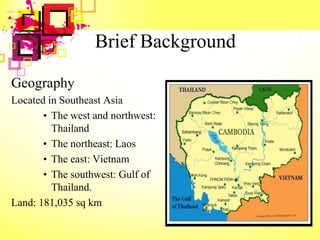
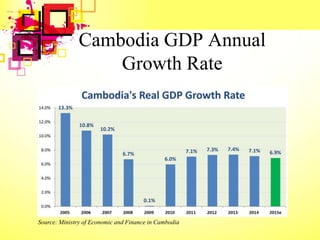
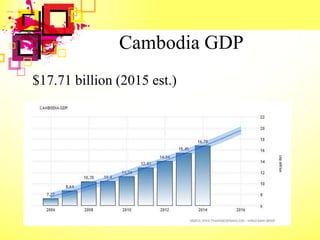
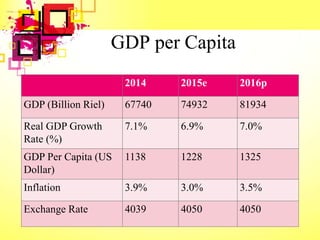
This document provides an overview of Cambodia's economy, including its GDP, GDP growth rate, key economic sectors, trade, and monetary policies. It notes that Cambodia has a GDP of $17.71 billion with economic growth averaging 7% annually in recent years. The economy relies heavily on agriculture, garment exports, tourism, and construction. It also discusses Cambodia's policy strategies to promote economic development, private sector growth, and human resource development through its Rectangular Strategy framework.