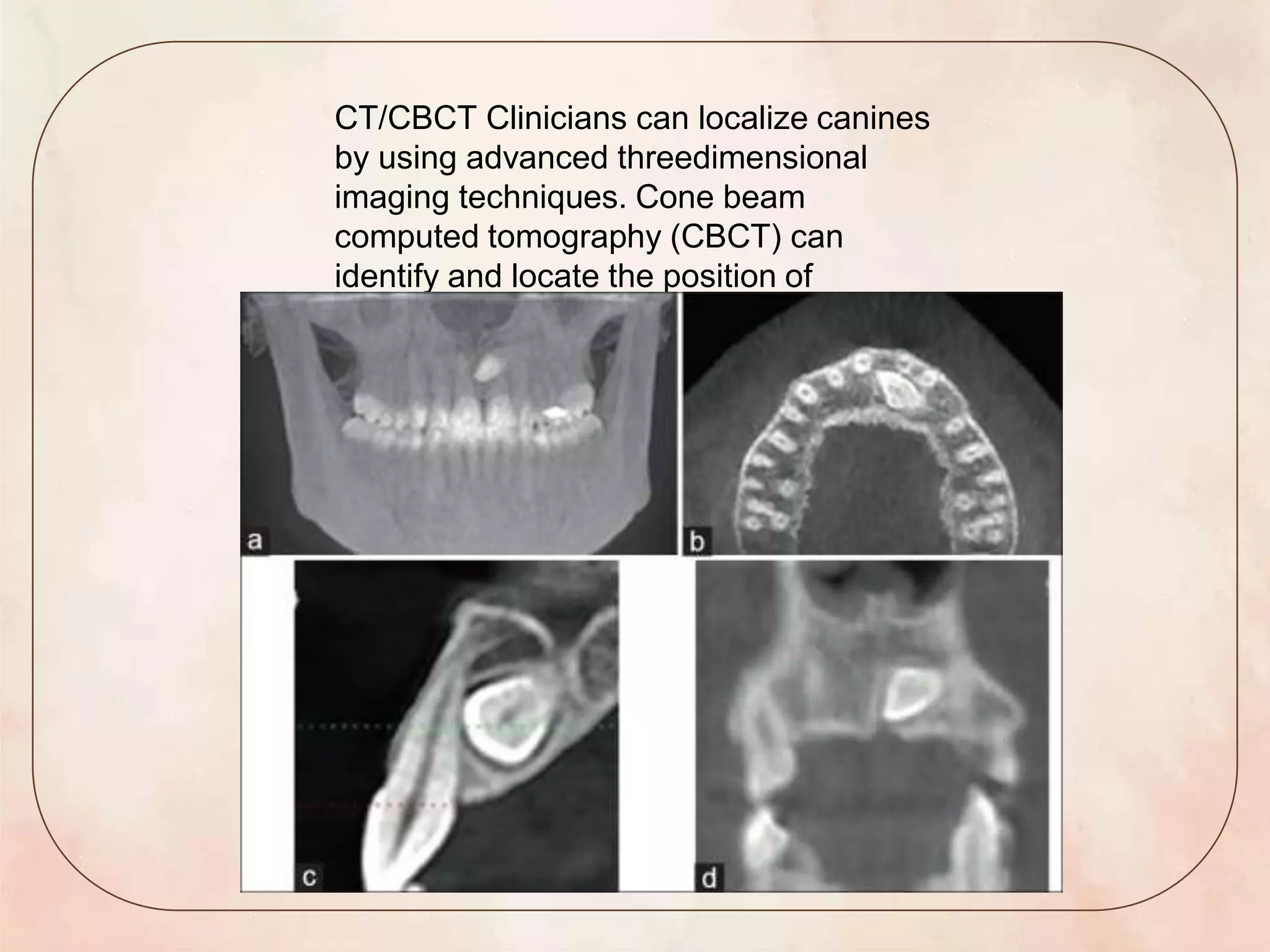
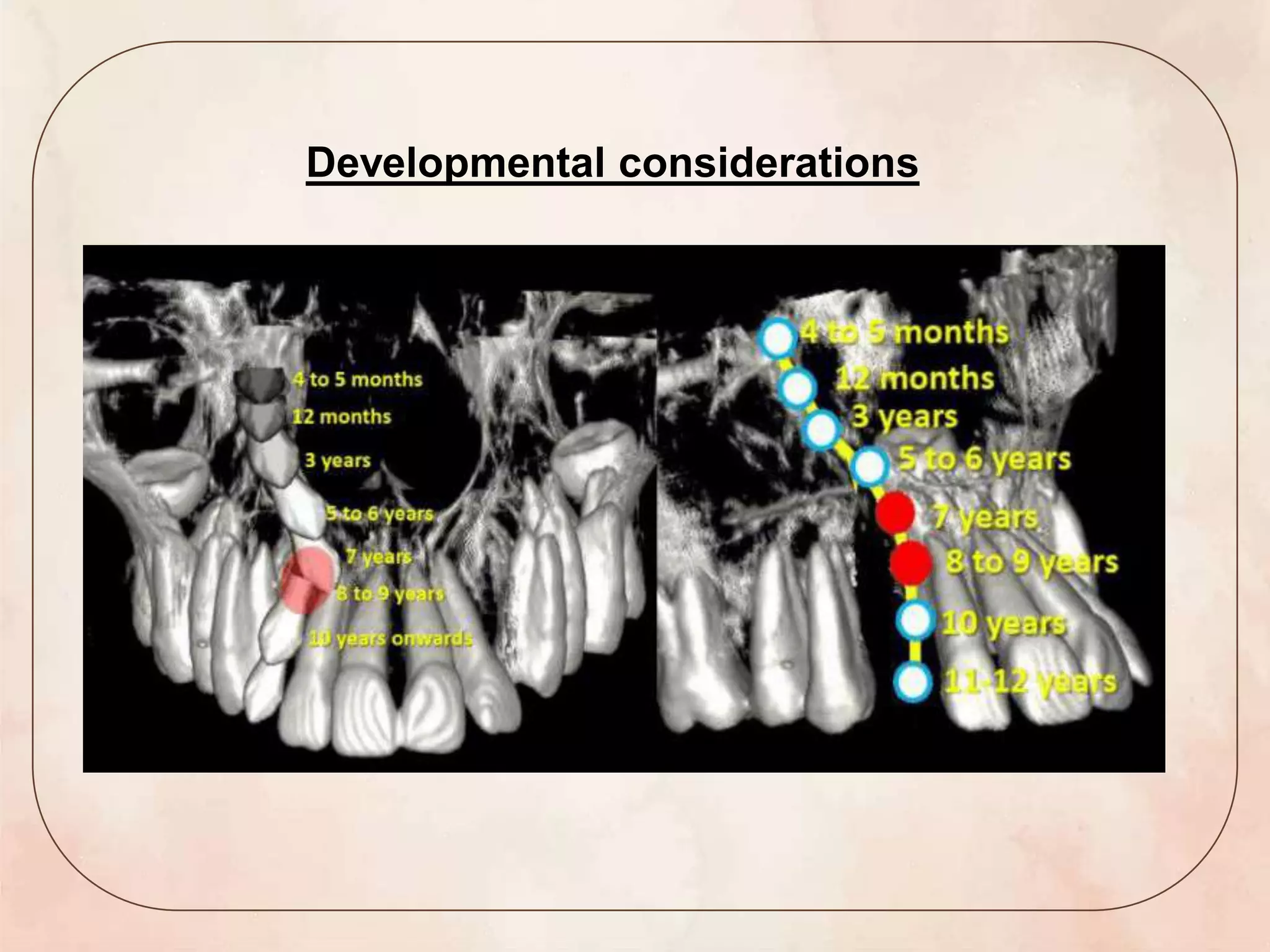
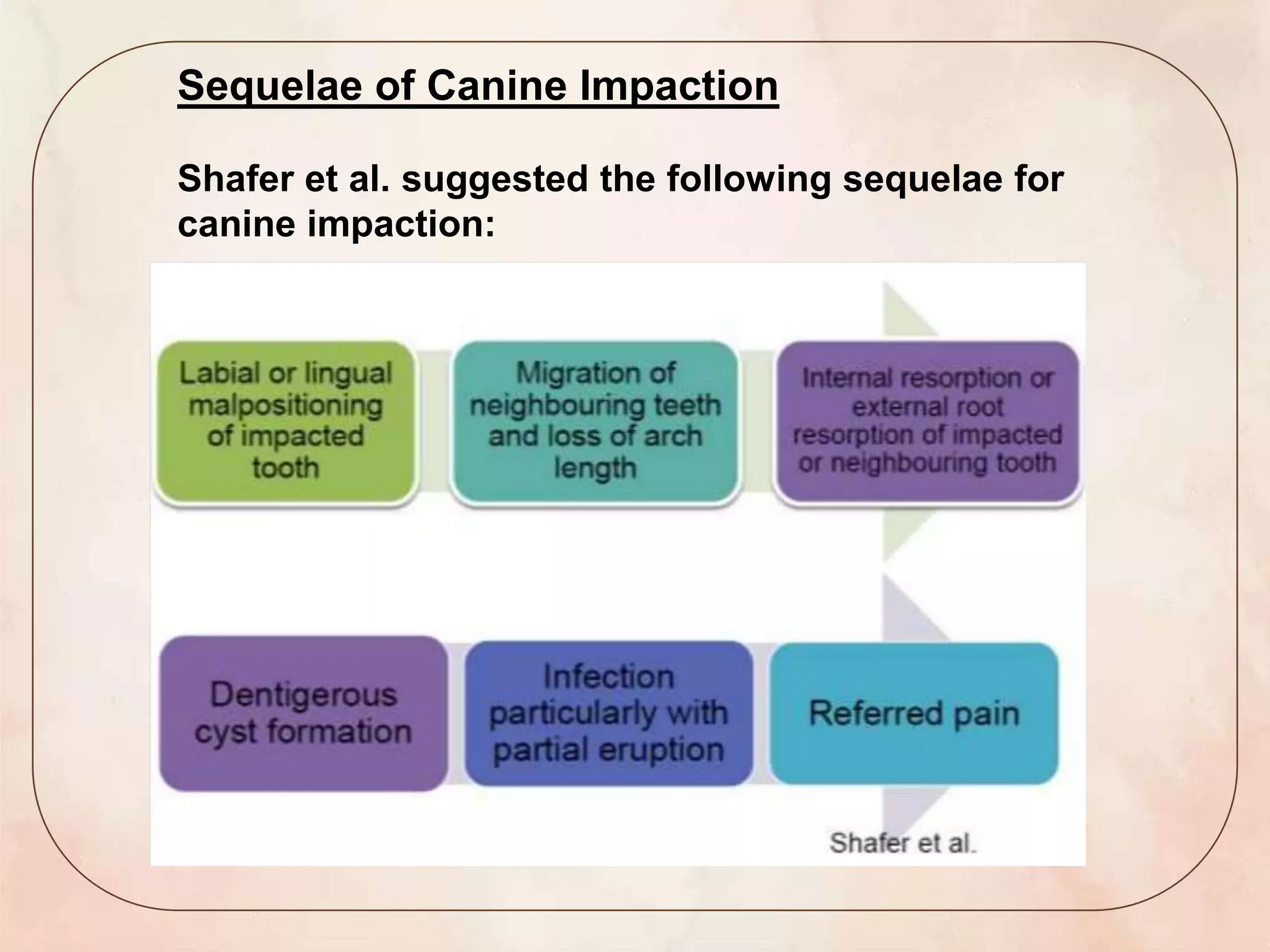
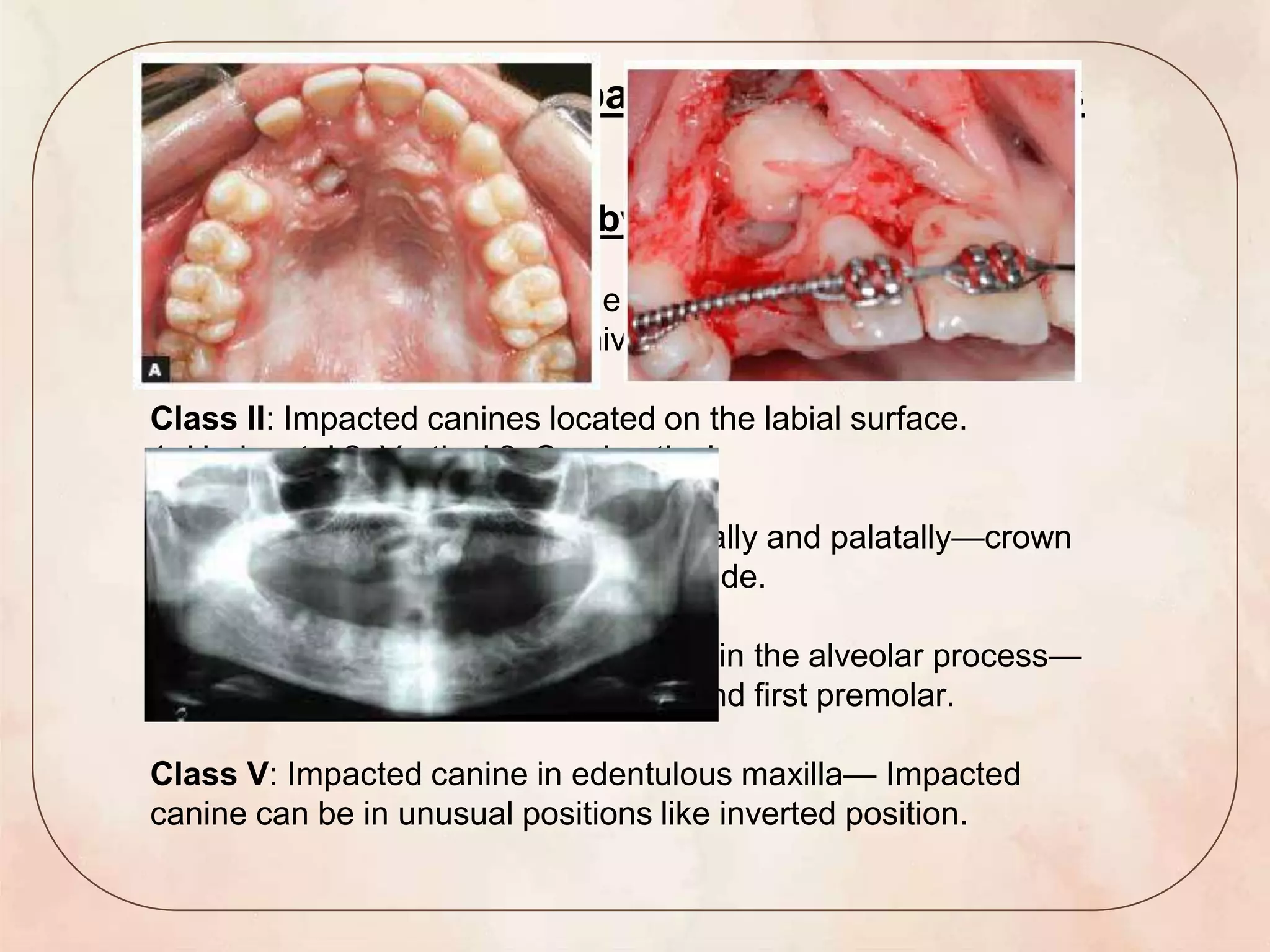
This document discusses canine impaction, including its causes, prevalence, classification, diagnosis, and management. It begins by introducing canine impaction and noting that it is usually diagnosed during routine dental exams. It then covers developmental considerations, etiology, prevalence, potential sequelae, and various classification systems for impacted maxillary and mandibular canines. The document outlines methods for clinical and radiographic diagnosis, and concludes by discussing various treatment options for impacted canines, including no treatment, interceptive treatment, extraction, auto transplantation, and surgical exposure with orthodontic alignment.









![The Yamamoto et al. [9] seven subtypes
classification](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canineimpaction1-230606153220-8f73da94/75/CANINE-IMPACTION-1-pptx-14-2048.jpg)




![Clinical assessments Impacted canine
teeth can be detected as early as the
age of 8 years. It is done with two
methods: Clinical inspection and
palpation [Figure 2].[2,3] Inspection
Clinical examination includes overall arch
inspection. Mobility or the absence of
primary canines past its eruption age.
Persistent median diastema, abnormality
or missing lateral incisor, ectopic
deviation of lateral incisor from its
position may all be signs of canine
impaction. Clinical examination for the
presence of bulge in the canine region
deep in the vestibule should be done
buccally as well as palatally](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canineimpaction1-230606153220-8f73da94/75/CANINE-IMPACTION-1-pptx-19-2048.jpg)