a resting cell is sequestered
in organelles, particularly the endoplasmic or
sarcoplasmic reticulum (ER or SR) and the
mitochondria.
• The free [Ca2+]i is kept to a low level
• The Ca2+ concentration in tissue fluid [Ca2+]o, is
high so there is a large concentration gradient
favouring Ca2+ entry.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-7-2048.jpg)
![Con.
• Regulation of [Ca2+]i involves Three main
mechanisms:
control of Ca2+ entry
control of Ca2+ extrusion
exchange of Ca2+ between the cytosol
and the intracellular stores.
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-8-2048.jpg)








![IP3R
• IP3R is a ligand-gated ion channel.
• It is activated by inositol trisphosphate (IP3).
• This is the main mechanism by which activation
of G-protein-coupled receptors causes an
increase in [Ca2+]i.
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-21-2048.jpg)
![RyR:
• So called because it was first identified through the
specific blocking action of the plant alkaloid
ryanodine.
• It is particularly important in skeletal muscle.
• It is activated by a small rise in [Ca2+]i, producing
the effect known as calcium-induced calcium
release (CICR), which serves to amplify the Ca2+
signal produced by other mechanisms.
• CICR means that release tends to be regenerative.
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-22-2048.jpg)






![• The membrane is selectively permeable to K+
because potassium channels are open at rest.
• Na+ ions are actively extruded from the cell in
exchange for K+ ions by the Na+ pump (or Na+-
K+ ATPase).
• The result is that [K+]i, is higher, and [Na+]i is
lower, than the respective extracellular
concentrations.
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-32-2048.jpg)








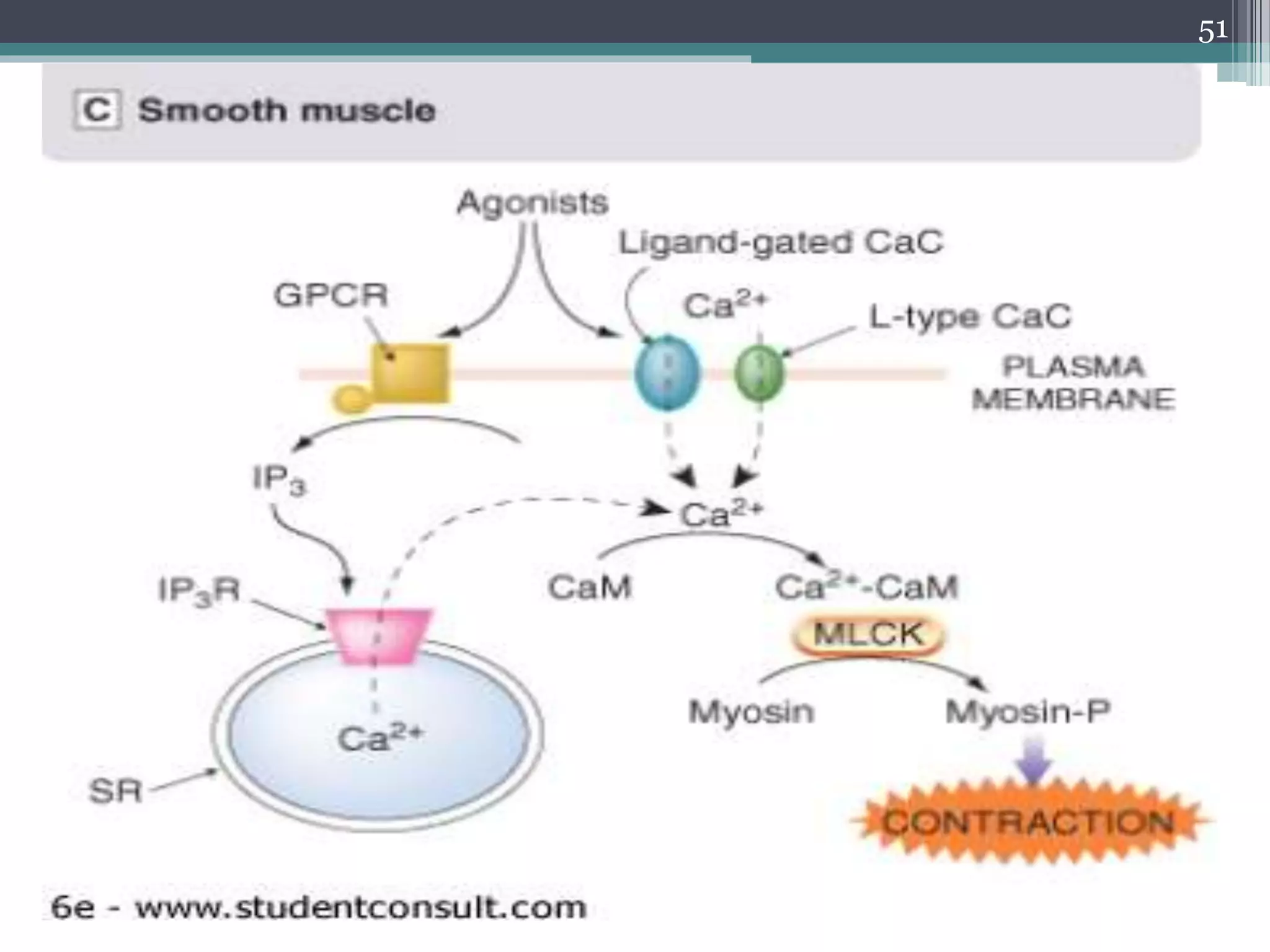
![MUSCLE CONTRACTION
• In all muscle types, the basic molecular basis of
contraction is similar, namely an interaction
between actin and myosin, fuelled by ATP and
initiated by an increase in [Ca2+]i,
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-41-2048.jpg)
![▫ However there are differences between
these three kinds of muscles in:
(a) the linkage between membrane
events and increase in [Ca2+]i.
(b) the mechanism by which [Ca2+]i
regulates contraction.
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-42-2048.jpg)


















![RELEASE OF CHEMICAL MEDIATORS
2. Mediators that are produced on demand
and are released by diffusion or by
membrane carriers.
This group includes nitric oxide and
many lipid mediators (e.g. prostanoids,
and endocannabinoids).
Calcium ions play a key role in both cases,
because a rise in [Ca2+]i initiates
exocytosis and is also the main activator
of the enzymes responsible for the
synthesis of diffusible mediators.
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-62-2048.jpg)
![RELEASE OF CHEMICAL MEDIATORS
• Drugs and other agents that affect the
various control mechanisms that regulate
[Ca2+]i will therefore also affect mediator
release, and this accounts for many of the
physiological effects that they produce.
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-63-2048.jpg)
![EXOCYTOSIS
• Exocytosis, occurring in response to an
increase of [Ca2+]i, is the principal
mechanism of transmitter release in the
peripheral and central nervous systems, as
well as in endocrine cells and mast cells.
• Exocytosis involves fusion between the
membrane of synaptic vesicles and the inner
surface of the plasma membrane.
• The vesicles are preloaded with stored
transmitter
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-64-2048.jpg)




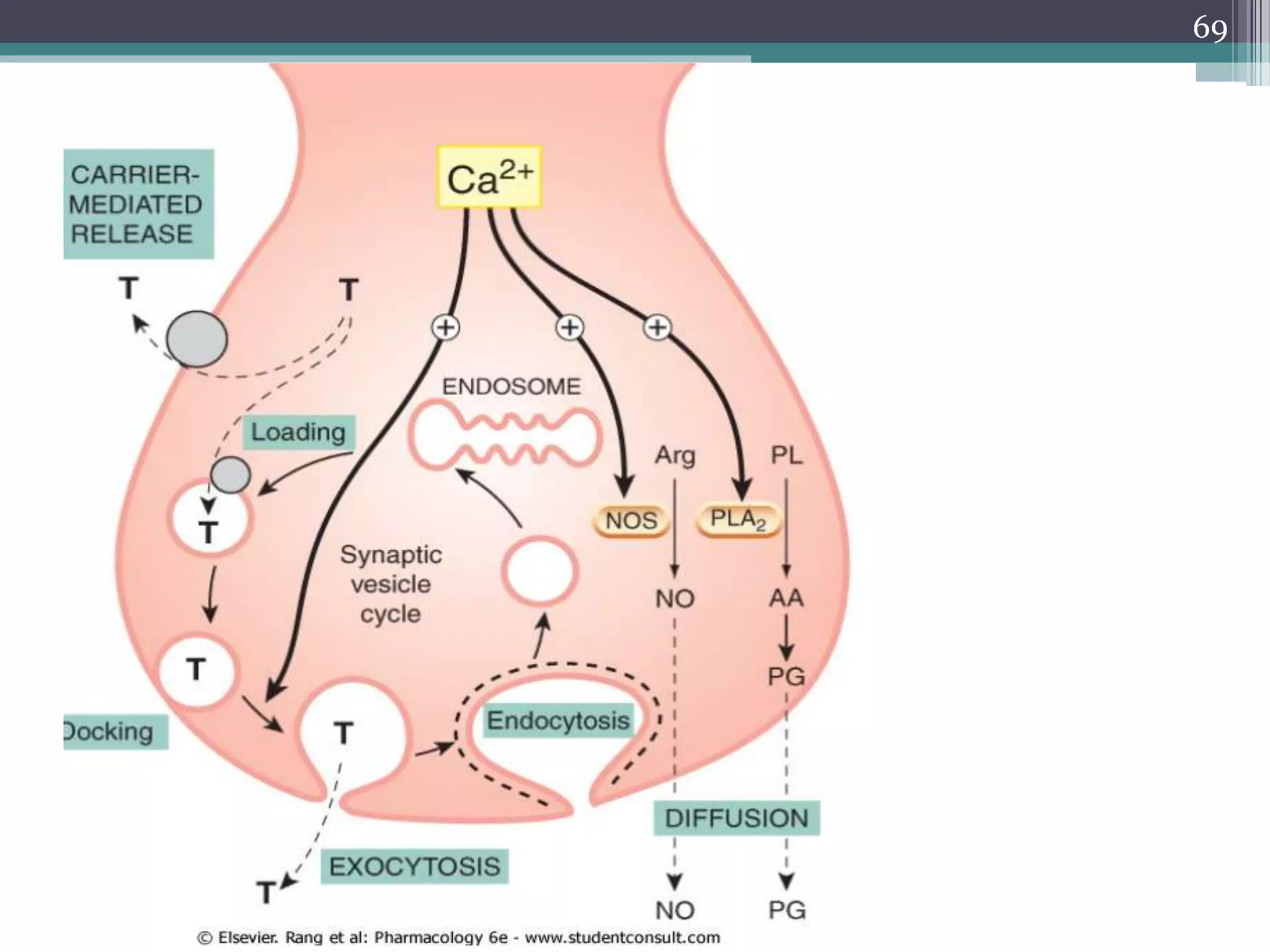

![NON-VESICULAR RELEASE MECHANISMS
• In such cases, the synthetic enzyme is activated
by Ca2+, and the moment-to-moment control of
the rate of synthesis depends on [Ca2+]i.
• This kind of release is necessarily slower than
the classic exocytotic mechanism, but in the case
of nitric oxide is fast enough for it to function as
a true transmitter.
71](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellularaspects-180208061128/75/Cellular-aspects-71-2048.jpg)