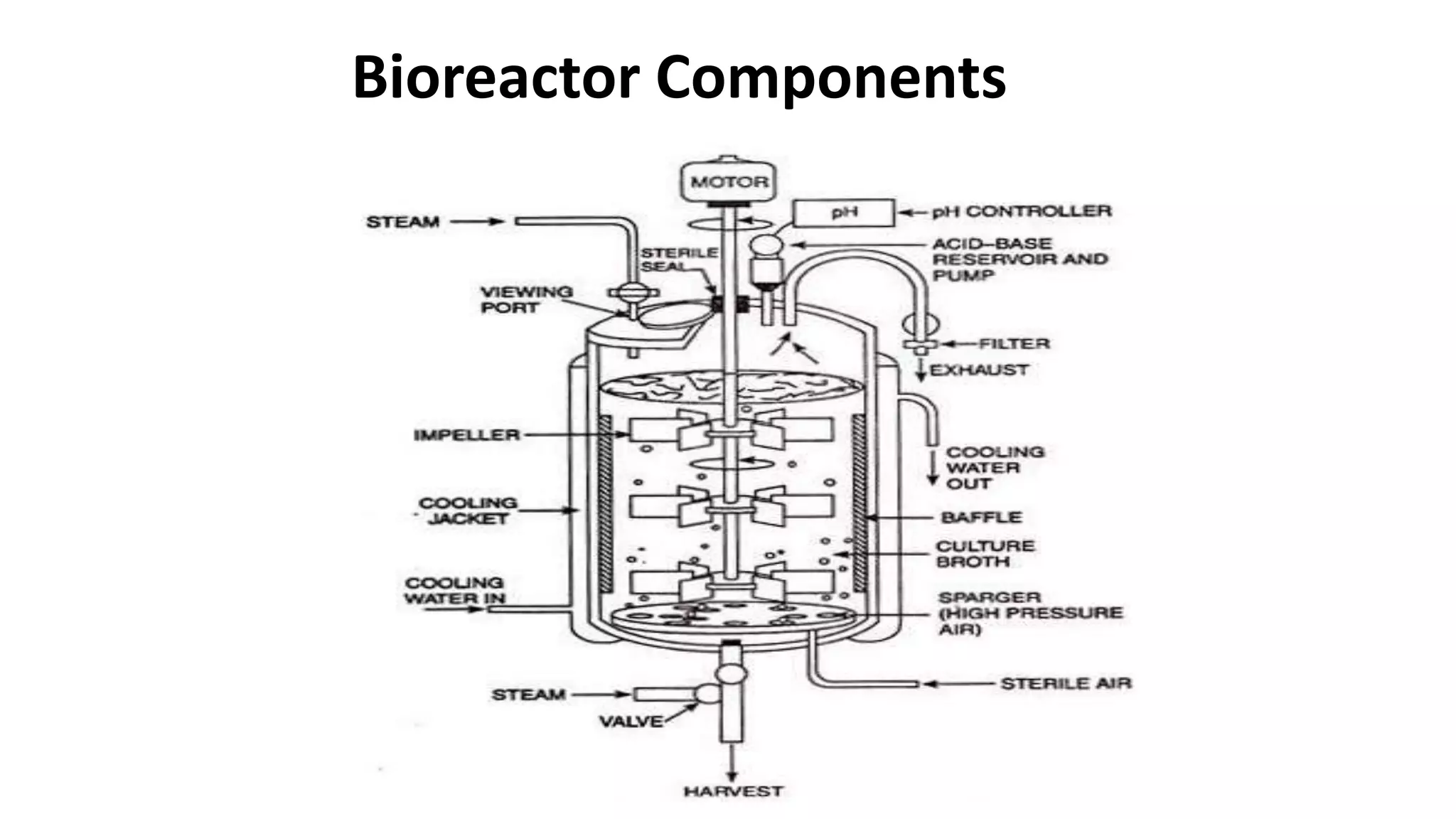
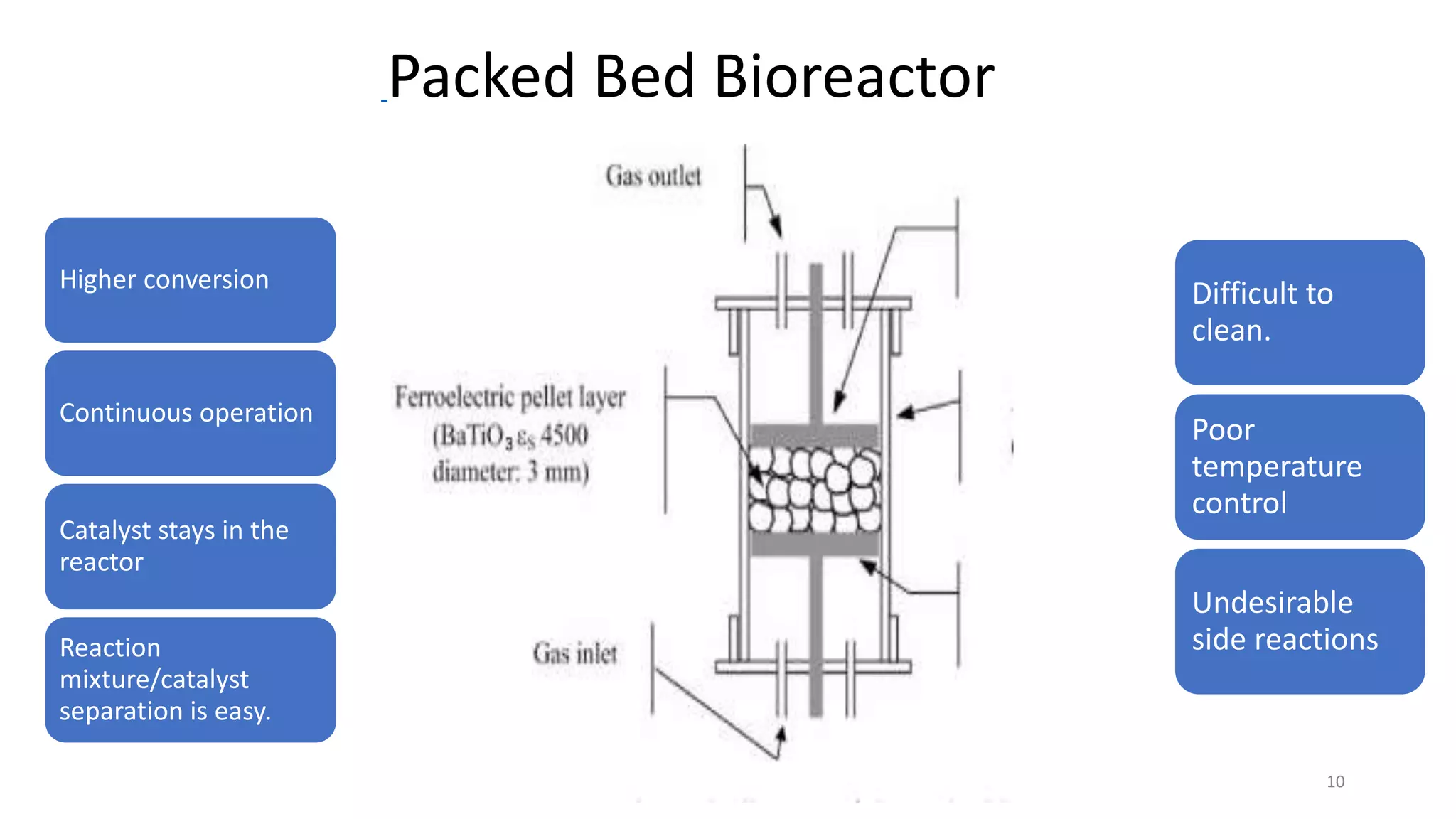
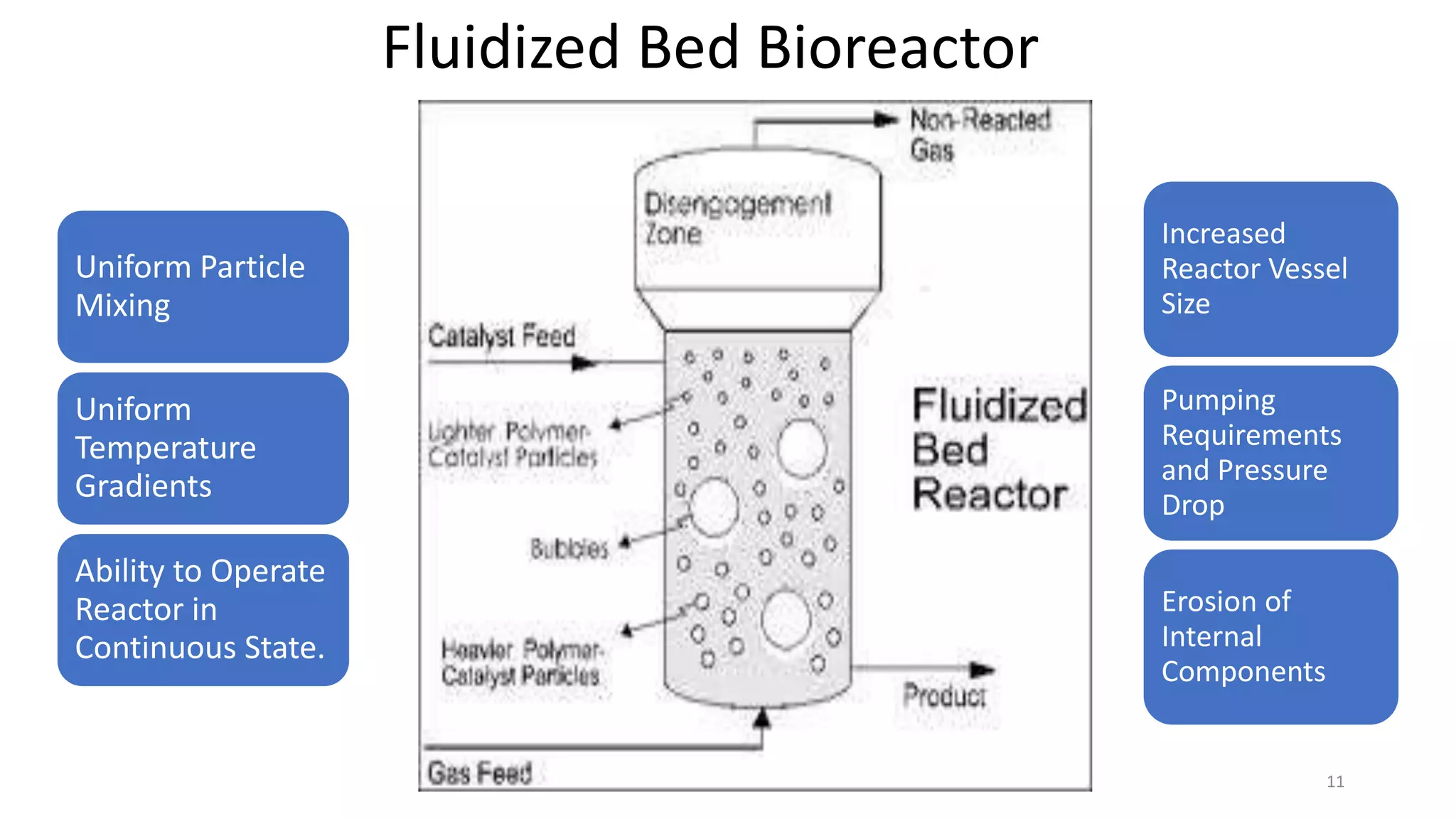
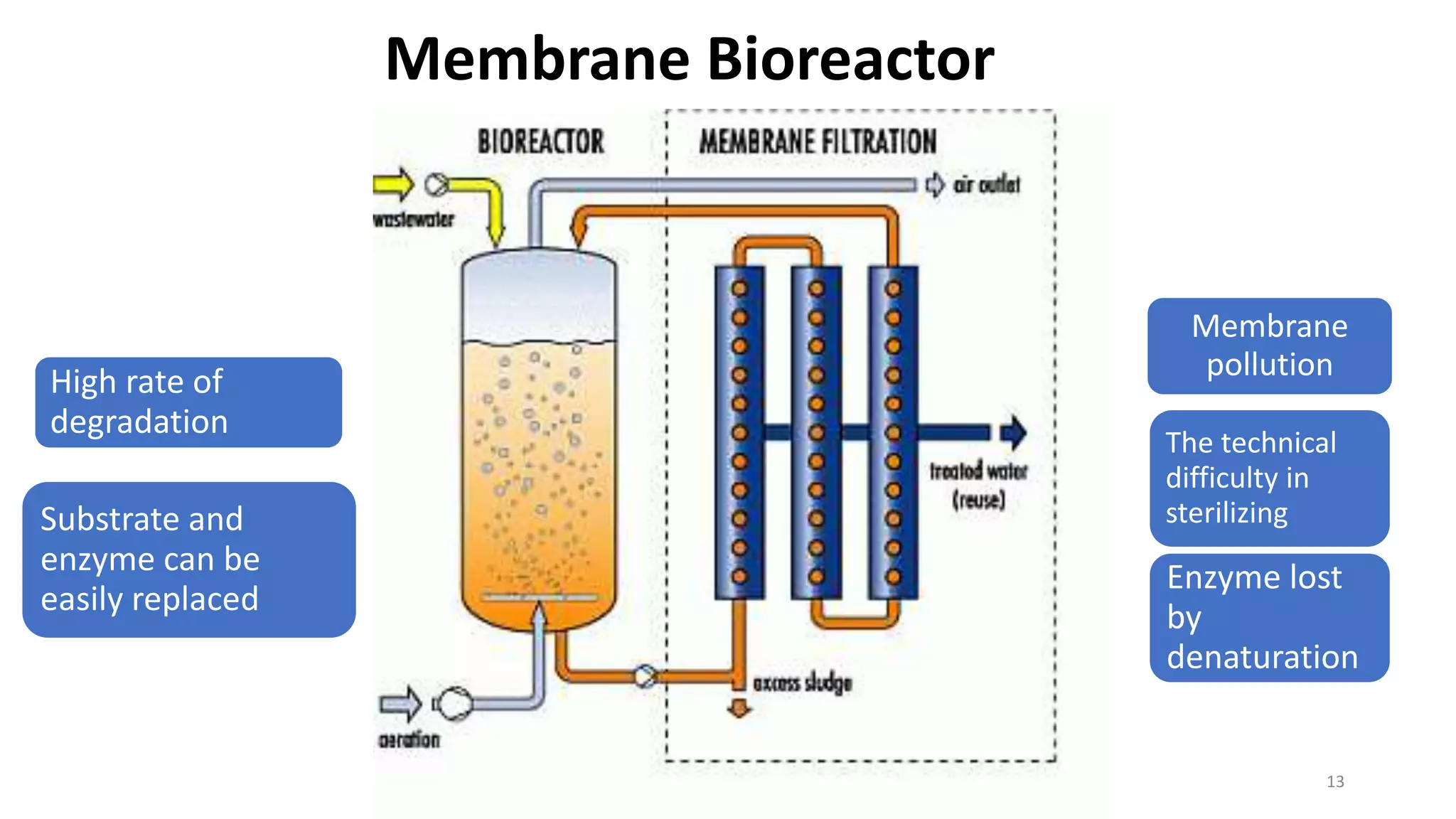
This document discusses bioreactors, which are vessels that house living organisms used to synthesize or break down substances. It describes key components and considerations in bioreactor design, including preventing contamination, optimal mixing and mass transfer, and controlling factors like temperature and pH. Recent advances include using scaffolds to seed cells at high densities. Ideal bioreactors are aseptic with controlled conditions and sampling abilities. Types of bioreactors mentioned are stirred tank, airlift, packed bed, fluidized bed, photobioreactor, and membrane bioreactors. Parameters like agitation, aeration, foaming, temperature, pH, and sterilization are also covered.