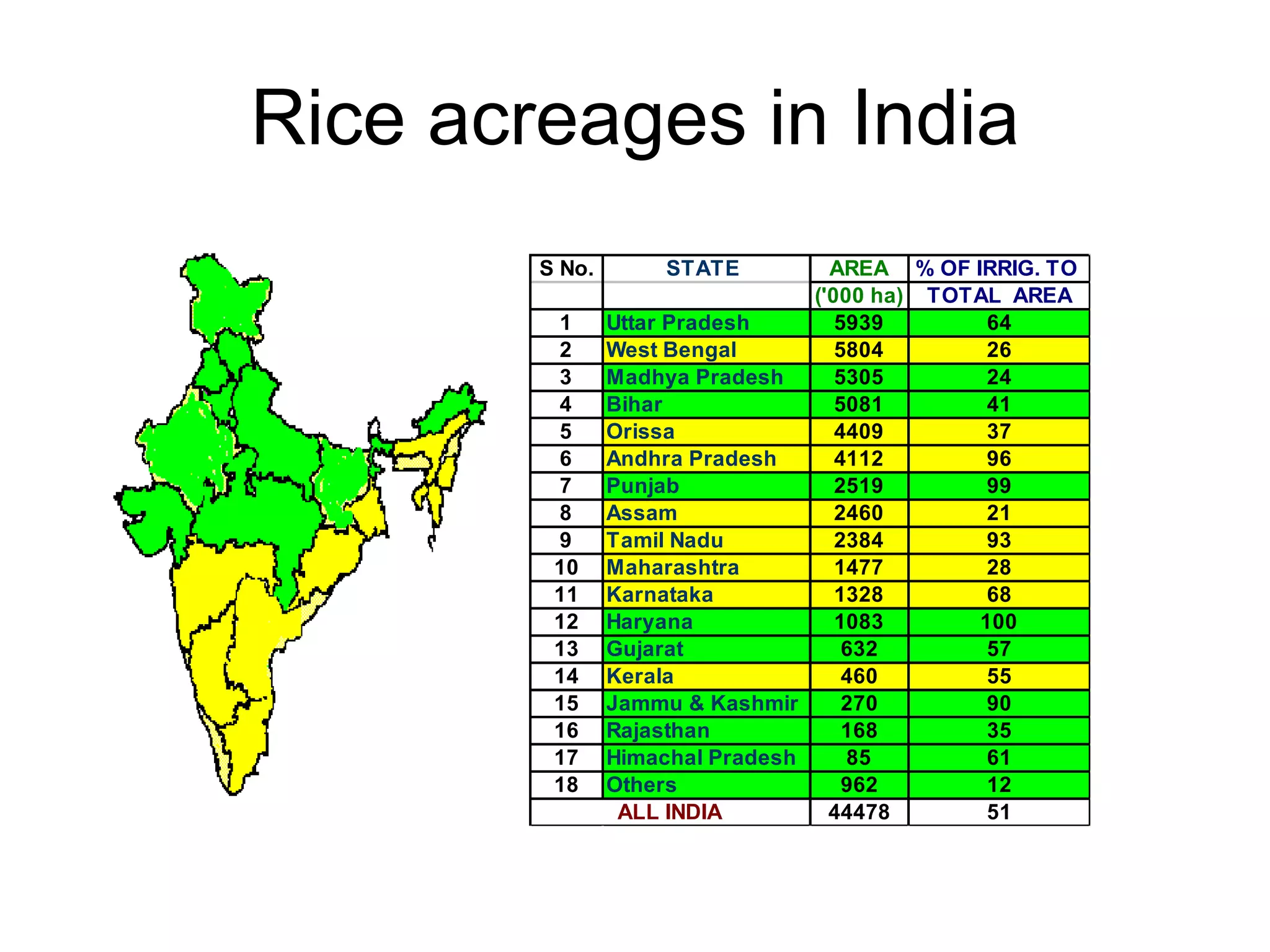
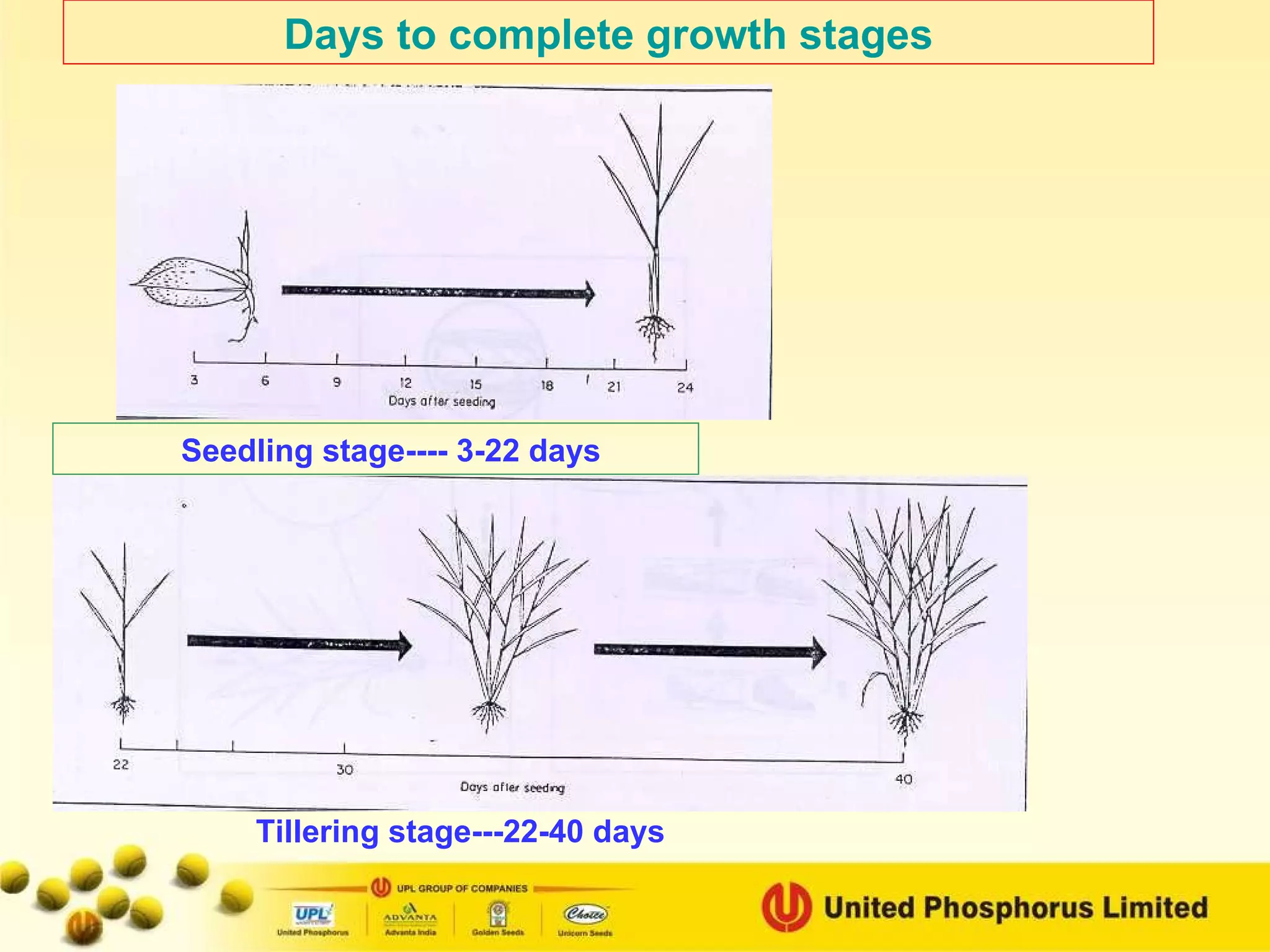
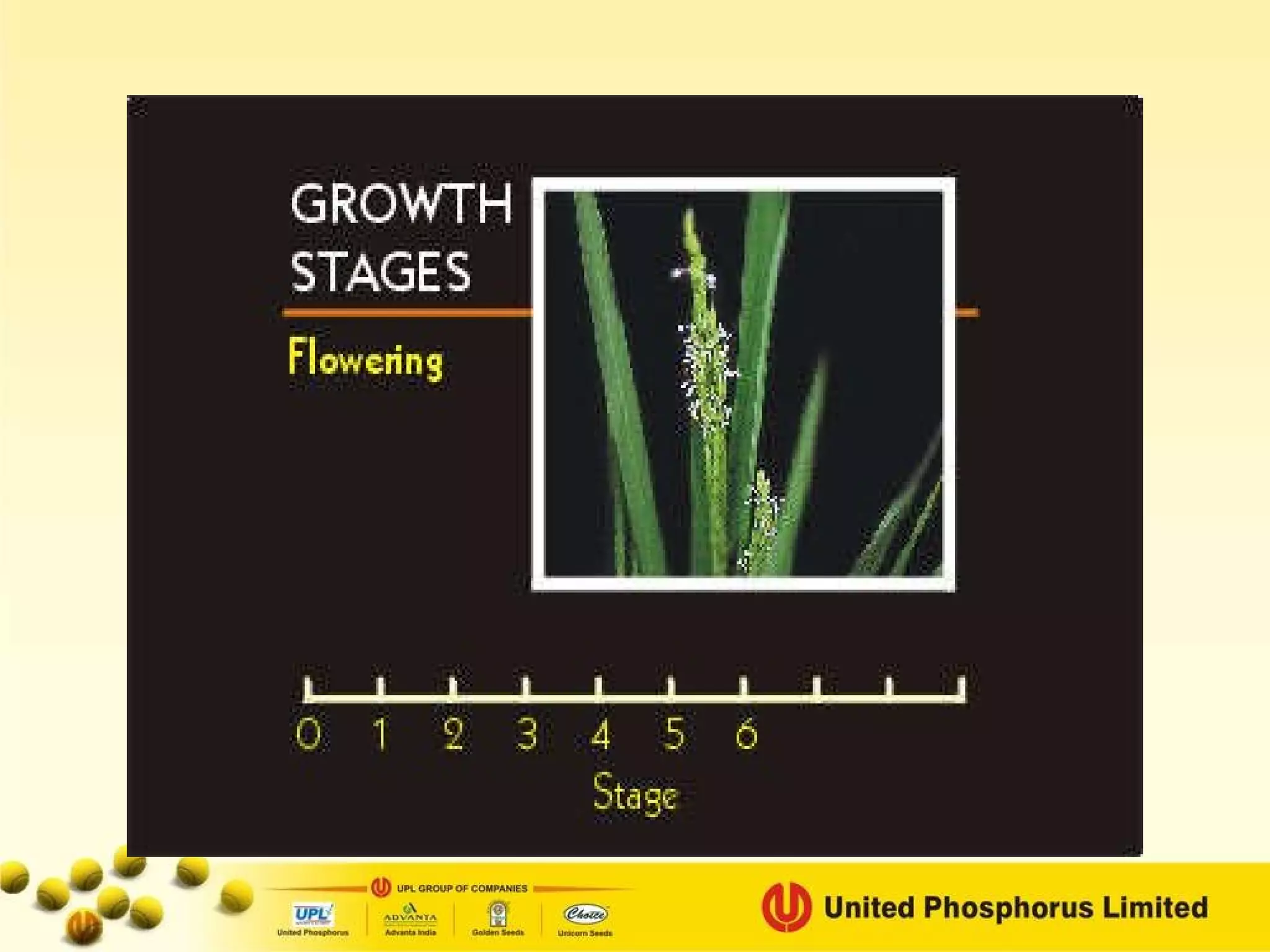
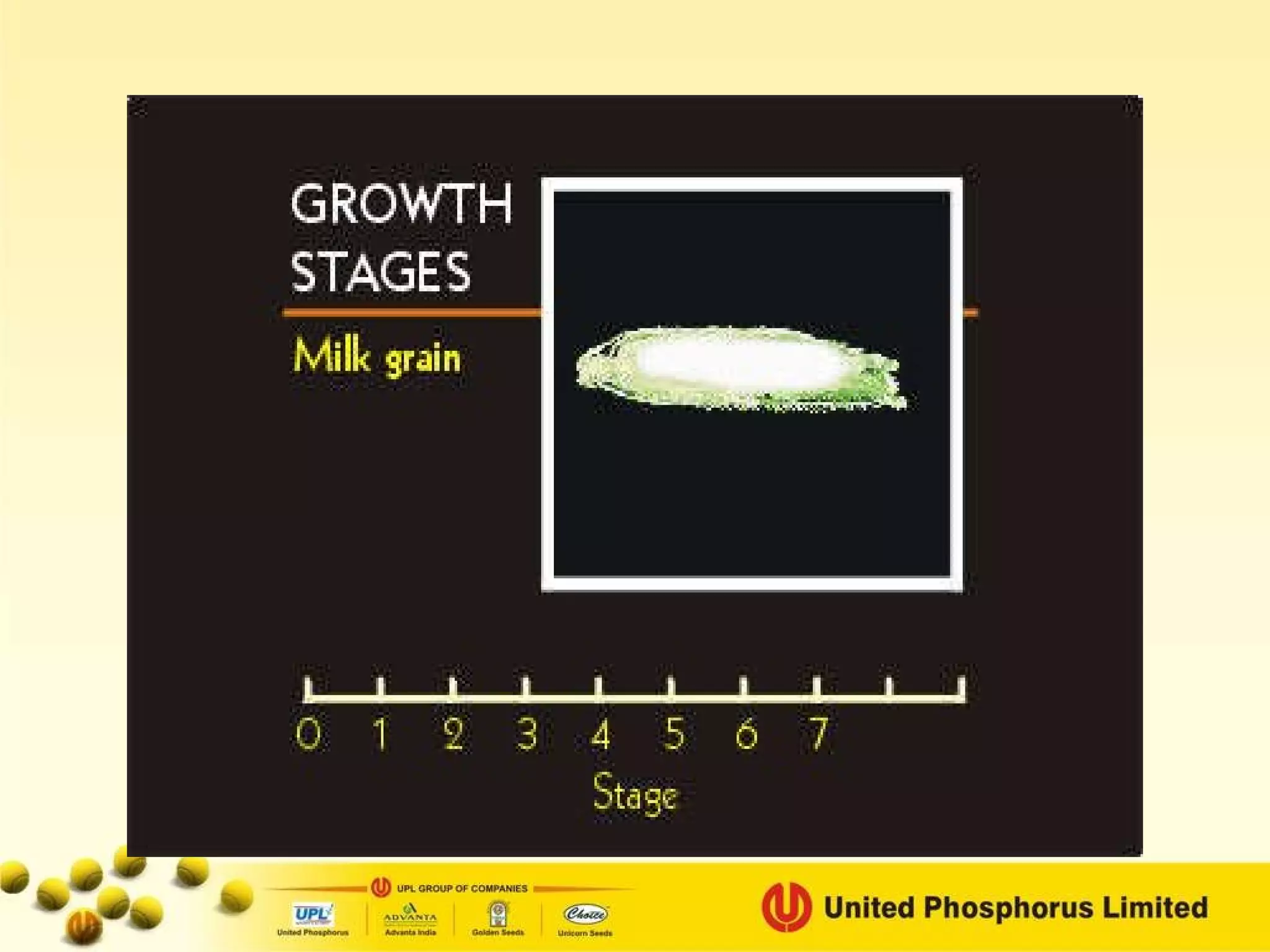
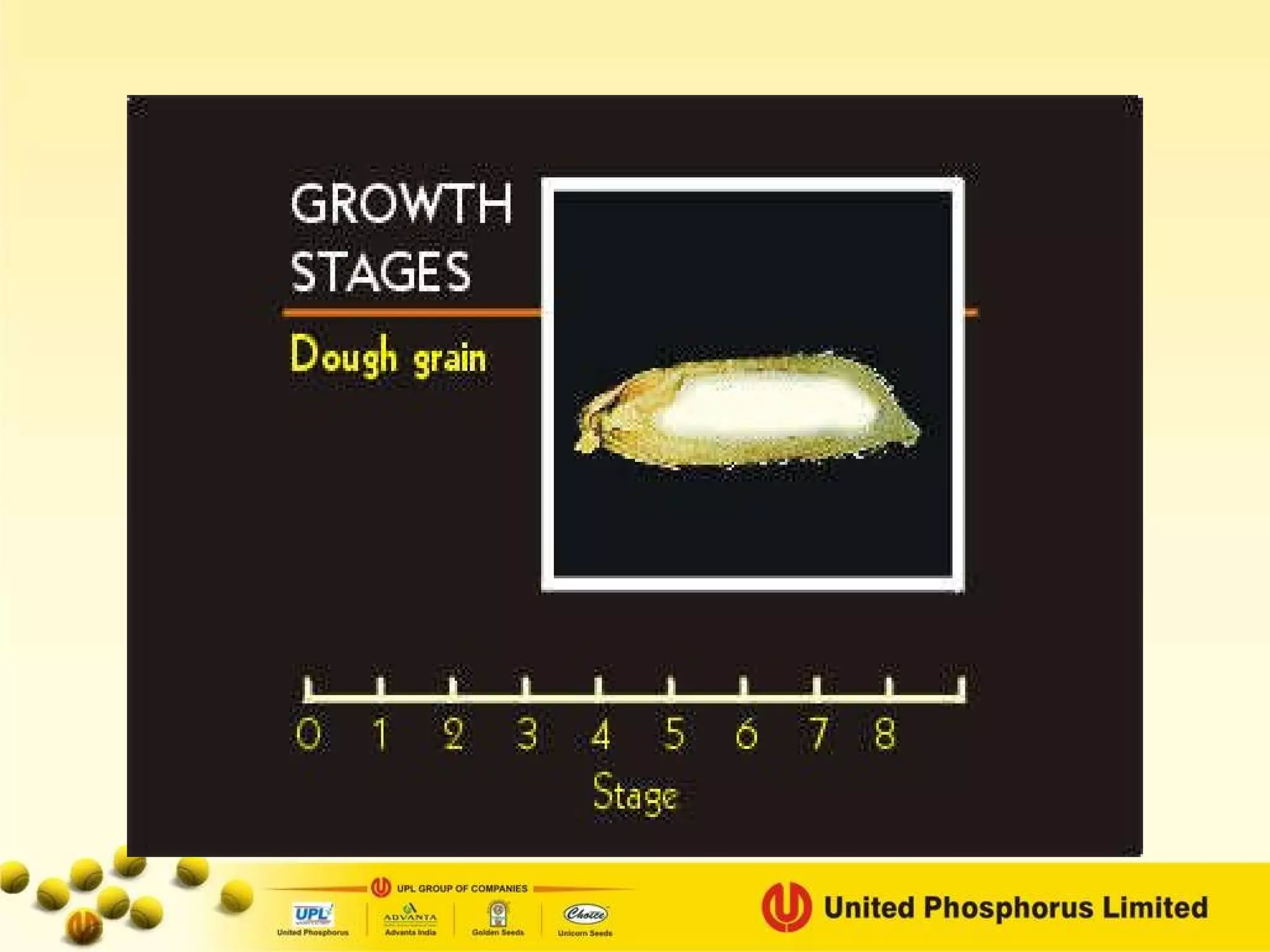
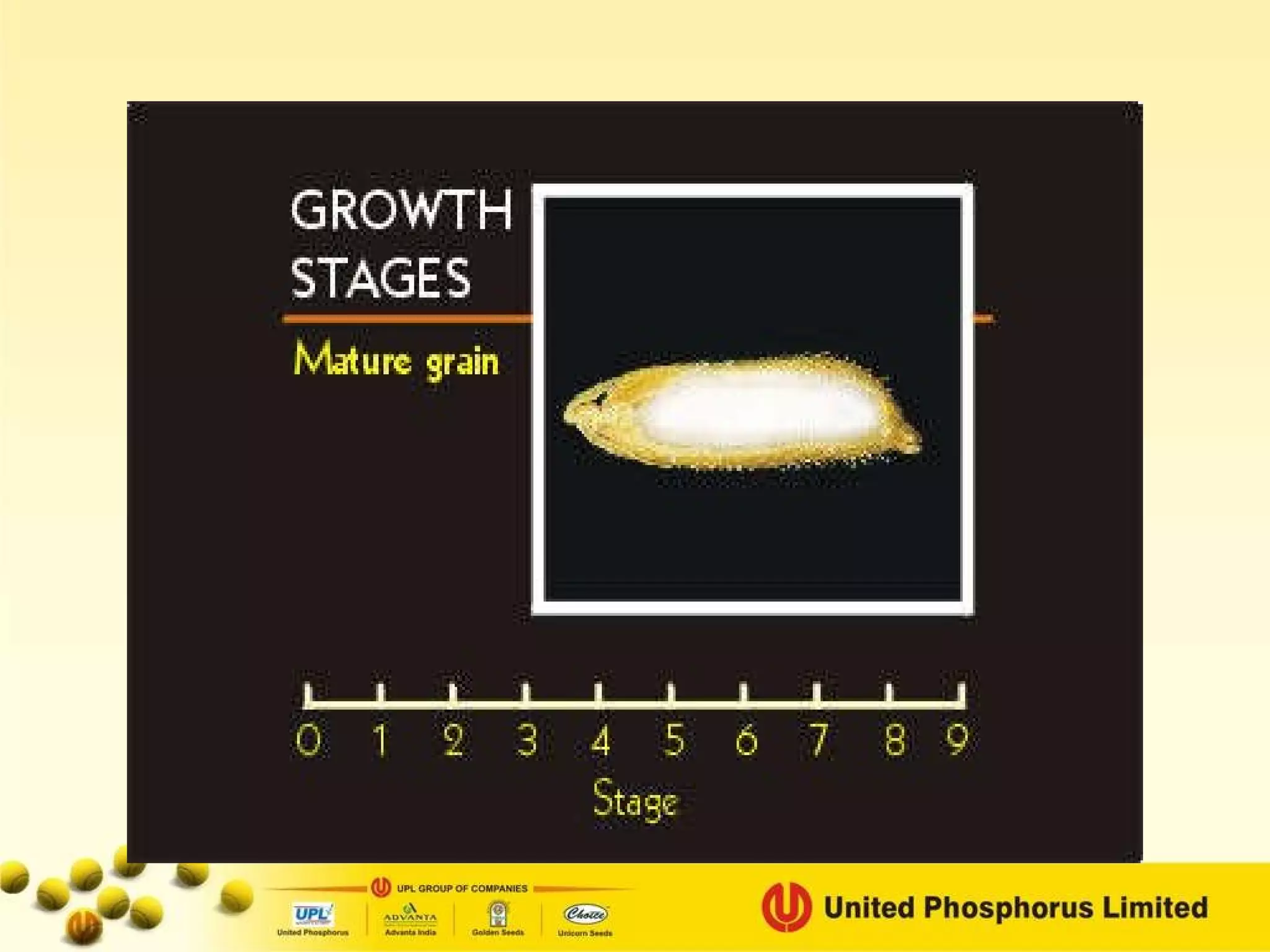
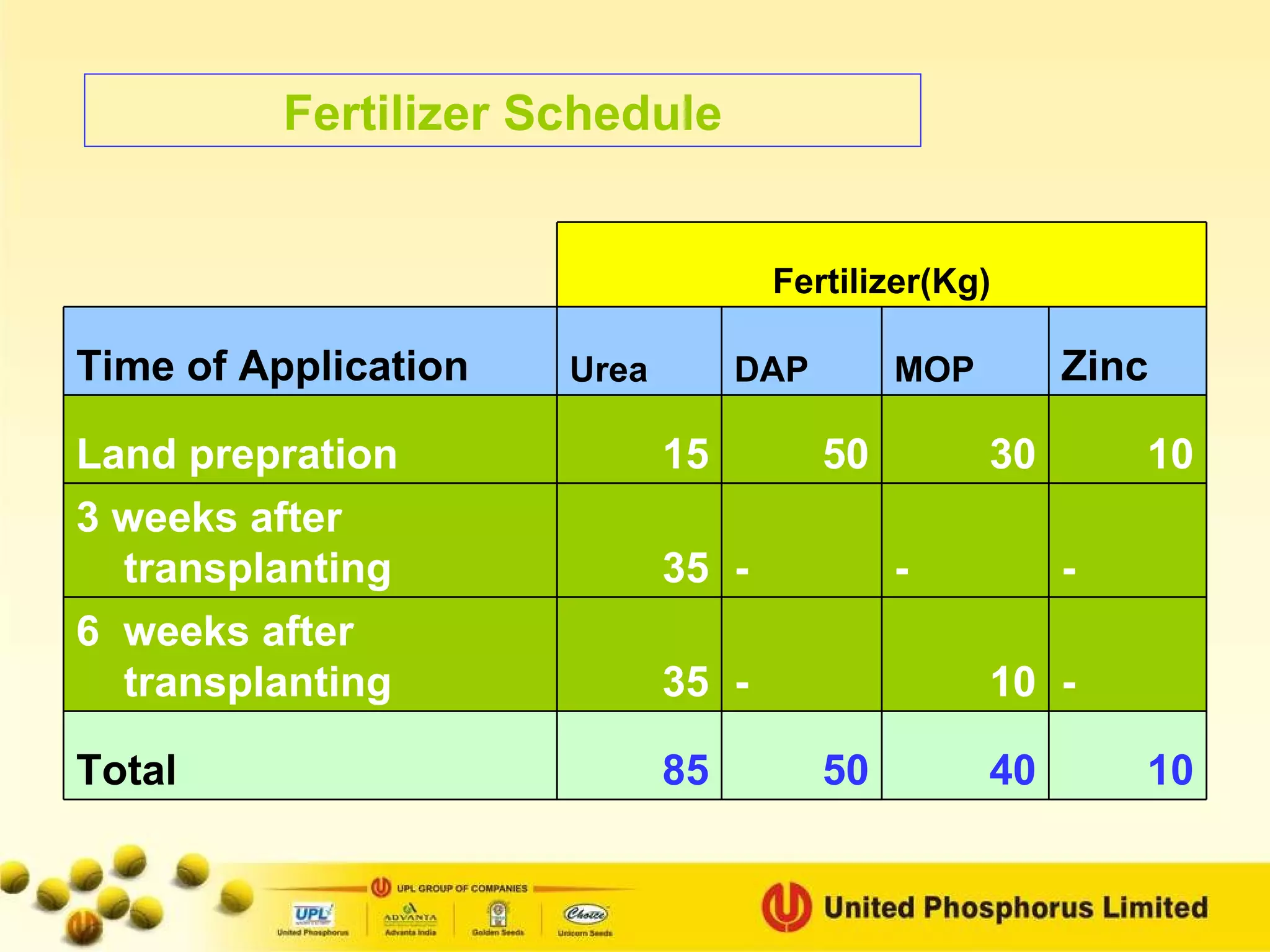
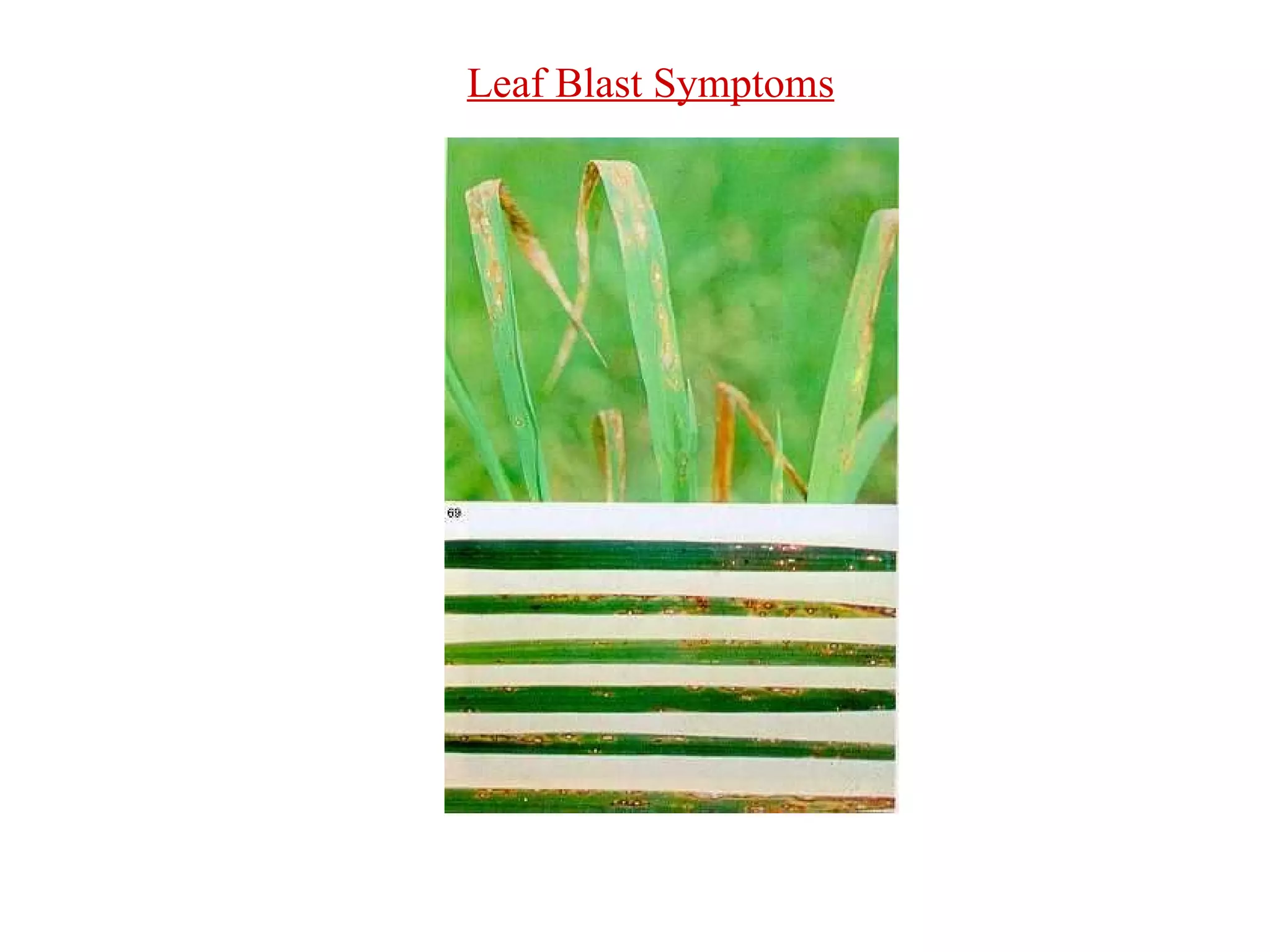
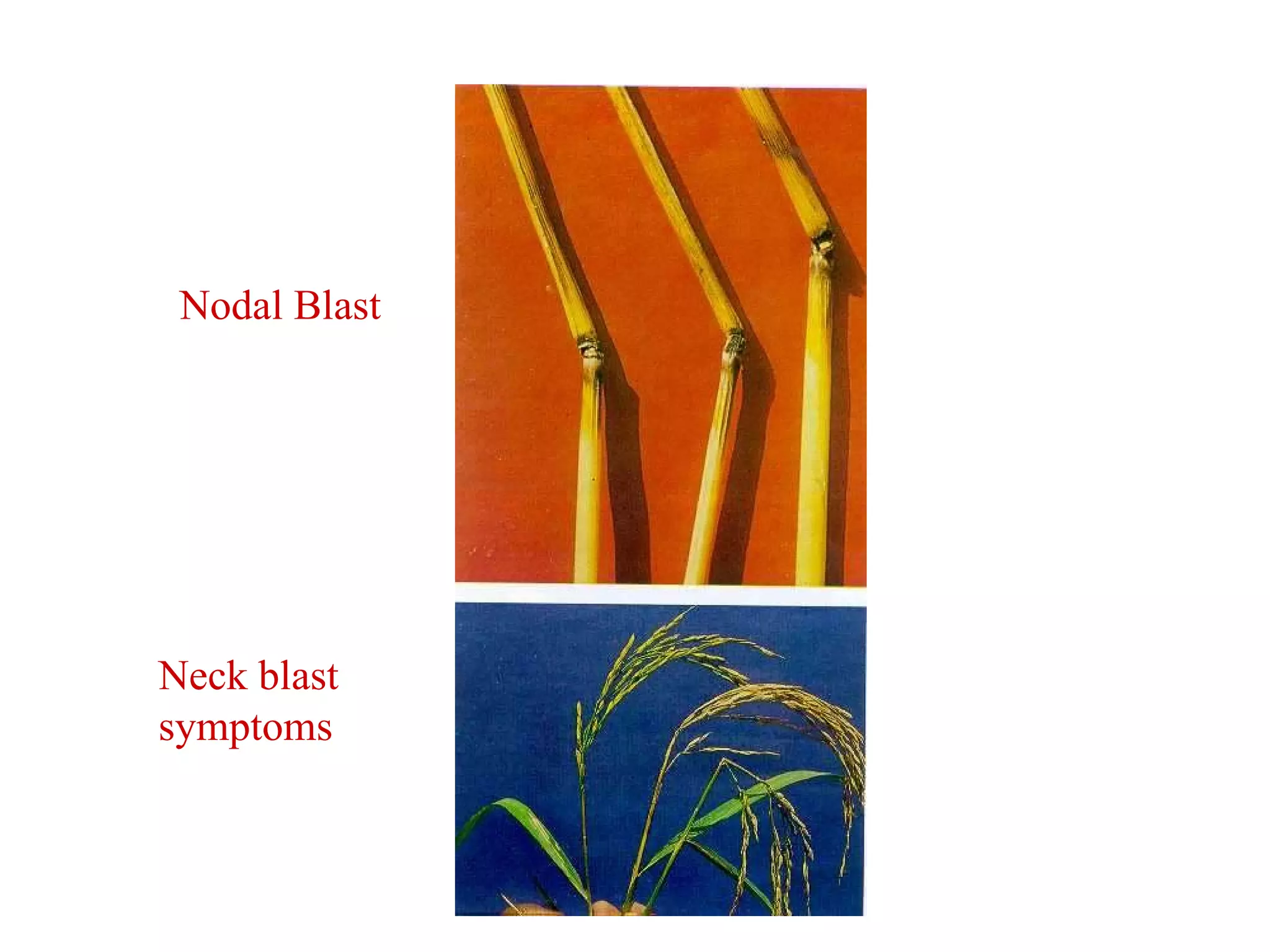
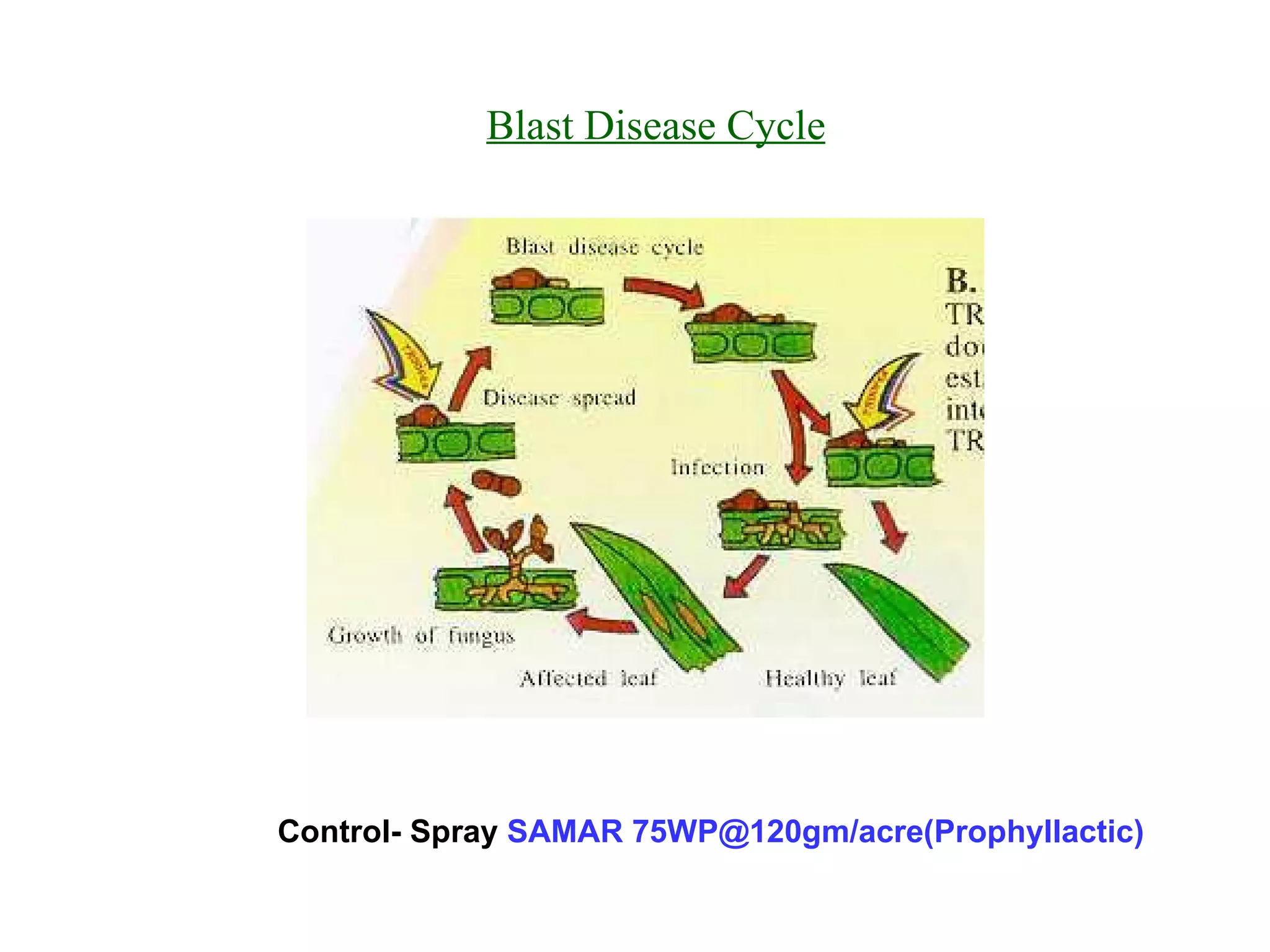
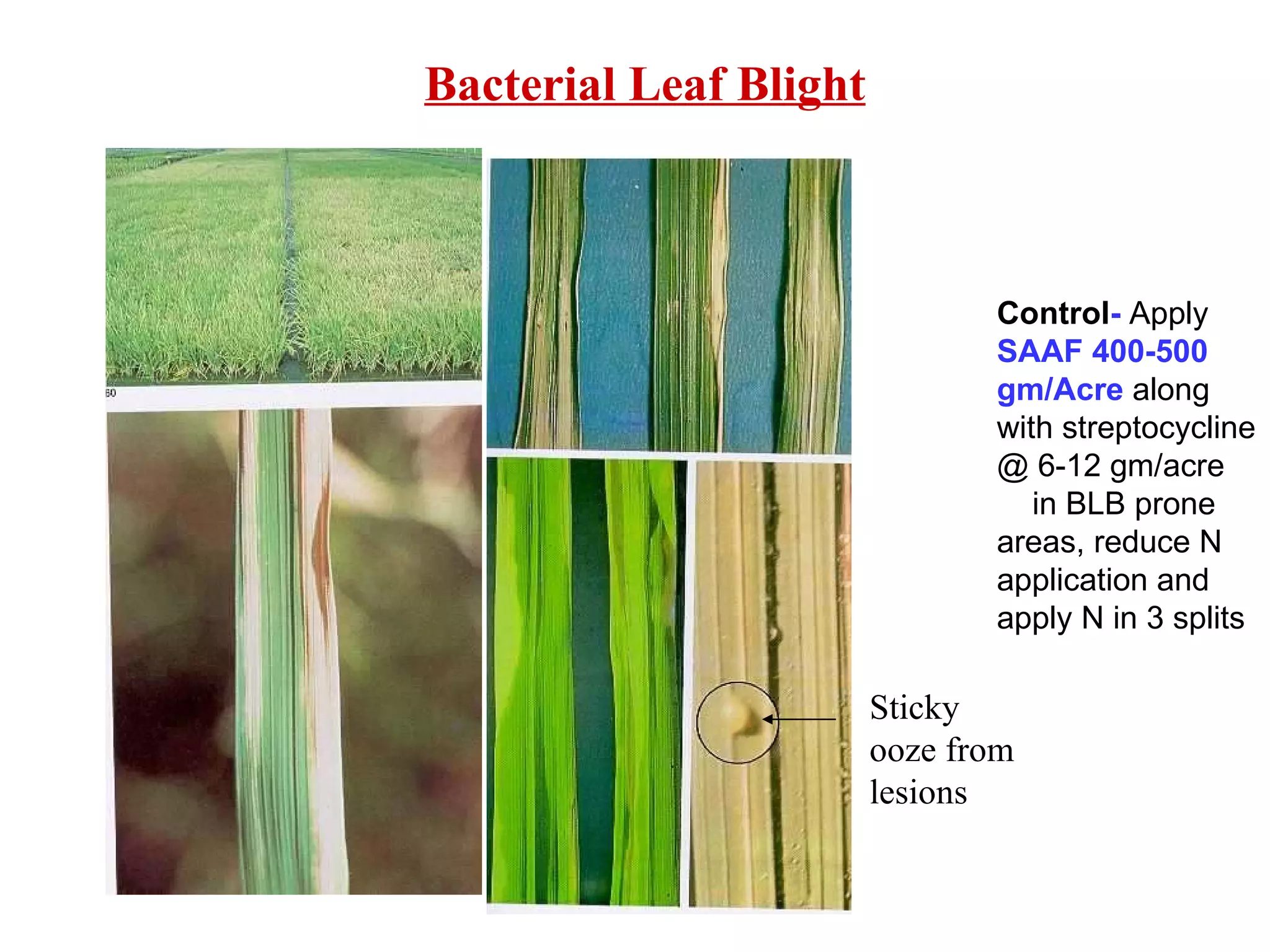
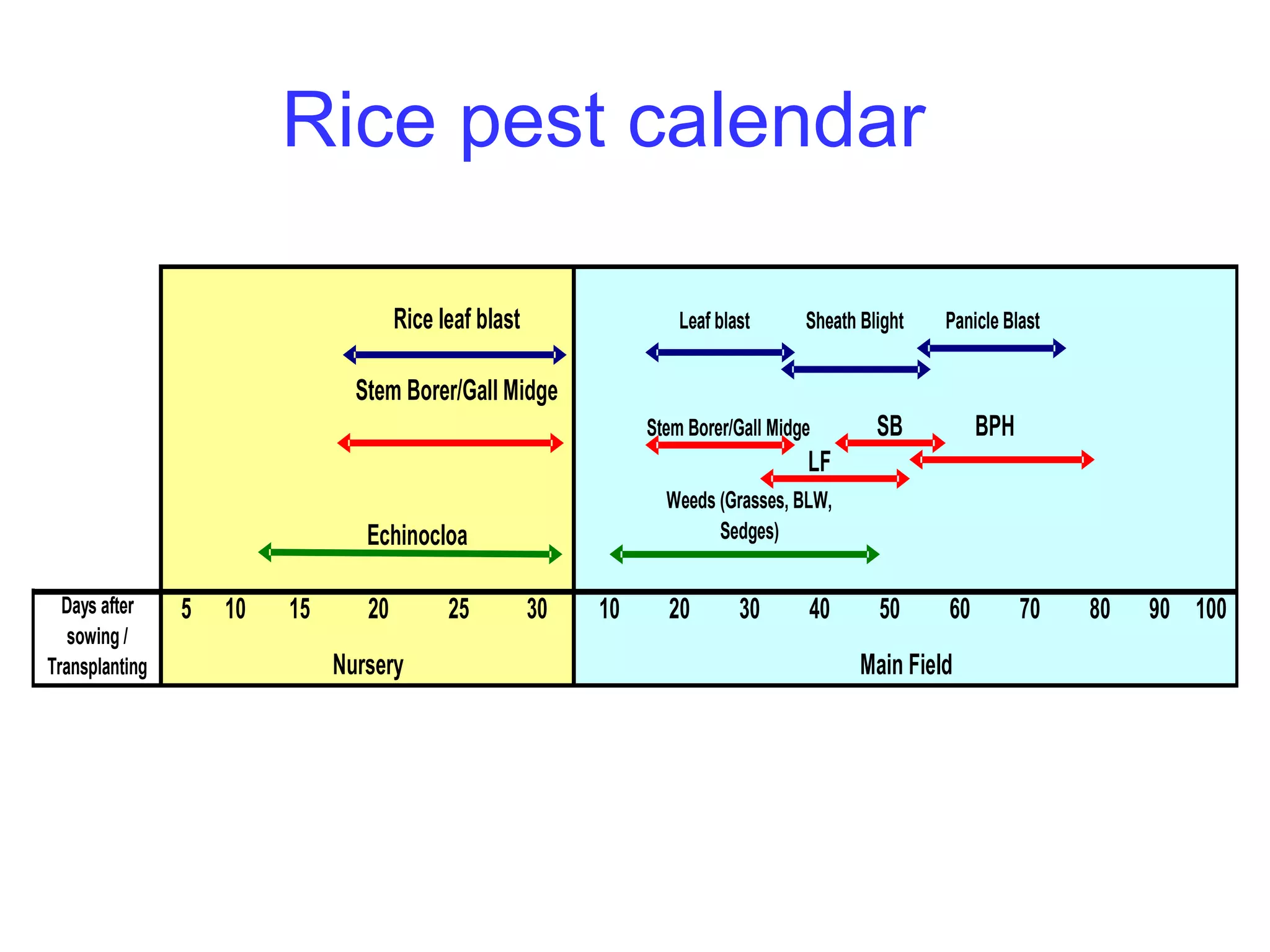
The document provides information on field staff training for rice production in Haryana, India. It discusses rice facts, growth stages of rice plants, packages of practices including planting methods, insect and disease management, and safe pesticide use. Key details covered include common rice pests like stem borer and their control methods, as well as diseases like blast and sheath blight and recommended fungicides for treatment.