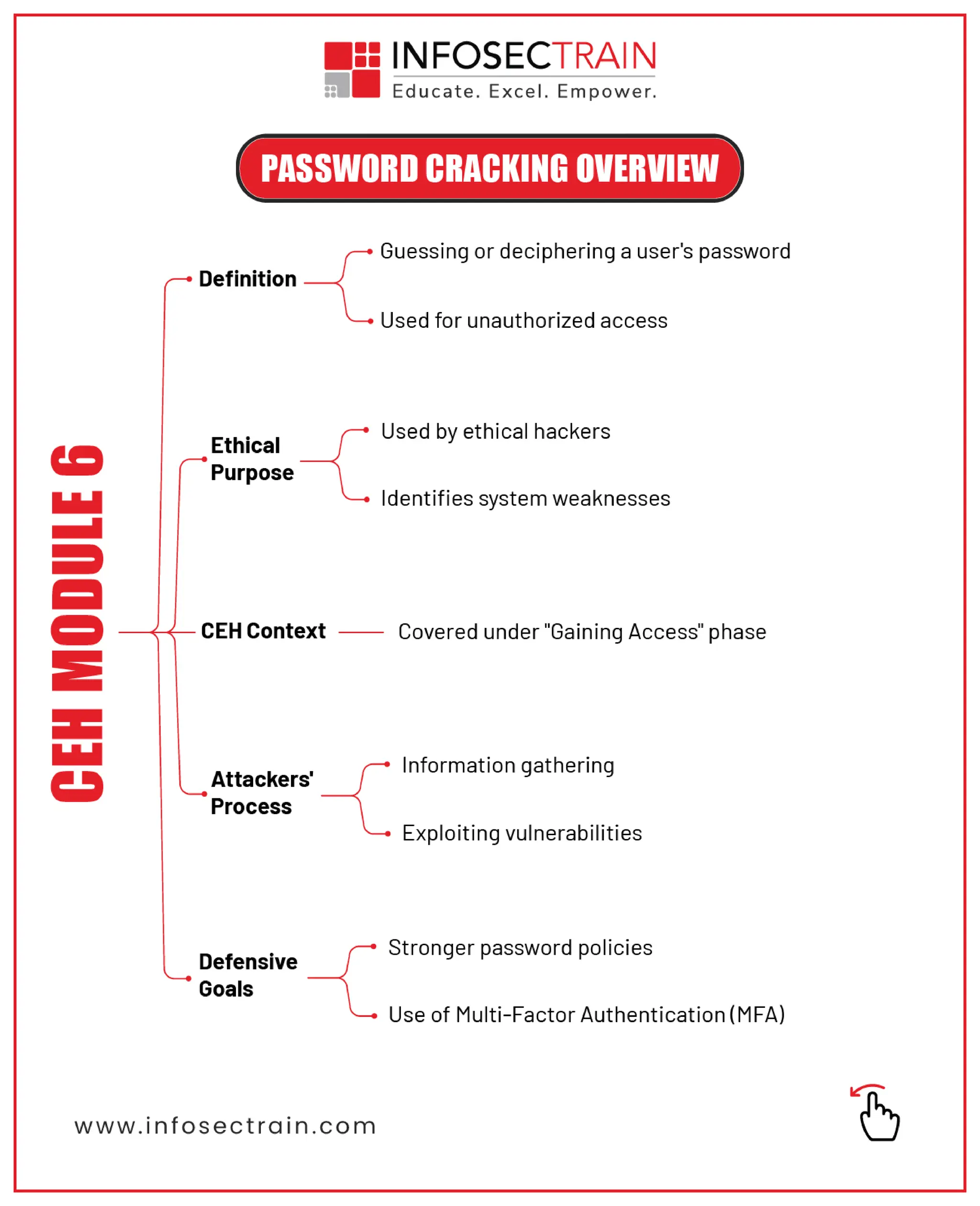
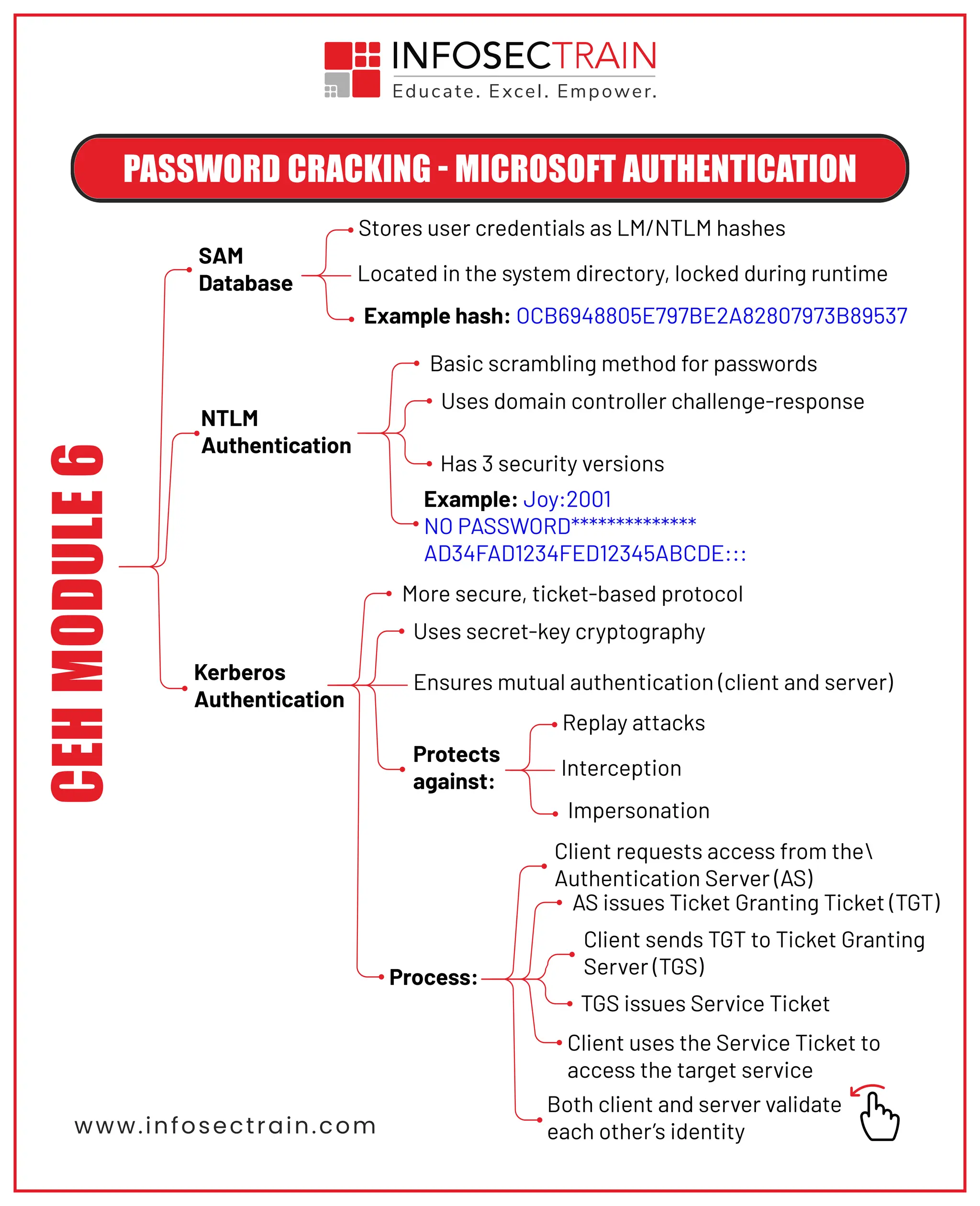
From cracking passwords to defending systems — this module dives deep into the “Gaining Access” phase of ethical hacking. 🔸 Password Cracking 101 – LM, NTLM, and Kerberos explained
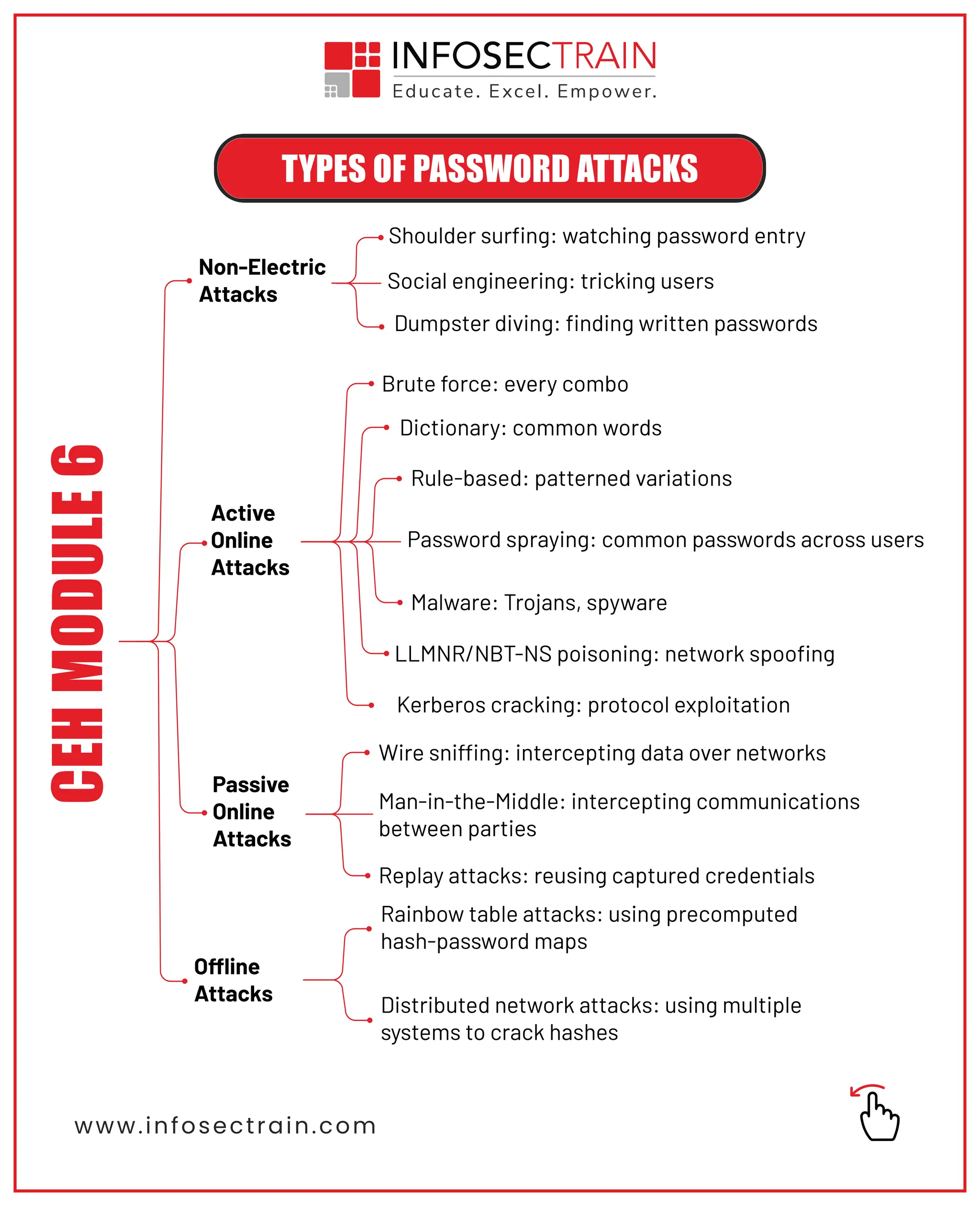
🔸 Common Attack Types – Brute Force, Dictionary, Spraying & More
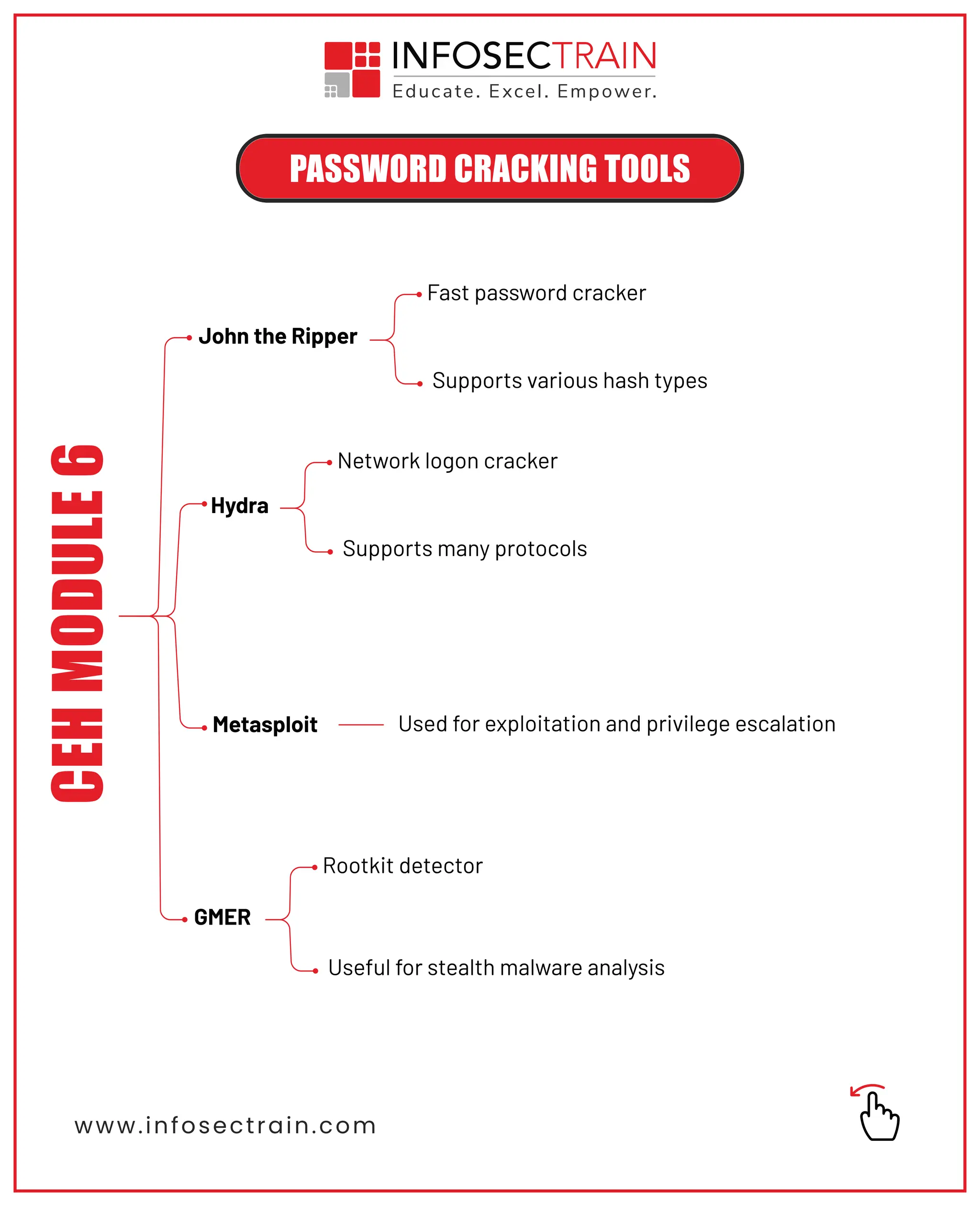
🔸 Top Tools – John the Ripper, Hydra, Metasploit, GMER
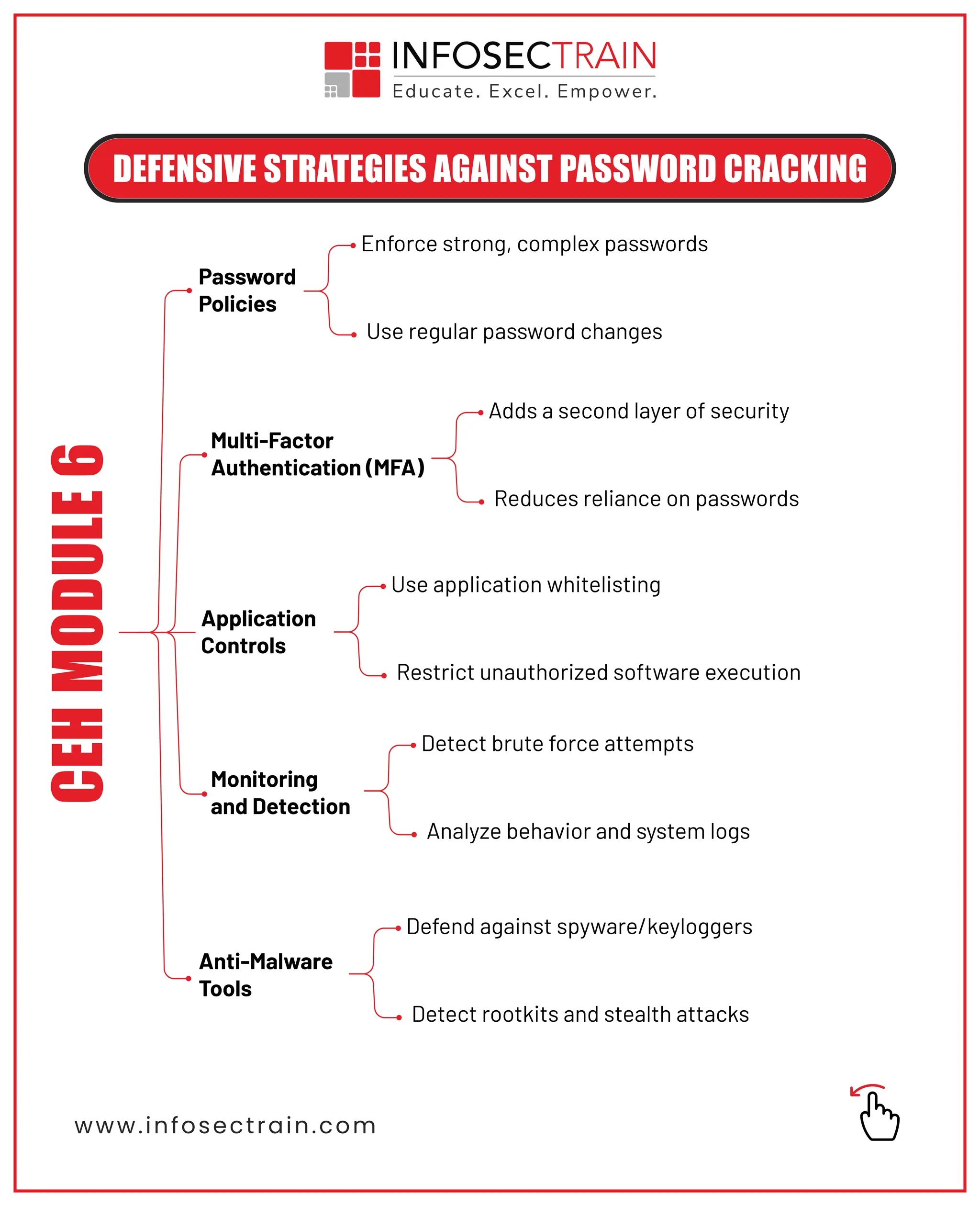
🔸 Defense Tactics – MFA, Password Policies, Monitoring, and Anti-Malware
Understand how attackers break in — so you can stop them before they do.