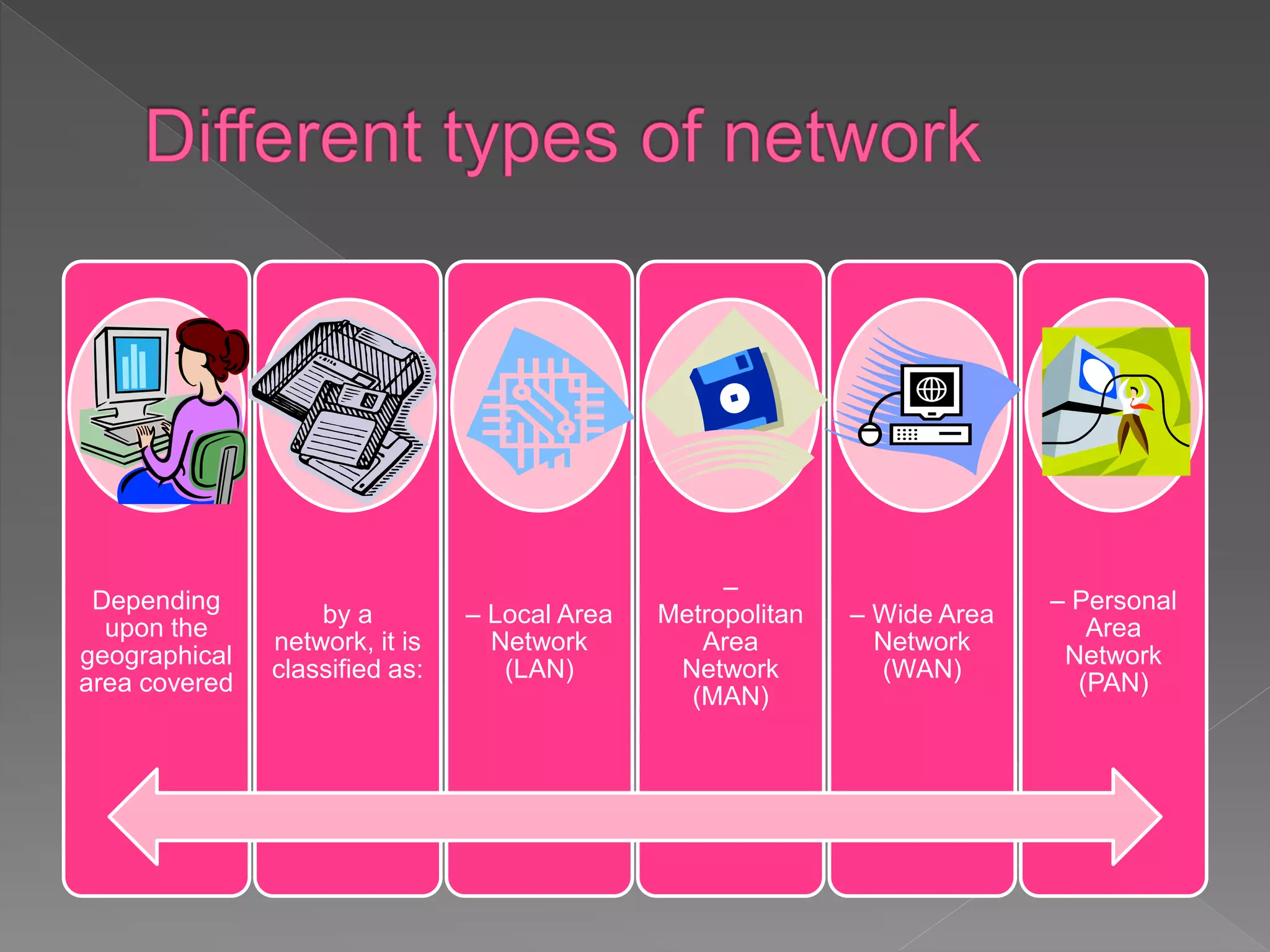
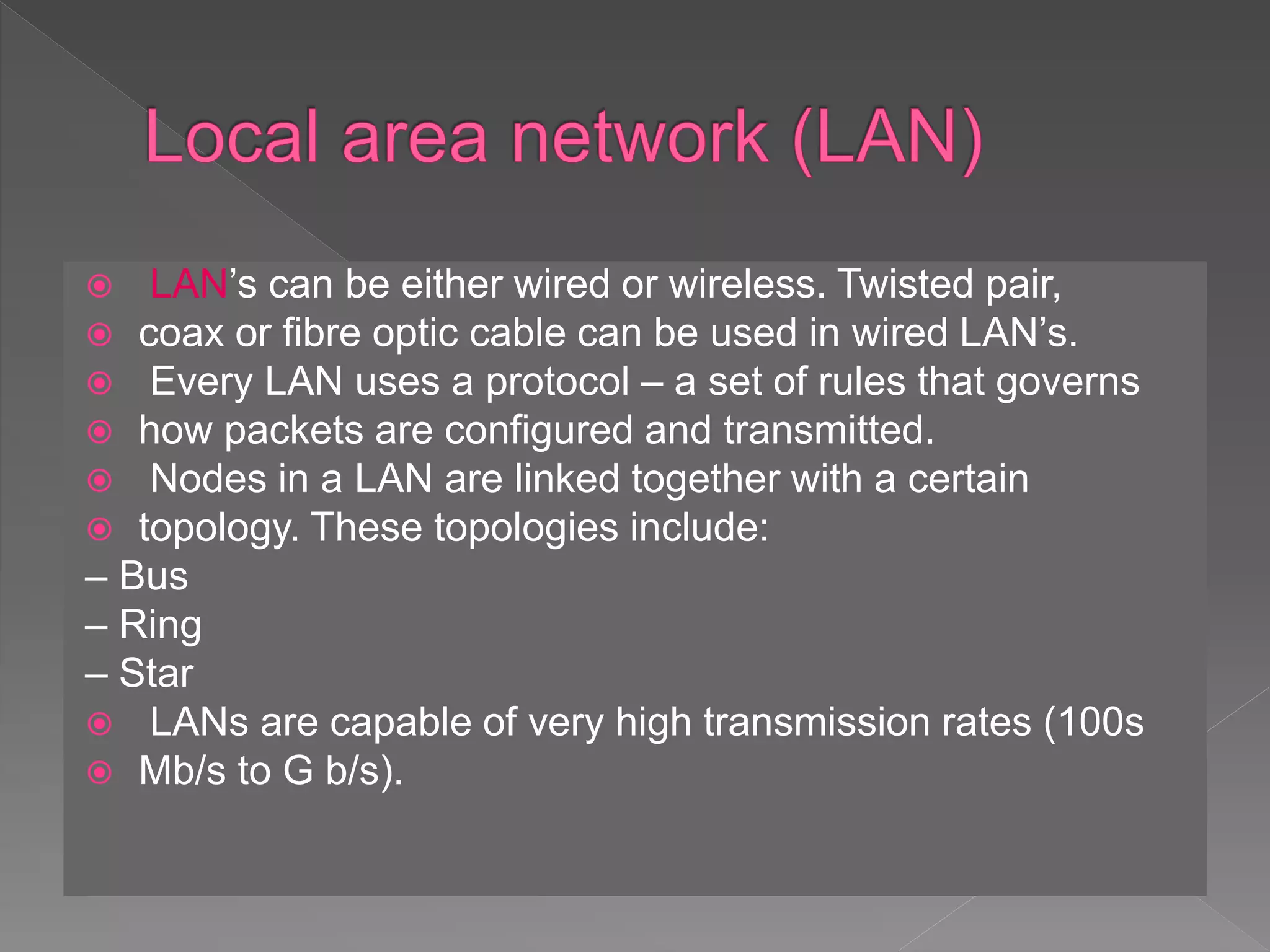
The document discusses different types of computer networks. It describes local area networks (LANs) that connect devices within a home or office using cables or wireless connections. Metropolitan area networks (MANs) span a larger region like a city using higher speed connections. Wide area networks (WANs) connect LANs over long distances using technologies like phone lines or satellites. Personal area networks (PANs) communicate among devices near an individual's body within a range of a few meters.