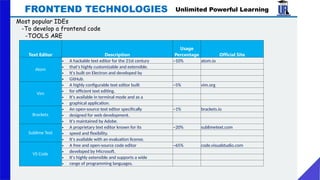
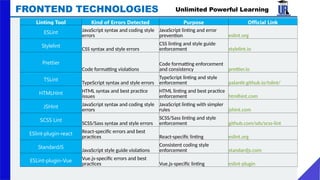
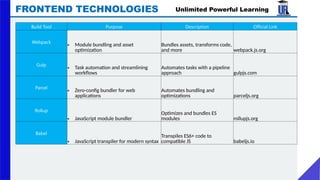
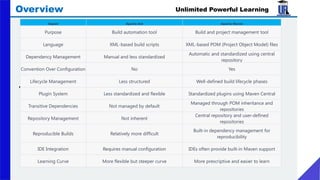
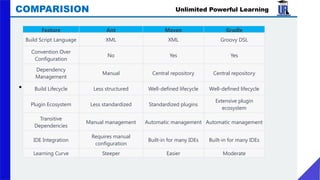
The document provides an extensive overview of web development, covering frontend and backend technologies, popular IDEs, linting tools, unit testing, package management, and build automation using tools like Ant, Maven, and Gradle. It highlights key aspects of frontend development, including the technologies utilized, the importance of linting and unit testing, and the role of package managers in managing dependencies efficiently. Additionally, it compares the strengths and weaknesses of different build tools, emphasizing the streamlined processes they offer for project setup and management.