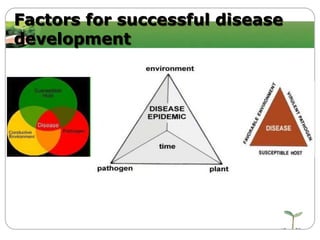
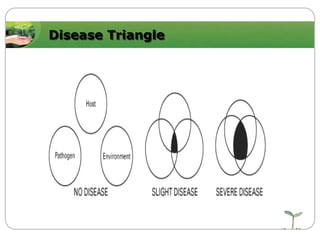
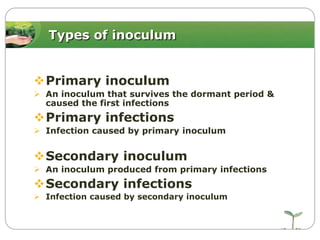
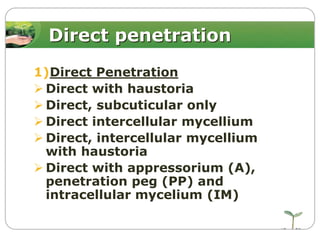
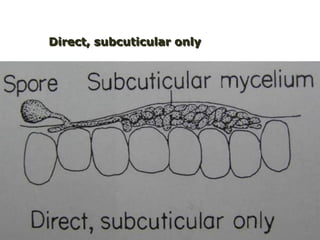
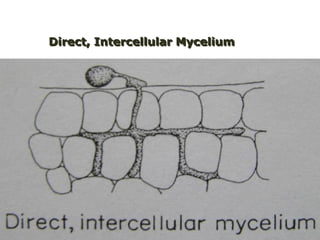
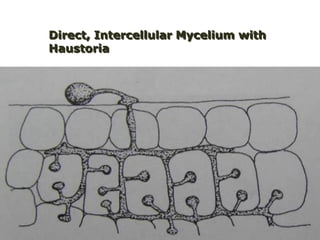
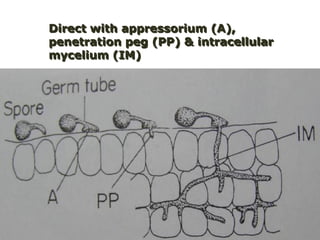
This document discusses plant disease development. It begins by outlining the objectives and topics to be covered, which include the disease triangle, factors for successful disease development, and stages of disease development. The disease triangle requires the presence of a susceptible host, virulent pathogen, and favorable environment. The factors for disease development include the properties of the pathogen, host, and environment. The stages of disease development are inoculation, penetration, infection, growth and reproduction of the pathogen, and dissemination of the pathogen.