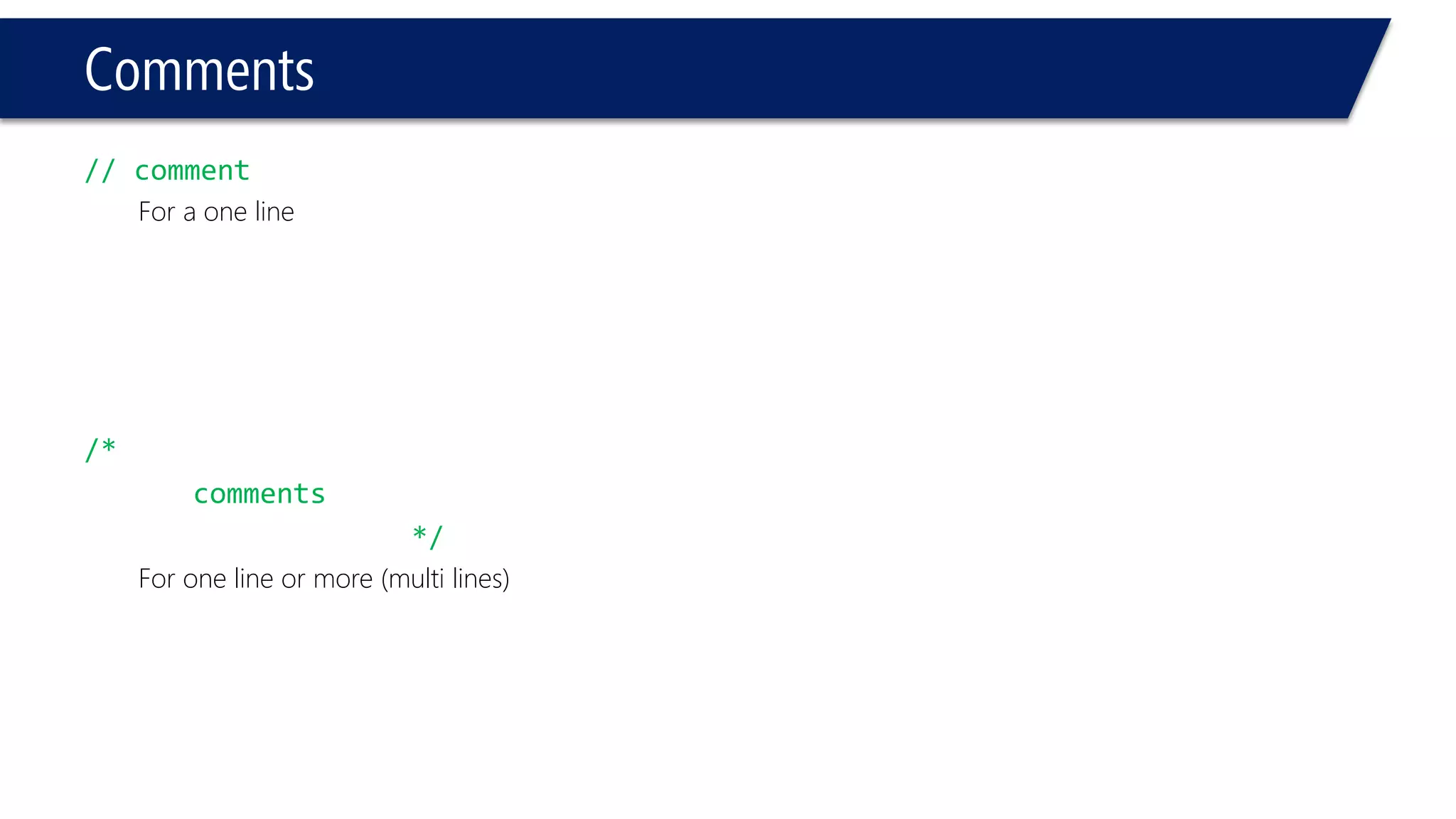
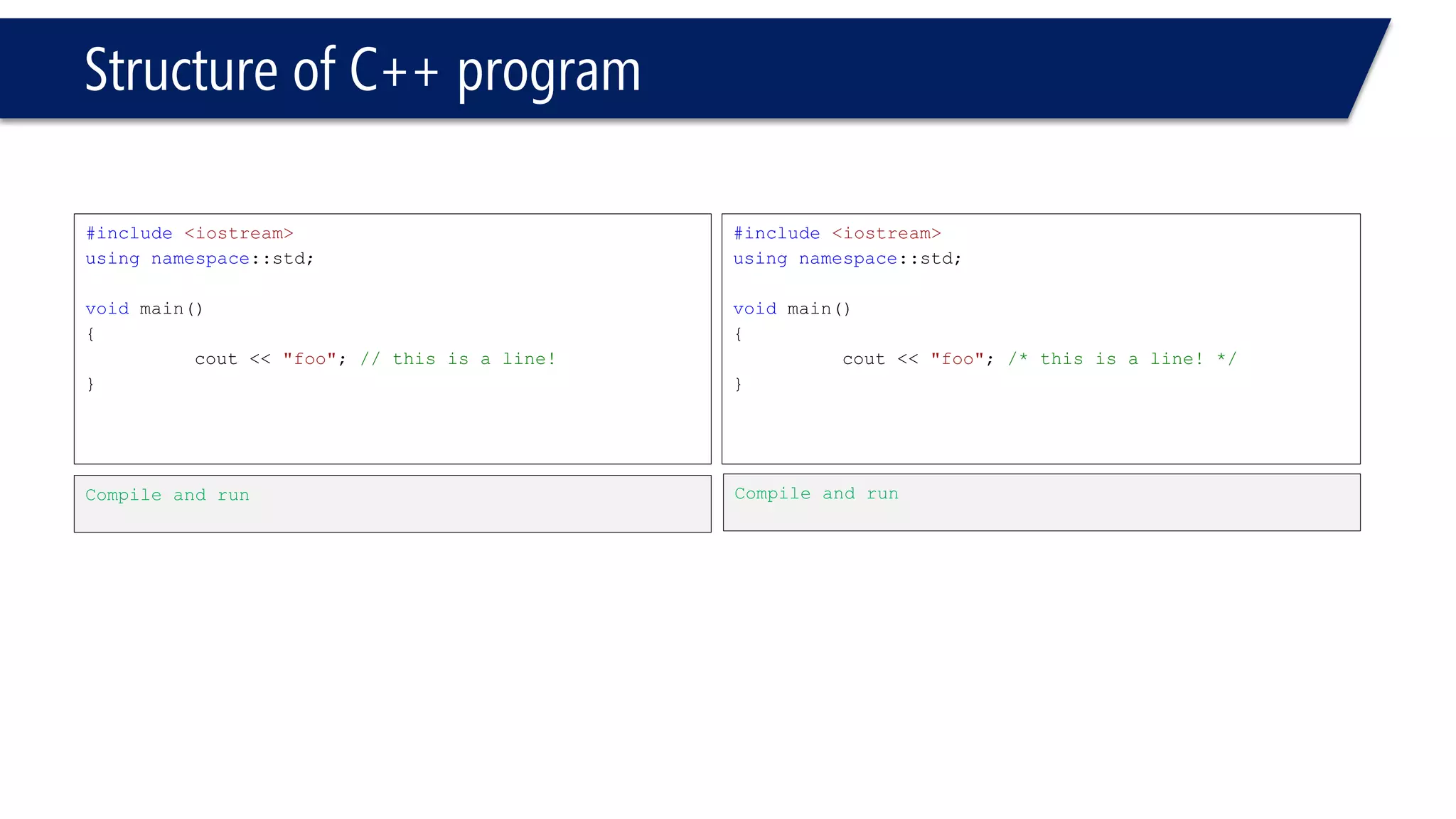
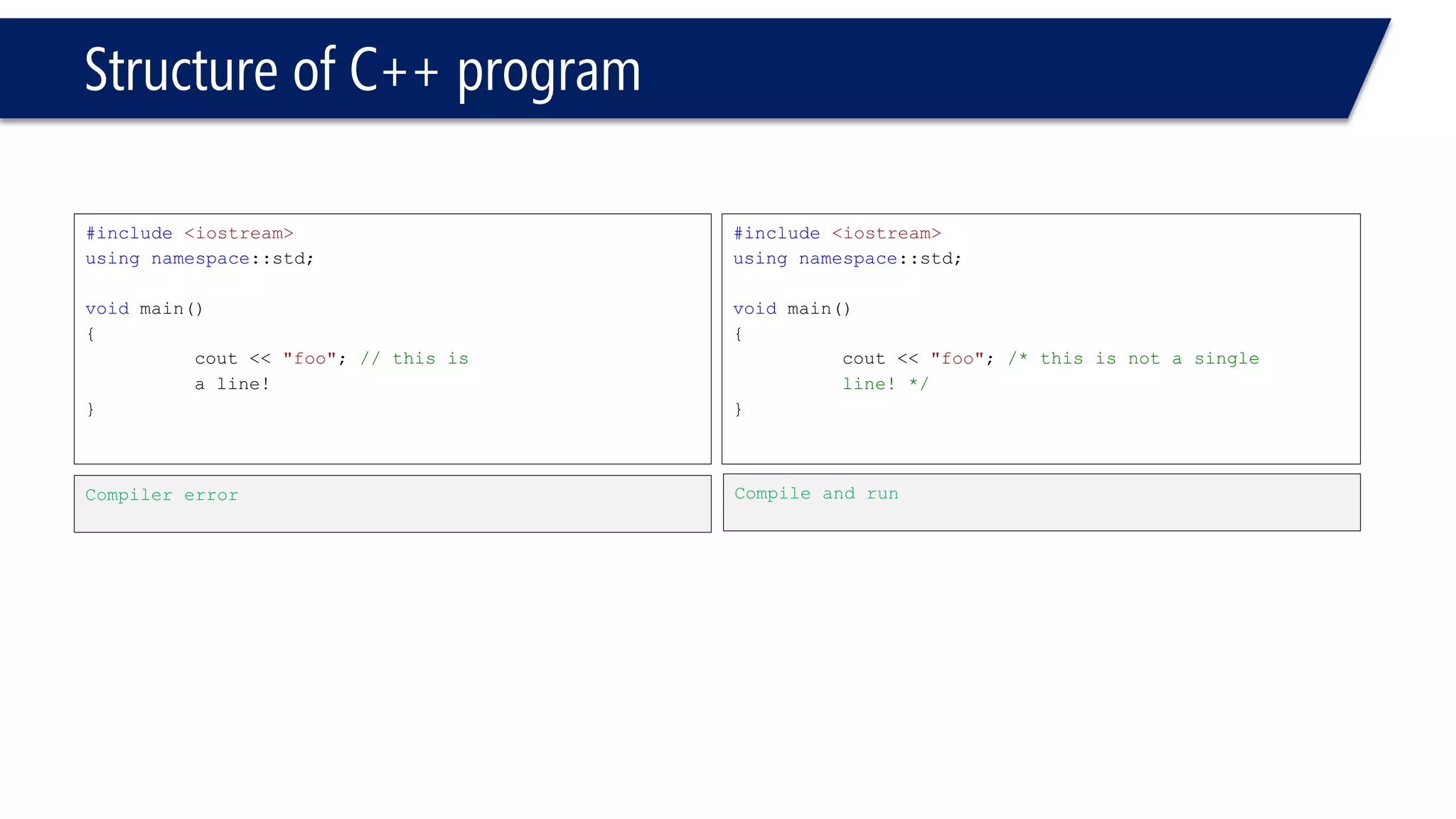
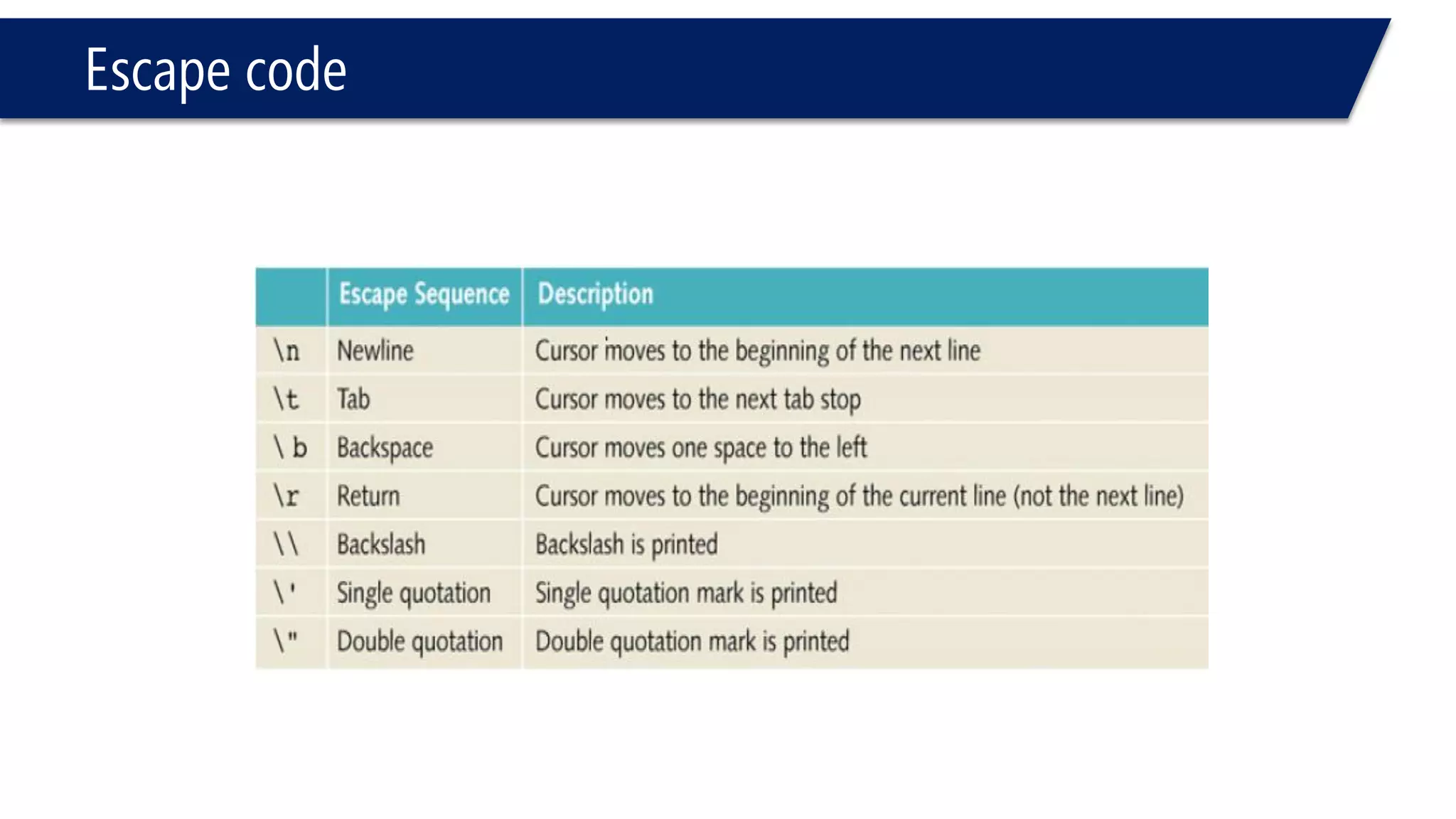
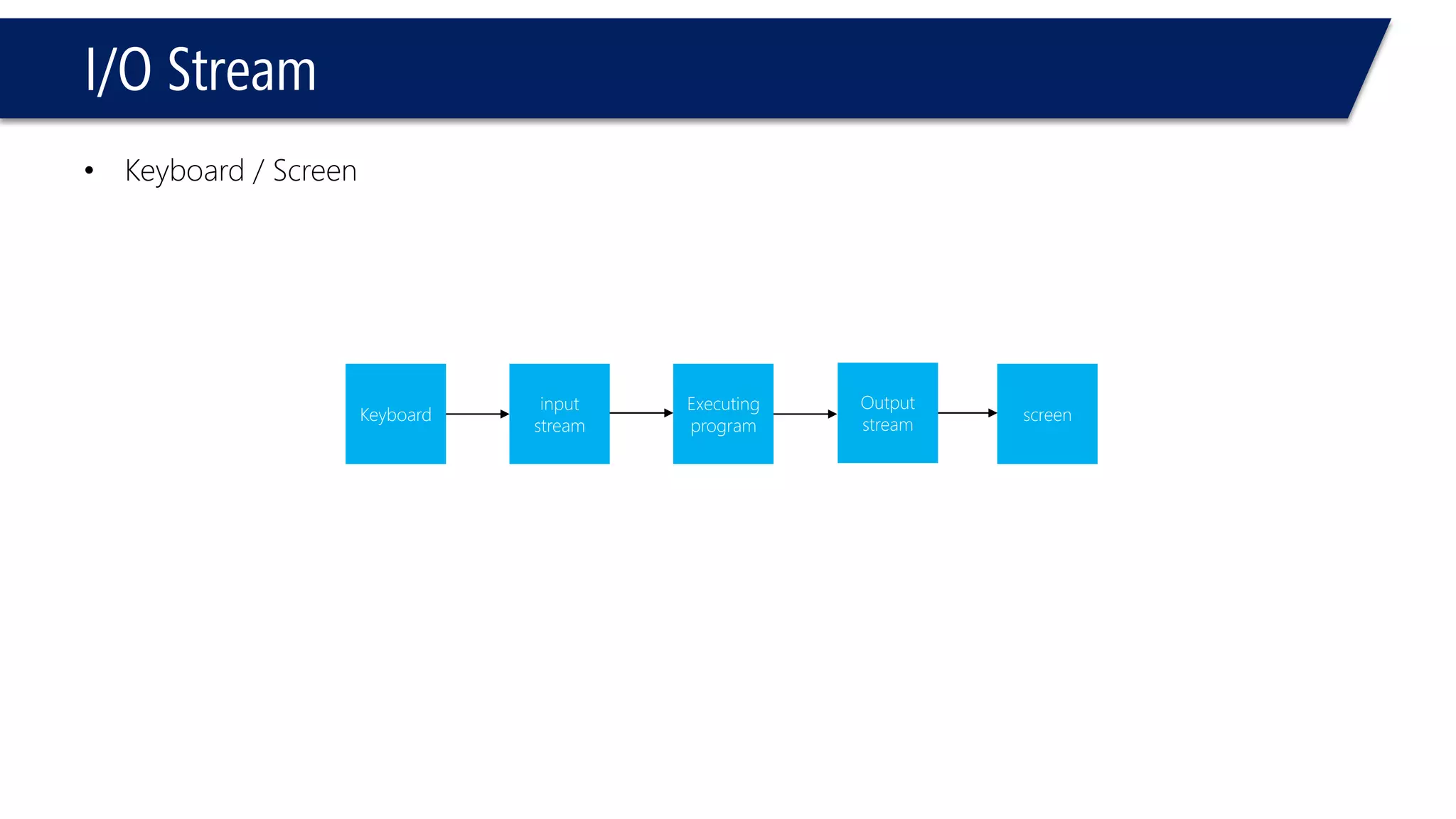
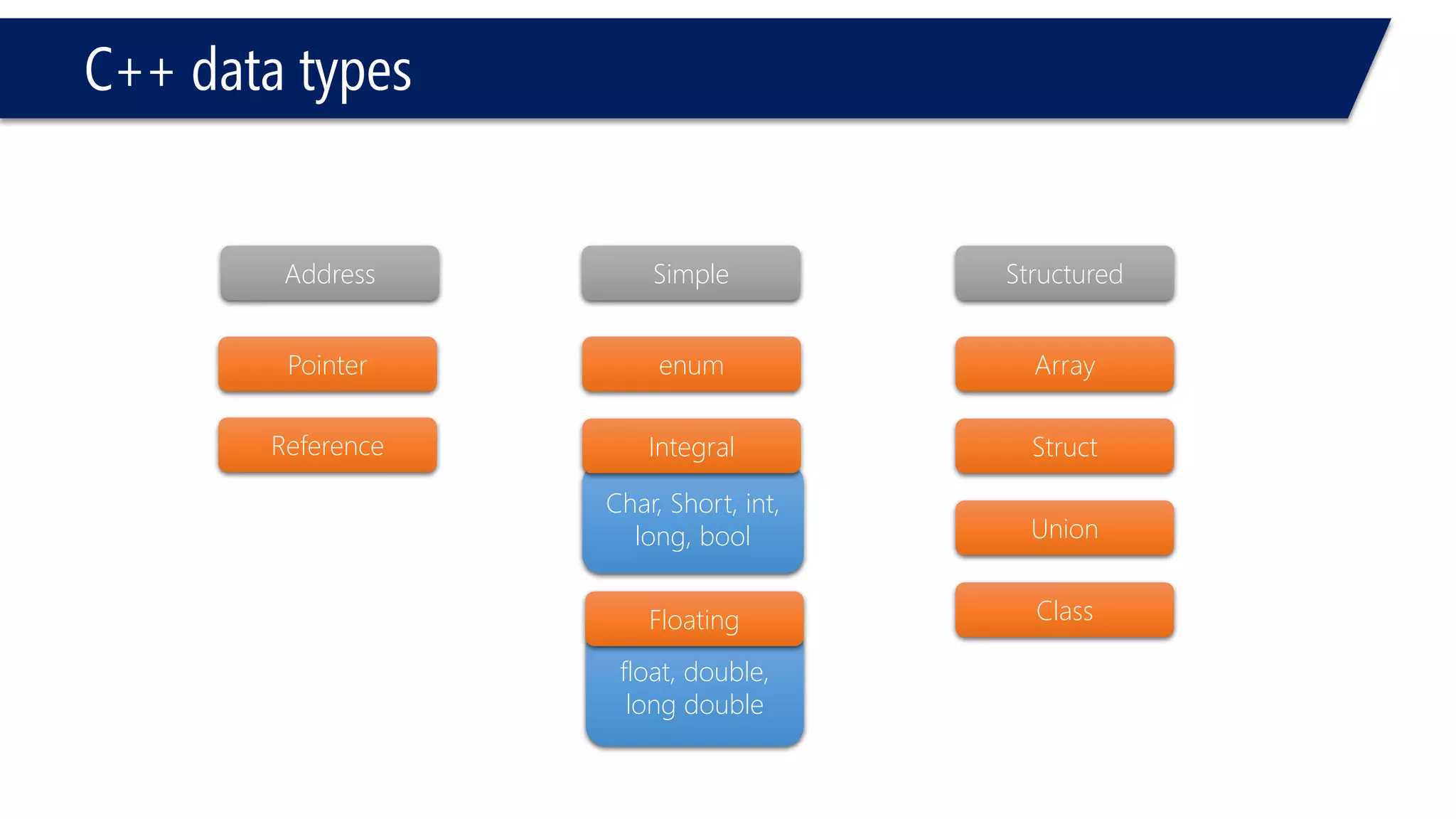
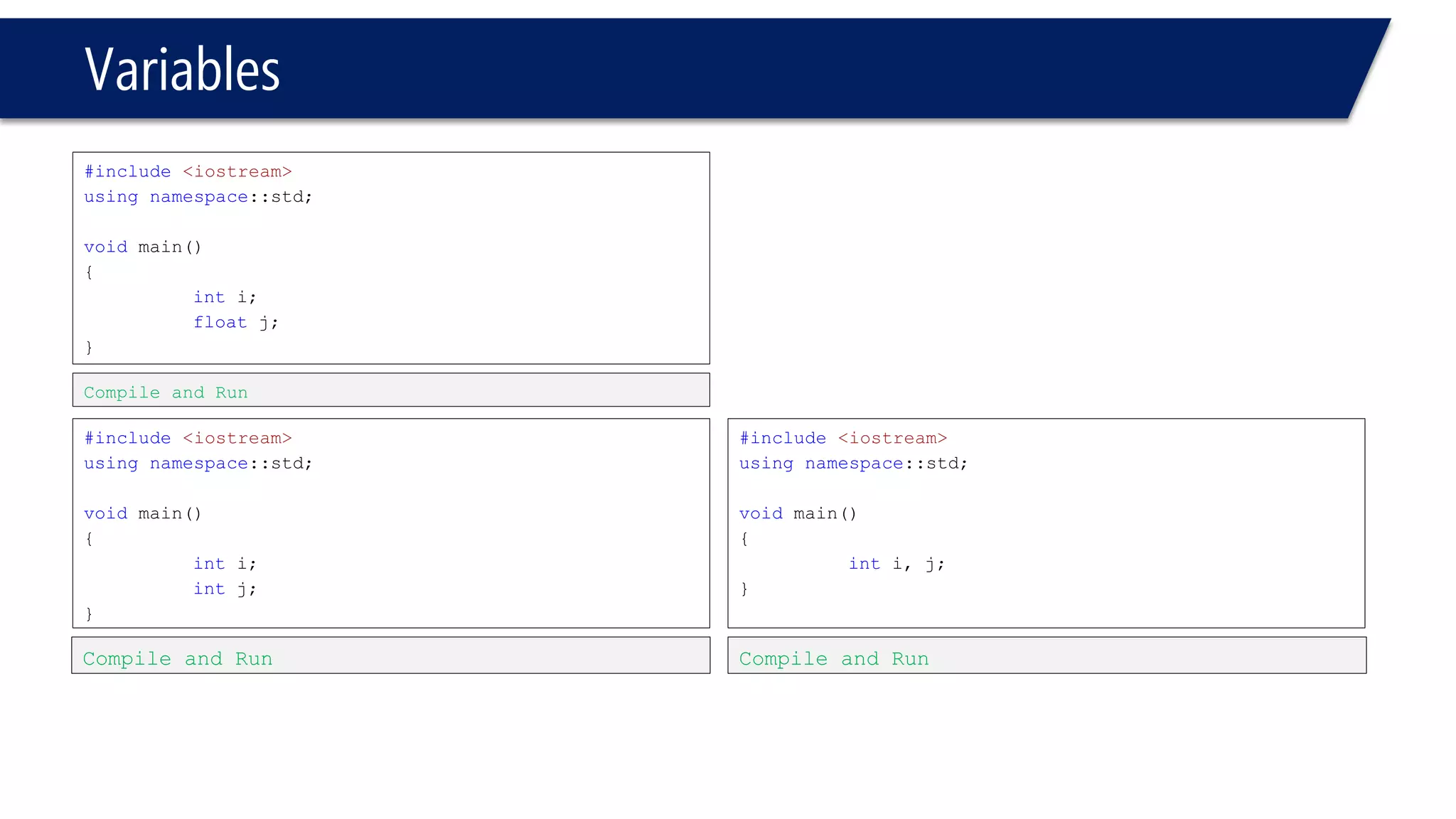
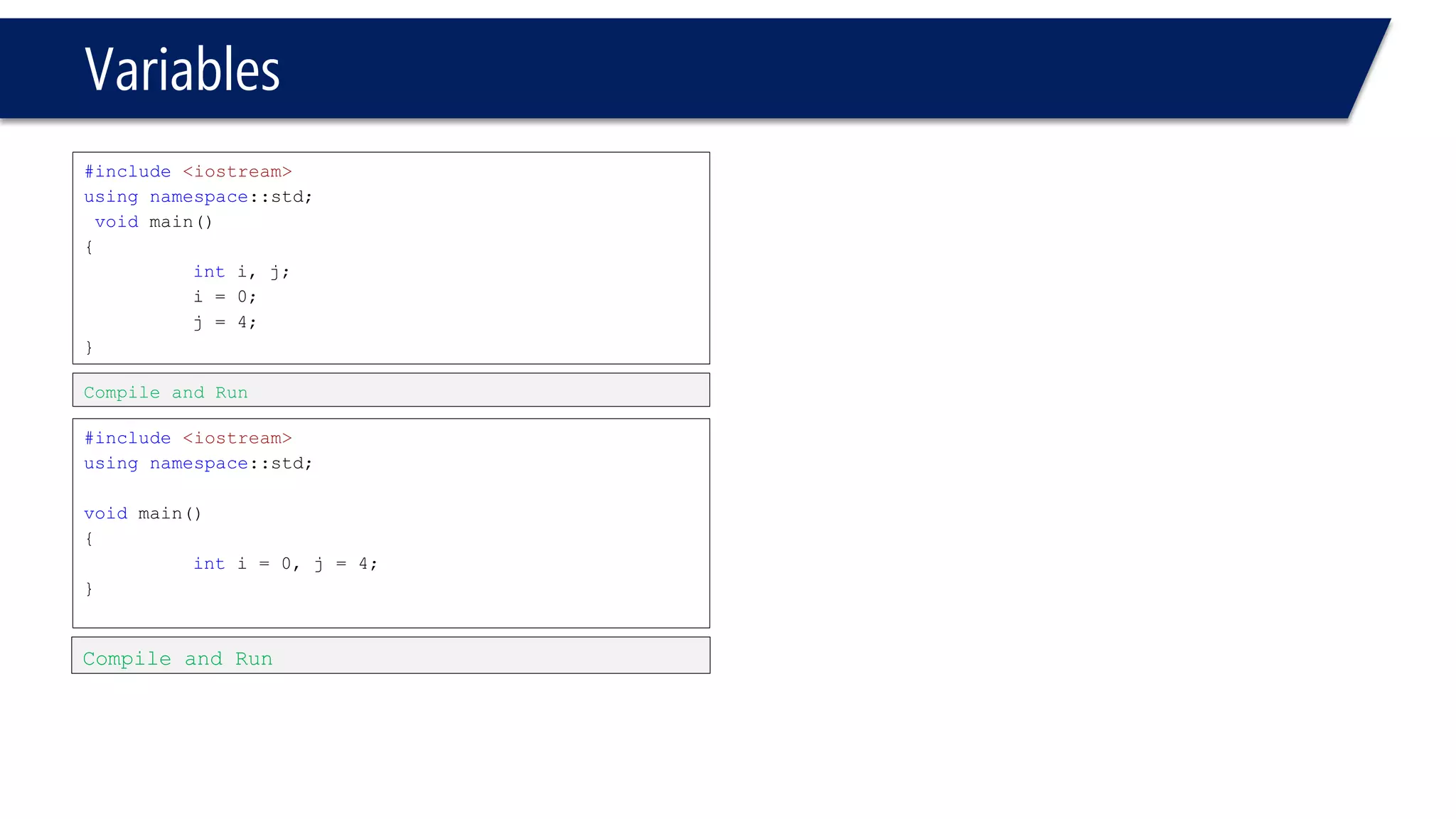
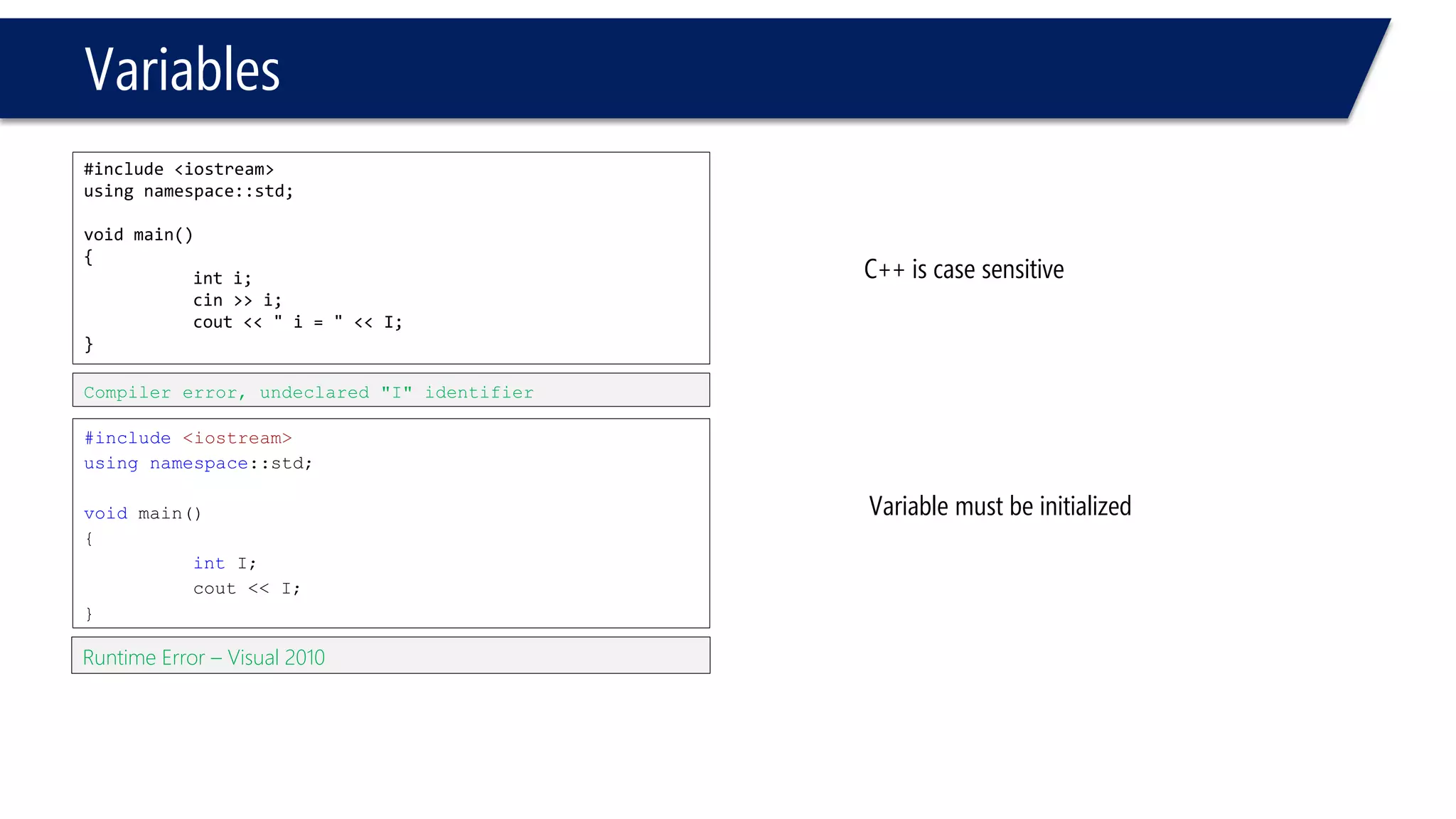
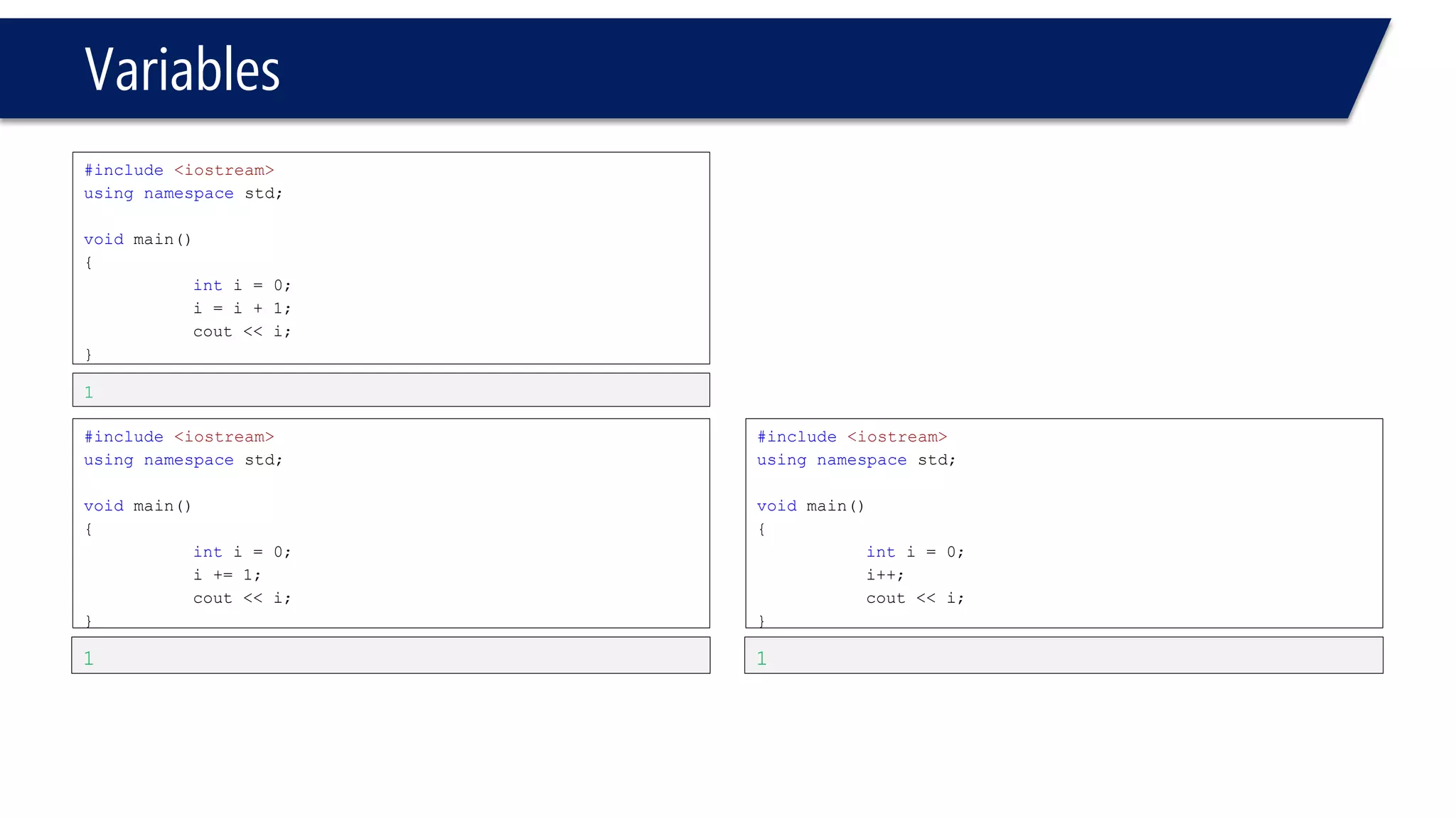
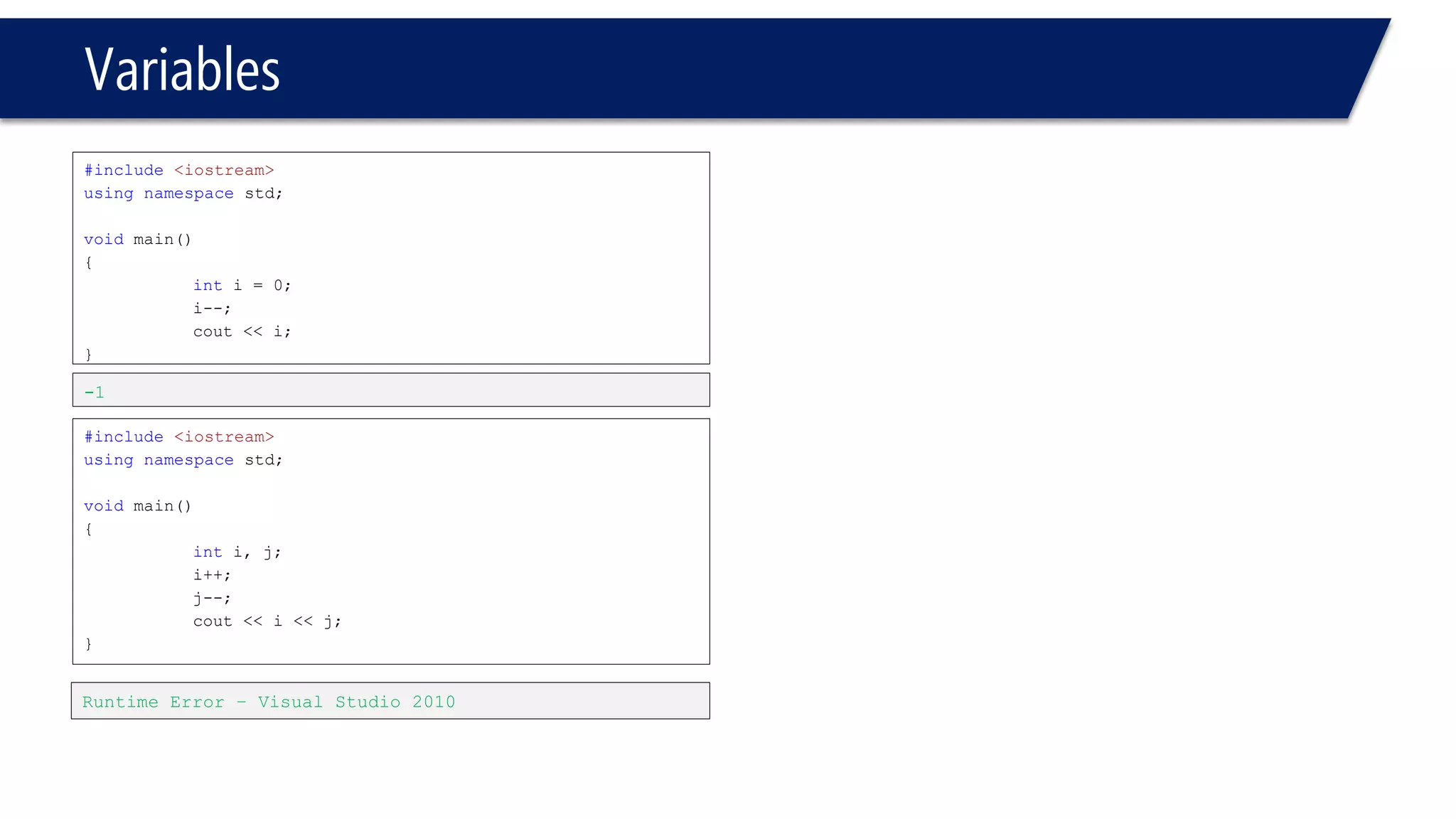
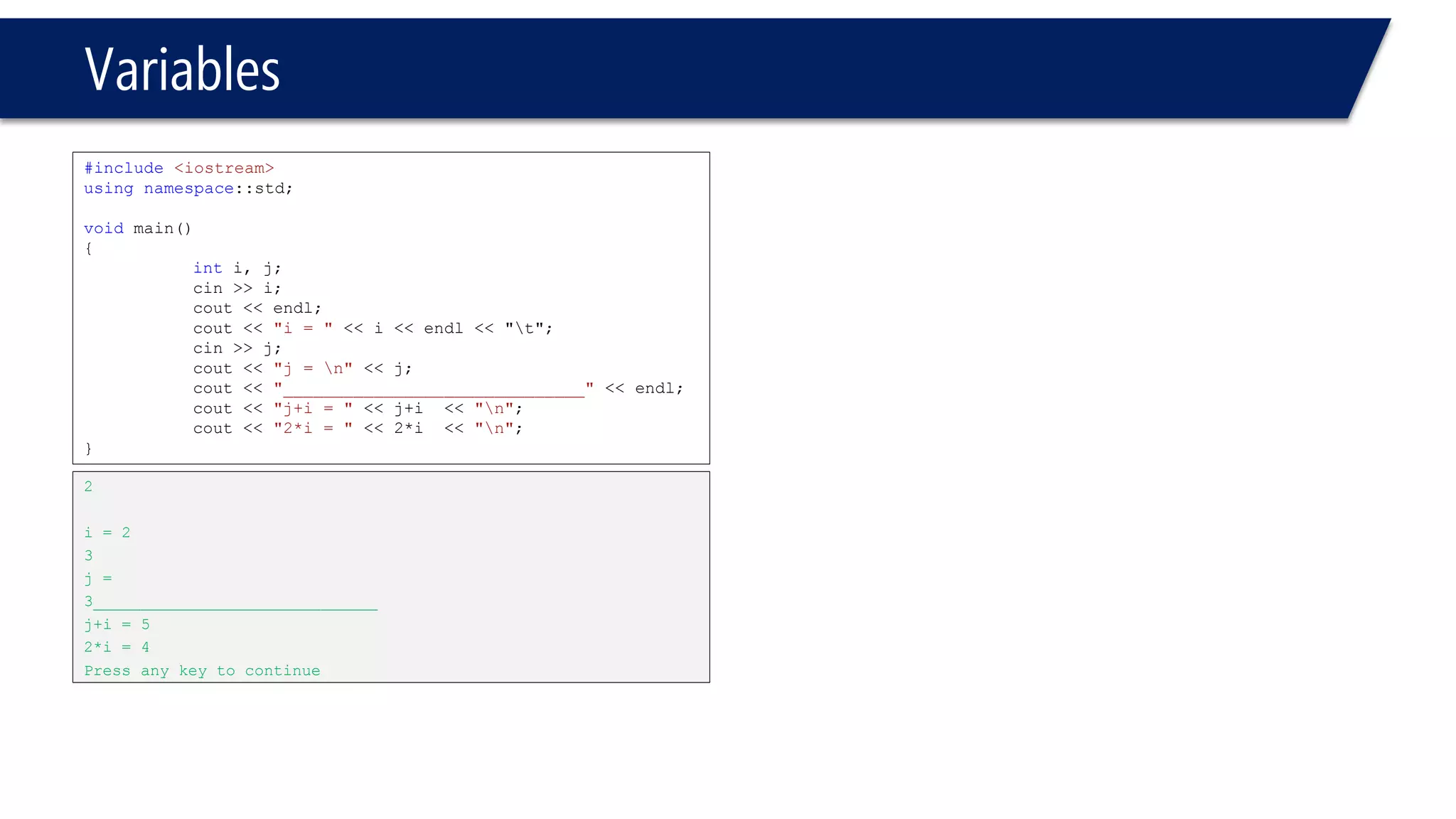
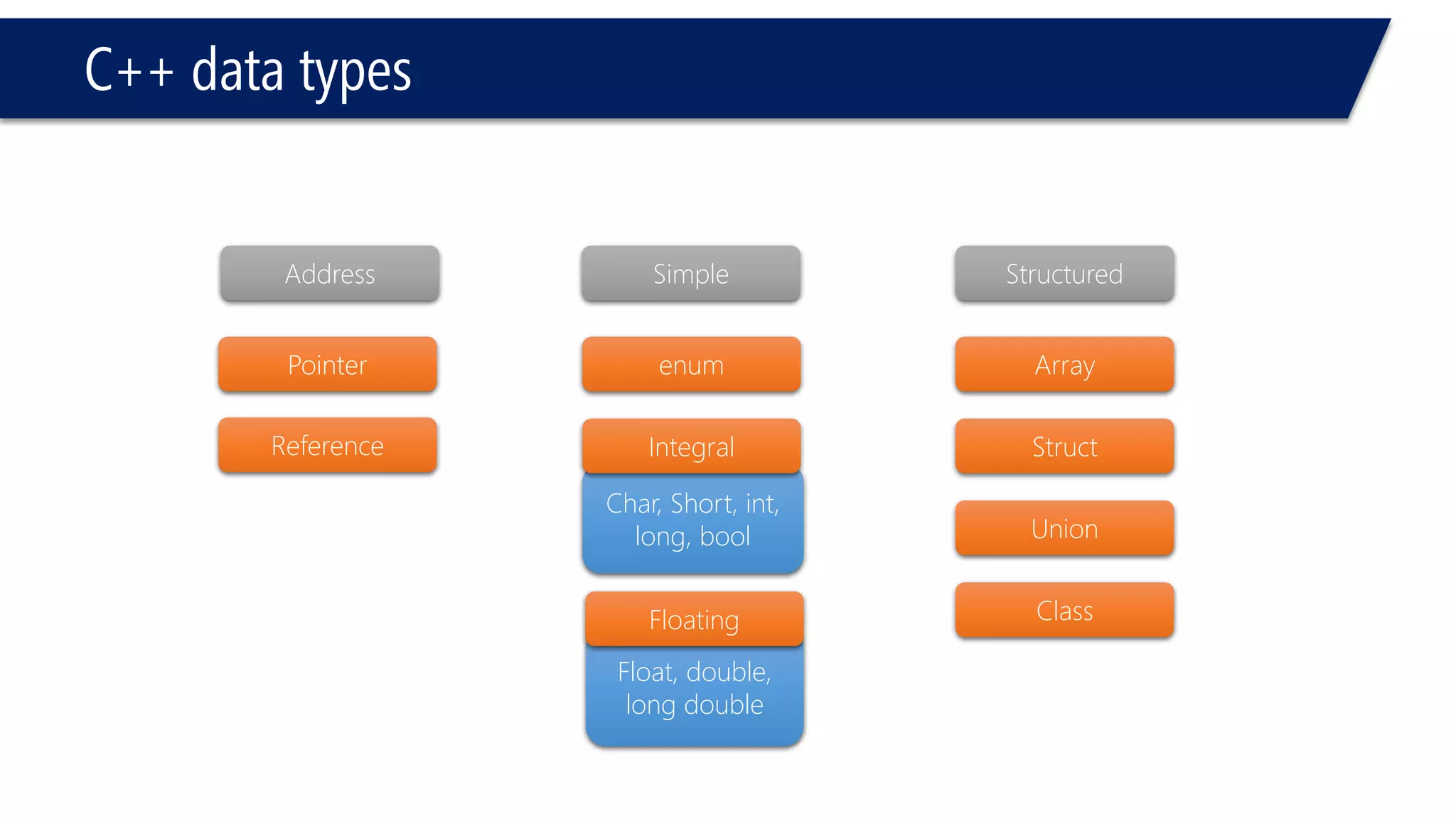
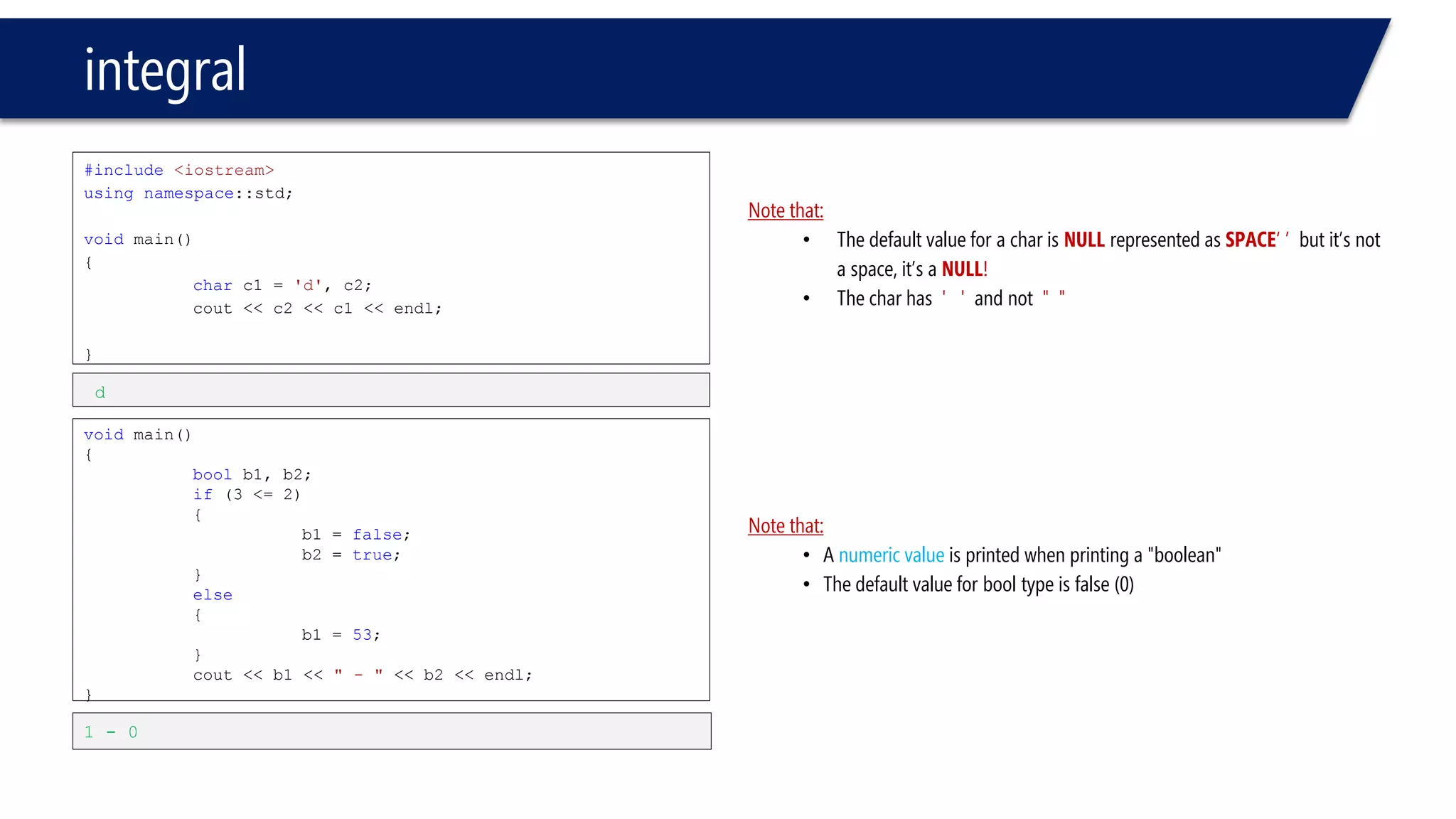
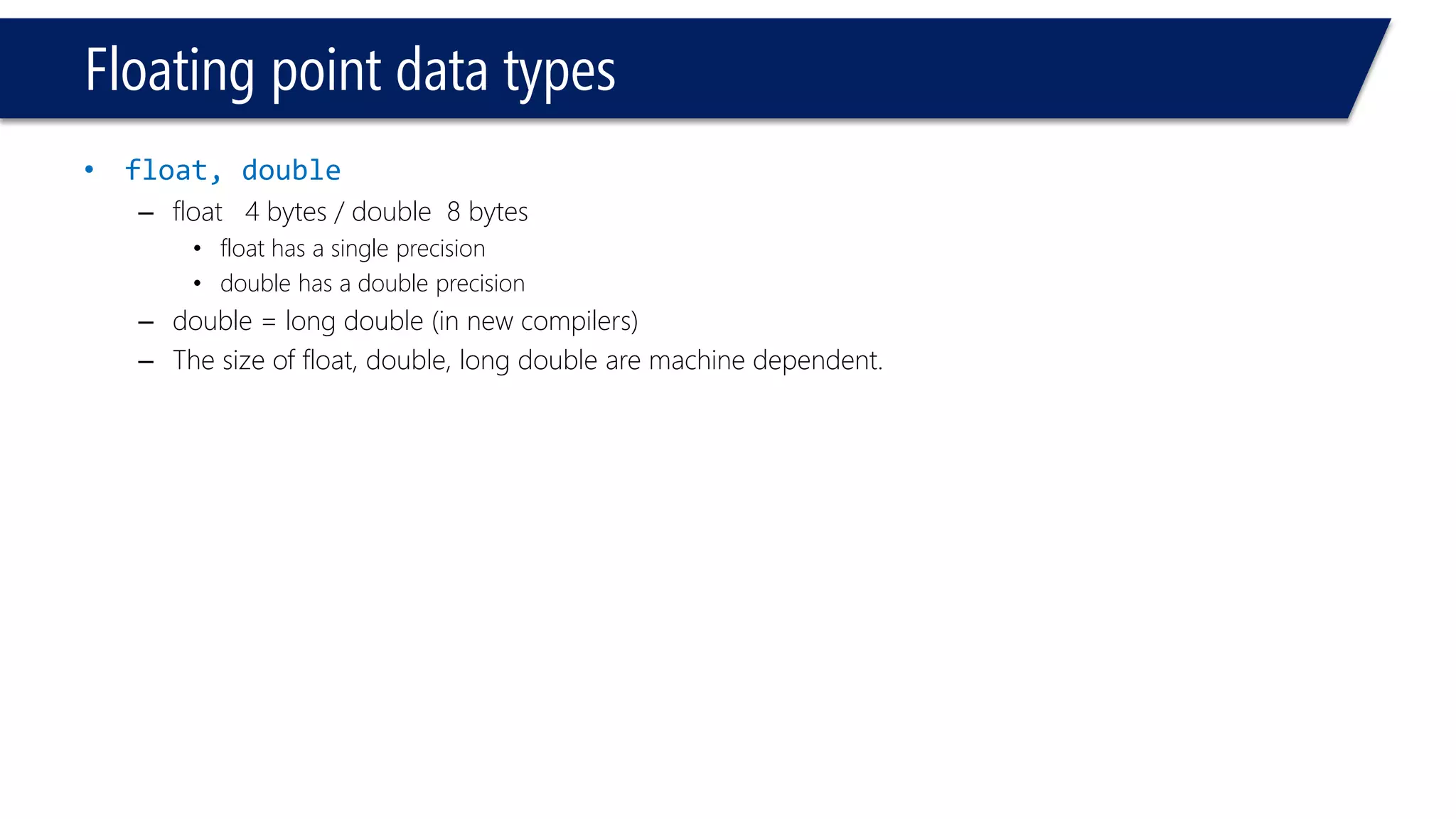
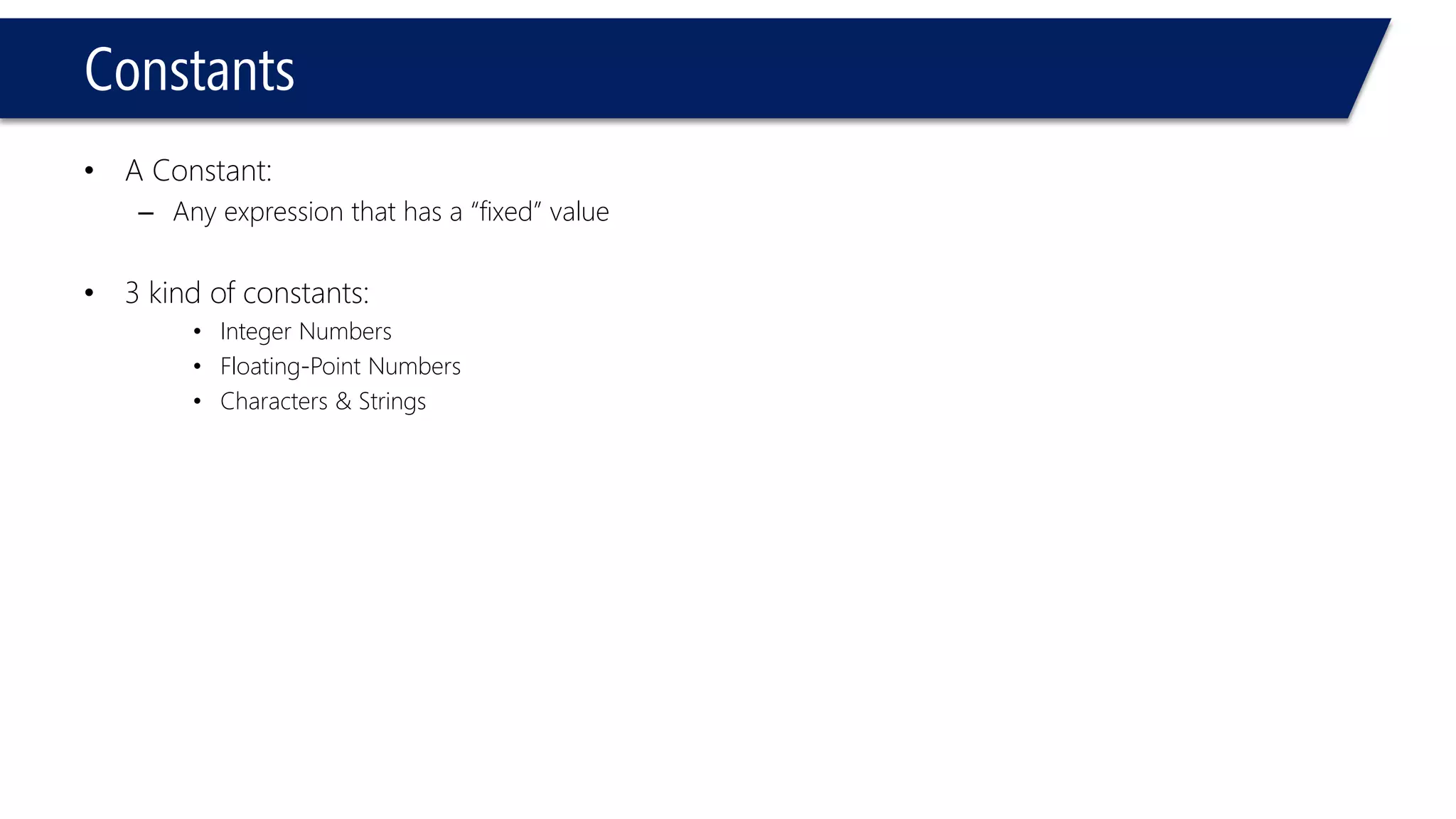
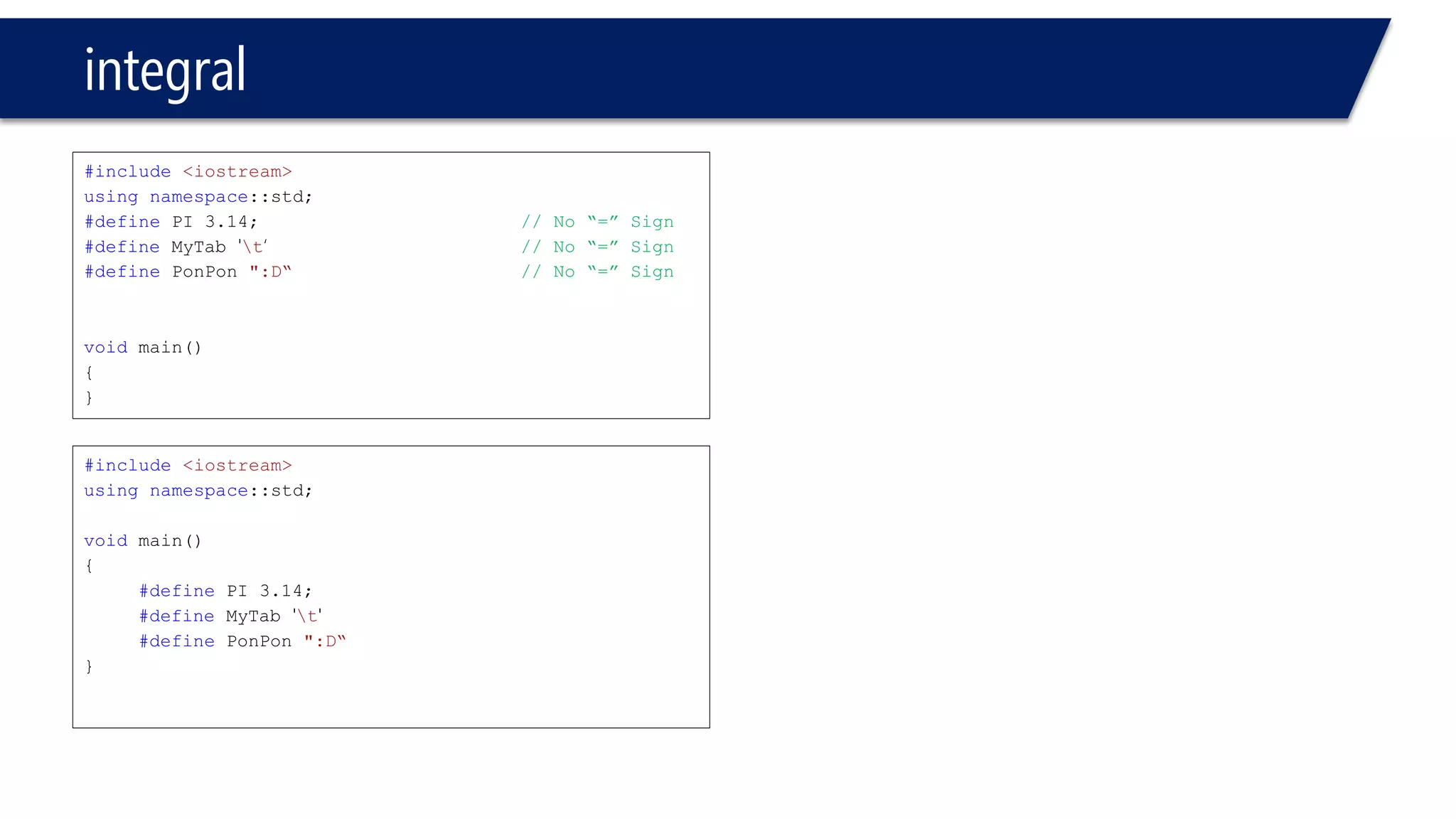
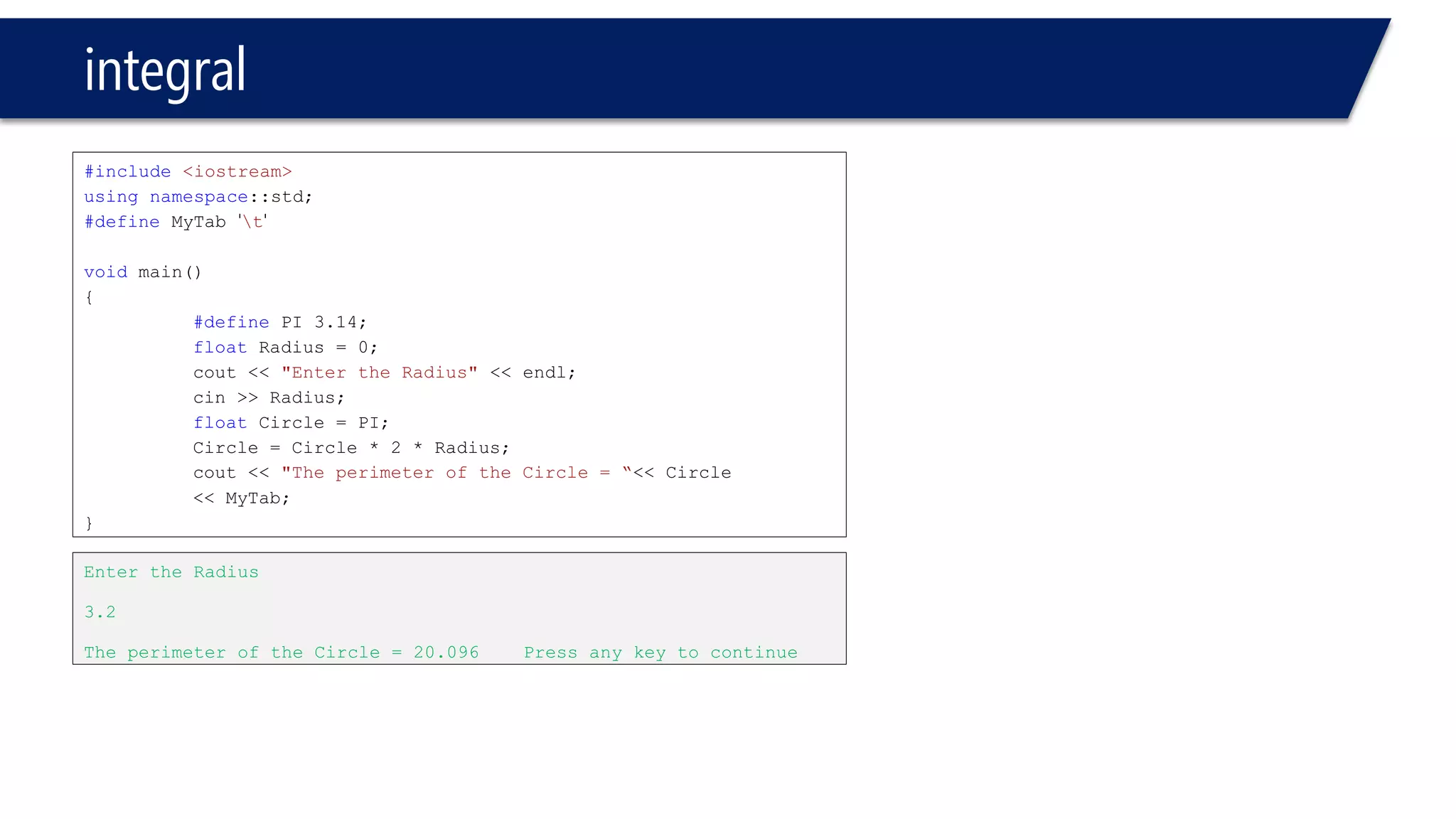
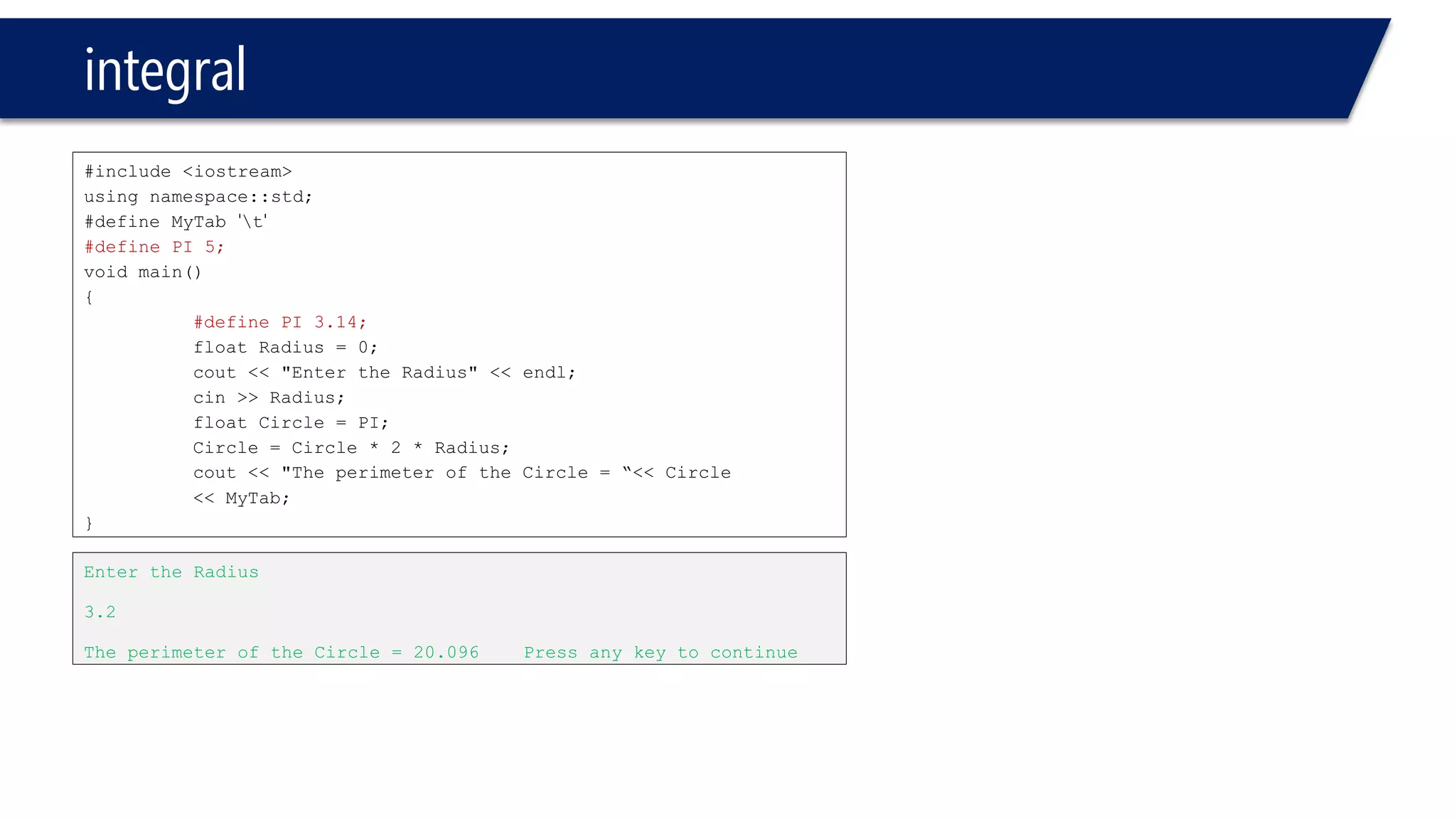
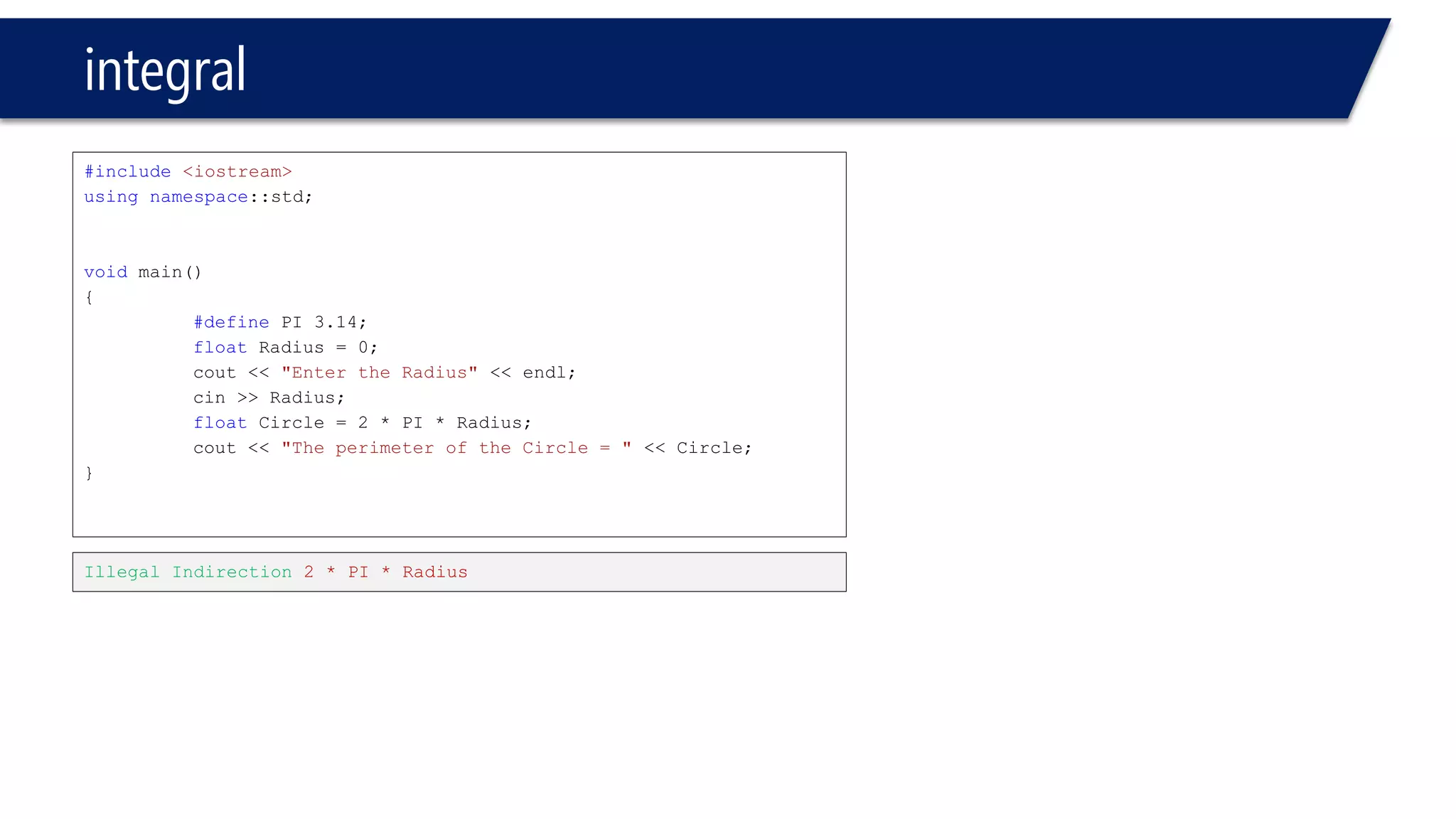
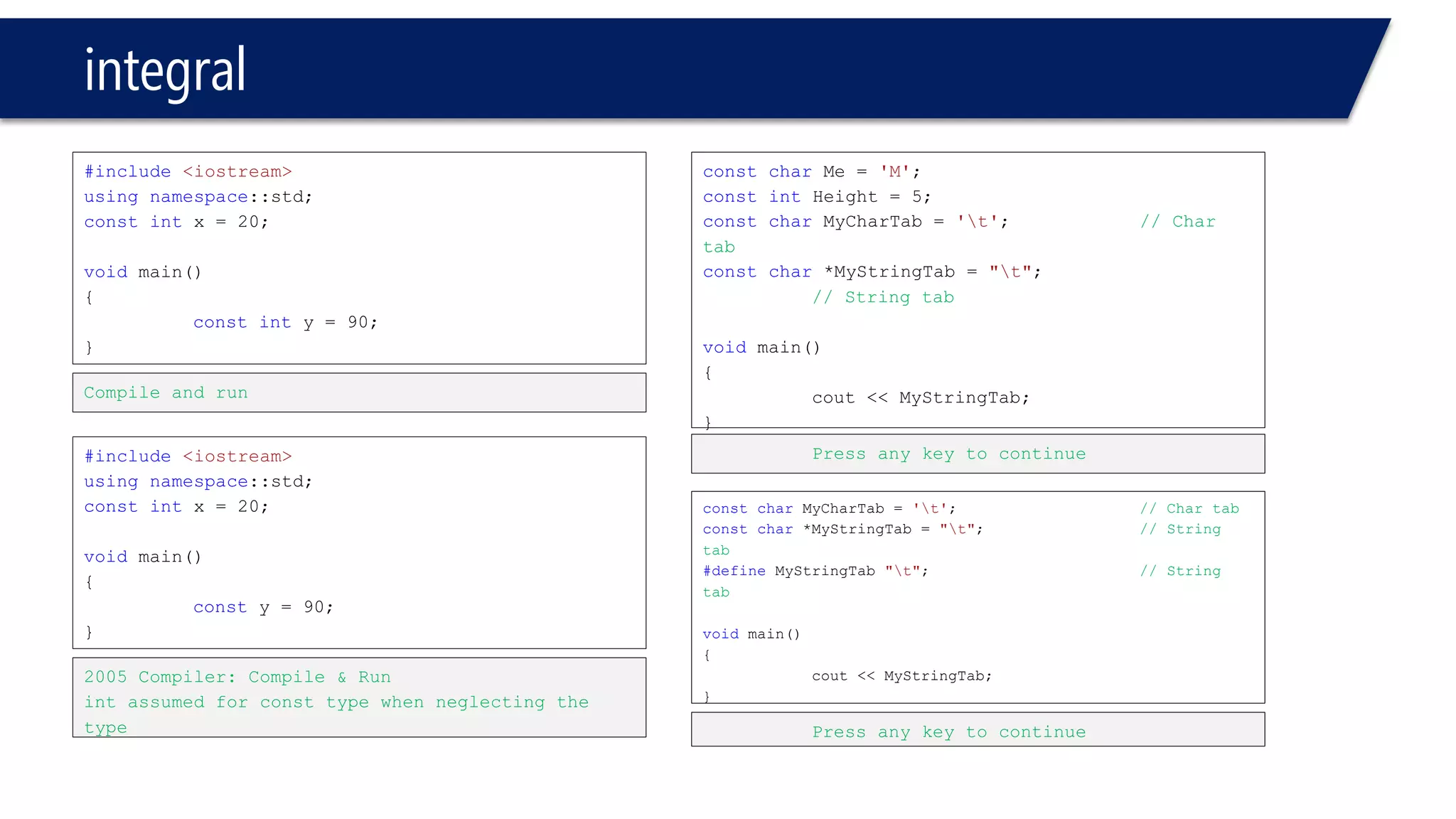
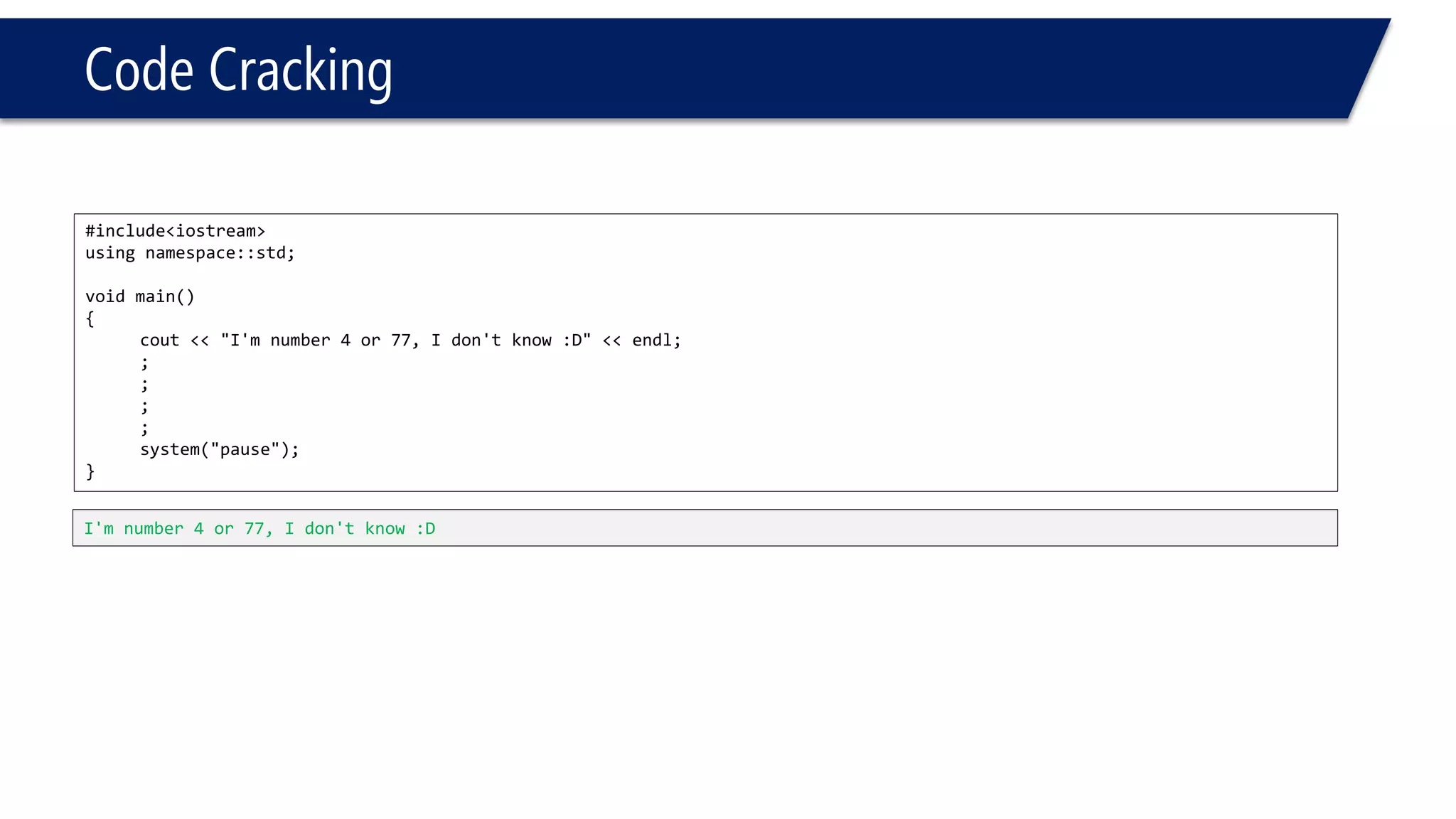
This document provides an introduction to C++ programming concepts including variables, data types, constants, and I/O streams. It discusses basic C++ code structure and comments. Integral data types like char, bool, and integers are explained. Floating point types float and double are also introduced. The document demonstrates declaring and initializing variables as well as basic math operations on variables. Constants and the const keyword are described along with the #define preprocessor directive.