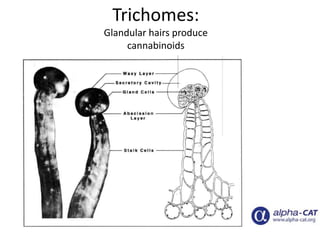
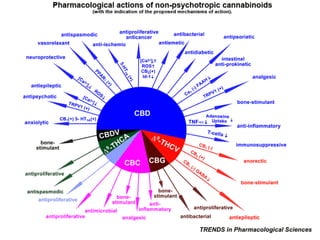
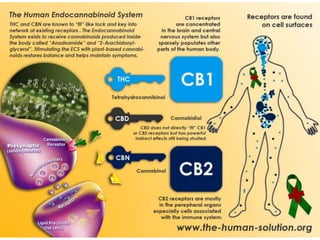
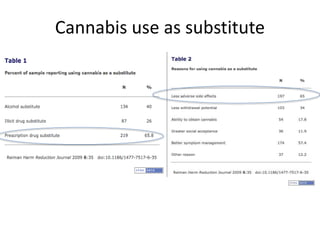
The document discusses the role of herbal cannabinoids, particularly cannabis, in harm reduction for substance use among individuals with various conditions. It highlights the potential of cannabidiol (CBD) in mitigating addiction, the impact of cannabis as a substitute for prescription drugs and alcohol, and emphasizes the need for better education and understanding of cannabis use. Furthermore, it outlines the legal landscape and societal perceptions surrounding cannabis consumption, particularly in the United States.