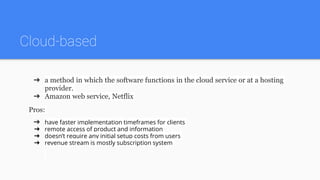
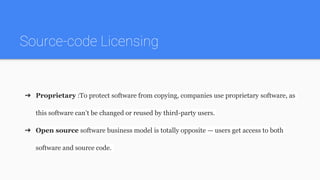
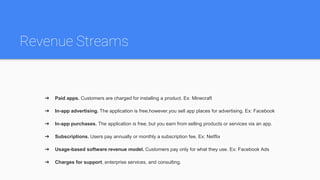
There are three main types of software development business models: on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid. On-premises software is installed locally by the client and allows for customization but requires local IT support. Cloud-based software is hosted remotely and has faster implementation but the provider is responsible for outages. Hybrid models combine on-premises and cloud-based elements. Revenue streams include paid apps, advertising, subscriptions, and usage-based fees. Source code can be proprietary or open source.